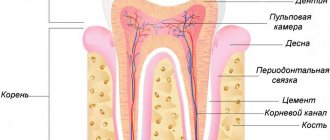
Pediatric dentistry can be considered a separate section of modern dental practice, because due to the structural features, the treatment of baby teeth is somewhat different from the treatment of permanent teeth. Unfortunately, many parents are still convinced that baby teeth do not need dental care - after all, they will soon break down and fall out anyway. Therefore, children are not taken to the dentist very often, and if they are taken to the doctor, it is with advanced diseases and multiple problems.
In fact, dental treatment should be carried out at any age, and the sooner you consult a doctor with a problem, the higher the likelihood of getting rid of it quickly and without any complications. If a child has bad baby teeth, this will inevitably affect the health of his permanent ones - this is what parents need to remember when they want to “pity” the baby and not take him to an appointment with the “evil dentist.”
Gum inflammation
The most common inflammatory gum diseases in children are stomatitis and gingivitis. Stomatitis, or, as it is usually called, thrush, is an infectious inflammatory process provoked by fungi of the genus Candida. Treatment is antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy, always carried out under the supervision and recommendations of a dentist. Self-medication can be dangerous, as some children may have allergic reactions to certain medications or antiseptics.
Gingivitis most often occurs due to plaque on baby teeth and insufficient general hygiene, but the reasons for their development can also be trauma to the gums during teething or other injuries, untreated caries. With this problem, you also need to contact a doctor, who will select the optimal treatment regimen and prevent gingivitis from developing into childhood periodontitis.
Light fillings for a child
Modern photopolymer materials used in the Natadent clinic can make dental treatment a quick and comfortable procedure, even for children. There is no need to doubt whether light fillings can be given to a child. The materials we use are absolutely harmless and do not affect children's health.
The main advantages of light fillings:
- Affordable price. Photopolymer fillings, despite all the advantages, are relatively inexpensive.
- Long service life. Contrary to popular misconceptions, light-curing fillings are strong and durable.
- Fast curing. Under the influence of special radiation, the material hardens in just a minute. Thanks to this, it is possible to place several fillings in one visit.
- Minimal tooth preparation. The viscous consistency of the polymer material allows it to reliably attach to chipped enamel and other surfaces after minimal processing.
- Completely harmless. High-quality photopolymer material is completely safe for children.
The use of light-curing materials greatly simplifies filling teeth for children, since it is difficult for a child to sit in one place for a long time (especially in a dental chair). The light filling is installed and hardens in minutes, allowing you to fill multiple teeth in one visit.
Caries, pulpitis and periodontitis of primary teeth in children
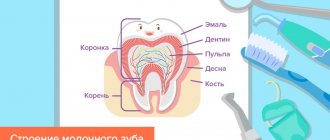
Milk teeth have thinner enamel and dentin layers than permanent teeth, they have a larger pulp chamber and, therefore, infection spreads faster to the pulp. They are more often susceptible to carious lesions - and not least because of night feeding or the habit of drinking drinks from a bottle at night (mostly sweet or sweetened - tea, juices).
In addition, caries is often provoked by plaque on baby teeth, which forms faster than in adults, and which not all parents are in a hurry to remove. Many people begin brushing their children’s teeth at a more or less conscious age, while a child should be taught hygiene and regularly remove plaque from the moment the first teeth erupt, that is, from about six months of age. Also, the cause of diseases of the dental system can be an insufficient amount of solid food in the baby’s diet, since chewing solid food helps to clean the dental surfaces themselves.
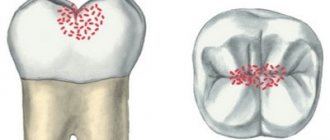
The child's nutritional habits, lack of hygiene, and too thin enamel layer provoke a phenomenon called circular caries of baby teeth - carious lesions spread over the entire tooth surface, as if encircling the crown.
Caries quickly turns into pulpitis - an inflammatory lesion of the dental pulp. Most often, a doctor is consulted precisely at this stage of the infectious process, ignoring the initial stages of damage to dental tissues. Pulpitis, in turn, provokes periodontitis of primary teeth in children - inflammation of the periodontal tissues near the tips of the tooth roots. This condition is usually accompanied by severe pain, severe swelling of the affected area, and often an increase in body temperature.
Treatment of baby teeth
At the initial stages, caries is treated without tissue preparation - remineralization of the enamel, as well as modern Icon technology, which allows filling without drilling, easily cope with carious lesions of the enamel layer. In later stages, when the dentinal layer is affected, as well as in the case of pulpitis and periodontitis, treatment of baby teeth with tissue preparation will be required. You should not be afraid of such procedures - modern methods of anesthesia allow them to be carried out completely painlessly and comfortably for a small patient. In addition, the anesthetics used are harmless, with a minimum concentration of the active substance. And the site of the upcoming injection itself is numbed by applying a special gel or spray (application anesthesia).
Experienced dentists try to carry out treatment quickly so that the child does not have time to get tired and capricious. If a child has bad baby teeth and a large amount of work is required, it is divided into several stages. It also happens that the child does not want to contact the doctor, is too afraid of treatment, or the volume of manipulation is too large and serious - in such a situation, it is possible to carry out therapy under anesthesia or with intravenous sedation (with a preliminary examination).
In case of pulpitis, the root canals are filled with special pastes that dissolve simultaneously with the “milky” root, so there is no chance that the medicinal material will remain in the tooth socket and will prevent the new tooth from growing properly.
Stages of filling
Diagnostics
The doctor conducts an examination and X-ray examination (sight or panoramic image) to assess the depth of enamel destruction. If inflammation spreads to surrounding tissues, treatment with the installation of a temporary filling will be required.
Preparation
The dentist cleans the teeth from soft deposits. Using a medical retractor and rubber dam, isolates the unit from saliva. Gives anesthesia. When working with children, the site of injection of the anesthetic is first numbed (a spray is sprayed or a gel is applied). Next, the doctor cleans the carious cavity (manually, chemically or using a drill) and removes all affected tissue of the dentinal layer. If necessary, remove the pulp and apply medicine for several days. Then he cleans the channels.
Sealing
The doctor checks the quality of canal filling. Then he places the filling material into the cleaned cavity, distributes it evenly and carefully seals the fissures. To make the material hard, a beam of light from a special lamp is directed at it. Removes excess composite and polishes the surface of the unit.
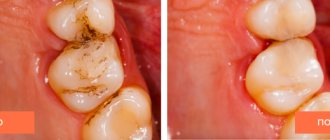
Restoration of baby teeth
If a child’s baby tooth breaks off or if the dental crown is severely damaged by caries, restoration is carried out. However, if for adult patients one of the most important aspects during restoration is aesthetics, then for children functionality is much more important. Therefore, restorative filling materials are always selected taking into account the patient’s age - for children, durability and impeccable aesthetics are not so important, a good marginal fit of the fillings and the preservation of dental tissues are much more important. Filling materials that are too strong can put pressure on dental tissues and contribute to their destruction, and therefore dentists choose materials that will recreate and maintain the integrity of the dental crown until the moment of natural tooth loss.
What components (materials) are used
The material for the filling is selected depending on how badly the tooth is damaged and where the defect is located. The doctor individually selects the best solution for each specific patient.
For permanent fillings in dentistry the following are used:
- Amalgams . Today, the use of various amalgams (alloys of metals with mercury) is minimized, since the use of this material for filling teeth requires a lot of time and high professionalism of dentists. In addition, the aesthetic properties of amalgams leave much to be desired - a polished filling is noticeable in the mouth. Such fillings are usually placed on chewing teeth. Among the advantages, amalgams last up to several decades; they can be installed in a moist tooth cavity.
- Cement based fillings . There are mineral (phosphate-based) and polymer (glass ionomer) cements. Such fillings have low adhesion properties and last no more than two years. The main advantage is low cost.
- Chemically cured composites . These materials are an excellent replacement for cement fillings. They usually contain porcelain. Composites are divided into:
- Acrylic-containing composites. A durable and reliable material, the downside is its high porosity, which over time leads to inflammation of the nerve and increases the possibility of developing recurrent caries.
- Composites based on epoxy resins. This material is more resistant to abrasion, but has insufficient strength characteristics and over time the material darkens noticeably.
- Light-curing composites. The material consists of filler and polymer, which hardens under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The fillings are highly durable and have good aesthetic characteristics (the doctor can choose a shade to match the natural color of the teeth). Disadvantages include poor adherence to the edge and shrinkage of the material - fillings made from light-curing composites last 7–8 years.
Removal of baby teeth in children
Removal of baby teeth in children is carried out only for specific indications or in the case when the tooth is ready to fall out on its own and just needs a little “help”. If there is a choice - to remove or treat, a competent dentist will always advise treatment, since the early loss of baby teeth leads to a number of serious disorders of the dental system, including the appearance of permanent bite defects.
Extraction operations should be carried out exclusively in the dentist’s office - attempts to remove teeth at home can lead to injury to soft tissues, infection of the socket, injury to the rudiment of a permanent dental unit, etc. The doctor will perform the extraction under local anesthesia quickly, competently and completely painlessly.
What types of fillings are there (temporary, permanent)
Depending on the purpose, fillings can be temporary or permanent. Temporary fillings are used for diagnosis and treatment. For example, a dentist will place a temporary filling to ensure that the nerve is affected. If after a certain time the patient experiences pain, the nerve must be removed. The doctor also applies a temporary filling if it is necessary to hide any medicine for a certain period. After this period, the doctor himself, without much effort, removes the temporary filling in order to replace it with a permanent one.
Permanent fillings should restore the anatomical shape of the tooth, its functionality and serve for many years.
What to do if baby teeth grow crookedly?
If parents notice that their child’s baby teeth are growing crookedly - for example, there is crowding or improper occlusion - this is a reason for a mandatory consultation with a pediatric orthodontist. It happens that due to anomalies of the facial skeleton (in particular, improper development of the jaws), defects are noticeable even with a primary bite, and with a permanent bite they will persist and worsen.
Therefore, it is recommended to show the child to an orthodontist from the age of three to determine whether there is pathology and find methods for its correction. There are malocclusions that are easily corrected at an early age and extremely difficult to correct in adults.
How fillings are done in Shifa dentistry
Dental treatment is possible only with the child’s consent, willingness to open his mouth and permission to put a filling. In case of a high level of anxiety, psychological preparation for treatment is indicated; it consists of preparatory teeth cleaning and demonstration of the stages of treatment on a model of artificial teeth. Give the pediatric dentist the opportunity to provide your child with details about the upcoming procedure at the first visit. Having experience communicating with children of different ages, the doctor can predict the child’s reaction.
For young children (up to 3 years old), as well as in the case of a child’s categorical refusal of treatment, sedation may be used.
The installation of children's fillings takes place in the following sequence:
- topical anesthesia - treatment of the gums with painkillers to reduce sensitivity at the site of the upcoming injection;
- local anesthesia - injection into the gums in the area of the upcoming treatment;
- cleaning the affected tooth structures using a bur under the control of a caries detector;
- direct filling;
- grinding and polishing the filling surface.
The installation of fillings in our clinic complies with international standards of pediatric dentistry.
How to protect baby teeth from caries?
Prevention is the best way to cope with any disease. Therefore, those parents who care about the health of their children should definitely think about caries prevention. How to protect baby teeth from caries? The recommendations of experts in this matter are as follows:
- The correct diet for the mother during pregnancy is with a sufficient amount of foods containing calcium, fluorine and phosphorus: cottage cheese, beef and beef liver, sea fish, nuts, fruits and vegetables, cereal porridges.
- Compliance with hygiene standards: daily brushing from the moment the first teeth appear, first with a cotton or gauze swab with boiled water, then with special baby brushes and pastes. Plaque on baby teeth should be removed promptly and thoroughly.
- A healthy diet for a child: as little fast carbohydrates, carbonated drinks, sweets as possible, more fruits and vegetables, cereals, and dairy products.
- Timely visits to the dentist for preventive examinations (at least once every six months).
It is important that parents develop a conscious attitude towards the health of their children's teeth and oral cavity in general. A timely visit to the dentist in case of any identified problems, as well as for regular medical examinations, will help maintain the health of the child’s dental system – and therefore the digestive system too.