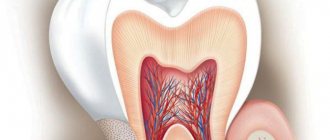
Anatomically, a tooth consists of three parts:
- crown
- neck
- root
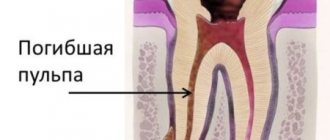
There is a cavity inside the crown and root. The pulp is localized in these cavities. The part of the pulp that is in the crown is called coronal, and in the root is called root.
The pulp itself consists of nerve endings, blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.
The pulp is the nerve of the tooth, together with blood and lymphatic vessels, providing the tooth with nutrients.
Inflammation of the pulp is called pulpitis.
Causes of pulp inflammation
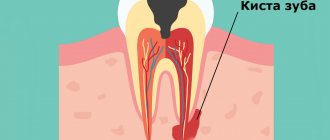
The main cause of pulpitis is the penetration of infection into the pulp cavity, in which a bundle of blood vessels and nerves is located.
The causative agents of the disease can be both pathogenic (Staphylococcus aureus) and conditionally pathogenic (lactobacillus) microorganisms. They can penetrate into the tooth in several ways:
- through the dentinal tubules in case of poor oral hygiene, accumulation of bacterial plaque and stone in the gum pockets;
- through cracks in the enamel caused by tooth trauma;
- through cracks due to a fracture of the dental crown;
- through the apical opening of the root canal against the background of periodontitis, osteitis and other chronic inflammatory processes of the oral cavity.
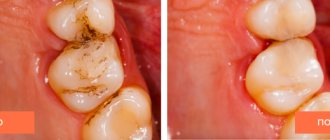
- Inflammation can also occur after treatment of deep caries
Etiology of pulpitis
Based on etiology, which implies the nature of the inflammatory process, pulpitis is divided into three types. The classification is carried out depending on the nature of the irritant acting on the pulp:
- Infectious pulpitis develops in acute, but more often chronic diseases of the teeth and oral cavity (caries, osteomyelitis, periodontitis, etc.). In rare cases, the infection enters the root canal and pulp through the circulatory system from other units of the jaw or internal organs.
- Traumatic pulpitis develops when a tooth is damaged with the opening of a traumatic cavity (crack, chip) into the pulp. Occurs with sports injuries, crown and root fractures.
- Iatrogenic, that is, occurring after dental treatment . Occurs after treatment of deep caries, when the internal tissues of the teeth are irritated by the use of chemical, mechanical or thermal irritants.
Knowledge of the etiology helps the dentist select the most appropriate treatment methods and avoid complications in the future.
Historical reference
In ancient times, humanity did not yet know the term “pulpitis,” but they were familiar with toothache in different parts of the world. The main means of getting rid of it was tooth extraction. In some countries, conspiracies and rituals with sacrifices were used “for medicinal purposes.” In ancient Egypt, according to information found in ancient papyri, doctors looked for ways to help the patient using anti-inflammatory ointments containing the juice of various plants, and pastes made from myrrh, ash, pumice and eggshells.
In the 1st century AD The personal physician of the Roman Emperor Trajan, the surgeon Archigenes, drilled a tooth for medicinal purposes. Around 150-160's. the famous physician and philosopher of antiquity, Claudius Galen, described in his works the differences between pulpitis and periodontitis, but this knowledge was forgotten for a long time. In the 9th century in the Middle East, the physician and pharmacist Muhammad al Rashid advised using arsenic to destroy the dental nerve that was causing pain to the patient. But in European countries this method became known much later.
In the 11th century, in some European countries, caries and the pulpitis caused by it were “treated” with laxatives and enemas, and if this did not help, the pulp was burned with a hot iron with “anesthesia” in the form of using alcohol-containing compounds before manipulation or even hitting the head with a board. , the so-called Rausch anesthesia. In the 15th century, a professor at the University of Bologna repeated the experiment described by Archigen - he removed the affected dental tissue by drilling, after which he cauterized the pulp and filled the tooth cavity with gold.
Pierre Fauchard, a French doctor who lived in the 18th century, learned to identify 102 types of toothache, studied and practiced various methods of eliminating it, and became the founder of the “dental” patient position. Before him, the patient was placed on a table or seated on the floor, pressing his head between his knees, and P. Fauchard insisted that the patient in this position experiences unwanted nervousness and it is necessary that he sit in a chair, and the doctor stands next to him.
After 1871, when James Morrison patented the dental drill, therapeutic dentistry began to develop rapidly. Tools, equipment, drugs for pain relief, technologies began to appear, some of which are still actively used by dentists. Today, modern dentistry has effective methods, modernized instruments, and improved technologies with the help of which dental diseases, including pulpitis, can be effectively treated.
Symptoms
Inflammation of the pulp is not difficult to differentiate already at the stage of examining the oral cavity and interviewing the patient. This disease is characterized by:
- sudden onset of pain and its intensification at night;
- a gradual increase in pain intensity and duration in the first 3-5 days from the onset of the disease;
- irradiation (spread) of pain to the ear, eye, chin, depending on the location of the diseased tooth.
A characteristic feature of pulpitis, which makes it possible to distinguish it from caries and other dental pathologies, is a sporadic increase in pain, which is not associated with thermal, mechanical or other effects on the tooth.
Price
The cost of treating pulpitis is influenced by many factors. First of all, these include the form and stage of pulpitis, diagnostic measures that make it possible to establish an accurate diagnosis and choose the most appropriate treatment method. In addition, the medications, materials, equipment and instruments used during treatment are important. Not the least important role is played by the qualifications of the doctor, additional consultations with specialists, as well as medical measures accompanying the main treatment, if necessary.
Many patients think that toothache is a temporary “little thing in life” that can be overcome with the use of modern painkillers. But this illusion quickly dissipates as soon as a person experiences unbearable pain... Remember that the sudden appearance of toothache is in all cases a serious signal warning of the presence of some kind of pathology in the maxillofacial system. In many cases, this pathology turns out to be pulpitis - a disease that, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to many complications, including tooth loss. But only a qualified doctor can determine the exact cause after conducting a thorough diagnostic examination. Therefore, visit the dental office as soon as possible. Your efficiency, combined with modern treatment methods and the professionalism of the doctor, is a guarantee that the disease that caused the pain will be completely cured and will not deprive you of the beauty of a full smile.
According to antiplagiat.ru, the uniqueness of the text as of October 16, 2018 is 97.5%.
Key words, tags: caries, periodontitis, periodontitis, deep caries, tooth extraction
1 Therapeutic dentistry. Dental diseases: textbook: in 3 hours / ed. E.A. Volkova, O.O. Yanushevich. - 2013. - Part 1.). 2 https://mkb-10.com * Images: - Domenico Ricucci, Jose Siqueira, “Endodontics. Clinical and biological aspects”, Publishing house “Azbuka”, Moscow, 2015. A book for dentists and endodontists. Edition in Russian, translated from English, 415 pages, 1682 illustrations, hardcover. The original edition of the book “Endodontology: An Integrated Biological and Clinical View (Ricucci, Domenico and Siqueira Jr, Jose)” was published in 2013. — Database of clinical photo protocols of the Dental Clinic Dr. Edranov; Personal archive of S.S. Edranova.
Forms and types
The classification of pulp inflammation divides the disease into two forms according to the nature of the development of the pathology:
- Acute pulpitis is a first-time inflammatory process that lasts from 3 to 5 days and is accompanied by intense symptoms.
- Chronic pulpitis is a long-term inflammation that develops in the absence of treatment for acute pulpitis. Symptoms tend to periodically worsen, and in the intervals between them there is no discomfort or it is very mild.
Both forms have several subtypes, which differ in localization, degree of spread, and the nature of the development of the inflammatory process.
Types of acute pulpitis
There are four types of acute pulp inflammation:
- Focal pulpitis . It is diagnosed during primary inflammation, when the carious cavity reaches the pulp. The localization of the pathological focus is the upper part of the tooth. This type of disease is accompanied by the most intense symptoms and signs of inflammation spreading along the trigeminal nerve and nearby lymph nodes.
- Diffuse pulpitis . Diagnosed 1-2 days after the onset of acute inflammation. The lesion is located throughout the coronal part of the tooth, sometimes down to the neck and root part of the pulp. Attacks of pain last relatively short time and worsen when the patient lies down.
- Serous pulpitis . An advanced form of acute pulpitis, accompanied by painful pain symptoms that do not subside.
- Purulent pulpitis . The final stage of acute inflammation, in which a focus of suppuration forms in the pulp. The process is accompanied by signs of acute intoxication of the body, increased pain when eating warm and hot food. Symptoms weaken when cold is applied to the diseased tooth.
Classification of chronic pulpitis
Chronic pulpitis occurs in three types:
- Fibrous inflammation is the most common variant and lasts about 3 months after the initial inflammation. It is accompanied by bleeding of the pulp when touched, periodic pain in the tooth when it comes into contact with cold or hot food.
- Hypertrophic inflammation is a condition accompanied by the formation of a polyp inside the pulp. It looks like a piece of gum growing out of a tooth. Pain with this type of chronic pulpitis is minimal or absent.
- Gangrenous inflammation is the most dangerous pathological process, which is accompanied by active necrosis of tooth tissue. Accompanied by an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth.
Good to know! In addition to the listed types of acute and chronic pulpitis, dentistry distinguishes deep root, two- and three-channel inflammation, as well as pulpitis under a filling.
Methods used in the clinic
We are adherents, first of all, of effective and then modern treatment methods that can quickly, efficiently and radically eliminate the cause of pulpitis and its consequences. But, in our work, we always try to “save” the pulp and preserve its viable properties using conservative methods and use them in all cases where possible.
At the same time, if removal of the dental nerve seems to be the only solution according to the indications, in many cases we use effective anesthesia of the “dental nerve”, after which we carry out its removal. We are convinced that advanced methods do not deny classical methods, but only complement, optimize, and improve them. That is why in our clinical practice we always try to follow the “classical” treatment algorithm. Its first stage is a complete comprehensive clinical diagnosis.
Treatment is carried out using a dental microscope and using perhaps the most modern instruments, which makes it possible to eliminate carious lesions without missing a single micron of the affected tissue, flexible and thin endodontic needles for the most effective cleaning of canals, and, of course, the safest filling materials. It is worth noting that filling includes work in the canals and in the crown of the tooth. If suddenly the patient experiences some deviations from the normal course of the adaptation process, patients may be prescribed conservative anti-inflammatory therapy, physiotherapy with ozone or laser treatment.
Complications
In the absence of adequate treatment, pulp inflammation spreads beyond the boundaries of the root canal, to the periodontium and periosteum. In addition to the formation of a purulent focus (abscess) that opens onto the mucous membranes of the oral cavity next to the affected tooth, there is a possibility of developing more serious complications:
- flux or inflammation of the periosteum, which leads to the loss of a diseased tooth, and sometimes healthy teeth located nearby;
- osteomyelitis or purulent inflammation of the bone, which requires complex, expensive therapy;
- phlegmon - lesions of the soft tissues of the face, their “melting” with purulent exudate.
Each of these complications can, with a certain degree of probability, lead to life-threatening conditions, for example, sepsis.
Clinical picture of initial K04.00
There is no history of spontaneous pain. When interviewed, it turns out that pain comes from various irritants, which quickly goes away after they are eliminated. A painful attack is provoked by cold and hot stimuli (temperature). Almost always the patient points to the causative tooth.
Pain from temperature stimuli quickly (within a few seconds) goes away. When talking with the patient, it turns out that the tooth has not hurt before.
- The tooth cavity is not opened.
- Percussion is painless.
- Probing is painful at one or more points.
- Electroodontometry - 10-12, and sometimes 20 microns (normally 2-6 microns).
- X-ray – no changes.
Treatment
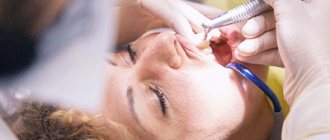
To treat pulpitis, exclusively surgical methods are used - vital or devital removal of the pulp followed by filling the cavity. During vital removal, the doctor injects an anesthetic and removes the inflamed pulp tissue with a bur or mechanically. During devital removal, the pulp is first exposed to special drugs that kill the neurovascular bundle.
Important! Treatment of a tooth with pulpitis with arsenic is an outdated method that is used extremely rarely.
After careful mechanical treatment of part or all of the pulp, the doctor performs a filling in several stages: first, he isolates the root canals, then places a photopolymer filling in the tooth crown. If a significant part of the crown is destroyed, there is intense purulent and necrotic processes, the doctor may remove the tooth.
Diagnosis of the disease
During the appointment, the doctor interviews the patient. Determines the nature of pain, the conditions for the manifestation of pain, intensity and duration. Then, he conducts an external inspection and tapping using hand tools. This allows us to identify the presence of a carious cavity, the density or, conversely, softness of the pulp, and assess the condition of the gums. After this, an x-ray is prescribed. It shows the condition of internal tissues and channels, the localization and extent of inflammation.
In some cases, electroodontodiagnosis is prescribed—this is an analysis of the tooth’s reaction to electricity. The study provides insight into the integrity and functionality of the nervous system. Normally, the pulp responds with a slight pain signal to the electricity passing through it. As caries progresses, degenerative processes occur that reduce the sensitivity of nerve receptors.
Pulpitis of baby teeth
Pulpitis of baby teeth is dangerous because the pathological process from the affected tooth can move to the rudiments of permanent units. If the inflammation has not become irreversible, biological treatment is carried out. This gentle technique involves suppressing infection and the inflammatory process with maximum organ preservation of the pulp and neurovascular bundle.
Good to know! In case of pulpitis of primary teeth, it is extremely undesirable to remove the nerve from the tooth and fill the root canals, since this part of the teeth is not yet formed.
After using antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs, preparations with calcium hydroxide and calcium hydroxyapatite are placed into the pulp. These products will stimulate the formation of secondary dentin within a week. Only after this the doctor will place a permanent filling.
Treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis in children by our experienced pediatric therapists:
- treatment with a smile, no stress for the child , no tears
- pediatric doctors become friends for young patients
- doctors save baby and permanent teeth
- more than 7,890 children who are happy to have their teeth treated with us
- While the child is getting his teeth treated, the parents go about their business
- quality treatment at prices in the residential area of Yasenevo