Dentistry under sedation is a modern method that allows you to go through an unpleasant procedure with comfort. Parts of the brain responsible for increased levels of anxiety are temporarily blocked with anesthetic drugs. Under their influence, a person quickly calms down, falls into a shallow sleep, while remaining conscious. Ideal conditions are created for the doctor’s comfortable work, helping to significantly improve the quality and efficiency of procedures and perform a large volume in one appointment.
What is sedation in dentistry? How is it different from anesthesia or anesthesia?
Anesthesia in dentistry – anesthesia of the treatment area (site). This is a mandatory manipulation - a traditional injection into the gum near the diseased tooth.
Sedation is a light medical sleep that relieves anxiety and fear. The patient in this state is asleep, but conscious, feels touch, hears the doctor. The main difference from anesthesia is that during sedation a person breathes completely independently. Sedation is accompanied by local anesthesia so that it is not scary or painful. Sedation allows the doctor to monitor the condition of a patient with concomitant diseases - kidney or heart problems, high blood pressure - so all procedures are comfortable and as safe as possible.
Anesthesia or general anesthesia is used during hospital treatment when a complex operation needs to be performed. In this case, the patient’s consciousness is completely turned off, local anesthesia - injections into the gums - is no longer needed, and breathing is controlled by equipment.
The use of sedation assumes the preservation of standard reflexes and the absence of depression of the nervous system. According to reviews from patients of different ages, during treatment they feel lightness and relaxation. On average, an hour after the end of the procedure, the person returns to his normal state and can go home with an escort. Our clinic has a small room where you can rest and sleep after treatment under sedation.
Complications after sedation
Do nausea and fainting occur after sedation, or can such nuances be clarified before it begins? Of course, the characteristics of patients may be different: for some it may be nausea, for others it may be dizziness, etc. All this, of course, is discussed in advance in consultation with an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. It determines the patient’s health characteristics and determines the reactions that are possible due to the action of the drug. Any sedative drug can cause:
- drowsiness throughout the day after the manipulation, especially if the treatment was carried out in the morning,
- weakness,
- mild nausea
- It may make some people feel hungry, while others may feel the opposite.
There may be peculiarities, and this is not something pathological or something negative, this is the norm.
Types of sedation: superficial and deep
The following sedative methods of relaxing and calming patients are used in dentistry:
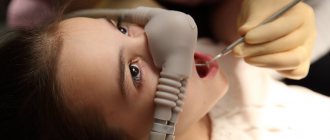
- Superficial is the best solution in a situation where the patient requires relaxation for a short period of treatment. Indicated for adults, as well as children from the age of three. A state of pleasant slumber is achieved by inhaling oxygen mixed with nitrous oxide. The nasal mask through which the gas passes is connected to the machine. The doctor can change the ratio of components and dosage based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Deep - the medication is administered through an intravenous injection. This technique copes better with severe fear and anxiety. The technique is used for adults and children at least 15 years old. The relaxed state lasts longer than with a superficial state. The patient will need to stay in the clinic for some time and stop driving for 8 hours.
Anesthesiologists at the Refformat dental clinic in Moscow have been working with a wide variety of patients for a long time and their experience makes treatment safe. Any intervention, preparation and installation of prostheses will be comfortable and unnoticeable.
Treatment method with sedation
To carry out superficial sedation of a patient, anesthesiologists use one of 3 methods:
- Inhalation.
- Oral.
- Intravenous.
The choice of technique is carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the person, the specifics of the procedure and medical indications.
In the inhalation method, nitrous oxide is used as the main active drug, inhaled through a face mask. At the same time, if it is not necessary to treat teeth under anesthesia , additional medications are not used. Inhalation results in minimal sedation without complete loss of patient consciousness. Often, respiratory functions are not affected, but the entire procedure must be supervised by an anesthesiologist.
How is the sedation procedure performed?
The procedure consists of several stages. First, you need to get a consultation with a dentist - you meet the doctor and draw up a treatment plan.
For sedation, the patient will need to do a few simple tests:
- ECG.
- Donate blood for general analysis and biochemistry (detailed).
- Donate blood and get test results for hospitalization (for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis).
- If you have diseases, obtain permission from a specialized specialist.
The finished results are sent to the clinic administrators. Be sure to write the surname, initials of the patient and the dentist. The documents are submitted for review to the anesthesiologist, who decides on admission to the operation under sedation and takes into account the possible consequences.
The administrator contacts the patient to clarify the date and time of arrival at the center. On the appointed day, it is recommended to arrive early for the appointment, but do not use personal transport. If necessary, administrators will help you call a taxi to get you back home.
Before the procedure begins, there is a conversation with the anesthesiologist. In the operating room, an individually selected dose of anesthetic will be administered through a nasal catheter and wire. Unlike anesthesia, the patient continues to breathe on his own, plunging into a pleasant half-sleep, without negative sensations. At the end of treatment, the patient is escorted to the rest room, where he has the opportunity to lie down and rest.
Methods of dental sedation
The most common method of sedation is the use of oral medications - capsules, cocktails or tablets. This technique is the most effective, eliminates the spraying of the drug throughout the office and allows for precise dosing of drugs. Usually, on the eve of the procedure, the patient takes diazepam, temazepam or Valium, and before treatment, an additional tranquilizer, which puts him into medicated sleep.
Intravenous sedation is indicated for people over 2 years of age. Before the procedure, eating is allowed, but more than 2 hours before the drug is administered, but after treatment the patient cannot drink alcohol or drive a car for at least 24 hours. The main intravenous tranquilizer is midazolam, which does not provide anesthesia, but causes loss of consciousness and memory. Propofol, which has a similar effect, is also used, but in dentistry in Minsk it is used less frequently because it does not have an antidote. During the operation, the patient's vital signs are always monitored.
Methods of drug administration
Dentistry with sedation in Moscow is represented by various methods of administering medications: inhalation, oral and injection.
Inhalation method
Most often used in pediatric dentistry. The procedure uses nitrous oxide. “Laughing gas” evokes positive emotions in a child from visiting a doctor’s office and undergoing lengthy procedures. At the same time, the doctor’s work becomes significantly easier and more effective.
Oral route
Oral drug sedation is a method of calming in which a drug that eliminates agitation is taken an hour before the main treatment procedure begins. Using this sedation technique, an initial level of stress relief is provided, and the main stage, at which an anesthetic is administered intravenously or an oxygen mask is used, is facilitated.
Injection method
Intravenous sedation is recommended primarily during dental treatment in adults. The injection method involves administering drugs intravenously, directly into the hematopoietic bed. This method is good because it allows you to control the degree of both physical and emotional relaxation.
Indications for the use of pain relief
European and American dentists use sedation in dentistry when performing any manipulations. In Russia, such a procedure can not be performed in every clinic. Treatment and removal of teeth under sedation at Refformat dentistry allows patients to completely calm down and undergo all manipulations in complete relaxation.
Indications for use:
- Severe fear, fear of visiting the dentist, panic.
- Increased vomiting.
- The desire to receive a service with high comfort.
- Reduced pain threshold.
- The need for a long period of simultaneous treatment.
- Vascular or cardiac pathologies (additional consultation with a therapist is required).
- A symptom of cramped (enclosed) spaces.
- A sharp increase in blood pressure due to stress.
How can a person in a state of sedation respond to any verbal signals?
During human development, the part of the brain responsible for speech functions and verbal activity forms a certain automatism, which is subsequently triggered in certain situations, for example, emergency ones. It is these mechanisms that people who practice NLP influence.
Nitrous oxide - oxygen sedation, relieves anxiety, removes negative memories of the manipulation itself, which is especially important if this is a complex surgical procedure: removal of eighth teeth, implantation, especially massive if, for example, the patient is completely edentulous. No matter how hard the doctors try and no matter how high-quality the anesthesia is, the unpleasant sensations from the same sinus lift or removal of wisdom teeth cannot be eliminated. As you know, a lot depends on the type of nervous organization of a person. People who lead a very active, stressful lifestyle have a lower pain threshold, and the nervous system is often exhausted and more easily excitable. They are the most common candidates for sedation.
Contraindications
Sedation is not anesthesia, which has an extensive list of prohibitions on its use. Its negative impact on the human body is minimal. However, this gentle method of sedation also has a certain number of contraindications:
- individual intolerance, allergies to medications;
- colds, flu, ARVI;
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, hepatitis);
- certain types of chronic diseases;
- myasthenia gravis;
- mental disorders;
- pregnancy;
- alcoholism, drug addiction.
Can everyone use sedation: consider contraindications
Even the safest medical techniques have contraindications and limitations for use. Sedation is no exception; it cannot be used:
- For hypertension, hypotension;
- With diagnosed neurological and mental diseases;
- In severe pathological processes affecting the respiratory system.
Do not resort to sedation for any acute infectious diseases.
To exclude possible contraindications to the technique, before using sedation, a comprehensive examination is carried out, tests are prescribed, the patient himself must be frank with his doctor and honestly and in detail tell about all the diseases in the anamnesis, the presence of allergic reactions, and his condition at the current moment in time.
Pros and cons of sedation in dentistry
The main advantage of treatment, removal or prosthetics of teeth under sedation is that it is much easier and more convenient for the doctor to work with a patient who is in a relaxed state. The patient does not experience negative emotions and a persistent feeling of fear from visiting the doctor’s office. In the future, people will more often visit the dental clinic for preventive purposes.
The procedure also has disadvantages, although there are not many of them. The patient should spend an additional hour in the rest room. The cost remains quite high, which is fully explained by the high price of imported materials, high-quality equipment, as well as the duration of treatment. Initially, you will need to spend time and money on tests and consultation with specialists.
What is the difference with anesthesia
Sedation is a relatively new technology, which most people have a vague idea about, and therefore quite often confuse it with general anesthesia. However, the difference between the techniques is fundamental. It consists of the following main points:
- Sedation does not lead to blocking the body’s main reflexes (cough, gag), which are “switched off” when using general anesthesia, and therefore dangerous disorders of the respiratory function during manipulations are completely excluded;
- The person remains conscious, and therefore the connection between him and the doctor remains. When general anesthesia is used, consciousness is switched off under the influence of drugs;
- Sedation has fewer contraindications and does not require lengthy preparation and rehabilitation.
Teeth are treated under sedation with constant monitoring of the patient’s condition, for which special equipment is used. After completing all the necessary procedures, the person is under the supervision of specialists for some time, but can return home on the same day. After using anesthesia, you will have to stay in the clinic for at least 1-2 days.
While talking about the difference between sedation and general anesthesia, it is also important to note the fact that dental treatment during sleep does not involve the risk of unpleasant and dangerous side effects that are common after using general anesthesia.
What should parents know before dental treatment for children under medicated sleep conditions?
Parents need to know a lot about it, even if they are not dentists and do not want to “get into” the terminology and treatment methods. When it comes to issues of a child’s health, no matter who the parents are, they will have to go through a certain kind of “educational education” so that the decision about treatment is made consciously. Therefore, usually a consultation on treatment under medicated sleep lasts at least 45 minutes, and sometimes more. And here's what's being discussed:
- What is medicated sleep?
Dental treatment for a child under medicinal sleep conditions is one of the methods used in children of any age (when they already have teeth) according to indications. During treatment, the child is in a state of deep sleep, consciousness is turned off, there is no understanding of what is happening and no memories of it. The term “medicated sleep” is similar to the term “deep sedation.”
- Medicines, why is it safe?
At the moment, the drugs of choice for this condition are Sevoflurane (Sevoran) and Diprivan (Propofol, Pofol). Sevoran is a gas supplied using a high-precision device through a mask or tube into the lungs. Propofol is a white liquid that is administered intravenously using a special syringe.
Most often, a combination of these drugs is used, but the decision on the choice of drug or their combination remains under the jurisdiction of the anesthesiologist-resuscitator. These drugs are the most “clean” in modern reality and do not have the side effects that were characteristic of similar drugs of the last century. After treatment with Sevoran and Diprivan, there is no nausea and vomiting, no dizziness and disorientation in space, no neurological “kickbacks”. Therefore, treatment with medicated sleep is used in children with diagnoses such as cerebral palsy, mental retardation, autism, Down syndrome and others. Such children are most often in constant cycles of rehabilitation and, after undergoing treatment with Sevoran and Diprivan, do not lose the achieved results.
- Indications and contraindications
In dentistry, indications for treating children in medicated sleep are:
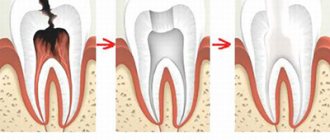
– multiple dental caries under the age of 3 years
— malformations of the central nervous system (Down syndrome, mental retardation, cerebral palsy, etc.)
- a large volume of intervention that must be carried out at one time for the child’s psychological comfort
- insurmountable fear of dental treatment (dentophobia), inability to adapt
- purulent-inflammatory diseases, abscesses, if it is impossible to carry out sufficient local anesthesia
- allergy to local anesthetics
Contraindications:
- decompensation of the underlying general disease
- acute and exacerbation of chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract
Treatment in medicated sleep (hereinafter referred to as MS) may be denied if the preparation regime is violated, in the form of eating after a set time.
So, the parents realized that their child had indications for such treatment, and learned the basics - what MS is and how it is carried out. Next, I think it’s logical to talk about how all this happens, describing everything in detail. So that while listening or reading, you can imagine and “primarily experience” the whole process.
- Logistics from registration to departure home and beyond
After understanding the need for dental treatment for a child with MS, parents usually have a question of choice - “where to treat”, “how does this happen”? This is also accompanied by a hundred more questions like “how will he fall asleep?”, “how will he wake up?”, “will he be in pain?” and so on. Therefore, we provide the following information, which provides answers to most questions.
When the day of treatment arrives and the baby and his parents arrive at the clinic, everything begins like this.
The administrator copies the tests brought and takes a certificate from the pediatrician. Doctors come, greet and sign consent for their interventions: an anesthesiologist-resuscitator and a pediatric dentist. The previously drawn up treatment plan is discussed again. At this moment, parents can still express their wishes, for example, ask to still do the sealing, which was initially refused, or, conversely, write a refusal to treat a specific tooth. After a short time (~15 minutes), mother (or father) and child are invited to an office, on the walls of which there are pictures of animals sleeping peacefully on clouds.
There are 4 people in the office who will carry out the treatment. These are anesthesiologist-resuscitator, nurse anesthetist, pediatric dentist and dental assistant. When the baby falls asleep, there is also a full-time psychologist in the office. The baby is asked to lie down on an unfolded dental chair covered with a blanket and a disposable sheet, and the mother sits next to her on a chair, hugging the child. The anesthesiologist talks to the mother and baby, explaining what will happen now. A mask containing sevoran is applied to the child’s face. At this moment, the mother hugs, strokes the baby, tells him what exactly to do or simply encourages him. After 10-15 seconds of deep breaths of sevoran, initial sleep occurs, the baby closes his eyes and at this moment does not know where he is. After this, the coordinated work of the medical staff begins, mom or dad is escorted by a psychologist to the prepared waiting room, and the doctors begin their work.
The dentist takes all necessary diagnostic images and an initial photo protocol. He adjusts the preliminary treatment plan, depending on the expected diagnoses for specific teeth, and goes to the parents, telling them what will change in the plan and why.
This baby's sleep time is not wasted. While the doctor is talking, an experienced assistant is already carrying out professional hygiene of all teeth, without which high-quality treatment is impossible. When the doctor returns to the office, he immediately begins to work with the child’s already clean teeth.
During treatment, parents may experience anxiety about the child’s condition, however, by contacting the administrators, they can receive feedback in the form: “everything is fine, treatment is underway” or “the right side has been cured,” “crowns are being tried on,” etc.
After treatment, having completed his work, the doctor takes control photographs and a photo protocol is sent to the parents with a report on the treatment performed. In the 5-10 minutes that they have to discuss the results, the anesthesiologists finish their part of the work and bring the still sleeping baby to the waking room to the parents. Next, the dentist and anesthesiologist come to the parents in turn with recommendations and a description of further actions. Each of them tells how to behave at home, what the child feels in his mouth, what support he needs, what cannot be done, and what is absolutely necessary. Within half an hour, the baby wakes up, is given ice cream (if possible and age allows) and for another 15-20 minutes he finally comes to his senses, after which he can go home.
It is important to note that the work is carried out in a coordinated manner, and care for the child is deeply embedded in the standards of treatment created by the chief physician of the clinic. The child will wake up pained, and you will be told how to maintain this condition! You shouldn’t have the fear that “he’s in pain”!
Then you can’t forget about dentists for a couple of years. After treatment, we meet with the child on average 3 months later (the date is set by the doctor) for the purpose of examining and... correctly, ADAPTING him to the dental office. Now our goal is to carefully, systematically, raising the bar each time, to create conditions in which a person will grow up without dental phobia and will perceive preventive and therapeutic visits to the dentist as one of the aspects of self-care.
- Openness and reporting
All stages of the work are photographed, and after treatment, parents receive a photo report in one form or another. Usually we make collages on which we mark the key points of treatment - how many teeth were cured, where there was pulpitis, where there was pus, where there were difficulties in saving the tooth due to severe decay, or another 10 minutes wasted due to inflammation and bleeding of the gums. Thus, it becomes clear to parents what is now in the child’s mouth, what should not be allowed, and what results we expect from this or that tooth.
So, the virtual treatment took place, the thought in my head was “everything suits me, what should I do now to make the treatment take place”?
- Analyzes and preparation
It is necessary to select a date and time of treatment with the administrator and collect tests by this date. Here is their list:
— clinical blood test (acceptable from a finger, in case of difficulties with blood sampling)
- general urine analysis
— ECG or echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) for children, or if the child is restless
- certificate from a pediatrician
Additionally, you need a certificate from a specialist who registers the child if there is an underlying disease. For example, a neurologist for cerebral palsy or a cardiologist for heart disease.
It is logical to take tests first, and get a certificate from the pediatrician last, so that he has the opportunity to assess the child’s condition based on tests, among other things.
Important! On the day of treatment, it is necessary to observe a fasting break and not allow the child to eat or drink for 2 to 4 hours. This is described in detail in our instructions that you receive after the consultation.
- What to do if the tests are ready and the child is sick?
This happens, and the key to success in order to get out of this situation calmly is communication. Yes, don't be surprised. If a child, a couple of days before treatment or right in the morning on the day of treatment, suddenly starts sneezing, or has a fever, or has a runny nose... you can’t wait and think. The first thing that should happen is a call to the anesthesiologist
! You found out who your doctor is at the time you select the date and time, and the phone number is printed on the memo. The anesthesiologist will guide you, assess how much the condition is interfering with treatment, make recommendations, and you will know what to do next. How and when treatment will take place in this case. Without unnecessary assumptions, you will receive guidance for action.
What else do parents need to know?
Dear parents, I am deeply convinced that most disputes, conflicts and misunderstandings are born from closedness, stereotypes and lack of communication. I repeat to everyone during consultations many times - we are here for you, we are in touch. Please, if you have any questions, ask us. You have entrusted or are still choosing whether to entrust us with the treatment of your child, and there should be no room for doubts and “look on the Internet”, all questions can be discussed openly.
- Trust and feedback
You can always contact your dentist or anesthesiologist directly, and we will answer you. You receive a photo report of the work done with the stages of treatment and comments. You receive recommendations and guidelines for action. You receive our willingness to follow the path of adaptation with the child, find a common language with him and move on.
At the end of the article, I would like to note that, as a rule, it is still very important for parents to know what materials, devices and methods will be used for treatment. This is the topic of a whole separate article, but this information is also discussed during the pre-treatment consultation.
The key to successful dental treatment for a child during medicated sleep, in my opinion, is open communication and parents’ trust in the team of doctors. The doctors at the Belaya Medveditsa clinic work for the health of your children and are open to discuss all issues.