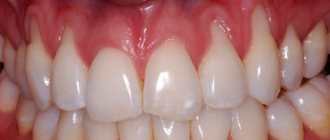
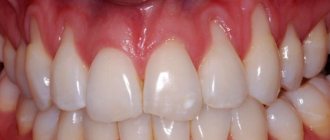
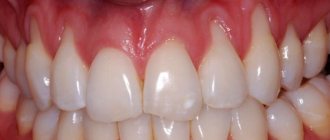
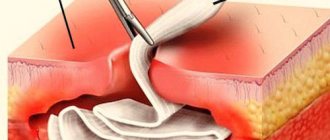
Hematoma
Description
If there is a swollen lump on the gum filled with blood, most likely it is a hematoma. This tumor occurs as a result of an incorrectly removed tooth or injury. Such a lump on the gum above the tooth, as a rule, does not hurt.
Treatment
Dissolves on its own. But if the lump hurts, consult your dentist for advice. The doctor will prescribe painkillers.
Lump at the base of the tooth after installing a permanent crown
If the prosthetics are carried out correctly, the doctor did not make mistakes, no neoplasms should appear in the mouth. If, after the end of treatment, the gums swell and a painful blister forms on it, it means that something did not go according to plan.
Most likely, the doctor poorly prepared the unit for prosthetics. Depulpation must be carried out extremely carefully. There should be no air bubbles in the canals to be filled. Under no circumstances should you leave fragments of dental instruments in them. Poor depulpation creates conditions for the development of an infectious process and subsequent periodontitis.
It is also possible that the lump was formed due to shortcomings that were made at the time of fixation of the artificial unit. Then the glued structure begins to put pressure on the mucous membranes and rub the tissue. Abscesses, growths, and purulent lumps form. To eliminate these unpleasant symptoms, you need to adjust the shape of the prosthesis.
If the crown is installed correctly, it will never interfere. This needs to be understood. Only in the first hours after its fixation may an unusual sensation of a foreign body in the mouth persist. But then the person stops noticing the structure altogether.
Epulis
Treatment
The lump on the root of the tooth is attached to a stalk and is either red or gum-colored. It affects the lower jaw and occurs as a result of malocclusion, permanent mechanical damage, and poor quality dentures. Often observed in women with hormonal imbalance.
Treatment
It is removed by one of three methods: scalpel, diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia.
Types of dental abscess
- Osteomyelitis
- Phlegmon
- Tooth loss
Osteomyelitis
When pus remains in the soft tissues, complications arise. Dense formations with pus form in the bone tissues, and swelling of the lymph nodes also occurs.
Phlegmon
A life-threatening complication occurs when the infection spreads into the soft tissues of the gums. The growth of pus leads to chronic pathologies.
Tooth loss
If the infected fluid spreads to the base of the tooth, painful swelling appears, which may lead to tooth extraction.
Periodontitis
Description
A hard lump on the gum, an abscess formed at the base of the tooth root. In the absence of therapy, it transforms into a benign tumor.
Treatment
If such compaction of the gums under the tooth appears, contact your dentist. The teeth are unfilled and root canals are cleaned. After removing the exudate, oral baths with medicinal herbs or soda solution are prescribed. Treatment for periodontitis may require multiple visits to the doctor.
Treatment
How to get rid of a lump that appears on the gum? Treatment is based on eliminating the causes and symptoms of the underlying disease.
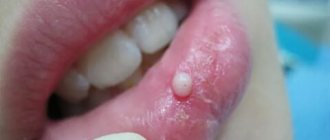
Fistula.
When a fistula occurs, the main goal is to eliminate the source of infection and remove the pus. To do this, rinse the mouth with a solution of soda and salt in a 1:1 ratio (half a teaspoon per glass). The procedure is repeated daily every 1.5-2 hours until the seal completely disappears.
Exostosis.
Exostosis is treated only surgically if there are indications for removal of the lump: pain, rapid growth, or the presence of a cosmetic defect.
During surgery, overgrown areas of tissue are removed with a chisel, then the bone is smoothed out. Worth knowing!
In children, exostoses often disappear on their own over time, so there may be no need for surgery.
Epulis.
Treatment of epulis begins with eliminating the causes that caused it - removing tartar, treating caries, adjusting prosthetic structures. Then observation is carried out and, if necessary, surgical excision of the cones to healthy tissue.
Periodontitis.
To treat periodontitis, the filling is removed from the diseased tooth, the canals are sanitized and widened (to allow pus to escape) and the affected periodontal tissues are removed. Antiseptic treatment is carried out and antibiotics are prescribed. Then a temporary filling is placed, which is later replaced with a permanent one.
Periostitis.
Treatment for periostitis is similar to the sanitation of periodontitis, with a difference in the duration of the procedure due to the more serious consequences of the disease. The tooth is unfilled, the canals are cleaned and expanded. Medicine is placed under the temporary filling and it is removed after 2 months. The tooth is washed with antiseptics, then the temporary filling procedure is repeated again. When the symptoms of the disease are eliminated, a permanent filling is applied; if there is no result, the tooth is removed.
Periodontitis.
Treatment takes place on an outpatient basis. The doctor removes tartar and performs antiseptic treatment of dental pockets. For serious lesions, treatment is performed surgically.
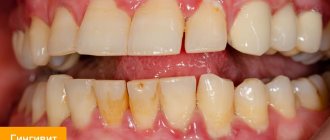
Gingivitis.
Gingivitis can be treated at home, using ointments, gels and rinses prescribed by your doctor.
But the main thing is proper oral hygiene. Important!
Treatment of diseases, depending on their complexity and nature, can be carried out on an outpatient basis or at home. One thing is certain: only a specialist should make a diagnosis and prescribe procedures (even at home!)!
Flux (periostitis)
Description
An inflammatory process of bone tissue, which is accompanied by pain, elevated body temperature, enlarged lymph nodes, and swelling of the oral mucosa. The seals have purulent contents. The cause is an infection of the oral cavity resulting from untreated caries.
Treatment
A visit to the doctor is required to treat the lump. The dentist opens the tooth, places special medications in the cavity, and closes it with a temporary filling. If treatment does not bring positive results, the tooth is removed.
Infectious diseases
| Gingivitis and periodontitis Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease, often accompanied by the appearance of a red ball-shaped growth near the tooth. The next stage is periodontitis. With it, purulent discharge is observed, and the lump acquires a grayish or beige tint. |
| Granuloma or cyst When pulpitis is advanced, the inflammatory process reaches the apex of the root, where a granuloma forms. Often this process goes unnoticed by the patient, so he is in no hurry to see a doctor. Over time, the pathology can develop into a fistula - a white formation on the gum. |
| Flux Purulent inflammation on the gums occurs against the background of advanced caries or pulpitis, a poorly treated root canal. At the first stage, minor pain appears; on the second - swelling and redness; on the third, the temperature may rise and the cheek may swell; on the fourth – the pain becomes sharp and throbbing, swelling increases. |
Fibroma
Description
Benign tumor of epithelial cells. Initially, the bumps on the gums above the tooth are small in size and do not hurt. However, mechanical stress and other negative factors can lead to the transformation of fibroma into a malignant tumor.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out surgically. The doctor excises the tumor, applies stitches, and prescribes rinses. Further follow-up visits may be required to monitor the recovery process.
Non-communicable diseases
| Epulis This is a benign formation. It has a stem and a cap. Most often it occurs due to malocclusion, improper prosthetics, and hormonal changes. In the absence of adequate treatment, the tumor can develop into a malignant one. |
| Exostosis A bone growth that occurs against the background of a jaw abnormality - the bone extends beyond its usual boundaries, forming a lump. Most often, the reason lies in a genetic predisposition, less often - as a result of injury or complex tooth extraction. |
| Hematoma As a rule, it is formed as a result of an impact and goes away on its own over time. If there is damage to the tissue, then surgical intervention is necessary. |
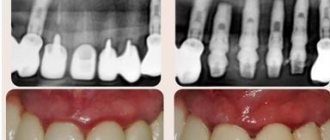
Cyst
Description
A hard, bone-like compaction of gums under a tooth, up to 1 cm in diameter. Occurs in people with weakened immunity, genetic predisposition, as well as due to acute infectious diseases, mechanical damage to the soft tissue of the oral cavity.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in the same way as for fibroma - by excision. After surgery, mouth rinses and baths are necessary, as well as repeated visits to the doctor to monitor recovery.
Why does a lump appear on the gum?
The accumulation of conditionally pathogenic and pathogenic microflora due to improper oral care leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane. Other reasons why a ball appears on the gum include:
- chemical, thermal or mechanical trauma to the periodontium;
- carious formations and their complications: periodontitis, pulpitis;
- inflammation of the wisdom tooth;
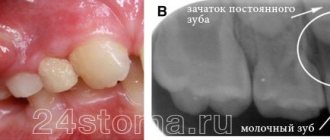
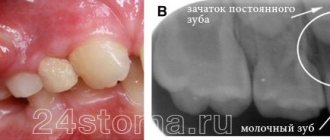
- eruption of molars;
- jawbone overgrowth;
- weak immune system;
- infectious pathologies of the oral cavity: herpes, candidiasis, stomatitis.
A lump in the mouth also occurs under other conditions: epulis, exostosis, fibroma, focal fibromatosis, malignancy, cyst and flux. The main thing is to promptly establish the causes of the pathology and begin treatment.
Gum cancer
Description
A rare dangerous disease. It is characterized by the formation of a dense lump on the gum at the root of the tooth; it can develop asymptomatically for several months.
Treatment
Requires serious medical intervention, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, long-term recovery and follow-up.
Gum cancer, if detected early, is curable, otherwise it ends in death. Red and white bumps on the gums appear in both adults and children. Only a doctor can correctly identify the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. The sooner you see a dentist, the greater the chances of a quick recovery.
Don't self-medicate! If a ball is inflated on your gum and you don’t know what to do, contact a dentist in Odintsovo. The doctor will conduct a full examination of the oral cavity, accurately diagnose the disease, and prescribe effective treatment.
You can make an appointment for a consultation, as well as find out the cost of admission and treatment by calling the clinic in Odintsovo.
Folk remedies
The use of effective folk methods and recipes as a supplement to basic drug treatment can significantly speed up the healing process.
- Rinse with saline solutions. Per liter of boiled water - 4 tbsp. spoons of salt, leave to brew for an hour. Afterwards, warm the solution a little and sanitize the oral cavity. Salt disinfects, relieves swelling, and soothes.
- Gargling with herbal infusions. Chamomile, eucalyptus, calendula, and yarrow are suitable for these purposes. 4 tbsp. l. herbs are brewed in 1 liter of boiling water and infused for half an hour. Herbs have a calming and antiseptic effect on the mucous membrane and promote the resorption of compactions.
- Kalanchoe juice. Nourishes and heals inflamed gum tissue, strengthens tooth enamel. Freshly squeezed juice is rubbed into the gums, or a washed leaf, freed from the outer skin, is simply chewed.
- Salt with honey. Healing tandem - salt softens inflamed tissues and helps remove purulent exudate, and honey disinfects, nourishes, and soothes. A mixture of honey and salt is prepared in a 2:1 ratio.
- Garlic tincture. It removes pus well and is a powerful antiseptic, but to avoid burns it should not be used for more than 3 days. The infusion is prepared from 4 heads of garlic, 5 lemons and 700 grams of vodka. The crushed ingredients are infused in alcohol for 3 days. Then rinse the mouth with the solution every 4 hours.
Important! Traditional methods are auxiliary methods of combating the disease, not a panacea, and will not replace drug treatment prescribed by a dentist.