Wisdom teeth or “eight” teeth grow in adults. By this age, the jaw is fully formed, there are 28 permanent teeth. Eruption takes about a month and a half, then roots form within 3-4 years. The first period is almost always accompanied by painful sensations and inflammatory processes. During root formation, discomfort rarely occurs. In the case of pathological eruption, inflammation and pain may continue for a long time. Whether discomfort is an indication for removal of the “eight” will be determined by the doctor during a diagnostic examination.
Why can wisdom teeth hurt?
Currently, dentists consider the third molar to be a vestigial organ, which in the process of evolution has lost its functional load and relevance. For ancient man, it served to chew hard food, which is practically absent in the modern diet, which means there is no longer any need to use the wisdom tooth when chewing. This fact is supported by the presence of approximately 10% of the planet's population, whose representatives do not have eights at all, which is not a pathology. The remaining 90% of the population faces unpleasant wisdom tooth problems. The third molar can hurt and bother you for various reasons.
When teething
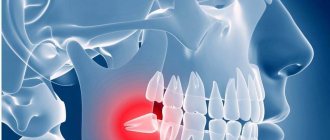
By the age of 18–25, a person’s jaw is already formed. And, naturally, when a wisdom tooth is cut, it may simply not have enough space in the dentition. The eight begins to put pressure on the seven in front, which in turn puts pressure on the sixth molar, etc. As a result, the entire jaw hurts and “aches.”
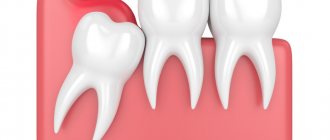
Often the third molar does not find a place for itself in the dentition and begins to grow dystopically - it deviates to the side, turns around its axis, moves forward or backward. In this case, the gums near the wisdom tooth hurt and inflammation may occur. Not to mention the fact that in adulthood the gums have a fairly dense structure, the resistance of which must be overcome by the figure eight. And in order to erupt safely, it literally tears the soft tissue. Naturally, this process is accompanied by pain and discomfort.
For dental disease
An already formed wisdom tooth will hurt if it is susceptible to any disease. The most common are caries, pulpitis and periodontitis.
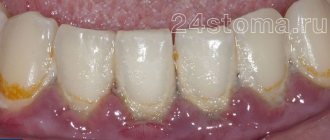
- Caries is a pathological process that leads to the destruction of hard tooth tissues, which is initially accompanied by increased sensitivity of the enamel, and subsequently severe pain in the wisdom tooth.
- Pulpitis - inflammation of the internal tissue of the figure eight (pulp) is a consequence of untreated caries. In rare cases, infection enters the pulp through the apical foramen, which may be due to improper position of the molar. With pulpitis, the wisdom tooth hurts very much, since the pulp is penetrated by a large number of nerve endings.
- Periodontitis - inflammation of the periodontium (connective tissue surrounding the tooth) can be caused by injury to the gums or infection during the eruption of the figure eight. In this case, localized, constant pain is observed, which gradually increases and becomes pulsating, which indicates a purulent course of the process.
Important! If an already erupted wisdom tooth suddenly begins to hurt, then you need to show it to the dentist as soon as possible. Timely diagnosis will avoid infection of the pulp, periodontium and the development of complications.
For pericoronitis
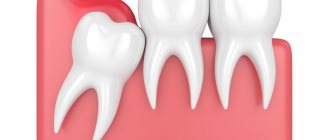
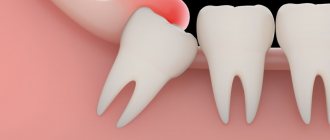
Pericoronitis - inflammation of the soft tissue of the gums surrounding the erupting figure eight, is the most common. The problem is that when a wisdom tooth comes in, it first cuts through the mucous membrane with its tubercles, forming a so-called “hood” above itself - part of the gum. Thus, partly the third molar is already visible, and partly is still covered by the “hood” of the gums. Hanging over the figure eight, it creates favorable conditions for the accumulation of food particles, plaque, and microbes, which, sooner or later, leads to inflammation. The development of pericoronitis will also be accompanied by pain.
Important! If the gum above the wisdom tooth forms a “hood” and is inflamed, then it must be excised (removed). The procedure is carried out in the sterile conditions of a dental clinic.
Emergency measures
What to do if your wisdom tooth is cutting out and your gums hurt? It is not always possible to consult a specialist at the first pathological signs. It is also possible to relieve discomfort at home. To do this, the oral cavity is rinsed with soda or saline solutions. They will help slow down the spread of pathogenic flora and reduce the intensity of inflammation. Solutions are prepared according to the following recipe: 1 tsp. soda or salt is dissolved in 200 ml of boiling water. The rinsing procedure is carried out every 2 hours.
If the cheek is swollen due to caries, then it is better to use herbal tinctures and decoctions. The ideal option is crushed horsetail mixed with honey. To rinse the mouth if there is a problem, use an alcoholic tincture of fennel and horseradish: the plants are crushed and mixed in equal proportions. Plant materials are poured with vodka and left for 3-4 hours. The use of alcohol tinctures is prohibited for patients who have ulcers in the mouth. Otherwise, emergency measures will lead to burns of the mucous membranes.
Freshly squeezed onion juice will help temporarily relieve pain during wisdom tooth growth. A gauze swab is moistened in the product and applied to the problem area for 2-3 minutes.
What painkillers can be used if a wisdom tooth is coming out and your cheek hurts? In this situation, potent tablets, which are usually prescribed by a doctor, are suitable. When taken independently, side effects may develop, such as stomach bleeding or lack of effect from taking the medication. For this reason, taking painkillers for more than 3-5 days without consulting a doctor is prohibited.
A common group of medications used for toothaches are analgesics. Medicines provide a calming effect for several hours before visiting the dentist. From this group of drugs Analgin, Pentalgin, Tempalgin are used. Ibuprofen-based products - Nurofen, Nimesil, Bonifen - have a more powerful therapeutic effect. The drugs not only reduce pain, but also have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Aspirin and Paracetamol will help relieve suffering. You should not count on a powerful pain-relieving effect from taking these medications.
What does a wisdom tooth look like?
List of the most powerful drugs used for pain in the cheek during teething:
- Nise;
- Ketarol;
- Ketanov;
- Nimesil;
- Ketorolac.
The effect of taking the drug lasts for a long time, more than 4 hours. Frequent use of the above medications threatens complications from internal organs.
If the cause of the problem is related to the eruption of a rotten third molar, then an anesthetic can be applied to the tooth. To do this, the tablet is crushed into powder and poured into the carious cavity. It is necessary to ensure that the drug does not get on the gums and mucous membranes, otherwise even greater inflammation may develop.
To treat carious lesions, it is most convenient to use Lidocaine spray. The drug is sprayed on the side on which pain is noted.
Cooling gels - Cholisal, Kamistad, Dentol, Metrogyl - will help temporarily cope with the signs of a growing figure eight. Additionally, the sore spot is rinsed with antiseptics - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin.
What to do if your cheek is swollen from a wisdom tooth, and you don’t have the appropriate medications at hand? You can soak a cotton swab in propolis tincture or valerian and apply it to the problem area. You can rinse your mouth with vodka (in the absence of ulcers and open wounds on the mucous membranes). Sea buckthorn oil has a good anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. It does not damage the mucous membranes and is considered safe in the treatment of toothaches.
How long will the cutting and toothache last?
The process of cutting through the figure eight is long and highly individual. In some patients it “appears” in 3–4 months, in others it may take 1–2 years, and in others it remains incompletely erupted. Quite often, a wave-like “appearance” of the third molar is observed - either it is intensively cut, or it freezes.
As for severe pain, as a rule, it is present only at the beginning of the process - at the stage when the figure eight cuts through the dense gum tissue. And again, this moment can happen quite quickly or drag on for a long time.
When the first signs of figure eight eruption appear, it is better not to postpone a visit to the doctor. Even if the process does not cause severe pain or discomfort, it is better to show it to the dentist. An experienced specialist will examine the condition of the third molar and provide assistance that will facilitate the process of “the birth of the tooth.”
Symptoms of pathological changes in intervertebral discs
- The pain intensifies when turning the head.
- Spasms are observed in the jaw.
- Nausea and dizziness.
- Numbness of the limbs.
- Noise in ears.
To rule out acute dental diseases, including deep caries, a visit to the dentist will be required. Treatment methods for osteochondrosis are selected individually by the attending physician. In case of serious complications, compression of blood vessels, surgery is prescribed. Drug therapy for osteochondrosis includes taking anti-inflammatory drugs and antispasmodics. During the treatment process, it is important to adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations and comments.
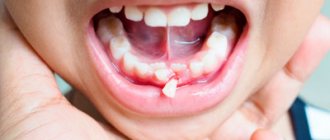
How to understand that a wisdom tooth is cutting?
It's not difficult to understand. Normally, this process is accompanied by discomfort, engorgement and slight swelling of the gums in the place where the tooth is cut. At the moment of eruption, increased salivation, a feeling of fullness and tolerable pain will be observed. They can intensify during eating and hygiene procedures. Visually and by touching the tongue, you can see and feel the protruding tubercles of the figure eight.
In the pathological course of the process, the following symptoms may join the above-described symptoms.
- Redness and swelling of the gums indicate inflammation of the “hood”.
- It hurts to open your mouth - the inflammation process is progressing and has spread to the masticatory muscle.
- It hurts to swallow - a symptom indicates the presence of purulent inflammation of the soft tissues closer to the tongue.
- High temperature - the inflammatory process progresses.
- The third molar, the adjacent tooth and gums are very painful - most likely, the figure eight is growing in the wrong direction.
Additionally, symptoms may occur depending on the location of the wisdom tooth.
- The upper eights can erupt towards the cheek and injure its mucous membrane, causing pain.
- The lower molars often form a “hood” and grow with an inclination towards the seven, forming a gap. It is difficult to clean with a brush. Over time, a stable plaque and tartar form in it, which leads to the development of caries.
You should not trust various kinds of myths, they say, the appearance of a wisdom tooth is always excruciatingly painful, very problematic and you just need to endure it. It is not true! Normally, the process does not cause excruciating pain and passes with tolerable discomfort. On the contrary, problem eights hurt a lot, provoking the development of inflammation and complications. Therefore, it is better not to delay visiting the dentist.
How does the eighth molar make itself known?
- Discomfort when chewing;
- severe pain in the area of molar eruption;
- swelling, redness of the gums;
- inflammation of the submandibular lymph node;
- limited jaw mobility (difficult to even open your mouth);
- painful swallowing;
- deterioration in general health;
- temperature increase.
More often problems arise with the lower eights. The wisdom tooth below hurts more than the erupting extreme molar on the upper jaw. The latter, much less often, grows incorrectly and almost never involves a neighboring unit in the process. This reduces the risk of gum injury and discomfort during teething. The eighth molar on the lower jaw causes more problems. The bone tissue around it often becomes inflamed, causing significant discomfort and pain.
Does it make sense to treat wisdom teeth?
An experienced and self-respecting dentist will always fight for every tooth to the last. And wisdom teeth in this case are no exception. After all, no one knows how the patient’s life will turn out in the future. Perhaps in the future he will need prosthetics, and the figure eight will be used as a supporting tooth for installing a prosthesis. Therefore, if the appearance of a third molar does not pose a threat to neighboring teeth and oral health, the dentist will take actions aimed at facilitating the process and preserving the tooth. Well, unless, of course, the patient insists on its removal.
If the current situation is serious, then removal of the wisdom tooth is inevitable. Including in those cases when the figure eight does not hurt much (or does not hurt at all), but is covered with caries and is gradually destroyed. It is more rational and safer to remove such a tooth and forget about the problems.
Occurrence of complications
Operations to pull out figure eights are considered complex dental procedures, which are due to:
- difficult access;
- frequent retention;
- unpredictable structure;
- features of the location of the mandibular alveolar nerve.
Such procedures are very traumatic, which creates the preconditions for the occurrence of general and specific types of complications.
Are common
The nature of complications largely depends on the location of the tooth: on the upper or lower jaw. But there are also general complications that arise in almost everyone, regardless of the location of the figure eight and its initial condition. The most common overall effects are listed below.
Painful sensations
Approximately 2-3 hours after molar extraction, you will experience noticeable pain in the gums. This is a normal reaction of the body to trauma, which is dental surgery. During it, soft tissues are torn or cut, the bone is injured (if the tooth is located under it), blood vessels and nerves are damaged. Painful sensations should completely disappear after 2-4 days, and for some people disappear within a few hours. They can be reduced with the help of painkillers prescribed by the dentist. If the pain does not go away, and the cheek is very swollen, it means that the gum healing process is proceeding with complications.
Swelling of the tissues of the face and neck
Often after figure eight extraction, especially impacted ones, swelling of the soft tissues of the gums or cheeks is observed. This is also a reaction to injury, which can be called a normal consequence of a dental procedure. In addition to swelling, the following symptoms may occur:
- swelling of the lymph nodes;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- painful sensations during mouth movements, radiating to the ear.
Normally, severe swelling should go away completely in 2-3 days, and if it doesn’t go away, then we can talk about more dangerous consequences. If the condition worsens every day, difficulties arise when breathing, fainting, the temperature rises and the skin becomes covered with a rash, then such swelling is provoked by an allergy and it can lead to anaphylactic shock.
Hematomas
Hematoma due to extraction is usually expressed by minimal bluishness of the cheek, which goes away after a few days. But there are situations when the appearance of a bruise is accompanied by severe pain, swelling, and an increase in temperature. In such a situation, medical attention is needed. Hematomas form after vascular damage in people with increased capillary fragility, as well as when the patient has hypertension.
Alveolitis
complications after wisdom teeth removal
Alveolitis is often provoked by non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations after treatment procedures. It is a local inflammation of the gums with the following additional symptoms:
- the gums swell and turn red;
- local pain and headache are observed;
- sore throat;
- the temperature rises, muscle aches appear;
- lymph nodes become inflamed, most often the submandibular ones.
If inflammation occurs, the cause is often the loss of a blood clot from the socket and infection. Various infections that enter the wound due to poor hygiene can provoke extensive inflammation. In advanced cases, the above complication develops into osteomyelitis, which is expressed by:
- increased persistent temperature;
- poor general health;
- severe migraine-like pain;
- nausea;
- other signs of intoxication of the body.
Increased body temperature
A slight increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 °C also often occurs in the postoperative period. This complication occurs due to a reaction to inflammation. The temperature should completely return to normal within the first day, and if it continues to rise and rise, it means that more serious pathologies have arisen and you need to go to the hospital again.
Bleeding
The dentist will never dismiss a patient with severe bleeding, especially if it is complicated. After removing the figure eight, the bleeding is stopped in the hospital, and then sent home with a gauze pad on the hole. If blood clotting is normal, then the bleeding will stop within 10-15 minutes, after which the tampon must be removed. Severe prolonged bleeding is provoked by:
- rupture of large vessels;
- capillary fragility;
- hypertension.
Damage to the roots of adjacent teeth
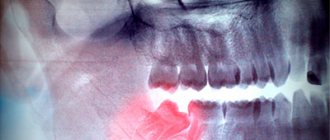
Such a complication is observed extremely rarely and only if the patient did not undergo X-ray diagnostics before the procedure. This procedure is mandatory for all people with indications for the removal of figure eights and allows you to fully assess the condition, location, as well as other features of the tooth and its roots.
Flux
Flux in the postoperative period develops in cases where the gums become infected due to the fault of the dentist or patient, after which the infection quickly reaches the periosteum and provokes its inflammation. This complication is not considered normal and acceptable and must be treated. Main signs of flux:
- redness, suppuration and swelling of the gums;
- severe shooting pain;
- temperature increase;
- weakness.
Others
Among other common complications, the most commonly observed are:
- displacement of the seventh tooth (2 molars);
- mouth rupture; cut gums or cheeks;
- jaw injuries.
In addition, complex extraction of the 8th tooth can cause the formation of a cyst. This is a small tumor located at the root of the tooth and filled with fluid. The cyst often serves as an insulator for infected cells from healthy ones. To prevent its occurrence, the dentist prescribes antibiotics, and the treatment in this case (if the cyst is located at the roots of the tooth) will be resection.
When do you need to see a dentist urgently?
Contacting a dentist is required in the following cases.
- Pericoronitis
– the “hood” will be excised. - The figure eight puts pressure on neighboring teeth
- it needs to be removed. - Initial caries
– treatment will be carried out. - Medium, deep caries or rotten tooth
- a clear removal of the figure eight. - The wisdom tooth is loose
- a diagnosis of its condition will be carried out, according to the results of which the molar will be treated or removed. - Pulpitis
– if the root canals are passable, they will be filled.
This list should also include the above symptoms of pathological teething - pain when opening the mouth, swallowing, high temperature. If they appear, you should contact your dentist immediately, since this is a serious inflammatory process, the localization of which requires adequate treatment.
The reason for contacting a specialist may also be the “normal behavior” of the number eight. In this case, the doctor will simply make a small incision on the gum, thereby facilitating the eruption of the wisdom tooth. After a simple procedure, the process will be less painful, and the incision site will heal quickly, after pain for 2 to 4 days.
Diagnosis of the disease
In order for the diagnosis to be made correctly, it is necessary to consult a professional doctor. Osteochondrosis is treated by a neurologist. To avoid complications, it is necessary to contact specialists in a timely manner. During the examination, the doctor will be able to objectively assess the mobility of the vertebrae and identify painful areas. Additional examinations include:
- Referral to a dentist.
- X-ray.
- CT and MRI.
- Dopplerography.
If pain from a tooth radiates to the neck, this is an alarming sign that requires immediate consultation with a doctor. If the discomfort is accompanied by a migraine, this indicates poor circulation.
When should a tooth be removed?
Direct indications for wisdom tooth removal are the following pathologies and conditions.
- There is no place in the dentition for a number eight.
- Dystopic tooth (molar occupies an anatomically incorrect position).
- The appearance of wisdom teeth threatens the molars in front.
- Severe forms of caries that destroy the tooth.
- The third degree of mobility of the figure eight.
- Upcoming installation of braces.
If removal is not carried out, the development of complications is inevitable. The number eight will destroy adjacent teeth and provoke the development of pulpitis, periodontitis, and extensive caries. Eventually it will fall out on its own, but at too great a cost to the patient.
There is no need to be afraid of wisdom tooth removal. Depending on the complexity of the problem, third molar extraction will last from 20 minutes to 2 hours. The operation is performed using local anesthesia or sedation, which ensures that the procedure is painless.
How to relieve pain?
When visiting the clinic, the attending physician gives valuable recommendations that will help relieve the process of the “appearance” of the figure eight. If you decide to act on your own, you can use the following medicines and folk remedies.
Pills and medicines
- Tablets: “Nimesil”, “Analgin”, “Solpadein”, “Tempalgin”, “Ketanov”, “Paracetamol”, “Ibuprofen” are used according to the instructions.
- Gels and ointments: “Cholisal”, “Kamistad”, “Kalgel”, “Metrogil Denta” are applied to the site of tooth eruption.
- Solutions: “Chlorhexidine”, “Miramistin” and “Furacilin” are used for antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity.
Folk remedies
- Soda, saline or soda-salt solution - 1 teaspoon of product for 1 glass of warm water, stir until completely dissolved, rinse the problem area every 2 - 3 hours.
- Sage, calendula, plantain, St. John's wort - to prepare a decoction, pour 1 tablespoon of the product into 1 glass of boiling water, leave for 20 - 30 minutes, use for rinsing every 2 - 3 hours.
Home methods of pain relief will be effective if there are no serious problems with the eruption of the figure eight. If inflammation occurs, the tooth is rotten or very loose, then they will not help, but will only aggravate the problem, which will lead to the development of complications.
Wisdom teeth removal with 20% discount
Moscow
Where can the pain go?
Quite often, the process of growth of eights is accompanied by uncharacteristic symptoms. Moreover, some of them are due to the growth of the molar itself, and the other part indicates the development of complications. Let's take a closer look - can a wisdom tooth give into...?
- Head
- in case of complicated teething it can. - Eye
– with complicated eruption of the upper molars and the development of an abscess, it can. - Tongue
- a symptom indicates the presence of purulent inflammation of the soft tissues closer to the tongue. - Ear
– indicates the development of inflammation, pulpitis or dental cyst. - Throat
- most likely we are talking about pulpitis. - Jaw
- a symptom characteristic of complicated teething and inflammation. - The neck
is unlikely, unless we are talking about the spread of infection and inflammation of the lymph nodes. - Temple
– Clicking and pain in the temple may be present due to tension in the temporomandibular joint, which occurs from constant pain. - The teeth are nearby
- of course, because the figure eight can put pressure on them.
Important! The above list is a serious signal to contact a dentist. Don't delay your visit to the clinic!
If your tooth hurts and radiates to your neck
Pain syndrome is a very common occurrence in dental practice. But sometimes discomfort is not a consequence of dental problems. Often, painful sensations in the jaw area are nothing more than a symptom of a diseased spine. Pinched nerve fibers often cause discomfort in different parts of the body. With osteochondrosis, not only the neck can hurt. This disease often occurs in middle-aged and older people. The central part of the intervertebral disc is replaced by fibrous fibers, becomes denser, and loses its ability to absorb shock. As a result of the development of the disease, acute pain in the neck appears. In addition, the mobility and flexibility of the neck decreases.