Often, the dentist prescribes antibiotics to the patient after the removal of a wisdom tooth in order to avoid unpleasant consequences or complications. The main indicators of antibiotic therapy include the development of the inflammatory process in the formed hole. More information about the choice of antibacterial drugs will be discussed in this article.
Antibiotics after wisdom tooth removal
Content:
- The use of antibiotics during tooth extraction for preventive purposes
- Antibiotics after tooth extraction with inflamed gums
- When you can't do without antibiotics
- Types of antibiotics used in dentistry
- What are the consequences of not taking antibiotics?
Only the dentist can decide whether to prescribe an antibacterial drug to a patient or not.
The need for its use does not always arise. If the operation was uncomplicated and the likelihood of complications is minimal, additional drug therapy is usually not required. Even if after tearing out a unit the body temperature has increased, this is not an indication for antibiotic therapy. The body adequately responds to the inflammatory process and does everything necessary to block the spread of pathogenic microflora. Normally, already on the 3-4th day the patient’s condition is completely normalized, the pain goes away, the swelling subsides.
Treatment rules
The oral cavity is home to “healthy” rich microflora. Taking antibacterial drugs causes the death of the necessary lacto- and bifidobacteria and leads to a rapid increase in the number of pathogenic strepto-, pneumo-, and staphylococci.
Important! Taking antibiotics for dental diseases harms the microflora of the oral cavity in any case, regardless of which dosage form of the drug was chosen by the attending physician (oral medications, injections, capsules, drops, applications).
Treatment with antibiotics excludes the use of alcoholic beverages, psychotropic, sleeping pills and narcotic drugs. If we are talking about tablets, capsules or local antibiotics, then they are used an hour before or 2 hours after a meal, otherwise the absorption of the drug will be complicated. Take the tablets with warm boiled water.
How many days to take antibiotics: if there is no therapeutic effect after 2-3 days from the start of treatment, the drug must be replaced (or the dosage adjusted). Pregnant and lactating women, children, and patients with chronic diseases can take antibiotics only after consulting a doctor.
Antibiotics do not cope with pain and swelling, so patients who have undergone extraction are additionally prescribed antihistamines, anti-inflammatory and painkillers
Antibiotics after tooth extraction with inflamed gums
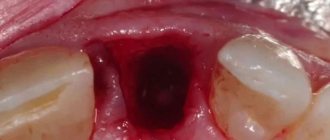
A few days after the extraction, the patient visits the dentist who performs the operation. The doctor assesses the course of regenerative processes. If it turns out that the inflammatory process has spread and there is a high probability of a bacterial infection, then antibiotics are immediately prescribed. They create conditions for the speedy restoration of damaged mucous membranes.
The most common reasons why antibiotic therapy is necessary after removal of radical units:
- non-compliance with medical prescriptions, due to which the hole became inflamed;
- too active rinsing of the mouth, which caused the displacement of the protective blood clot;
- slow healing associated with the individual characteristics of the human body.
After studying the specifics of the situation, the doctor decides which medications to prescribe. In some cases, it is possible to get by with local application of antibacterial gels and ointments. For severe inflammation, oral medications are prescribed.
Main activities after extraction
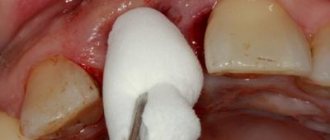
As soon as the tooth is removed, the doctor treats the empty socket and places a cotton swab soaked in the medicinal composition into it. In some cases, stitches may be required. On the recommendation of the dentist, the tampon is removed several hours after the manipulations.
During this time period, it is forbidden to eat, smoke, drink, talk, that is, it is better not to open your mouth at all. You should also not touch the hole with your fingers or insert foreign objects into it. To disinfect (disinfect) the oral cavity, you should use Furacilin, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt.
Important! To prevent postoperative bleeding, you should not bend over, lift heavy objects, visit saunas, or take hot baths.
Upon completion of the extraction, patients can be prescribed antibacterial compounds in various dosage forms - tablets, capsules, drops, local solutions and applications
When you can't do without antibiotics
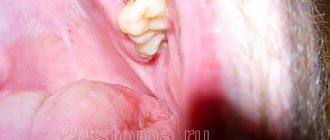
If after extraction a secondary inflammatory process has developed, affecting the trigeminal nerve, alveolar ridge, periosteum, there is nowhere without antibiotic therapy. It is also carried out if:
- the operation was complex (for example, the “eight” was pulled out);
- a large amount of purulent exudate is released from the hole;
- alveolitis has developed, body temperature is elevated, the wound is infected;
- periodontitis was diagnosed, spreading to the tissues that are located next to the extracted tooth;
- osteomyelitis was identified, which contributes to the formation of fistulas;
- periostitis progresses, has spread to the periosteum;
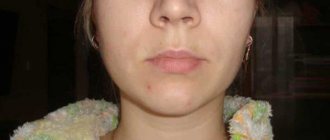
- After the operation, flux developed at the removal site, and the face became very swollen.
It is very important that in case of any complications the patient visits the dental clinic and does not self-medicate, experimenting with different pharmaceutical drugs and folk recipes.
Possible complications
Incorrect dosage, non-compliance with the rules for taking medications, as well as incorrectly selected medications can provoke the following unpleasant consequences:
- Alveolitis is an inflammation of the socket of an extracted tooth.
- Periodontitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the soft tissues surrounding the empty socket.
- Flux is inflammation of the periosteum.
- Osteomyelitis is purulent-necrotic processes affecting the jaw bone tissue.
So, in modern dental practice, after tooth extraction, if there are indications (inflammatory processes, certain chronic diseases, problems with blood clotting), it is customary to prescribe antibacterial therapy. Why are such drugs needed?
The main task of antibiotics is to fight pathogenic microflora: pathogens of inflammation, the cause of suppuration and a number of other postoperative complications. Whether it is necessary to take medications is decided in each specific case by the dentist, based on the characteristics of the individual patient’s body and the presence of concomitant dental (systemic) diseases.
Types of antibiotics used in dentistry
To eliminate the symptoms and consequences of dental diseases, antibiotics of the following pharmacological groups can be used:
- Penicillins. The largest category of antibacterial agents. They are characterized by a wide spectrum of action and effectively destroy pathogenic microorganisms. They can be injected or used in tablet form.
- Macrolides. Remedies that are often used for diseases of the ENT organs. Dentists prescribe them only if the patient has poor tolerance to other antibacterial drugs or the pathogen is insensitive to penicillins.
- Cephalosporins. Medicines exhibiting excellent bactericidal properties. In dental practice, two representatives of the group are most often used - Cefaclor and Cephalexin.
- Lincosamides. Medicines that effectively control the inflammatory process. With their help, you can quickly eliminate inflammation and prevent further progression of dental complications. A popular representative of lincosamides is Lincomycin. It can be bought in the form of tablets, injections, ointments. The latter is suitable for tamponade of the inflamed socket.
- Fluoroquinols. Contains tsifran - a component that quickly destroys pathogenic flora. Indicated for purulent complications.
- Aminoglycosides. They are prescribed after extensive dental operations, if the wound is infected or the infection has entered the blood.
- Tetracyclines. They act by blocking protein synthesis in microbial cells. These include Oletetrin, Doxycycline. It should be noted that today tetracyclines are used less and less, since many modern infections are little sensitive to their active substance.
Contraindications
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed exclusively by a doctor, as drugs in this group have a wide range of contraindications. This takes into account the physiological characteristics of the body, the presence of chronic diseases and the age category of the patient.
Antibacterial drugs should not be used in the following cases:
- Each antibacterial drug has its own list of main contraindications and features of its use.
Dysfunction of the digestive system.
- Breastfeeding period.
- During gestation of an intrauterine fetus.
- Individual intolerance to the drug.
- The presence of allergic reactions to the components of the antibiotic.
- Kidney failure.
- Liver diseases of any etiology.
- Age category up to 12 years.
- Diabetes mellitus of any type.
- Arterial hyperplasia.
Each antibacterial drug has its own list of main contraindications and features of its use. Therefore, before using it, it is recommended to study the annotation for it.
What are the consequences of not taking antibiotics?
If a doctor has prescribed a medicine, but the patient does not want to take it because of some personal beliefs, the situation often turns against him. It may turn out that the doctor’s worst fears will come true - the inflammatory process will spread to the jaw bone. Then osteomyelitis will develop.
This purulent disease is quite insidious. It can affect internal organs and cause sepsis, which, in turn, can be fatal. Therefore, you should not argue with the dental surgeon and ignore his appointments. Take care of your health.
Tooth abscess - symptoms and treatment
A tooth abscess does not go away without treatment. If you open it yourself, the pain may decrease significantly, but this does not eliminate the need for dental treatment. If the abscess is not drained, the infection can spread to the jaw tissue and other areas of the head and neck, which can lead to various complications.
Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
When the veins are located close to the source of infection, a serious complication such as thrombophlebitis develops - inflammation of the vein with subsequent formation of a blood clot. First, the inflammatory process affects the walls of blood vessels (phlebitis), then spreads to the tissue surrounding the vein (periphlebitis) and finally covers the entire wall of the vein. Due to damage to the vessel, blood flow becomes slower, the composition of the blood changes, and clotting increases. All this contributes to the formation of a blood clot. In some cases, blood clots form in the venous sinuses of the brain.
Mediastinitis
Mediastinitis is an inflammation of the mediastinum (a complex of organs located in the chest cavity between the left and right mediastinal pleura, the posterior surface of the sternum and the thoracic spine and rib necks). Can be fatal.
The infection can penetrate into the mediastinum by contact, through the blood or lymph flow. The purulent exudate is so active that it can melt the intermuscular septa and walls of large arteries. In this regard, the infectious process spreads quickly and creates the risk of severe bleeding.
The source of the spread of infection leading to mediastinitis is usually inflammation in the area of the apex of the tooth root (sometimes in combination with infection of the tonsils or damage to the oral mucosa).
Acute or chronic sepsis
Sepsis is the most severe complication of a tooth abscess, which occurs when the immune system fails. The body cannot resist the infection, and it spreads throughout the body. Depending on the speed of onset of symptoms, sepsis can be fulminant (1-2 days), acute (5-7 days), subacute (1-2 weeks) and chronic. First of all, the functioning of the lungs is disrupted, and then other organs: liver, kidneys, etc. Subsequently, septic shock develops: blood circulation in the organ tissues slows down, and failure of several organ systems develops - multiple organ failure syndrome. When this syndrome occurs, most patients die within 2-3 days [8].
Meningeal diseases
Meningeal complications of a tooth abscess (meningitis, brain abscess, etc.) are not so common, but their mortality rate is quite high: it reaches 40-90%. Most often, these diseases arise due to the spread of infection from primary foci, the temporal region, pterygopalatine or infratemporal fossa.