When we are seriously faced with the issue of restoring missing teeth, we have to solve several issues at once:
- choice of prosthetic technique;
- selection of material for the prosthesis.
The range of materials for dental prosthetics is now wide, which is better? Metal, plastic or ceramics, or maybe a combination of them? In this article we will try to highlight all the features of metal-ceramic prostheses, as well as the pros and cons of the increasingly popular prostheses made of metal-free ceramics.
What is cermet?
When we say “metal-ceramics,” we most often mean crowns and bridges on a metal frame coated with ceramic. Otherwise, it is an orthopedic base made of metal, repeating the shape of a tooth ground for a crown, which is covered on top with a layer of thin ceramics. Ceramic metal is less likely than other materials to cause allergies. Metal-ceramics are used mainly for dental prosthetics in the chewing region, where preference is given not so much to aesthetic qualities as to reliability and functionality.
Which crown is better for a chewing tooth?
On the one hand, the answer to the question of which crowns are best to place on chewing teeth is obvious. Molars are tireless workers who bear almost the entire chewing load, so they need to be restored with very strong and reliable crowns. The issue of functionality really comes first, but you shouldn’t focus only on it. Despite the fact that molars are not so noticeable when smiling, it is simply criminal not to worry about aesthetics in this day and age. In addition, the choice of crown is also important from the point of view of the compatibility of its material with soft tissues.
Source
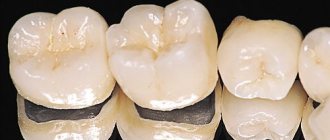
Prosthetics with metal-ceramics.
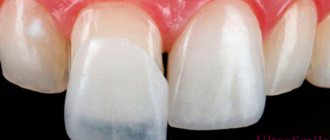
As already noted, metal-ceramics have found their application more in the prosthetics of chewing teeth, where the main thing is strength, not appearance. However, this does not mean that metal ceramics are completely devoid of aesthetics, not at all. The widest range of ceramic coatings allows metal-ceramic crowns to perfectly imitate the shade and structure of natural tooth tissue.
The problem may arise when prosthetics are placed on the front teeth. It is as follows: a dark metal frame can show through a layer of ceramics, that is, the metal simply shines through the translucent coating. Therefore, when replacing anterior teeth, it is most often recommended to use metal-free ceramics or ceramics based on zirconium (zirconium dioxide) - this is, in fact, the same metal ceramics, but the frame material is white metal - zirconium, by the way, is absolutely biocompatible with the human body .
Metal-plastic
Like metal-ceramics, metal-plastic prostheses consist of a metal frame and coating. The only difference is in the material from which the top layer is made. For this purpose, high-strength dental plastic is used, which is characterized by non-toxicity, a strong connection with the metal, and the ability to well imitate the surface of the tooth.
Plastic crowns
Such prostheses are installed in the following situations:
- as temporary structures designed to replace missing teeth while metal-ceramic dentures are being manufactured;
- as an external coating for implants with a metal base;
- when combining several types of prosthetics to restore the dentition;
- for prosthetics of individual front or chewing teeth.
Metal-plastic cast crowns
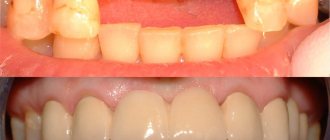
Metal-ceramic prostheses.
What is a metal-ceramic prosthesis upon closer examination? First of all, it is a metal frame covered with a layer of hypoallergenic ceramics. If we compare modern metal-ceramic prostheses with their predecessors made of various composites, we will see the undoubted advantages of metal-ceramics:
- firstly, metal-ceramics reproduces the color and texture of natural tooth tissues quite well;
- secondly, it does not fade, does not absorb dyes and, therefore, does not change color over time;
- thirdly, dental ceramics used in dentures are hypoallergenic and do not cause rejection, except in rare cases;
- and finally, cermets are very durable.
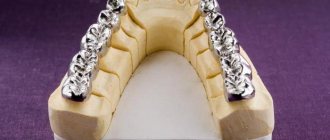
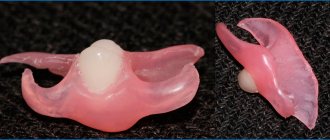
If we are talking about removable dentures made of metal ceramics, then we are talking about a clasp denture. “Bugel” (clasp) means “arc”, and the prosthesis itself is precisely a metal arch with metal-ceramic crowns attached to it. Removable metal-ceramic structures are used when there are contraindications to installing a permanent metal-ceramic prosthesis.
Types of dental crowns: which ones are better?
Dental clinics use many crowns for different clinical cases. How do they differ from each other and how important are these differences for the patient? How to choose a prosthesis with optimal aesthetics and functionality among such a variety?