Studies using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner are informative. A distinctive feature of MRI is a targeted examination of a selected area and the ability to detect pathology at the very beginning of development. But patients are prevented from undergoing this procedure by the presence of contraindications. Many people are particularly interested in whether it is possible to do MRI of the pituitary gland or other parts of the body with dental implants and metal crowns. More details later in the article.
Safety of MR Imaging in Patients with Dental Appliances and Devices
An MRI scanner generates the powerful magnetic fields needed to produce images. Metals interact with magnetic fields in different ways. As a result of this interaction, a number of effects arise that affect the results of the examination - dark spots or so-called artifacts appear on the images, which can complicate or make diagnosis impossible, metal products can heat up or move under the influence of a magnetic field. The degree of this influence depends on what metal was used for the manufacture of metal structures for dental purposes.
Artifacts
Most often in dentistry, inert metals are used - titanium, gold and its alloys, zirconium, nickel, zinc, chromium, copper, silver, iron (stainless steel) - which do not interact with living tissues. Depending on the ability of these materials to cause artifacts, a distinction is made between MRI-compatible and non-MRI metals.
MRI-compatible metals that cause no or minimal artifacts include zirconium (the metal from which dental crowns are made), silver, zinc, copper alloys, titanium and its alloys, gold and its alloys, nickel and its alloys. Stainless steel, alloys containing large amounts of chromium and cobalt are not compatible with MRI and cause artifacts that complicate diagnosis. You can find out detailed information about the composition of the materials used to make dental structures from your dentist.
Heating the metal
The magnetic fields generated by an MRI machine can cause heating of metal products, up to temperatures sufficient to cause a burn. However, this is only true for metal objects that are on the surface of the patient's body - which is why it is recommended to remove all metal objects, jewelry, piercings and jewelry before the examination. Metal crowns, dental pins, implants, and dentures are less susceptible to this effect - studies on the safety of MRI in the presence of metal in the mouth have found that the heating of such products during research does not exceed 2-3 degrees Celsius. Therefore, MRI of the head or internal organs is a safe procedure for the patient, even in the presence of dental structures.
Displacement of metal structures for dental purposes
The magnetic fields generated during magnetic resonance imaging are capable of attracting metal objects made from magnetic metals, giving them significant acceleration. It is for this reason that before performing an MRI of the brain, spine or any other parts of the body, it is strictly forbidden to carry any metal objects on you. Otherwise, a piece of metal flying into the tomograph magnet can cause serious injury. In this case, is it possible to do an MRI with metal crowns on the teeth, with pins or braces? It is possible, since the mass of such products does not exceed several grams, and the structure itself is firmly fixed in the oral cavity. The exception is braces, dental crowns, bridges and dentures made of stainless steel. Removable structures must be removed before performing the procedure - this will not only make the examination safer, but will also improve the quality of the resulting images. If the structure is not removable, it is recommended to consult a dentist to check the strength of the fastening and prevent the product from moving.
Is it possible to perform MRI with metal-ceramic crowns?
Is it possible to do MRI with metal ceramics? It is possible, but it is necessary to inform the doctor in advance about the presence of such crowns in the patient’s mouth, and it is also very desirable to know what kind of alloy the frame of the crowns is made of (this point can always be clarified with the dentist who handled the prosthetics).
When conducting an examination of the spine, upper and lower extremities, as well as abdominal organs, prosthetic structures do not play any role and do not affect the accuracy of diagnosis. When examining the head and brain, distortions are possible when ferromagnetic materials are present in prosthetic structures. Therefore, in each specific situation, the decision on the advisability of the procedure is made jointly by the doctor and the patient.
Source link
Prices for metal-ceramic crowns in Novokuybyshevsk at the Favorit clinic
With which implants is MRI of the brain contraindicated?
Implants are not a contraindication for brain MRI, since they are mainly made of titanium. Titanium and its alloys are compatible with MRI and result in virtually no artifacts in images. However, if non-removable stainless steel dental products are installed in the oral cavity, artifacts can cover most of the cervical spine and head, making the diagnosis of diseases of the brain and neck uninformative. If this happens, such research will not be paid for. You can obtain more detailed information from the doctors of our medical center.
| MRI of the head and neck, which shows |
| Stroke on MRI of the brain |
| MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast, what does it show? |
| MRI of the brain with contrast, how is it done? |
| Decoding MRI of the brain |
| MRI of cerebral vessels, which shows |
Why are things made of metals removed before an MRI?
The principle of operation of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is to create its own magnetic field in which the patient is located. Hydrogen atoms in the patient's body resonate with a magnetic field and the result is recorded as a series of images. These are virtual sections of organs and tissues that help make an accurate diagnosis.
Doctors ask that metal objects be left outside the room with the tomograph so that any metal or alloy that can be magnetized does not accidentally enter the magnetic field. All substances are divided into:
- Diamagnets
. Their magnetic susceptibility is negative. Silicon, gold, silver are diamagnetic. - Paramagnets
. They are capable of magnetization, but their magnetic susceptibility is very weak and difficult to detect, so only scientists understand the difference between dia- and paramagnets. Platinum and aluminum are paramagnetic. - Ferromagnets
. The magnetic susceptibility of such metals is high; they are capable of magnetization and change location under the influence of a magnetic field. Iron, cobalt, nickel are ferromagnetic.
Based on these properties, doctors ask to remove metal objects during magnetic tomography. Ferromagnets not only distort images and heat up in a magnetic field, but can also shift under its influence.
When and who should not undergo the study
In response to the question: “Is it possible to perform MRI with dental implants?”, doctors answer in the affirmative. But a number of conditions must be observed - they do not relate to the implants themselves, but are of a general nature. First, let's systematize the contraindications to this study. They are divided into 2 groups – relative and absolute. The following are considered absolute contraindications:
- any large ferromagnets in the human body: large metal implants on bones, middle ear prostheses, metal fragments in soft tissues. But dental implants are not included here,
- electronic stimulators: on the heart, middle ear prosthesis.
Ferromagnets are substances and alloys containing nickel, chromium, steel, cobalt, and any compounds with a large percentage of iron. Highly susceptible to magnetism. In a powerful magnetic field, ferromagnets can move if they are located in soft tissues. The consequences of such a movement are almost always unpredictable and can cause harm.
Relative contraindications - this term hides restrictions on MRI that can be circumvented. For example, undergo diagnostics later or on a different device. Let's consider the relative contraindications to MRI:
- inability to lie still during the examination: this may include small children and patients with nervous disorders. They are put into a short medicated sleep,
- early pregnancy: due to the lack of confirmed data on the harmful effects of the magnetic field on the fetus,
- hemostatic clamps in blood vessels,
- tattoos: if metal is present among the components of the pigment, then it will heat up in the device, even causing burns,
- braces, crowns or other prosthetic devices that contain ferromagnetic metals - primarily steel. But there are some peculiarities - if the prosthesis is in the mouth, and you do an MRI of the leg, then there are no risks.
Contraindications mainly relate specifically to MRI, and the closed type - when the patient is completely placed in the machine. There are also open-type tomographs - they have fewer restrictions for diagnosis, but their accuracy is lower.
What can replace MRI?
If a patient is contraindicated to undergo magnetic resonance imaging, and he does not want to remove metal-ceramic crowns, you can try to find an alternative. To do this, the following methods can be used, which can be found in the table.
| Procedure | Information content |
| Second place in terms of information content | |
| Relatively effective, sometimes requires confirmation with MRI | |
| Effective in some cases | |
| Not very informative, used only in combination | |
| It is advisable to use only in combination. |
Attention! Despite the possibility of using an alternative option, only magnetic resonance therapy can give the most accurate result, identifying even the slightest abnormalities that are not yet visible on ultrasound and any other tests.
Regardless of how many metal-ceramic crowns you have and what part of the body you are undergoing an MRI procedure for, you should always warn your doctor about the presence of a foreign body in your teeth.
If it is impossible to undergo an examination, the specialist will prescribe other procedures that can give an accurate picture of the state of health. If magnetic resonance imaging cannot be done, a computer diagnostic method is usually used.
How does a patient with metal ceramics feel during the procedure?
During a diagnostic examination in the presence of metal-ceramic structures, the patient will not experience any discomfort, much less acute pain or other painful sensations. The patient's life is also in perfect order and nothing threatens her.
If for one reason or another you are denied an examination, this will be due to the fact that your metal-ceramic crowns will greatly distort the final result. This will happen due to the resonance of the metal elements of the dental structure and the magnetic field of the tomograph. As a result, the doctor will either not be able to see the tissues he needs, or marks will appear on them that will give a false diagnosis.
Attention! Patients with metal-ceramic crowns are often denied examination due to the high cost of MRI. Since it is difficult to predict the final result, some laboratories prefer to refuse treatment to the patient, especially when it is carried out on a budgetary basis, when it is not the patient who pays, but the clinic.
Do metal dental implants move during examination?
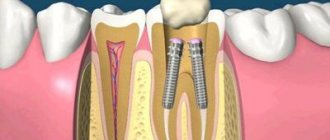
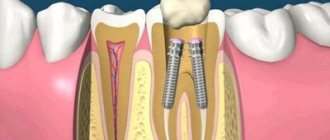
To understand whether an implant can move under the influence of a magnet, you need to know what it consists of. Dental implants are a modern replacement for your own lost teeth. It consists of a metal implant (reliably fixed in the jaw bone and replaces the tooth root), an abutment (connecting part) and a crown - an analogue of the upper part of the tooth. If the prosthesis is installed efficiently, then it is not at all perceived as a foreign body. It looks like it's your own tooth. These sensations are achieved thanks to the special structure of the implant - it contains micropores, and bone grows into them over time. Thus, it fully replaces the tooth root and does not wobble.
Why the implant does not move during MRI:
- rigid fixation in the jaw: the bone securely holds the tooth root prosthesis in place,
- consists of titanium: i.e. does not magnetize and does not heat up.