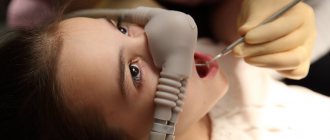
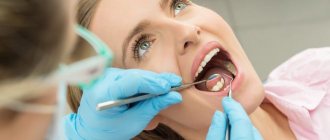
The priority of modern scientific dentistry is the most painless and comfortable treatment, leaving only pleasant memories. But those patients who have been afraid of dentists since childhood are often recommended to undergo procedures under sedation.
Sedation (from the Latin sedatio - to calm down), or drug-induced sleep, is a condition in which the areas of the brain responsible for fear and anxiety are blocked: the patient falls into a light slumber. Consciousness is maintained, and the patient can follow the doctor’s instructions - for example, turn his head or open his mouth. Other centers of the brain that support breathing or coughing are not inhibited, and treatment in the oral cavity occurs safely.
Sedation is indicated for patients who are afraid of pain and discomfort. People who lead an active, stressful lifestyle often resort to dental treatment under sedation in Moscow - they often have a low pain threshold, their nervous system is easily excitable, and any dental procedures cause severe discomfort. Sedation can be intravenous or inhalational. With intravenous sedation, the drug is injected into a vein through a catheter, dosed very precisely, and the anesthesiologist monitors the patient's condition, administering an additional dose if necessary. Intravenous sedation itself does not provide pain relief, so local anesthesia is additionally administered. Intravenous sedation is performed only in adult patients. For mask or inhalation sedation, a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen is used. The use of this method may be justified, for example, in case of allergies to local anesthetics, but the most modern and frequently used method for adults is intravenous sedation.
No matter how attractive the idea of “dental treatment in your sleep” is, there are also contraindications :
- acute diseases of the upper respiratory tract, in which nasal breathing is difficult;
- mental illnesses accompanied by agitation or aggression;
- epilepsy;
- myasthenia gravis;
- pregnancy;
- age under 3 years.
High blood pressure, angina pectoris, traumatic brain injury, heart attacks or strokes in history are not an absolute contraindication, but consultation with a therapist, careful examination and monitoring of the condition during the procedure are required.
What is sedation?
Sedation is a process of relaxation and anxiety relief. The word itself comes from the Latin “sedatio”, which translates as “calm”. In dentistry, various sedatives are used for these purposes, which are administered by inhalation or intravenously. Thus, it is customary to distinguish several types of such anesthesia:
- inhalation sedation: for this direction we use the inert gas xenon, which does not anesthetize, but relaxes before introducing the main anesthesia (usually local, that is, infiltration or conduction, which allows you to anesthetize the tissues of the oral cavity).
- intravenous sedation: sedatives are administered through a catheter directly into a vein. The patient becomes drowsy (sleeping or dozing),
- general anesthesia: drugs are administered intravenously (inhalation is also possible, but this type of anesthesia is not used in dentistry). The person goes into medicated sleep for several hours.
Types of sedation: superficial and deep
The following sedative methods of relaxing and calming patients are used in dentistry:
- Superficial is the best solution in a situation where the patient requires relaxation for a short period of treatment. Indicated for adults, as well as children from the age of three. A state of pleasant slumber is achieved by inhaling oxygen mixed with nitrous oxide. The nasal mask through which the gas passes is connected to the machine. The doctor can change the ratio of components and dosage based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Deep - the medication is administered through an intravenous injection. This technique copes better with severe fear and anxiety. The technique is used for adults and children at least 15 years old. The relaxed state lasts longer than with a superficial state. The patient will need to stay in the clinic for some time and stop driving for 8 hours.
Anesthesiologists at the Refformat dental clinic in Moscow have been working with a wide variety of patients for a long time and their experience makes treatment safe. Any intervention, preparation and installation of prostheses will be comfortable and unnoticeable.
How is intravenous sedation different from general anesthesia?
The main difference is in the drugs used. As a consequence - in the duration of medicated sleep, the quality and effect of anesthesia, the severity of side effects and consequences, as well as in the subsequent rehabilitation of the patient.
- number of drugs: with intravenous sedation, only one drug is used, and it can be in different dosages (and, of course, is selected strictly individually based on the results of in-depth diagnostics). The patient will be in medicated sleep during the entire period of the operation, or in a relaxed state, half asleep. With general anesthesia, 2 or more drugs are used, including tranquilizers and narcotics, which puts a greater burden on the body,
- anesthetic and analgesic effects: during general anesthesia all receptors are “switched off”, during sedation - partially, which occurs due to a decrease in general sensitivity,
- consequences: after general anesthesia, side effects may appear within 2-3 days after surgery. This is not just dizziness and confusion, but also lethargy and even hallucinations. With sedation, there is no need for hospitalization or a long stay in the clinic - complete recovery occurs within 1-2 hours. All side effects are short-term and mild.
Which is better, sedation or general anesthesia?
Intravenous sedation is carried out using lighter and simpler drugs, so it is the more preferable method of pain relief when carrying out large-scale work. And not only in dentistry, but also in many other branches of medicine. Fewer side effects, including prolonged action (with general anesthesia, they can appear even within a year after treatment), less stress on the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular and nervous system.
In general, the advantages of intravenous sedation are as follows:
- you fall asleep - you don’t feel pain, you don’t see how treatment or surgical procedures are carried out, and what instruments the doctor uses (and all this causes extreme stress for those who are afraid of the dentist),
- all treatment is carried out at one time, which is especially important in case of multiple scattered caries or in case of total restoration of teeth on implants,
- the quality of treatment improves and the risk of postoperative complications decreases, since the doctor is not distracted by the patient’s emotions,
- It is possible to carry out treatment in patients who are not affected by classical “freezing” or have allergic reactions to the drugs used.
With us you will stop being afraid of dentists! Individual selection of drugs, the most modern equipment and certified doctors who professionally work with all types of anesthesia.
Enroll now
Main indications for the use of sedation
Sedation is a technology whose use is justified:
- For patients experiencing severe fear and panic of dentists and dental treatment;
- With a low pain threshold;
- With a pronounced gag reflex that can prevent the doctor from performing all the necessary manipulations;
- With a significant volume of procedures to be performed during treatment. For example, dental sedation will allow treatment of multiple caries and dental implantation without pain and discomfort;
- In case of traumatic dental intervention. Sedation in dentistry can be used for complex tooth extractions - a lengthy operation that involves making incisions in the gums and other complex manipulations. Tooth extraction under sedation will be painless.
Dental treatment under sedation is also recommended for patients suffering from diseases of the heart and cardiovascular system. People with these conditions may experience severe anxiety before visiting the dentist's office and procedures, which can be completely eliminated by sedation. Quite often, sedation is used when dental treatment is necessary in children. The technique ensures the little patient’s perseverance in the chair, and in addition, it will relieve them of tears, fear and stress, and will help to form the right attitude towards dental treatment in the future. If treatment at an early age is not associated with negative emotions, then dentophobia (fear of dental treatment) will not arise in adulthood.
How is treatment performed under intravenous sedation?
The essence of using intravenous sedation is that certain anesthetics are introduced into the body, which put the person into sleep. The drug itself and its dosage are selected based on the patient’s weight, health status, and the duration of the procedure. If necessary, the drug can be reintroduced during surgery.
A catheter is inserted into a vein in the arm through which the medication is administered. The catheter remains in place until the end of the entire treatment, as repeated administration of the drug may be required.
The operation is performed on an empty stomach: you cannot eat or drink for 6 hours before sedation. The procedure is not limited in time. The patient wakes up naturally within 20 minutes after the end of the drug and is under the supervision of specialists for a maximum of 1-2 hours who will monitor their health.
After treatment under sedation, it is strictly not recommended to drive, as concentration decreases. There are no more restrictions.
How will you feel?
Nothing, because sedation relieves all unpleasant sensations. At the same time, it can be superficial - you will be in a state of half-asleep or half-asleep (answering doctors’ questions, periodically falling asleep, but remaining in a relaxed state), or complete, when you will be sleeping throughout the entire time the operation lasts . Here the choice is yours. But in both cases you will not feel anything. The maximum is the “moving” of the instruments in the oral cavity, because you understand that the doctor is doing some kind of work.
Comfortable treatment without pain! We carry out thorough diagnostics, select medications and dosages strictly individually. It's safe here!
Enroll now
Features of tooth extraction under anesthesia
Anesthesia for tooth extraction is no different from that used for other types of dental procedures. Indications and contraindications remain the same, as can be said about the technique.
At the same time, we note that the use of anesthesia to remove one tooth is not always considered appropriate, since there are less radical and no less effective methods of pain relief.
Doctors will advise you on all issues, develop an individual treatment plan based on the characteristics of your specific clinical situation, and also agree on all the nuances of subsequent work.
Will it hurt during and after treatment?
No, there won't be any pain either. 1-2 hours after treatment, when the anesthesia wears off, tolerable pain may occur. It is associated exclusively with tissue injury. The doctor will prescribe painkillers for you: whether to take them or not is up to you to decide, based on your own condition. More than half of our patients after dental implantation take painkillers only for the sake of prevention - so that the pain does not overtake them in the middle of the night while sleeping, about 30% do not take them at all, and the rest do not take them as prescribed, because there is slight discomfort.
Literature
- Boisson-Bertrand, Ravussin P. 4th meeting of the anesthesia-resuscitation section of the ORL Department. Lausanne//Ann. Fr. Anesth. Reanim. – 1991.- Vol. 10(1).- 1A-2A.
- Buck M., Blumer J. Opioids and other analgesics: Adverse effects in the intensive care unit // Crit. Care Clin. — 1991.- Vol. 7.- R. 615-637.
- Chollet-Rivier M, Chiolero RL. Anaesthesia for procedures in the intensive care unit. // Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. – 2001 – V. 14(4) – P. 447-51.
- Cohen D., Horiuchi K., Kemper M. et al. Modulating effects of propofol on metabolic and cardiopulmonary responses to stressful intensive care unit procedures // Crit Care Med.- 1996.- Vol. 24.- R.612-617.
- Cohen IL, Abraham E., Dasta JF, Gallagher TJ, Papadakos PJ, Pohlman AS Management of the agitated intensive care unit patient // Crit. Care Med. - 2002. - Vol. 30. – R. 97-123.
- Durbin CGJ Sedation of the agitated, critically ill patient without an artificial airway // Crit. Care Clin. - 1995. - Vol. 11. – R. 913-936.
- Ely E.W. Delirium in Intensive Care Unit: Textbook of Critical Care Fifth Edition MP Fink. E.Abraham, JLVincent, PM Kochanek - Flsevier, 2005.- 2358 p.
- Frye MA, Coudreaut MF, Hakeman SM et al. Continuous droperidol infusion for management of agitated delirium in an intensive care unit // Psychosomatics. - 1995. - Vol. 36. – R. 301-305.
- Harvey M. Managing agitation in critically ill patients // Am. J. Crit. Care - 1996. - Vol. 5. – R. 7-15.
- Kress IP, Lacy M., Pliskin N., Pohlman A. The long term psychological effect of daily sedative interruption in critically ill patients // Am. Respira. With rit. With are Med. - 2001. - Vol. 163. R .954
- Kress JP, Pohlman AS, Hall JB Sedation and Analgesia in the Intensive Care Unit // Am. J. Respira. Crit. Care Med. – 2002.- Vol. 166. – R. 1024-1028.
- Lewis K., Whipple J., Michael K., Quehbeman EJ. Effect of analgesic treatment on the physiological consequences of acute pain // Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. - 1994. –Vol. 51. – R. 1539-1554.
- Liu J., Singh H., White PF Electroencephalographic bispectral index correlates with intra-operative recall and depth of propofol-induced sedation // Anesth. Analg. — 1997. –Vol. 84. – R. 185-189.
- Mehta S. Sedation Strategies in the Critically II // Yearbook of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine - Edited by JI.Vincent -Elsevier - 2005.- R. 78-
- Milbrandt E.W., Ely E.W. Agitation and delirium. Critical Care. Fifth edition. Finc MR, Abraham E, 2005, chapter 2.
- Park G, Lane M, Rogers S, Bassett P. A comparison of hypnotic and analgesic based sedation in a general intensive care unit. // Br J Anaesth. – 2007. – V.98(1). – P.76-82.
- Rhoney DH, Parker DJ Use of sedative and analgesic agents in neurotrauma patients: effects on cerebral physiology // Neurol. Res. - 2001. –Vol. 23. – R. 237-259.
- Terao Y., Miura K., Saito M., Sekino M., Fukusaki M., Sumikawa K. Quantitative analysis of the relationship between sedation and resting energy expenditure in postoperative patients // Crit. Care Med. — 2003. –Vol. 31(3). - R . 830-833.
- Vinik H. Intravenous anaesthetic drug interactions: practical applications. //Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. Suppl. – 1995. – V.12. –P.13-19.
What if something goes wrong? Is this really safe?
Yes, it is completely safe: the administration of the anesthetic, as well as monitoring the patient’s condition, is carried out by professional and licensed anesthesiologists. The participation of professional anesthesiologists in the operation who monitor the patient’s condition allows the implant surgeon or maxillofacial surgeon at our clinic to fully concentrate on the operation. Constant monitoring of all vital indicators of the patient’s health status is mandatory.
In addition, there is an ambulance station in close proximity (up to 1 km) from each clinic. And this is an additional guarantee of your safety, because in case of complications, every second will count.
“Like you, we are sincerely interested in safe treatment and high-quality restoration of your health, so we make every effort to provide comfortable treatment: we focus on diagnosis, the correct selection of medications, and monitoring the condition during surgery.”
Namdakov Nikolay Vladimirovich maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist, orthopedist, work experience over 18 years make an appointment
Contraindications
Despite its apparent safety, sedation is not indicated for all categories of patients. Below is a list of who may benefit from local anesthesia only:
- small children under 3 years old. Due to their age, they cannot describe their feelings and condition;
- patients with respiratory diseases. Breathing may be impaired;
- pregnant women. There is concern that exposure to the gas will negatively affect the fetus. This is especially true for the first and third trimesters;
- patients with epilepsy. The gas can trigger an attack;
- people who have recently suffered a traumatic brain injury. Increased intracranial pressure may worsen the condition;
- patients with mental disorders. Their inadequate reaction can interfere with the smooth conduct of dental treatment.
What do patients say about treatment under sedation?
Most of our patients sleep during surgery and wake up after the doctor has finished treatment. Many people note that they sleep well during this time. If they remain conscious (lighter sedatives are used), then they do not feel pain, but there is a feeling of a slight “crawling” in the mouth from the knowledge that the doctor is removing/treating teeth or implanting implants.
Svetlana Yurievna
“They sat me at a table, put me on an IV, then transferred me to a chair and I don’t remember anything else. Before the operation, the doctor noted that he would look at my condition and see how much medication I would need. To be honest, this scared me. Because I thought that at some point the sedative would end, it would hurt and I would feel it. But nothing like that happened, I turned my head - they put additional medicine in my IV, and everything ended well. I am immensely happy!”
- treatment WITHOUT FEAR and pain
- guaranteed safety
- minimal health risks
- with condition monitoring and professional supervision
watch a video with the patient
When should you not resort to drug sedation and can you do without it?
1. In the case when the doctor himself causes you fear. This is stupid, because the doctor will not do anything bad to you, but will only cure your teeth.
2. When you feel that it will be best to treat your teeth with your participation and consciousness, because the doctor often has questions about resolving a particular dental situation.
3. When you think that medical dental sedation will simplify and facilitate your doctor’s work. Maybe sometimes this statement makes sense, but just for the sake of this you should not resort to sedation treatment and agree to such an extreme measure.
How to prepare for treatment
To ensure that sedation does not have any negative effects on the patient’s body, a thorough diagnosis of the health status before it is necessary - it will allow you to exclude possible contraindications, choose medications, and also find out what difficulties may arise during medicated sleep.
Tests and examinations before treatment under sedation
Before treatment or dental restoration under anesthesia, you will need to take a number of tests and undergo some examinations. You can take tests directly in our clinics completely free of charge: they are included in all types of dental implantation.
- general and biochemical blood test (AST, ALT, urea, creatinine, total protein, glucose, electrolytes), valid for 14 days,
- blood test for HIV, hepatitis C and B, syphilis, blood group and Rh factor, valid for 3 months,
- hemostasiogram or coagulogram (blood test), valid for 1 month.
All of the above tests are performed directly in our clinics completely free of charge. It is also additionally necessary to provide the results of the following examinations:
- ECG (electrocardiogram),
- Chest x-ray or fluorography – research results for the last 6 months are accepted: images or a specialist’s opinion (description of the images),
- For patients over 50 years of age, consult a general practitioner or cardiologist.
In a number of laboratories, these tests can be performed in a comprehensive manner: medical companies are developing special profiles called “hospital” profiles, in particular “for hospitalization in a surgical hospital.”
Lifestyle before treatment under sedation
- the operation is carried out without signs of acute respiratory viral infections and other infections. If you feel sick or become ill, be sure to notify your personal manager to reschedule your surgery,
- food: on the day before surgery, a light breakfast is allowed: dry toast, tea or weak coffee without milk. If the operation is in the morning, then you need to limit yourself to dinner only,
Important! Before surgery, under sedation, you cannot eat for 6 hours!
- drinks: stop drinking liquids 2 hours before surgery,
- alcohol: prohibited 2-3 days before surgery,
- taking medications: orally – no later than 2 hours before surgery,
- women are advised not to use cosmetics and must also remove all coating from their nails,
- After the operation, we do not recommend driving, so you must come to the clinic by taxi/public transport or ask someone you know to bring you.
Follow the link to study a detailed reminder about preparing for implantation.
Are there any disadvantages to sedation?
Naturally, dental treatment or implantation under general anesthesia has certain disadvantages. In particular, the need for rehabilitation after the administration of the drug and a fairly large list of contraindications. However, our clinic conducts a thorough diagnosis of the body’s condition before using any anesthetics. If the doctor identifies certain risks, you will be denied sedation and will not take any risks. In addition, by working with professional anesthesiologists, any unpleasant consequences are reduced to a minimum.
Consequences of sedation in dentistry
Specific problems with the use of mind control drugs depend on the route of administration and the mechanism of action of the drugs.
At the beginning of the procedure, you may experience increased activity, physical restlessness, talkativeness, and increased sociability.
A common symptom is an obsessive cough. This problem can be stopped by reducing the dose of the drug. Complications after sedation can appear both immediately and in a delayed period.
Possible short-term complications
- Breathing disorders (slow breathing, lack of oxygen);
- problems with hemodynamics (drop in blood pressure, irregular heart rhythm);
- depression of the central nervous system;
- intestinal dysfunction, vomiting.
Delayed symptoms
- Development of psychoses;
- hallucinatory syndrome;
- paralysis.
Is sedation dangerous? No, if it is carried out by an experienced doctor who has undergone special training, and the clinic is equipped with everything necessary to eliminate the consequences. But this is not a magic pill that can be prescribed to everyone without thinking about the consequences.