The eruption of wisdom teeth is often accompanied by various complications. This is due to the lack of space in the dentition for the number eight, which erupts last. In dental clinical practice, third molar retention is often encountered - incomplete eruption of the crown above the gum. Removing a wisdom tooth in the gum is a small operation that requires not only extraction of the tooth, but also the creation of access and an incision in the gum. Our dental clinic performs extractions even in the most complex clinical cases. Dentists have extensive experience and high qualifications, and perform procedures painlessly and safely.
A wisdom tooth remains in the gum - is this critical?
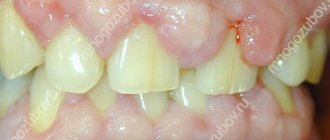
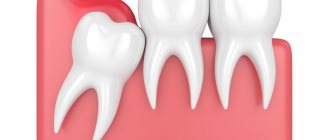
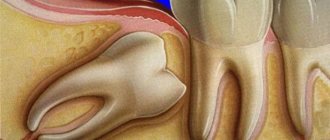
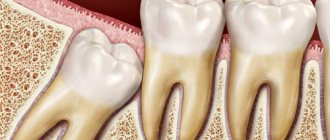
Retention or partial eruption is characterized by incomplete emergence of the crown above the gum. Only 1-2 bumps or part of the tooth crown may appear. Retention can be independent or together with dystopia - incorrect positioning of the molar. Symptoms of the disease will depend on the individual clinical situation.
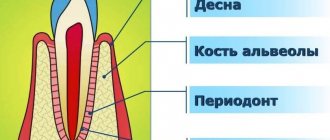
Depending on the location, retention can be vertical, horizontal or angular. With a vertical crown, the tooth crown is located normally in the bone, in accordance with other teeth. Horizontal is characterized by the location of the tooth perpendicular to the others, horizontally to the arch of the jaw. With angular retention, the crown is tilted to the side. According to the depth of its location, the tooth can be covered only by gum, but by a bone plate.
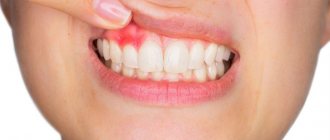
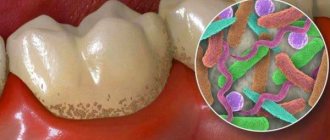
Retention is accompanied by the ingress of food debris and plaque under the gum. This causes inflammation, redness, tissue swelling, and pain. Pericoronaritis may occur - acute inflammation of the gums and mucous hood above the crown of the impacted tooth. The disease can be serous and purulent, causes acute pain, hyperemia, tissue swelling, and makes it difficult to open the mouth.
In most cases, a tooth in the gum is a source of various complications: pericoronitis, the formation of caries and its complications, cysts, stomatitis, periostitis, abscess. Therefore, in case of pathology, dentists recommend removal.
To date, exact methods for preventing retention are unknown. General measures include proper hygienic care of the oral cavity and monitoring the correct development of the child’s jaws and bite. As well as timely and correct orthodontic treatment of malocclusions.
Hypertrophic pulpitis
Overgrowth of gum tissue is a serious pathology that requires immediate attention to a dental clinic.
The gum comes out of the tooth often with advanced hypertrophic pulpitis, which occurs in two possible chronic forms:
- Excessive volume of soft tissue is formed due to the granulation process. The development of the process is preceded by the presence of a huge carious hole over a long period of time. Due to its presence, soft structures are constantly injured, transmitting irritation to the pulp.
- A dense polyp forms in the pulp area due to the growth and layering of flesh on top.
The disease is mostly asymptomatic. And only eating rough food provokes aching pain. The gums in the problem area may also bleed. But the main sign of hypertrophic pulpitis is the appearance of “wild meat” in the hole of the dental unit. Over time, it grows so much that it fills the entire cavity and goes beyond its limits. Pain and discomfort interfere with proper hygienic care. Aggressive microflora contributes to halitosis (bad breath).
Swelling of the mucous membrane due to traumatic or deep carious destruction of the crown
Gum receding occurs when the walls of the tooth are completely or almost completely destroyed. It becomes inflamed due to constant injury and accumulation of food particles. Plaque thickens over time, puts pressure on the gums, and populates it with pathogenic microflora. The proliferation of aggressive microorganisms contributes to the development of swelling and hyperemia. The gums increase in volume and it seems that meat is sticking out of the cavity of the dental unit. The patient experiences pain and severe burning when eating salty and sour foods. The jaw row reacts sharply not only to taste, but also to temperature stimuli. There is discomfort from hot/cold.
Indications for removal
Retention can manifest itself as a stage of eruption. Over time, the crown completely appears above the gum and the tooth can function normally. Therefore, the decision on the need for removal should be made by a doctor only after examining and diagnosing the condition of the dental system. Indications for surgery are the following clinical cases:
- Constant pain;
- Complications of eruption;
- Trauma to an adjacent molar;
- Pressure on the dentition and its deformation;
- Horizontal or angular position of the third molar in the jaw;
- Dental crowding, which can be aggravated by wisdom teeth;
- Orthodontic and orthopedic indications, that is, the need for extraction to correct the bite or prosthetics.
Features of treatment of fistula with concomitant diseases
Are there any particularities in the treatment of fistula if the process is accompanied by other diseases in the oral cavity, such as periodontitis? No, in fact there is no particular connection. Periodontitis is an inflammation of the periodontium of a tooth, while periodontitis is an inflammation of the apical tissues surrounding the tooth. Of course, in some very severe forms, periodontitis can lead to the formation of fistulas, but often these are all unrelated, and one should be treated separately. First, cure periodontitis, if the tooth is healthy, if it does not wobble and can be preserved, and then treat periodontitis.
How long does it take for a patient to recover after fistula treatment?
The treatment of chronic periodontitis itself is not quick, since the patient must first open the tooth canal, clean it, disinfect it with special antimicrobial drugs, and only after that the tooth canal is sealed. If we talk about rehabilitation, when the results are visible, the fistula “goes away” almost immediately, and the bone takes a long time to recover.
If we talk about the surgical method
treatment of periodontitis, when the apical part of the tooth is opened according to the type of resection, but the apical part of the root is polished, the mucous membrane is restored quite quickly - this is
3-5 days
.
The process of removing a wisdom tooth in the gum
The removal operation consists of the following steps:
- Preparation. To reduce the risk of postoperative deposits, sanitation of the oral cavity and professional hygiene are carried out with the removal of dental deposits. Elimination of pathological microorganisms and foci of infection promotes rapid wound healing without complications.
- Anesthesia. Before the operation, local anesthesia is performed using a carpule syringe and modern painkillers. The anesthetic is selected for each individual, taking into account individual sensitivity, age, and medical history.
- Creating access to the tooth. In case of retention, the dentist must provide good access so that the forceps can be securely fixed. To do this, size the gums and, if necessary, remove the bone and gingival hood.
- Extraction. The difficulty of molar removal depends on the type of retention and the individual situation. The tooth is fixed with forceps and dislocated; if necessary, additional instruments are used.
- Procedures after removal. After extraction, the tooth socket is inspected and bone fragments and protrusions are removed. The doctor applies a gauze pad and, if necessary, medications to stop bleeding. Sutures are placed on the gum to speed up healing.
- After surgery, the patient is given instructions, advice, and recommendations in the postoperative period.
How to prevent a relapse?
Any treatment, including surgery, unfortunately, does not exclude recurrences of the disease.
Simple measures taken by the patient himself will help minimize their risk. Necessary:
- Give up some habits. Namely, stop smoking, minimize alcohol, give up soda. Dishes and drinks should be consumed warm. Too hot or cold promotes chemical/thermal damage and usually relapse.
- Brush your teeth with soft bristles (low or medium hardness) and Sensitive toothpastes for painfully sensitive teeth. Initially, after treatment, it is better to use baby hygiene products that are mild and without aggressive components.
- Visit the dental office regularly to monitor the process of regeneration of operated tissues and prevent any unhealthy changes. It is necessary to come to the doctor for examination every 1-1.5 months.
Prevention after surgery
The rehabilitation period after removal of an impacted wisdom tooth lasts longer than after a normal one. Healing of the gum socket can take up to 2-3 weeks. During this period, it is important to follow the doctor's recommendations to prevent complications. It is necessary to carefully but delicately carry out hygienic care of the oral cavity. For the first days after the intervention, take painkillers and follow a gentle diet. Too hard, burning foods can damage the gums and cause tissue inflammation.
Dentists also recommend rinsing the mouth after each meal using antiseptic solutions, herbal decoctions, or just water. During the week, you must avoid physical activity, visiting the gym, baths, saunas. If any complications occur, you should not self-medicate; you must immediately seek help from a doctor.
If it hurts, what should you do?
In case of acute pain in the area of the impacted tooth or after extraction, you can take an anesthetic. For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are best suited - Nimessil, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Ketanov. At home, you can also carry out hygienic cleaning and rinsing the mouth with antiseptics. For a professional examination and treatment, you must visit a dentist.
Ingrowth of gingival papillae
Pathology develops due to chipping/destruction of molars or incisors on one side. The tissue between the teeth is constantly injured, which contributes to its abnormal growth. The flesh increases in volume, filling the free space. At the beginning of the activation of abnormal processes, the patient experiences pain and discomfort. In the latent state, pain decreases. However, the papilla continues to grow and causes discomfort when it reaches a large size. When eating food or brushing teeth, the gums are constantly injured.
Diagnosis of tooth loss
If the first signs of disease are detected, and even more so of loose teeth. If the problem is ignored, the tooth will be lost forever. The doctor will ask you to take the necessary tests, take pictures, make a diagnosis, taking into account information about previous or existing diseases, and prescribe treatment. The main diagnostic methods are x-rays and, in some cases, dental computed tomography.
In the case when a patient suffers from a chronic disease, tooth loss is a consequence, the elimination of which will be an insufficient measure. The solution is comprehensive treatment of the underlying disease together with a specialized specialist.
For what reasons are the roots of teeth exposed?
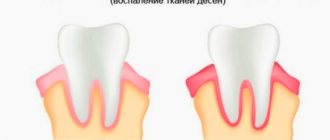
The phenomenon of exposed teeth in dentistry has a name - gum recession, but usually recession is only a symptom behind which another dental disease is hidden. Most often, it is the lower row of teeth that suffers from recession, since it bears the brunt of the load.
A common disease that causes gums to become exposed is periodontitis, during which inflammatory processes begin to occur in the periodontal tissues; if such a disease is started, it can become chronic.
Typically, periodontitis is a consequence of poor oral hygiene. Plaque and food debris that accumulate between the teeth and on the surface gradually enter the soft tissues and provoke inflammatory processes.
Inflammation significantly weakens the gums, making them weak and unable to maintain their shape. Then they descend and expose the neck of the teeth, which can lead to their loosening and loss. Periodontitis can also be caused by natural pathology.
The second most common cause of exposed roots is periodontal disease, which, unlike periodontitis, is not an inflammatory disease. During such a disease, the gums decrease in size due to atrophy of soft tissues, or disruption of metabolic processes in them.
Other reasons that cause denudation of teeth include:
- Improper brushing of teeth, namely too much pressure of the brush on the gums.
- Tooth decay close to the gums due to caries.
- Malocclusion, short frenulum of the tongue and other pathologies of the oral cavity.
- Malfunctions of the thyroid gland and gastrointestinal tract.
- Caries that has penetrated deep into the dental tissue often causes the gums to detach from the tooth.
To eliminate the defect, it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. If the disease is allowed to progress, the gums will eventually recede to the point where the tooth can fall out. Considering that most of the causes of such a defect are not local, but affect the entire oral cavity, refusal of treatment can lead to the loss of all affected teeth.