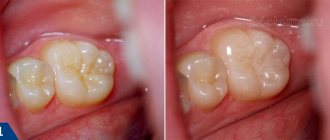
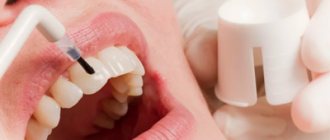
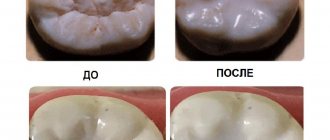
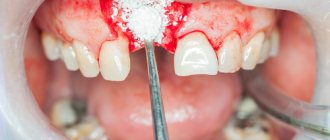
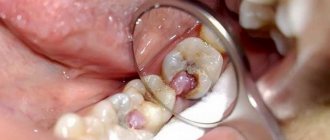
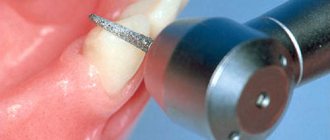
Sealing is the filling of the grooves in the teeth with a special composition that allows them to block the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
The grooves in the teeth are called “fissures” and are characteristic mainly of the posterior chewing teeth - molars. They are very thin, and the bristles of the brush are not able to clean everything that is at the bottom of the fissures. As a result of lack of regular brushing, plaque can accumulate in a child's teeth, which will subsequently destroy the enamel, cause tooth decay and possibly reach a nerve (are there also nerves in baby teeth).
What is dental fissure sealing?
Fissure sealing is a safe dental procedure during which a specialist fills the natural crevices of the chewing surface of the teeth with a special liquid polymer (sealant). The fissure of the tooth is sealed with a sealant, which prevents the accumulation of food debris in the cavities of the recesses, which helps prevent the formation of plaque and reduce the risk of developing caries.
According to statistics, timely sealing of fissures can reduce the formation of caries by 90% or more. Therefore, sealing the tooth fissure with a sealant is recognized as an effective method of preventing dental disease and its complications - pulpitis, periodontal inflammation, tooth loss.
What is dental sealing in children?
In order to prevent such problems, there is the so-called sealing of teeth in children - both milk and permanent. This is a process in which the dentist fills the fissures with a special compound - a sealant. It evenly and accurately fills all hard-to-reach and deep places where a toothbrush could not reach and will make the tooth surface even and smooth, improving the quality of cleaning many times over. The procedure is paid, but compared to the amount of money, nerves and time spent on treating caries, not to mention restoring a damaged tooth, it is worth the money.
Modern sealing methods
The fissure sealing procedure begins with a thorough diagnosis of the general condition of the oral cavity. During its implementation, specialists from the Dental Center on Shabolovka assess the condition of the tooth enamel, the presence or absence of a carious process, the depth and structure of the fissures themselves. After this, one of the methods of sealing the tooth grooves will be selected - non-invasive or invasive.
- A non-invasive sealing technique
is used for open fissures. It does not involve additional opening of natural grooves, and comes down to simply filling visible gaps with dental sealant. - The invasive technique
is used in the presence of deep or closed fissures, the condition of which cannot be monitored visually. To do this, they are first “opened” and then sealed with sealant.
Both sealing methods are safe for the patient's health. At the same time, the non-invasive technique is absolutely painless and does not require the use of anesthesia. While during invasive sealing, the patient may experience discomfort and unpleasant sensations caused by micropreparation of the surface tissues of the tooth. Therefore, the procedure can be performed using local anesthesia, which eliminates any pain.
Invasive and non-invasive sealing
Sealing can be carried out using two different methods: invasive and non-invasive. The first is used in cases where the condition of the furrows cannot be assessed by visual inspection. This may be due to their great depth or their special, closed structure. This technology involves several stages. At the first stage, the dentist must carry out professional cleaning of the oral cavity, during which he removes plaque and other hard deposits from the enamel. Next, he proceeds to carefully prepare and open the fissures using special tools.
Next comes the stage of thoroughly drying and insulating the desired area. After this, the tissues are treated with special means, for example, orthophosphoric acid (32% solution); filling material is placed into the resulting cavity. The sealant hardens under the influence of an ultraviolet lamp. After all manipulations, the surface must be ground and polished. Treatment is carried out under local anesthesia; in rare cases, general anesthesia may be prescribed.
Non-invasive technology is recommended for teeth with open fissures. In this case, there is no need for preparation, the grooves are simply filled with a sealing substance, and the tooth surface is leveled. The sequence of actions is exactly the same as for an invasive procedure.
How sealing occurs: stages
To achieve the maximum preventive effect, the sealing procedure is carried out in several mandatory stages, the sequence of which depends on the chosen technique.
The non-invasive sealing method involves the following steps.
- Thorough cleansing of the treated area from food debris and plaque.
- Drying the tooth surface and fissures.
- Isolation of the treated area from the penetration of saliva with special dental rollers.
- Applying a 32% solution of orthophosphoric acid to the fissure area, which makes the enamel slightly rough, which ensures good adhesion of its surface to the sealant.
- Phosphoric acid is kept on the tooth surface for 30–40 seconds, after which it is thoroughly washed off with distilled water, and the fissures are dried again.
- Carefully apply dental sealant (sealant), which immediately hardens under the influence of a UV lamp.
- Removal of excess sealant by grinding and subsequent polishing of the chewing surface of the tooth. As a result, the sealed fissures look as natural as possible and do not create any discomfort for the patient.
Invasive sealing is very similar to non-invasive sealing, with the only difference being that it involves a few additional steps.
- Cleansing from dental plaque.
- Opening of fissures through micropreparation.
- Drying and isolating the treated area.
- Treatment with 32% phosphoric acid solution.
- Filling open fissures with filling material.
- After the filling material has hardened, the cracks are sealed with sealant.
- Treatment of fissures with a UV lamp.
- Removal of excess material, grinding and polishing.
Regardless of the chosen sealing technique, after the procedure, remineralization and fluoridation of the teeth can be carried out. Thanks to this, it is possible to achieve a high level of dental caries resistance and reliably protect them from disease.
When are children's teeth sealed?
The procedure is most effective at a time when children's teeth are not yet affected by caries. If the teeth have very deep and complex fissures, then almost immediately after eruption they begin to fill with microorganisms and food debris, after which caries develops very quickly, followed by tooth decay. Therefore, it is best to do the procedure immediately after the molars erupt. Typically, the first permanent molars appear at the age of 6-8 years, and the second - at 12-14 years. Immediately after their complete eruption, we can say that it is time to do this procedure.
Manipulations can also be performed on baby teeth. Even small children tolerate them well.
What is the procedure for sealing teeth in children?
Before the procedure, you need to visit a dentist for a consultation on how exactly to seal your child’s teeth and whether it is absolutely necessary to do this. The doctor will conduct a thorough examination and evaluate the positive effect of such manipulations, determine the exact cost of the procedure and materials needed in your case.
The procedure itself is absolutely painless, but both local and injection anesthesia are possible. In newly erupted teeth, the fissures are very narrow, soft and deep due to incompletely formed enamel, which contains much less essential minerals. This almost guarantees that by the time you visit the dentist, certain food debris has already accumulated in them and will need to be removed. The procedure is performed with special equipment.
After cleaning, the tooth is filled with a sealant - a self-hardening sealant that fills empty spaces, hardens and thus prevents the penetration of microorganisms and food debris into them. In addition, the tooth becomes much easier to clean, which creates additional protection.
After cleaning the tooth with all necessary means, the dentist clears the oral cavity of saliva using special rollers and equipment. A special composition is applied to the tooth to facilitate the adhesion of the sealant to the surface, after which the tooth is dried and the sealant itself is applied to it. Due to its fluidity, it is perfectly distributed over the entire surface of the tooth, filling even the narrowest and deepest fissures and making the tooth completely protected from harmful factors.
After the sealant has completely filled the grooves, the dentist uses a special lamp to cure it, or waits a while when using a self-curing agent. The main thing after hardening is the absence of discomfort when closing the jaws. The doctor checks this with special paper and, in the case of too much material, removes it with special rotating devices, which is also absolutely painless. After completing the entire procedure, the tooth is coated with a special varnish or gel.
Sealants can be different both in their properties and in cost. They often contain fluoride to better strengthen tooth enamel, so in addition to the barrier value, the procedure also has hygienic and preventive purposes.
Which fissures need to be “sealed”?
The thinnest and deepest. After all, the thinner and deeper the fissure, the more difficult it is to clean; the most difficult ones are not cleaned at all. In addition, the sealant penetrates best into thin and deep “pits”, therefore, the thinner and deeper the area being filled, the more successful and useful the procedure.
All this applies to the posterior chewing teeth, since they usually have the narrowest and deepest “grooves.” Such teeth require the creation of a barrier that will protect them from the adverse effects of microorganisms, acids and the environment.
Only the dentist himself can determine what needs to be sealed and what is optional. He conducts an examination to identify deep fissures.
Do all fissures in children need to be sealed?
There are fissures on all posterior chewing teeth. However, not all of them are pronounced; there are also open fissures that can be easily cleaned with a toothbrush, and there is no need to carry out this procedure on them. Still, sealing teeth in children is an intervention and if it is not required, you should not do it just like that.
However, if at the time of preparation for sealing caries has already appeared inside the fissures or on the teeth themselves, then it is necessary to carefully get rid of it by sanding the affected areas and treating these places with a special compound.
How long will the effect of the procedure last?
For about two to three years, the sealant will reliably protect the child’s teeth from microorganisms. However, it is necessary to see a dentist twice a year to monitor the condition of teeth in general and sealed baby or permanent teeth in particular. In general, as practice shows, even after 5-10 years, the sealant completely protects the tooth from acids and caries.
It is considered that the procedure was carried out correctly and successfully if the sealant on the tooth has been preserved well for 3-5 years. However, even if it lasted less, it is necessary to remember that protecting the tooth from caries all this time was worth it.
Reviews about sealing teeth in children
At the moment, reviews from both doctors and patients indicate that sealing baby and permanent teeth in children is a procedure that, with almost complete absence of negative aspects, is exceptionally effective in protecting the posterior chewing teeth from caries and destruction. This is exactly the case when, with a correctly performed sealing procedure for both primary and permanent teeth in children, everyone remains satisfied: doctors, parents, and young patients.
To keep your teeth healthy even longer, use the right toothpastes. Asepta products from the Baby, Kids and Teens series will protect and strengthen the enamel, keeping teeth snow-white and strong. They are designed taking into account age-related needs, replenish the lack of minerals in the enamel, and protect the oral cavity from acids. At the same time, our pastes have a pleasant taste that children like!
Take care of your family with Asepta!
What material is the sealant made of?
To seal fissures, special dental sealants are used, which are characterized by good fluidity, allowing them to penetrate even the smallest crevices of the tooth surface. Essentially, these are modern polymers based on methacrylate and polyurethane. Each of them has its own properties, wear resistance, and can harden naturally or under the influence of a UV lamp. Often their composition is additionally enriched with fluoride ions, which strengthens tooth enamel, thereby inhibiting the development of the carious process.
Sealants for sealing fissures differ not only in their composition, but also in their transparency.
- Transparent sealants
allow you to visually monitor the condition of fissures. But due to their colorlessness, they are practically invisible on the surface of the tooth, which makes it difficult to assess the condition of the sealant itself. - Opaque sealants
are sealants that contain titanium dioxide. They are painted in a pleasant milky white color, are hardly noticeable on the chewing surface of the teeth and allow you to monitor the general condition of the sealant during use.
Any sealant composition is well tolerated by the human body, does not cause allergic reactions and does not harm tooth enamel.
Methods for studying fissure caries
Correct and timely diagnosis of caries is the key to successful treatment of the patient. It includes:
- Visual examination of the oral cavity. Allows you to identify the presence of a carious process in shallow fissures;
- Probing. Using a metal instrument, the dentist examines the density of tooth tissue. The affected tissues have a loose consistency, they retain the probe, it seems to “fall through”;
- Percussion. Using the blunt end of the instrument, the dentist checks for the presence of pain and the involvement of periodontal tissue in the process.
Additional methods for diagnosing fissure caries
- X-ray examination makes it possible to identify foci of destruction of enamel and dentin in the images, as well as to detect the spread of the process even at the initial stages;
- Using the transillumination method, the dentist can see the affected tissue without preparing the tooth. In bright light, the carious process has a brown color;
- Fissurotomy is an option for diagnosing pathology. A diamond bur is used to grind the affected enamel down to the border of healthy tissue. This method is minimally invasive and allows you to assess the extent of caries spread.
Fissure sealing in children: pros and cons
Sealing the tooth fissure with sealant can be done at any age. This procedure is especially indicated for children whose tooth enamel is just beginning to form and the accumulation of plaque in the fissures often provokes the onset of the carious process.
The problem is that a child's baby teeth have a low level of mineralization, which makes them especially vulnerable to tooth decay. Therefore, a preventive examination and the first fissure sealing in children are recommended to be carried out 6 months after the eruption of baby teeth. The effect achieved during the procedure will last for 1 – 2 years, during which it is necessary to undergo a preventive examination by a dentist every 6 months.
Among the advantages of early fissure sealing, the following points can be highlighted.
- The presence of sealant does not disrupt the natural development of the tooth.
- Sealants do not reduce the level of natural mineralization of enamel.
- Sealing the gaps does not have any effect on the formation of a correct bite in the child.
In both children and adults, the presence of sealants in fissures does not cause a feeling of discomfort or stress on the tooth.
Note! To avoid the development of complications, the procedure for sealing cracks should be carried out only by an experienced specialist – a dentist.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
Features of the procedure
Absolutely every person's teeth numbered 6, 7 and 8 on both jaws have special grooves. Quite often food particles get into them, which leads to the active proliferation of bacteria. As a result of their vital activity, acids are produced, which gradually destroy tooth enamel and lead to the formation of caries.
This pathology is the most common in both children and adults; it is diagnosed in 99% of the population. What is fissure sealing? This is the sealing of a surface to protect it from dirt and germs. For this purpose, a special filling compound is used. As a result of this treatment, the tooth becomes stronger and more resistant to the destructive effects of pathogens.
Sealing is prescribed by a doctor only on the basis of the diagnosis and if there are serious indications for this procedure. It is very important to study the structure, depth and location of the grooves and only after that make a final decision on the need to apply filling material.
Indications and contraindications
Since fissures are natural crevices on the chewing surface of every person’s teeth, we can say with complete confidence that their sealing is recommended for absolutely everyone. It is especially needed by small children, whose tooth enamel is just forming, and adults, who have deep and narrow fissures that are difficult to clean during daily hygienic brushing.
But we should not forget that natural cracks of a wide structure that communicate with each other can self-clean naturally. Therefore, if there is no threat of caries development, then they do not need to be sealed. In this case, only a dentist can determine the feasibility of the procedure. In addition, sealing may be refused if the following contraindications are present:
- The presence of a carious process that requires treatment.
- If visible fissures do not develop caries within 4 years.
- If a tooth has not fully erupted, its surface cannot be sealed.
- Unsatisfactory general condition of teeth caused by improper or insufficient oral hygiene.
Note! Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a dentist, who will help identify contraindications to sealing.
Fissure caries clinic
The carious process begins secretly and painlessly. Most patients do not attach importance to discoloration in the area of natural recesses of molars and premolars, due to which the pathology intensively develops and spreads to the deeper tissues of the tooth. The main symptoms of fissure caries:
- Changing the natural color of teeth. Due to destruction (destruction) and the activity of microorganisms, dental tissues darken. The fissures become dark brown and clearly visible;
- Hyperesthesia (increased tooth sensitivity). The tooth reacts to temperature and taste stimuli, the patient complains of pain, which goes away when the triggers are eliminated;
- Independent pain syndrome that does not stop after eliminating irritating factors. The pathological process spreads to the dental pulp, which consists of nerve fibers and blood vessels; patients note the nocturnal nature of the attacks. If the pain continues to intensify, caries develops into acute pulpitis.
Prevention
According to statistics, 80% of sealants retain their integrity and tightness for 2 to 3 years after the procedure. Over the next 5–7 years, about 70% of sealants successfully withstand. After 10 years, only 30% of sealants remain intact and functional. Thus, modern sealants can serve the patient for a long time. The main thing is to undergo preventive examinations at the dentist in a timely manner and monitor their condition. To do this, you need to visit a specialist at least 1–2 times a year and regularly inspect the sealed fissures yourself. If you notice that part of the sealant has fallen out, you should immediately contact your doctor. Otherwise, it is enough to adhere to the general recommendations of a specialist and pay due attention to daily oral hygiene.
Author: Elena Kopylova Dentist-therapist, endodontist, pediatric dentist. Work experience more than 7 years.
The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
The feasibility of treating pigmented fissures
Unfortunately, many experts are of the opinion that pigmented fissures need to be treated. When the slightest change in color is detected, various types of intervention are resorted to, including invasive opening and filling. However, it is worth understanding that even the highest quality filling lasts no more than 5-10 years, and there is nothing more reliable than natural tooth tissue.
In fact, pigmented fissures in themselves are not an indication for treatment. They can remain in one state for life and will never become an entry point for caries. An attentive, highly qualified dentist will recommend monitoring the development of the process, tracking the slightest violations of the enamel in pigmented fissures.
Prevention of fissure caries
Prevention of fissure caries is the key to successful treatment and avoidance of relapses. The following preventive measures are distinguished:
- Fissure sealing is the most effective method to date and almost completely eliminates the possibility of recurrence of caries. It is widely used among pediatric patients, is easy to perform and painless. After preparing the tooth for the procedure, it is treated with a flowable transparent composite or glass ionomer cement. The purpose of sealing is to prevent microbes from accessing the fissures.
- The stronger the enamel, the more prismatic elements it contains and the fewer free spaces. Remineralization therapy is indicated for patients with fragile enamel. The surface of the tooth crown is treated with fluoride varnishes, preparations with a high calcium content.
Dentist advice
Osmanov Konstantin Gennadievich
Sealing can only be done on the front part of the teeth. All other surfaces remain just as vulnerable to caries. Therefore, it is important to remember that after the procedure you should not neglect proper oral care.
Prevention of fissure caries at home
It is important to observe prevention not only at dental appointments, but also at home. Oral hygiene is a complex procedure. It includes:
- Individual cleaning with a medium-hard brush. The necessary components of toothpaste are active calcium (ROCS, Colgate, etc.) and fluoride (President Classis, Splat, etc.);
- Using dental floss to clean the interdental spaces;
- For more thorough hygiene, it is recommended to use an irrigator;
- After traditional brushing, do not forget to rinse your mouth with sodium fluoride solutions. The optimal fluorine concentration in the solution is 250 ppm.
The prognosis for fissure caries is favorable. Thanks to planned treatment, oral sanitation and good hygiene, relapse can be prevented and complications can be avoided. To improve the condition of your teeth, you need to take care of them, as well as adhere to a balanced diet and exclude carbohydrates from your diet. Remember: healthy teeth are the guarantee of a snow-white smile.
Make an appointment with a therapist by phone+7(985)532-21-01