When a person starts to have a toothache, he consults a doctor with the sole purpose of stopping the pain. It is not for nothing that toothache is recognized as the most difficult to bear. No stoic can withstand it for a long time. If a tooth is treated, it will no longer cause pain. Following this logic, the patient goes to the dentist.
Sealing
The specialist does what he's supposed to do. Cleans the canals, removes the source of infection or necrotic fragments of tooth tissue, sanitizes the oral cavity, and places a filling. All this is unpleasant, painful, and does not bring pleasure. But now the treatment ends, the doctor did everything to make the tooth stop hurting. However, after some time, the tooth begins to hurt again under the new filling that was installed according to the rules. Why does this happen, and what to do in this case.
Tooth hurts after root canal filling
Why does it hurt?
The first thing you need to understand is the impact on the enamel coating of a tooth or its underlying tissue (dentin) with a drill drill or any instrument penetrating into the tissue, and even more so, cleaning the canals is a real surgical intervention. In the process of working with a drill, the dental nerves are usually affected by an anesthetic injection; when it stops its effect, the pain becomes obvious and can be felt quite strongly for a short time. The surgical wound heals, the body recovers, this should take a certain period of time, such pain after filling the canal is considered normal.
Toothache after root canal filling is acceptable
How to understand at what point a deviation from the norm occurs, and when you need to seek help or take independent auxiliary measures?
By the way. There are certain criteria by which they calculate whether it is normal or deviation. With a natural pain reaction, it is enough to wait for some time. If something goes wrong and the pain continues and even intensifies, the algorithm of actions will be different.
Criteria for determining pain norm.
- The nature and level (depth) of the treatment performed.
- The presence of complications after treatment, or non-standard reactions of the patient’s body.
- Duration of pain.
- Dynamics of pain.
- Nature of pain.
Pain may indicate complications after surgery
What causes pain? They are divided into objective and subjective. The second category includes typical medical errors, errors in diagnosis, incorrect treatment or insufficiently high technology of the clinic’s equipment.
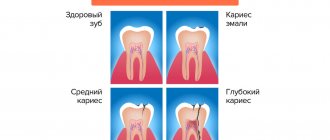
Caries or pulpitis
Deep caries
Unfortunately, very often, even in expensive dental clinics, it happens that the doctor incorrectly identifies the patient’s problem. For example, deep caries is confused with chronic pulpitis. Yes, they are similar and have almost identical manifestation. But if caries is suspected, especially when the doctor, with the best of intentions, seeks to avoid root canal treatment, this mistake can cost the patient not only a long period of pain, but also tooth loss. If you apply a filling for any form of pulpitis or periodonitis without cleaning and filling the canal, the tooth will hurt deep down until the inflammatory process reaches its culmination stage and tooth extraction is required. Thus, paradoxically, the first cause of pain may be that the doctor did not fill the canals.
Pulpitis
Burn pain
It would seem like getting a burn in the dentist's office? Overheating and tooth burns are a problem mainly in small budget clinics that have outdated equipment that does not provide for the use of water-air cooling.
During treatment, tooth enamel may burn
If the fragment of tooth tissue processed by the drill is not cooled enough, it overheats and burns the pulp tissue. As a result, a necrotic area is formed, which in the future will cause pain under the filling. The killed tissue will decompose, giving inflammation of the pulp, periodontitis, pulpitis and further, as in the previous paragraph.
- Tooth hurts under temporary filling
Overbite
Few patients take this source of pain seriously. After filling the canal, a closing filling is applied to the dentin. At the moment of biting, a tooth from the opposite row presses on the filling. If the bite level is normal, the pressure is distributed over the entire dentition. But if it is too high, the entire jaw puts pressure on the filled tooth.
Overbite filling
By the way. Patients, and even doctors, tend to believe that a protruding filling will “wear in” over time. This is a big misconception; modern filling materials are durable. It may take years to “grind in.” And at this time, each bite will not only cause pain in the tooth, but also injure the peri-root tissue. As a result, traumatic periodontitis will develop.
The specialist must carefully monitor the height of the bite, since the patient himself, by feeling, cannot accurately determine whether it is too high. The treatment takes place under anesthesia. There is numbness in the mouth. Feelings are blurry and unclear.
To check the bite filling, use special paper, similar to a copy.
Important! If, after filling, the tooth hurts when pressed, you need to go to the dentist and grind the filling down to a comfortable level.
Shrinkage of the filling
Another reason that most patients are not even aware of is polymerization stress. Happens when installing light-curing composites (so-called light fillings). They subsequently shrink and begin to hurt. This happens because a special lamp is used to harden the filling material. After its exposure, the composite material decreases in volume. Of course, this is not at all the shrinkage that occurs if you wash woolen fabric in boiling water, but even a slight decrease in the volume of the filling causes stress on the surrounding tooth walls. If the filling is multi-layered, the tension is greater, the stress is greater. A light filling may hurt for several weeks, or may cause discomfort for a long time.
Close-up view of light filling
Let's look at the root: how are the root canals of teeth filled?
The more a person is afraid of dentists, the more closely he eventually has to interact with them and the longer the dental treatment will be for him - a simple and banal truth, but, unfortunately, not all people take note of it. If caries treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the infection gradually spreads “inward”, capturing more and more new territories and reaching the pulp chamber. Pulpitis develops - an extremely painful and unpleasant disease, which is popularly called “inflammation of the dental nerve.” This is where most people don’t just go to the dentist, but run – because the pain prevents them from sleeping, eating, or working normally. And if the patient has already begun to have inflammation of the tooth canals, treatment will require quite serious and lengthy treatment: cleaning the tooth canals from infected and dead tissue, their special antibacterial treatment, careful filling of both the canals themselves and the dental crown with the cavity.
Almost everyone knows about such a dental procedure as treatment and filling of dental canals, and many people have encountered it from personal experience. But most people usually don’t know the intricacies of the process, how exactly such treatment takes place, why it is needed and what it gives in the end. So what are the standards for filling canals, why and how exactly is this procedure carried out, and what can a poorly filled canal threaten a patient with? Dentist-therapist at the 32 Dent clinic Larisa Aleksandrovna Kravtsova will help you get reliable answers to all these questions.
What hurts if there is no nerve?
All of the above cases can be attributed to partial filling. What if all the root canals are closed with fillings, and the nerves from them have been previously removed? Where does the pain come from if the tooth is “not alive”?
Many experts believe that there should be no pain in this case. But, since it still occurs, and in a significant number of patients, the question of the origin of pain in a tooth without nerves remains open and hotly debated.
The tooth may hurt even after the nerve is removed
In what cases can you not worry that after filling the canals under a temporary or permanent filling, pain continues?
Important! Short-term pain in a tooth where there is no nerve, even if all the work on removing nerves, cleaning and filling canals was carried out according to the protocol and without errors, is a normal phenomenon.
Table. Nature of pain after root canal filling
| How it manifests itself | Description | Cause | What to do |
| Pain during biting | After the installation of a filling, usually temporary, is completed, pain occurs several hours or days later. There are painful symptoms when biting (from pressure). | If the level of occlusion is not too high, the reason is the reaction of the peri-root tissues to the extraction of the nerve. The root canal is expanded and filling material is introduced into it. The body reacts to a stimulus. | In this case, you can do nothing. The pain lasts from 5 days to 3 weeks. Pain dynamics should be positive (gradually subsiding, until disappearance). |
| Aching pain under the filling | After the anesthesia wears off, aching pain remains under the filling. | This is also due to the body’s reaction to the removal of the nerve. The disturbed canal walls “whine.” | The pain can last from two hours to a day. If it continues longer, you should consult a doctor. |
| Jerking pain inside the canal | This type of pain is rare. It’s as if something is tugging in the tooth; the sensation may resemble the beginning of inflammation of the pulp. | It occurs exclusively as an individual reaction of the body to the expansion of the canal or to the filling material itself (its structural component). | The tooth can also “tug” from hours to days. In a maximum of a day everything should go away. |
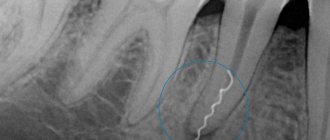
The nerve was removed, but the canal was not sealed
Such situation. On the X-ray of my teeth, they saw that in my six, in which the nerves were ripped out, only one canal was sealed. My employee’s nerve was removed and the canal was also not sealed - the filling was only placed on top. The fillings are not temporary, but permanent. It turned out to be completely random - during a check when another tooth (mine) was hurting. And the employee was sick after that, the hollow one.
Is there any reasonable explanation for the fact that the nerve is removed, but the canal is not filled and the filling is left only on top, or is this real negligence?
There are several options. Possibly negligence. But if one channel is sealed, then most likely there is another option. I haven't completed channels 5 and 6 yet. This turned out to be the case in the USA. The previous dentist in the USA turned a blind eye to this. We moved and took the new one to a specialist to do a refilling. Well. I did it in a cool place, with a cool specialist, a professor. I paid more than 3 tons of dollars for two teeth (5 and 6 on the lower left). And still, the channels have not been completed completely. He told me that you have very narrow and winding canals, plus 4 roots. The Russians used a different technology to fill the filling, but it surprisingly didn’t work too badly. Don't touch your teeth anymore. If inflammation occurs, you will have one way out - open the gum, bite off the tip of the root and fill it at the other end.
How to relieve post-filling pain
Most experts advise doing nothing. If the pain is normal, it will go away on its own in due time. But, if the pain is strong and interferes with the normal flow of life, you do not have to endure it. You can use folk remedies or official medicine.
By the way. The most famous “dental relievers” have long been considered soda and salt. They have several effects at once - antiseptic, relieves inflammation, removes tumors.
Soda and salt for preparing the solution
If your tooth hurts after permanent or temporary root canal filling, rinsing is effective.
Baking soda rinse procedure
A warm, but not hot solution is made in the proportion of 5 g of soda per 200 ml of water. Boil the water first. It is advisable to carry out up to four rinses per hour, that is, every quarter of an hour.
Preparation of the solution
Salt rinsing procedure
The proportions are the same as when preparing a soda solution. You can rinse five times an hour. It is preferable to use iodized salt. If the salt is ordinary table salt, add two drops (per 200 ml of solution) of pharmaceutical iodine, with a concentration of 5%.
Salt solution with iodine
Important! Iodine is used only by patients who do not have thyroid problems and who do not have an individual intolerance to this component.
Medicines
From your home first aid kit you can use the following drugs to relieve dental pain after root canal filling: Ketorol, Ketanov, Baralgin, Nise and others.
Painkiller "Ketorol" tablets
What materials are used to fill canals?
The main requirements for such filling materials are dense, hermetically sealed filling of the canals, chemical inertness (the material should not dissolve under the influence of body fluids), radiopacity (it should be clearly visible in the picture). Today, the following types of materials are used for filling dental canals:
- Solid fillers (fillers).
These include gutta-percha (a latex processing product), silver and titanium pins. Silver pins have recently been rarely used, since despite their good antibacterial properties they have a significant drawback - they do not provide complete tightness. - Polymer and natural pastes (sealers)
. A more preferable option is polymer sealers, which adhere better to the walls, do not stain dental tissue and do not dissolve when interacting with tissue fluids. - Glass ionomer cements.
Good adhesion and radiopacity, high biocompatibility and minimal shrinkage are the main positive qualities of such materials. They also have significant drawbacks: low strength, which is why such fillings are short-lived and not designed for serious functional loads. - Calcium hydroxide cements
. Non-toxic, biocompatible, radiopaque materials that exhibit minimal shrinkage, are easily removed if necessary and have bactericidal properties. However, they are considered not too strong and can break under heavy loads on the dental crown. - Polydimethylsiloxanes
. Modern reliable sealants with good therapeutic and operational parameters. Perhaps their only drawback is that this is a new product on the dental market and experience in using such materials has not yet been accumulated. There is no reliable information yet about the experience of patients after such treatment.
When to see a doctor
If the pain does not decrease and does not go away within the time allotted for it according to the protocol, you should go to the doctor immediately. Without doing this, you will provoke serious complications that will lead to protracted and difficult to eliminate consequences.
Important! Especially if, after root canal filling, the gums are swollen and the pain increases, you should contact your dentist immediately.
If your gums are swollen, you should immediately contact your dentist.
To find out the cause of the pain, the specialist will conduct a palpable examination, tap the tooth (percussion), determine the viability of the pulp using electric current (ED) and prescribe x-ray diagnostics. If errors in treatment are identified or other causes of pain are discovered, the tooth must be re-treated. In emergency cases, when it is not possible to treat the tooth, it will be removed and a crown implant, bridge structure, or other recommended prosthesis will be installed in its place.
Crown on an implant