Publication date: 02/15/2021
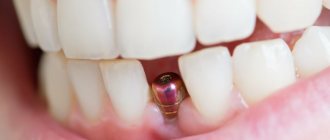
An implant is a multicomponent system consisting of an intraosseous element and an abutment, an adapter between an artificial root and a prosthesis. The implant/abutment connection is precisely calibrated, without micro-gaps, with well-designed abutment positioning. These are important factors on which the correct distribution of the chewing load on the implant and the durability of the orthopedic system depend.
When a crown on an implant is loose, there is always a reason for it. If the implant itself remains motionless, most likely the fixing screw has been loosened or the crown has become uncemented (if it is cemented).
What to do? Go to an appointment with an orthopedist, who will determine the cause of the looseness and effectively solve the problem - replace the fixing component or reinstall the crown. The main thing is to accurately install a loose implant or crown. Indeed, in the first situation, reimplantation may be required, and the second option involves a simple adjustment of the coronal part; the implant itself does not need to be changed.
Reasons for crown mobility
In most cases, the mobility of the prosthesis has nothing to do with the qualifications of the implantologist. Among the main reasons are:
- Loosening of the screw connection between the abutment and the prosthesis
. This is possible if products from different brands were used. For example, the implant is Nobel Biocare, and the superstructure is Osstem. It is important to use original products of the same brand, which are developed as a whole, otherwise the likelihood of failure of all components is too high. - Loss of properties of the cement composition
. As a rule, this occurs due to high chewing load on the tooth, adherence to too hot or cold foods. The prosthetic system is fixed to the abutment with a soft cement composition; under unfavorable conditions, it begins to collapse, is gradually washed out, and the crown becomes loose.
The crown can be reattached in the clinic where the implantation was performed. The orthopedist will tighten the screw with an implantation key and secure the prosthesis. With the cement method of fastening, the crown will be cleaned of the remnants of the old composition and “set” on the cement again. Things are different if not only the crown, but the implant along with it is loose. It is very difficult to independently determine whether the implant crown is loose or the fixation of the intraosseous element is weakened. This requires a medical assessment of the clinical picture and a diagnostic examination.
Why is this technique needed?
First of all, tooth preparation or grinding is necessary in order to:
- give the injured or damaged tooth a shape that will subsequently ensure the metal-ceramic crown fits as tightly as possible, and also create opportunities for a strong and durable fixation of the crown on the tooth;
Tooth preparation for durable crown fixation
- create the necessary relationship between the marginal surface of the future crown and the very edge of the gum near the tooth being prepared.
View of the anterior teeth after preparation for crowns
Specific grinding of teeth for metal-ceramic dentures has features that are unique to this method.
Before installing a new prosthesis, it is necessary to cut down some of the mineralized tooth tissue. In order to carry out this work, it is necessary to numb the area where these procedures will be performed as much as possible. Teeth with complex banded pulp are especially in need of anesthesia.
Before turning, anesthesia is performed
Implant mobility due to patient negligence
The main reason why the intraosseous structural element began to wobble is ignoring the recommendations regarding the care of implants and the orthopedic system fixed to them. If the surgeon performed the implantation without violating the protocol, 90% of the responsibility for rehabilitation lies with the patient. The following can lead to loosening of the structure:
- Refusal of medications prescribed by the surgeon for the speedy restoration of injured tissue, prevention of the inflammatory process, etc.
- Regular consumption of alcohol and smoking slow down the rate of engraftment of the artificial root, increases the risk of peri-implantitis, and impairs blood circulation in the tissues. Clinical studies have shown that implant failure in patients with bad habits is 3 times higher than in those who do not have them.
- Overload of the artificial root when chewing hard foods. Premature chewing load on the implant. Typically, the doctor recommends following a soft diet for 2-3 weeks after the intervention. Ignoring the recommendation leads to displacement of the implant in its bed, disruption of osseointegration and, as a consequence, rejection of the intraosseous element.
The survival rate of a titanium structure is also affected by systemic diseases accompanied by impaired regenerative processes. These include diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states, oncological processes, some pathologies of the central nervous system, and chronic processes in the oral cavity.
General overview
Dental implants, integrated into the structure of bone tissue or the oral mucosa, can serve as the basis for various types of prosthetic systems:
- Permanent bridge-type structures;
- Single fixed or conditionally removable systems;
- Removable structures of full or partial replacement.
The implant itself is a product made of a biologically compatible material - usually titanium, in its pure form, or with the addition of alloys - consisting of two parts:
- The intraosseous part, or body of the implant, shaped like a cone, cylinder, or something in between. In rare cases, the rod can also be made in the form of a plate. The main functional task is to replace the root section of a lost tooth, taking over and then distributing the chewing load. The body of the implant is implanted into the structure of the bone tissue, and in case of its insufficiency and restrictions on plastic surgery, into the zygomatic or basal bone.
- An abutment is a fixing element that acts as a connecting link between the pin and the artificial crown that replaces the outer part of the tooth. The abutment transfers the load to which the prosthesis is exposed to the intraosseous body, and also provides protection against damage to the internal tissues of the jaw by pathogenic infections. In some cases, a monolithic design is allowed, when the implant and abutment are a single whole.
Attaching an artificial crown or prosthesis to an abutment involves the use of dental cement, as well as screw or ball-shaped retainers.
What treatment methods are used
Treatment for mobility of the structure depends on the cause of the problem. If the implant crown is loose and the intraosseous element itself is motionless, it is again secured with a screw or cement. When the entire structure is wobbly, including the artificial root, treatment tactics are selected according to the clinical picture. The most favorable option is that the implant wobbles slightly, there is no inflammation around it, and the gums do not hurt.
In the second scenario, loosening of the artificial root occurs against the background of inflammation and pain in the jaw. Treatment includes:
- Cleaning the implant and nearby tissues - opening abscesses (if any), ultrasonic cleaning of plaque in the subgingival area.
- Osteoplasty using osteoplastic material and barrier membranes (according to indications).
- Antibacterial, antihistamine, anti-inflammatory agents.
- Treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic compounds.
- X-ray control at each stage of treatment.
After the inflammation is eliminated, the prosthesis is again fixed to the implant. If the intraosseous element is rejected, it is removed from the socket, necrotic tissue is removed, and bone grafting is performed. Re-implantation is possible only after 6-8 months, when the bone mass has taken root and the tissue has recovered to its parameters.
Structure and types
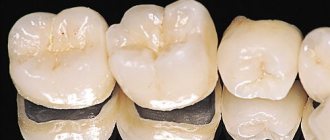
Metal-ceramic dental prosthetics got its name due to the structure of the structures: inside it has a cast metal frame with a thickness of 0.3-0.5 mm. The material of manufacture is cobalt or nickel-chromium alloys. In some cases, alloys of precious metals - platinum or gold, palladium and others in different proportions - can be used. Crowns are divided into corresponding types according to this parameter.
The use of gold has an undeniable advantage - due to the natural yellowness of the precious metal, it is possible to achieve a natural shade of the structure, which is especially in demand when it is necessary to replace the front teeth.
The metal frame is covered with ceramics. The base is veneered using manual layer-by-layer application of ceramic mass. The structure is fired in a kiln after each layer is applied - this allows for the best connection between metal and ceramics.
As for the structure of the structure, the following types of metal-ceramics in dental prosthetics are distinguished:
- Actually single crowns. They are widely used to restore teeth in the lateral zone when they are more than ⅔ destroyed.
- Bridges. They are designed to restore several missing teeth in a row. The most reliable design is considered to be two crowns for supporting teeth and 2 artificial teeth between them.
Rejection symptoms
Rejection of the intraosseous element is a serious complication leading to the loss of the metal pin. Usually, implant rejection is accompanied by quite eloquent symptoms:
- Swelling of the gums, which does not decrease within 5 days after the intervention, but, on the contrary, increases.
- Reddened mucous membrane around the artificial root.
- Severe pain that intensifies with any load on the structure.
- Bleeding of the gums around the implant for more than 4-5 days after implantation.
- Purulent discharge from a wound.
- The appearance of a putrid odor from the implantation area.
- Excessive mobility of the artificial root, exposure of its neck, subsidence of the gums.
- Deterioration in general health, increase in temperature.
A loose implant crown is a reason to urgently go to the dentist. Rejection is rarely treated. With such symptoms, the best option is to remove the implant from the bone with further drug therapy aimed at restoring the body and regenerating bone tissue.
Contraindications
This prosthetic method cannot be used for:
- periodontal disease;
- bruxism (in this case, it is important to first correct the condition or cure the disease, otherwise the structure may damage the teeth that come into contact with the crown when the jaws close);
- malocclusion;
- allergic reactions to metals and alloys;
- shortened crown parts of teeth;
- periodontitis is a temporary contraindication that requires preliminary treatment of the disease.
The implant fell out, what should I do?
In rare cases, the implant becomes unscrewed from the bone and may fall out. This occurs when the size of the socket and the intraosseous element do not match, as well as due to the weakness of the jaw bone. Such situations, when the implant loses its fixation and falls out, but there is no inflammation or other signs of rejection, can occur against the background of systemic diseases in which tissue regeneration is impaired (osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus). The problem is solved by reinstalling the structure using regenerative membranes (enriched with growth factors) that accelerate osseointegration, and prescribing a course of vitamin therapy.
Indications for metal-ceramic prosthetics
A doctor may recommend this method of tooth restoration for the following indications:
- severe tooth decay as a result of caries or injury - the impossibility of restoring it with fillings;
- anomalies of dental development that disrupt the function and aesthetics of the dentition;
- the absence of 2 or more teeth in a row and the presence of supporting teeth on the sides of the dentition defect (cermet bridges can be used here);
- inability or unwillingness to use other prosthetic methods.
Prevention
The best treatment is prevention. The positive outcome of the operation is influenced by:
- Professional approach
– you need to take the choice of a clinic and an implantologist seriously, since the success of treatment depends 90% on the professionalism of the doctor. - Quality of diagnosis and preparation
- you need to prepare seriously for the operation, eliminating all contraindications. To do this, you need to undergo tests and not hide health problems from the surgeon - the more the doctor knows about the patient’s health condition, the more accurately he will select the implantation protocol, and the better the implantation of the artificial root will be. - Oral hygiene
– at the preparation stage, all dental problems should be eliminated and the quality of hygiene procedures performed should be improved.
After implantation, be sure to follow medical recommendations regarding care, nutrition, and physical activity. Do not skip control and preventative examinations.
First aid rules at home
Loss of prosthesis fixation quite often occurs unexpectedly for a person who is confused at first and does not understand what to do. Therefore, you need to know what to do if a dental crown comes off:
- carefully remove it from your mouth immediately and do not swallow anything that is currently in your mouth,
- rinse your mouth immediately: first with warm water and then with an antiseptic solution (for example, Chlorhexidine),
- rinse the denture with water and antiseptic: be careful that the product does not fall into the drain hole. It is better to rinse it over some container and in a well-lit place,
- dry the prosthesis, wrap it in a sterile bandage and put it in a dry, clean container,
- make an appointment with an orthodontist in the near future: it is better to go to the doctor who installed the prosthesis that fell out,
- while waiting for your appointment, you can take a painkiller tablet if there is bothersome pain: if there is no pain, then there is no need for medication,
- switch to a gentle menu: exclude hard, viscous, spicy foods, as well as canned food with acetic acid. The temperature of the food should be approximately equal to body temperature,
- try not to chew on the “affected” side and rinse your mouth with an antiseptic after each meal: so as not to damage the stump and not “introduce” infection into the root canals.
How to make artificial teeth last longer
To avoid the problem of “flying” dentures, the patient first needs to contact an experienced orthopedic dentist who will help create a high-quality and precisely fitting structure. It is also important that the clinic has its own dental laboratory equipped with modern equipment.
Another aspect that must be taken into account is the careful attitude towards restorations on the part of the patient himself. With new teeth, you cannot chew nuts, candies, bite off pieces of hard vegetables and fruits, chew toffees, or toffees. Care should be carried out as if you were caring for your own teeth - use a toothbrush with toothpaste without abrasives 2-3 times a day. After each meal, you should rinse your mouth, especially if you have eaten soft cookies or brightly colored foods - berries, carrots, beets, or drank strong coffee. Then the restored smile will not only not cause inconvenience to its owner, but will also retain its aesthetic appearance.
COMMENTS
QUESTION Hello, my metal-ceramic crown fell out, and underneath it was a white tooth, without caries. And chewing doesn’t hurt them at all. I made an appointment with the doctor, but I’m afraid that he will tell me to get a new crown, but I would like to still wear the old one, it’s completely free of cracks, and nothing has broken off. Christina
ANSWER Hello, Christina. In order not to be afraid and not to speculate, it is better to go for a consultation with an orthopedist, undergo an examination and listen to the specialist’s verdict. It is possible that the fallen crown can indeed be returned to its place, but it is possible that the tooth will have to be drilled or the stump tab removed if it is movable. Try not to load the area of the dentition where the defect has now formed - the food should be soft and not hot. And carefully rinse the fallen crown and place it in a clean box, after wrapping it with a piece of bandage.
1Dawson P.E. Functional occlusion: from the temporomandibular joint to smile planning, 2016.
Author: Chorny S.V. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)