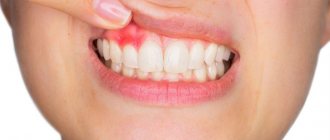
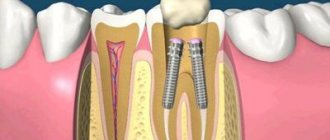
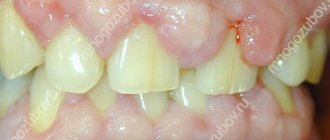
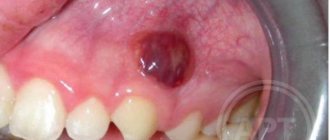
A tooth abscess is an acute infectious process accompanied by the accumulation of pus in the inner or outer surface of the alveolar processes (the area of the bone of the upper and lower jaws in which the tooth sockets are located). A tooth abscess can be periapical—flowing around the apical third of the tooth root—or periodontal—developing inside a periodontal pocket. The main symptom of an abscess is acute pain and swelling of the jaw. Treatment consists of removing purulent exudate and anti-inflammatory treatment of the canals. If the inflammation cannot be stopped, the tooth will have to be removed.
When to see a doctor
Since an abscess is an infectious disease, it has pronounced symptoms. You need to go to a specialist as early as possible. An infection diagnosed in time is easier to treat. Evidence of the spread of infection may include:
- A whitish or reddish swelling on the gum.
- Spread of swelling from the gums to the soft tissues of the face.
- Formation of an ulcer with purulent contents at the site of swelling.
- Severe throbbing pain while brushing teeth or eating.
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth, which cannot be eliminated by ordinary daily hygiene products.
- Bitter taste in the mouth.
If there is no treatment and the infection continues to spread, general symptoms will also appear. Body temperature rises, the patient may complain of sleep disturbances, lack of appetite, and depression.
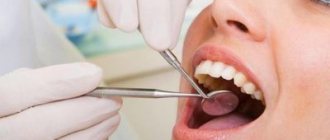
If even some of these symptoms appear, come for a consultation with a dentist at the ARDC clinic. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and clarify the diagnosis.
Signs of illness
It is almost impossible not to notice the presence of pathology - the symptoms are always very clear. Anyone, even those far from the medical field, can understand that something is wrong with their gums.
- First there is an acute toothache. It becomes more pronounced if you press on the unit, touch it, or knock on it. It intensifies if the patient drinks or eats something hot or cold.
- Soon the gums swell. Even the cheek may swell. This indicates that the inflammation is spreading quickly.
- A bulge forms on the gum. At first it is red or with a bluish tint. But it also happens that it is not there, and pus simply begins to ooze from the gums.
Due to the purulent masses, the patient has an unpleasant taste and a foul odor appears from the mouth. It is not possible to remove it using standard hygiene products - a toothbrush and toothpaste, since pus continues to actively form after brushing your teeth.
An advanced abscess contributes to an increase in body temperature, decreased appetite, and decreased performance. In many patients, the cervical lymph nodes become enlarged.
Why does a tooth abscess develop?
The main cause of abscess development is bacteria. They are always present in the oral cavity, but in order for an infectious process to develop, provoking factors are needed. The development of an abscess can be provoked by:
- Violation of the rules of daily hygiene. Bacteria multiply quickly in the favorable environment of dental plaque. When there are a lot of them, a pathological process develops.
- Dental procedures. During tooth extraction, an antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity is performed. When this treatment is insufficient or the procedure was carried out in violation of antiseptic rules, pathogenic bacteria can penetrate the tissue.
The risk of developing a tooth abscess increases if the patient has a weakened immune system or has systemic diseases, for example, diabetes, cancer. Chronic tonsillitis often provokes the development of a purulent process. This is due to the fact that with chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, there is a focus of infection in the body. It may spread to other areas.
Patients with dental problems are also at risk:
- Caries.
- Mechanical damage to the enamel (chips, cracks).
- Periodontal diseases.
- Gingivitis.
Treatment of gum suppuration
Minor or severe pain requires the help of a dentist. The choice of methods to eliminate suppuration remains with the doctor. Treatment begins after a survey, external examination, and X-ray diagnosis of the patient. The specialist’s main goal is to remove accumulated pus as a source of infection. Depending on the severity, surgical treatment may be required.
Surgery
Treatment methods depending on the type of inflammation:
- With a gingival abscess, the pocket with pus is opened, and then cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
- In cases of periodontal inflammation, it may be necessary to cut the boil to gain access and eliminate the infection. The pus is removed through auxiliary dental canals so that the infection does not spread further through the blood vessels. After eliminating the purulent process and residual infection, curettage of the periodontal pocket and other procedures for the treatment of periodontitis are performed.
- Patients with a periapical abscess are most often prescribed cleaning and refilling of the root canals according to the periodontitis treatment regimen, as well as removal of pus by opening and draining the flux.
- To eliminate a pericoronal abscess, it is necessary to remove the tissue that is preventing the tooth from erupting.
Don't forget antibiotics!
After surgery, the doctor prescribes a course of antibacterial therapy: anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, as well as a course of home antiseptic rinses.
Read more about surgical and conservative methods of treating abscess.
Treating an abscess at home
At home, it is impossible to completely cure gum suppuration, but you can significantly reduce the pain.
Before visiting the dentist, you can use the following home remedies:
- a decoction of chamomile and oak bark for rinsing the mouth;
- rinsing with a solution of salt, soda or chlorhexidine;
- local application of ointments and internal administration of analgesics.
Types of abscess
The type of abscess is determined by its location. Based on this feature, periodontal and periapical types are distinguished. Both can occur in acute or chronic form.
- Periodontal abscess. Develops in the space between the gum and the crown of the tooth. In the acute form there are pronounced symptoms - an abscess on the gum, severe pain when closing the teeth. In the chronic form, such pronounced symptoms are not observed. In case of chronic periodontal abscess of a tooth, a fistula develops at the site of purulent inflammation.
- Periapical abscess. The source of infection is located inside the tooth. Often this type of disease develops as a complication of periodontal disease. The process proceeds as follows. Pus begins to accumulate at the top of the tooth root. If the suppuration is deep and the pus cannot come out, it continues to spread inside the gums, under the mucous membranes. The bone is gradually affected and begins to deteriorate.
Content:
- What is a tooth abscess
- Classification of abscess in dentistry
- Causes of the disease
- Signs of illness
- Breakthrough of purulent masses with an abscess
- Treatment of the disease
- How to prevent a tooth abscess from occurring
A tooth abscess is an unpleasant and dangerous dental disease. It can occur in anyone. It is impossible not to notice its presence, since acute pain appears in the affected area and accumulations of pus form. Let's take a closer look at what this disease is, how to recognize it and treat it.
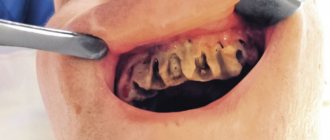
After tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a dental operation during which the gums are injured. If antiseptic rules have been violated or the patient does not provide the necessary postoperative care, infection can enter the wound. Bacteria will multiply quickly. Suppuration forms. If there is no treatment, the abscess affects the soft tissue.
Suppuration as a result of medical error after removal is rare. At the ARDC clinic, dentists use modern equipment, consumables, and medications. You can be confident in the quality of the procedure and compliance with the treatment protocol.
Improper postoperative care is a more common cause of abscess after removal. After the operation, the dentist must give recommendations on how to care for the wound. Careful adherence to all these rules will reduce the risk of suppuration at the site of the extracted tooth.
Is it really that dangerous if left untreated?
☣️ You can endure the pain, but the abscess will not go away so easily. As the purulent abscess develops, it provokes pathological processes in the gums:
- secondary lesions with pus appear;
- the breakdown of red blood cells in the blood plasma begins (intravascular hemolysis);
- the body is poisoned (toxemia);
- blood clots form (DIC syndrome);
- blood pressure decreases;
- infectious-toxic shock occurs.
As a result, the abscess destroys the structures of the periosteum and periodontium. The bone tissue of the jaw decreases, the tooth at the site of the abscess becomes loose. The pus will begin to spread through the blood and lymph unless a fistula is formed or the abscess is opened surgically. If the course is prolonged, the risk of losing a tooth or implant increases.