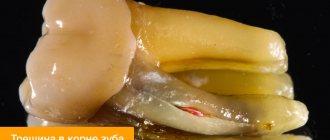
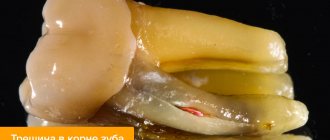
Changing the color of tooth enamel is an alarming signal that cannot be ignored. Dark spots can be associated not only with the consumption of coloring foods and drinks, but also with the development of various pathological processes. If the tooth has turned black at the root, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible. Do not wait for pain and other symptoms to appear, as they indicate extensive damage to hard tissues or inflammation of the dental nerve. It is easier to treat any disease in the early stages, so do not delay visiting a doctor.
Content:
- Why isn't every spot a black tooth decay?
- When there is black caries, but it is still not treated
- How to deal with little black caries
- When black caries still needs to be filled?
Sooner or later, small dots or dark-colored depressions appear on the teeth of any person. They are usually perceived as caries. But, when visiting a dentist, the patient may be told that he does not need to treat his teeth. Why is this happening? Is it true that not every black spot on the crown of a tooth is a cavity?
Chromogenic components (food, drinks, other products)
The food we eat and other substances we use contain coloring agents (coffee, tea, cola, wine, tobacco, etc.) that can cause yellow, brown or bright orange spots to appear on the skin. teeth In most cases, the discoloration of teeth is generalized, which means that stains tend to form with equal success both on the entire surface of the tooth and in individual areas. If stains appear, it is better to make an appointment with an inexpensive dentist near your place of residence.
Why isn't every spot a black tooth decay?
There is no need to think that dentists are being cunning, wanting to deliberately turn an initial carious cavity into mid- or deep-stage caries.
After all, the more complex the problem, the more expensive its treatment. No doctor does this. It’s just that the identified violation has a completely different origin. In reality, dark spots can represent:
- Consequence of hypoplasia. This is a dental disorder in which, during the formation of a tooth, its crown part is underdeveloped. The disease is a consequence of metabolic disorders in the buds of teeth. It can also develop due to improper metabolism of proteins and minerals in the fetal body during its intrauterine development. Rickets, somatic pathologies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, severe infectious diseases - all these are also factors that provoke hypoplasia.
- The result of fluorosis. This disease occurs due to the constant and prolonged ingestion of large amounts of fluoride into the body. First, whitish spots form on the crowns, and then depressions resembling black caries. During examination, the doctor records destructive and erosive changes in the enamel.
- Erosion of teeth. Another type of non-carious lesion of tooth enamel. Defects occur on the outer layer of the crown and can even affect the dentin. Erosive defects are most often localized symmetrically. They provide an unsightly cosmetic effect and therefore require urgent correction.
In many non-carious pathologies, it is possible to improve the aesthetics of a smile through remineralization. The patient is prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes, calcium and phosphorus supplements, and local applications. Electrophoresis is used in many clinical situations.
Only with voluminous cavities reminiscent of black caries do they resort to filling material. If the damage is very severe (which happens when a person puts off visiting the dentist for a long time), even prosthetics may be required.
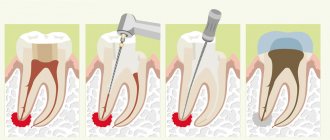
It is important to understand that caries is always a cavity of microbial origin. That is why it has to be drilled out to remove all damaged tissue and prevent further spread of pathogens. From this position, not every even point on the tooth requires the use of a drill.
Tooth granuloma: symptoms
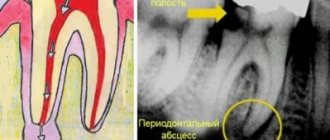
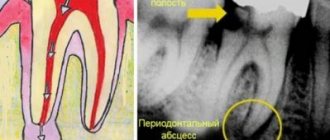
The diagnosis of “apical granuloma of the tooth” can only be made by an x-ray, on which a slight rounded darkening will be visible at the apex of the tooth root (Fig. 1). Darkening at the apex of the tooth root on an x-ray always indicates the presence of a chronic focus of inflammation and the presence of bone tissue resorption. As for the patient's complaints and other symptoms, in most cases they are not pronounced or may even be absent.
Most of the time, the tooth may not bother you at all, or periodically there may be pain when biting on the tooth or aching pain from hot foods. Those. These symptoms are standard symptoms of chronic apical periodontitis, one of the forms of which is tooth root granuloma. However, periodically (during periods of decreased immunity) an exacerbation of chronic, low-grade inflammation may occur.
An exacerbation is usually accompanied by acute pain, especially pronounced when biting on a tooth. In addition, the gums in the projection of the root apex may swell at such moments and be painful when touched. An exacerbation of the process may spontaneously subside (return to a chronic course), but can also lead to the development of severe purulent inflammation, which is popularly called gumboil. Regardless of the outcome of acute inflammation, you will ultimately need the help of a dentist to save your tooth.
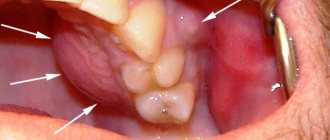
What does granuloma/cystogranuloma look like on the root of an extracted tooth:
When there is black caries, but it is still not treated
Many people have encountered a situation where a doctor, during an examination, confirmed the presence of the initial stage of caries, but refused to treat it according to the standard regimen. Why is this happening? The thing is that during drilling of dentin, much more hard tissue is damaged than it seems at first glance. But it is impossible to install a seal without drilling.
Trying to avoid unnecessary destruction of the crown, the doctor does not want to drill into black caries at the spot stage. Very often its dimensions do not change at all for a long time. The spot itself does not cause a person any discomfort. If you brush your teeth thoroughly after each meal, use high-quality toothpaste and remineralizing dental gel, you can maintain caries at its original size for several years, that is, avoid its increase.
Therefore, if the dentist says that there is no need to touch the tooth yet, you should listen to his words. This is a way to preserve hard tissues without changing their volume for the coming years.
Spots on teeth due to fluorosis
It is generally accepted that fluoride is a microelement beneficial for teeth, because it strengthens tooth enamel, increases its protective properties, and prevents the leaching of calcium. But with an excess of fluoride in the body, a disease such as fluorosis can develop. It causes destructive changes in the hard tissues of teeth. Fluorosis is typical for residents of regions where drinking water is fluoridated, as well as for those who constantly brush their teeth with fluoride paste and eat a lot of fluoridated foods. One of the most striking signs of the disease are spots on the enamel. At first they are light, but as the pathology develops they become yellow or dark brown.
Teeth with fluorosis lose strength, chewing surfaces quickly wear away, chips and areas of erosion may appear, and sometimes the disease leads to complete destruction of the dental crown. The choice of treatment method depends on the degree of tooth decay.
How to deal with little black caries
To prevent the cavity from turning into a large hole, you need to perform remineralization in the dentist's office. To do this, the doctor applies a special composition to the teeth, which quickly penetrates into the deep layers of the damaged units and, as it were, nourishes them from the inside. As a result, the teeth become stronger and more durable, and the rapid spread of the carious process is temporarily blocked.
In case of serious damage, the dentist can give the client a mouth guard and a special remineralizing composition. You need to use all this at night - before going to bed, put the product in a mouth guard and put it on your teeth. Remove in the morning. Repeat the procedure the number of times indicated by the doctor.
Surgical treatment of gum granuloma
Intervention is necessary in cases where conservative medicine has not had the desired effect. It is required when diagnosing destruction processes in the acute stage. Local or general anesthesia can be used for the operation. The simplest option is gingival excision to expose the purulent sac. The pus flows out, the cavity formed is washed and medicine is placed into it for disinfection and pain relief.
Root resection
During the procedure, the dental surgeon acts as follows:
- The gum tissue is peeled away to gain access to the top of the root system.
- The dental canals are opened and cleaned.
- The formed passages are filled with drugs.
- The granuloma is excised along with the upper part of the tooth.
- The place where the inflamed node used to be is filled with a special bone substitute.
- Filling is being done.
Interradicular hemisection of the root
It is necessary in case of severe damage, when it is no longer possible to cut off only the top while maintaining the main size. Key steps of the operation:
- Removal of the area located inside the alveolus, while the plate itself can be saved.
- Cleaning of periodontal tissues.
- Filling the cavity with a special compound.
- Implant installation.
For preventive purposes, it is necessary to monitor the operated area by regularly taking x-rays. This is an effective and fairly simple method that allows you to preserve a living dental plate, and a neat crown can be installed on the remaining areas in the future.
How to cure granuloma on the root of a tooth with cystotomy
This is a gradual elimination of a large focus of inflammation. To remove all the purulent exudate, an artificial canal is created that connects the inflamed node directly to the oral cavity. After removing the infected fluid, the area is treated with antibiotics and the wound is sutured. The resulting holes can be filled with artificial biomaterial - bone cells. This is a long operation, but it is usually performed without complications.
Removal
It is prescribed as a last resort if other procedures have shown to be ineffective, for example, when:
- Complications arise, an advanced stage.
- An external purulent pocket began to form on the gum.
- A longitudinal crack is formed - the dental plate simply splits into two parts.
- Bone tissue is destroyed (the tooth crumbles).
- Origin of root perforation.
- The canals are destroyed.
During the operation, the root system is completely removed, leaving a hole in the periodontium. It is filled with pus that needs to be washed out. 2-3 months after surgery, a pin can be placed on the healed area to place the implant. Additionally, the doctor prescribes rinsing solutions (for example, Chlorhexidine), gels for local anesthesia and disinfection (Cholisal), as well as antibiotics against bacterial infections and painkillers in tablets or injections.
When black caries still needs to be filled?
You need to clean a black spot using a drill if:
- the patient complains of increased sensitivity to sour, salty and sweet foods, temperature changes;
- when there is mechanical impact on the damaged crown, pain occurs;
- the hole is growing in size too quickly;
- the speck is located in the area of the neck of the tooth;
- there was an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- The black defect is localized on the incisors and spoils the smile.
In all these cases, the fight against carious lesions is carried out according to the classical scheme. The patient is injected with an anesthetic, after which the carious lesion is cleaned from altered tissues using a drill. The cleaned area is treated with an antiseptic and filled with a filling solution. The latter is dried with a lamp and then sanded to achieve the correct shape and perfect smoothness. As a result, the unit begins to look aesthetically pleasing, and its service life increases significantly.
Prevention of caries and dark spots on teeth
In most cases, darkening of the enamel can be prevented by following simple preventive measures.
- Brush your teeth regularly and correctly.
Clean the surface of your teeth, gums, and tongue from plaque at least twice a day using a therapeutic and prophylactic paste that is appropriate for the age and condition of your teeth. Do not use fluoride toothpaste without a doctor's recommendation to avoid fluorosis. To clean brace systems, purchase special brushes that will ensure high-quality removal of food debris and other contaminants in the areas where the braces adhere to the teeth. Use dental floss, irrigator, and mouth rinses to clean all hard-to-reach areas.
- For preventative purposes, visit the dentist twice a year.
Any dental problems, including dark spots, can be treated much easier and faster if they are detected at an early stage. Teeth affected by caries in the form of a small point are in some cases treated using non-invasive methods - without drilling or filling.
- Professional cleaning twice a year.
Once every six months, carry out ultrasonic or laser teeth cleaning to remove complex deposits.
- Rejection of bad habits.
If possible, reduce the consumption of coffee, tea, Coca-Cola, and stop smoking. This will have a beneficial effect on the appearance and condition of your teeth.
Therapy
If the filling on the front tooth or on any other tooth has darkened, there are three possible solutions to the problem, the choice of which should be determined by the diagnostic results:
- Removal: performed if the tooth is so damaged that it cannot be cured;
- Removing an old filling, treating caries and installing a new filling material;
- Installation of a dental crown after complete elimination of the pathology.
If complications develop and other diseases occur, additional therapeutic measures may be required to eliminate the source of infection and restore the tooth.
Why does the enamel color change?
Blackheads occur for many reasons, of which dentists identify the main ones:
- Presence of plaque if not cleaned regularly with a toothbrush.
- Hereditary factor.
- The presence of sealed teeth treated with metal fillings.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Long-term wearing of braces.
- Poor cleaning of dental canals due to caries.
- Erasure of enamel.
- Use of tetracycline antibiotics for treatment.