The level of effectiveness of a patient's dental treatment in dentistry largely depends on whether the treatment is painless. After all, the problem of pain in patients is important and quite relevant. People, by postponing a visit to their dentist, trigger the disease because they are afraid of the pain of dental treatment.
However, there are different methods of dental anesthesia, which can completely eliminate all pain through high-quality anesthesia. Effective local anesthetics in dentistry are an excellent solution to completely eliminate pain when treating the oral cavity or teeth, because they allow you to maintain a connection between the patient and the doctor. The anesthetic dulls the receptors, which leads to blocking pain during dental or oral treatment.
Types of anesthesia used in dental practice
When treating the oral cavity and teeth, anesthesia is used - general or local.
Anesthesia (general anesthesia) is used quite rarely. With this anesthesia, the patient is unconscious while the treatment is underway and does not feel anything. Anesthesia (general anesthesia) is used only for major operations or when treating children. This type has too many contraindications and all sorts of complications, so dentists almost always prefer local anesthesia. This is the best option for dental intervention.
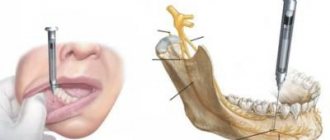
Local anesthesia - pain relief by freezing or injection into the gum. In this form, the anesthetic temporarily disables the sensitivity of pain in the area specified for treatment. Tactile sensations are preserved during local anesthesia. The patient feels touch or pressure on the tooth or gum, but the patient has no pain. To numb the patient's upper tooth, a local anesthetic is injected into the gum near the painful tooth. This is infiltration anesthesia. Lower teeth - by injecting the patient with a local anesthetic near the mandibular nerve. This will be a conduction anesthesia. It will lead to numbness of the tongue and lower jaw. In dental practice, there is also topical anesthesia, which will make treatment of a certain area of the oral mucosa painless by applying a special gel or spray to it. This anesthesia will be appropriate before infiltration anesthesia, so that the needle prick is imperceptible to the patient.
Why do they give the injection?
Even a small intervention requires maximum calm and relaxation from the patient, so care must be taken in advance to ensure that no pain occurs during the specialist’s work. Simple and complex removal of teeth, pulp, cleaning and filling of canals, as well as treatment of caries of varying degrees of complexity can cause discomfort, especially with increased tissue sensitivity.
It is important to note that another purpose of the injection is to introduce antibiotics and certain anti-inflammatory drugs into the gums. This is especially common during the treatment of diseases such as gingivitis and periodontal disease.
Most often, dentists perform local anesthesia, this allows them to achieve a targeted and quick effect. When medications are administered intramuscularly, the body reacts after a longer period of time, so the dentist’s appointment may be delayed. Anesthesia has contraindications: age under 3 years, period of pregnancy, allergies, presence of serious diseases or oncology.
Components of anesthetics
The anesthetic contains local anesthetics, preservatives, vasoconstrictors and stabilizers. The drug used for local anesthesia for pain relief may not contain all of the listed components. To effectively block impulses from nerve endings, one anesthetic is used, and to prolong the period of action and enhance the analgesic effect, vasoconstrictors (adrenaline) are needed. It is used to create and maintain a sufficient concentration of the drug in the treatment area. Preservatives and stabilizers are used in practice to increase the shelf life of anesthesia.
Anesthesia after tooth extraction
After the tooth has been removed and the anesthesia has begun to wear off, pain may occur. Sometimes the pain symptoms are very strong and unbearable to endure. In this case, they resort to repeated anesthesia. The most common pain reliever offered by dentists is Ketanov.
Ketanov is able to relieve a person from severe and sharp pain.
It is often prescribed after surgery. The drug can be used every six hours, but not more than one week.
Like any medicine, Ketanov has side effects. These include:
- drowsiness;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- the appearance of dry mouth;
- accelerated heartbeat.
The drug should not be taken by people who have:
- bronchial asthma;
- ulcer of the duodenum and stomach;
- kidney diseases.
It is also undesirable for women to use during lactation and pregnancy.
If after three days pain or swelling occurs again, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Basic requirements for modern anesthetics
An anesthetic is a unique substance that suppresses the excitability of the receptor, turns off the impulse to the patient’s nerve fibers, after which pain relief occurs.
The anesthetic has basic requirements:
- do not cause dilation of the patient’s blood vessels;
- do not provoke tissue irritation;
- high resistance to sterilization of the drug;
- slow absorption into the blood;
- greater strength and duration of analgesic effect;
- have low toxicity to the patient;
- good analgesic effect during dental treatment.
The local anesthetic has a direct inhibitory effect on the receptor and the permeability of the sodium channels in the patient begins to decrease, while the entry of sodium into the human cell is completely disrupted, after which an action potential is generated and this all leads to a lack of sensitivity and analgesia during treatment. Sensitivity is switched off one by one: at the beginning pain, then taste, then temperature and finally tactile. This is how the process of pain relief occurs.
To prolong the effect of painless treatment, a vasoconstrictor (for example, adrenaline) must be added to the local anesthetic. However, in patients with heart disease, it poses a greater risk of heart attack. A vasoconstrictor can cause the patient to relax the muscles of the bronchi and intestines, dilate the pupils, significantly increase blood sugar, increase tissue metabolism and cause many adverse reactions. But if you exclude adrenaline from the local anesthetic drug, this will lead to ineffectiveness and the patient will not experience pain relief.
The decision to use this substance in treatment should be made by an experienced dentist, as a last resort. After all, after adding adrenaline to the local anesthetic, the effectiveness of anesthesia itself during dental treatment increases significantly and its toxicity for the patient decreases. This occurs due to the very slow absorption of the painkiller into the blood. And sometimes toxic complications that appear during local anesthesia are mistakenly attributed to a side effect of the substance adrenaline.
How to treat caries with an injection step by step?
At other stages of caries, teeth are treated approximately according to the same scheme, which includes several stages:
- Cleaning teeth.
The doctor removes tartar and plaque from the surface of the tooth being treated.
- Selecting the shade of the filling.
The dentist selects the material for filling, focusing on the natural color of the enamel of the damaged tooth. To do this, he uses the so-called Vita scale - a plastic strip with samples of different shades.
- Anesthesia.
Anesthesia injections help make the procedure painless and reduce discomfort during the treatment of caries. The type of drug and dose are selected taking into account the age and individual characteristics of the patient. The anesthesia usually lasts from 40 minutes to several hours. Sometimes the gums hurt a little after the injection, but this does not compare with the pain when treating deep caries without anesthesia.
- Isolation of the tooth before treatment.
It is performed by placing a small plate - a rubber dam - on a row of teeth. As a result, one or more necessary teeth are completely isolated from the others. This allows the dentist to do a better job and prevent blood and saliva from getting on the cleaned surface, which guarantees its reliable connection to the filling in the future.
- Preparation of a carious cavity.
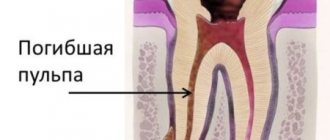
Cleansing the tooth of all tissues that have been damaged by caries and parts of the tooth enamel above the carious cavity. If you leave the caries at least partially and install a filling, after a couple of months the problem may recur. And in the future complications may develop - pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Formation of a carious cavity.
The doctor creates the best conditions for installing the filling by forming special support points. It makes indentations, notches, irregularities in the cavity, and smoothes the edges of the enamel. This is required for the filling to fit tightly to the walls of the tooth.
- Washing the cavity.
After the above procedures, the carious cavity is washed and sprayed with a stream of air to remove dentin sawdust.
- Medical treatment of carious cavity.
It is produced using antiseptic solutions to prevent the new development of caries. Then the doctor dries the cavity well so that drops of moisture do not interfere with the close contact of the filling with the tooth tissues.
- Acid etching.
It is performed so that the adhesive, which is applied after etching for a stronger fixation of the filling material, can penetrate deeper into the dental tissue. To do this, use a special gel with phosphoric acid. After etching, the gel is washed off well and the tooth is dried.
- Application of adhesive.
It is applied to the tooth to firmly fix the light-curing filling material; after absorption, it is illuminated using a special lamp.
- Application of a therapeutic and insulating pad.
This step can be performed either before or after acid etching. Spacers are an intermediate layer between the dentin or pulp and the filling material. Therapeutic pads protect the tooth from external adverse influences and help stop inflammation; they are most often used to treat deep caries. Isolating gaskets protect the pulp, the soft connective tissue of the tooth, from the negative effects of filling materials.
- Placing a filling.
The doctor takes turns, layer by layer, applying filling materials and drying each of them with a dental lamp.
- Grinding, polishing.
The restored tooth with filling is ground and polished to perfect smoothness and evenness. This gives it a natural shine and eliminates the smallest imperfections and gaps that cause inconvenience. At this stage, caries treatment ends. Thus, anesthesia with an injection is given at the very beginning of dental treatment, and all other stages are absolutely painless for the patient.
Classification of anesthetics in dentistry
Before dental treatment, the doctor should choose an effective local anesthetic agent individually for each person. The appropriate anesthetic is selected depending on the procedure itself, the duration of the procedure, and the patient's tolerance to the anesthetic drug.
Chemical properties divide the local anesthetic into groups such as substituted amides (articaine, lidocaine, trimecaine) and esters (novocaine, anesthesin, dicaine). These two groups have differences in biotransformation, and most importantly, in side effects for the patient.
Classification according to the method of administration divides local anesthetics in dentistry into those that are used for surface anesthesia and those that are used for conduction and infiltration anesthesia. Based on the duration of its action, anesthetics are classified into short, medium and long-acting.
Anesthesia methods
Anesthesia can be local or general. The local form is divided into external and injection methods.
The external method allows you to anesthetize superficial tissues using medicinal substances. These can be special ointments, gels, devices with electromagnetic waves, simply applications. The last method is used most often. The application is a cooling plate. It is applied to the gums, and the patient does not feel pain. This method is usually used to remove baby teeth in children.
The injection method involves injecting an anesthetic substance through a needle.
There are 4 types of anesthesia:
- Conductor. The method allows you to anesthetize several teeth at once. An anesthetic is injected into the area of the last tooth where the branch of the nerve is affected, resulting in blockage of the entire nerve.
- Infiltration. An anesthetic substance is injected into the projection area of the apex of the tooth root.
- Intraligamentous. The medicine is administered through the gum. As a result, the tooth and the surrounding gum area are numbed. For this method, a special syringe with a dispenser is used. It allows you to administer a minimum of anesthetic substance.
- Intraosseous. It is the best anesthesia. In this case, the injection is made directly into the spongy bone. It is she who covers the dental alveoli.
General anesthesia (anesthesia) is done very rarely.
It should not be used for people who have heart problems. This method of anesthesia is used only in the most difficult cases. Dentistry must be equipped with a special office and all the necessary equipment. And also during surgical operations, the presence of an anesthesiologist next to the patient is mandatory.
Only the doctor decides which anesthesia is best for tooth extraction. Everything will depend on the complexity of the procedures and the general condition of the tooth.
Local anesthetic preparations for dental treatment
For high-quality pain relief, the dental clinic uses the latest generation local anesthetic. To administer the drug with a local anesthetic, take carpules and carpule syringes, which already contain the solution itself. The quality of dental treatment for patients using such syringes is much higher than with a simple disposable syringe. After all, the needle is much thinner than simple disposable syringes and the injection is not so painful.
Carpule anesthetics in dentistry are good because they have the following advantages:
- Complete sterility, 100% guarantee against excess substances entering the local anesthetic.
- Exact dosage of the required components. The syringe contains a ready-made anesthetic drug.
- There is no pain from the injection, since the needle is thinner than that of a disposable simple syringe.
The previously used novocaine or lidocaine has long faded into the background, as they have low effectiveness and allergic manifestations. Today they are practically not used, mainly as anesthesia in public clinics.
In advanced dental clinics, effective drugs based on articaine or mepivacaine are used to provide good anesthesia.
Articaine is an effective anesthetic that is used for high-quality local anesthesia (for example, Ultracaine). It consists of articaine and adrenaline. Mepivacaine has a great ability to constrict blood vessels, but it also has a slightly less effect from local anesthesia. The drug is used for dental treatment in young children, pregnant women, as well as patients who have hypertension and those for whom adrenaline is completely contraindicated. In such cases, a drug that contains mepivacaine (for example, Scandonest) is used to treat the patient’s oral cavity.
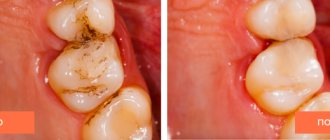
Is caries treatment painful?
Many people are convinced that caries is painful to treat, and therefore are afraid to go to the dentist. The problem goes back to the recent past, when anesthetics were not used in dentistry. Just a few decades ago, no one could even imagine that it was possible to treat teeth with anesthesia, and all manipulations were performed “live.”
In this article
- Is caries treatment painful?
- Is it painful to treat dental caries with anesthesia?
- Is anesthesia always necessary?
- How to treat caries with an injection step by step?
- Is it painful to treat caries on the front teeth?
- What anesthesia is used in the treatment of caries?
- Who is contraindicated for anesthesia?
- Conclusion
Of course, with this approach it was very painful to treat deep caries and other stages of this disease that affected the sensitive parts of the tooth. Fortunately, dental treatment methods have changed, modern safe anesthetics have appeared, and it has become easier to treat with an injection.
Criteria for choosing a high-quality local anesthetic
The main criterion for choosing an effective local anesthesia will be the nature of the upcoming dental intervention. The doctor selects the drug taking into account the required depth of treatment, the duration of local anesthesia according to the nature and scope of the upcoming intervention. The choice of anesthetic is influenced by pregnancy, great fear of the upcoming manipulation, and possible pathology in the patient. Take into account the presence of contraindications during treatment. There are age restrictions for the use of anesthetics. The dosage of anesthesia for dental treatment of the teeth of young children or elderly patients is always specified.
Medicines you shouldn't take
Many people use homemade medications for pain relief. But they have low efficiency and can provoke undesirable results:
- Aspirin. The medicine is intended to perform an antipyretic function. The analgesic effect is minimal. Aspirin is a good blood thinner. This may lead to delayed bleeding. Although this medicine is included in many painkillers.
- Paracetamol. The drug can only cope with mild headaches. It has no anti-inflammatory effect and has a negative effect on the liver. Included in painkillers as an adjuvant.
- No-shpa. Many people think that this medicine is a pain reliever. But that's not true. No-spa is an antispasmodic drug that only eliminates pain associated with spasms. The pain after tooth extraction is completely different and no-spa will not be able to cope with it.
Contraindications for the use of local anesthetic
To ensure that the local anesthetic is safe for the patient, contraindications for use should be taken into account. They can be grouped:
- Allergic manifestations in a patient to an anesthetic. It is a complete contraindication to the use of such a remedy to anesthetize the patient’s teeth. It is imperative to warn your dentist about the presence of allergic manifestations or a possible reaction to previous treatment of the oral cavity and teeth.
- There is a deficiency of metabolic systems. Many painkillers have a strong toxic effect in case of overdose of local anesthesia, insufficient metabolism and excretion. In this situation, it is better to use the drug in small doses.
- Age. For small children, the local anesthetic is taken in a lower dose than for anesthetizing the teeth of adult patients. To achieve effective dental pain relief, it is necessary to use a safe local anesthetic drug, limiting the dosage.
In modern dental practice, there is a wide selection of over-the-counter products that contain an anesthetic and will make dental treatment painless. After all, it is the main reason for the strong fear of patients in dental clinics.
Modern clinics offer painless treatment of the oral cavity or teeth using a local anesthetic. There is no need to be afraid of going to the doctor, put off this visit and make the disease worse, because today you can cure, remove a tooth or install an implant without pain. You need to decide on a dental clinic and choose a good doctor. He will be able to qualitatively cure the tooth by selecting an effective local anesthetic to numb the mouth or teeth. This is the key to painless treatment of the patient’s teeth and oral cavity.
Is it painful to treat caries on the front teeth?
Due to their location and structural features, caries on the front teeth is more difficult to treat. If the damage is severe, it is not always possible to put a filling, and then you will have to resort to prosthetics.
There are other features:
- The front teeth, compared to molars and premolars, have thinner and more sensitive enamel. It is easily destroyed, opening access to sensitive dentin, so the central incisors are more sensitive to pain.
- The front teeth, which are used for gripping and cutting food, are subject to high stress and wear out more quickly.
- A large cavity is often hidden under a small chalk point. And often caries is detected already at the stage when it is difficult to cure without pain. Therefore, in most cases, anesthesia is used in the treatment of caries of central incisors.
- Increased aesthetic demands are placed on the front teeth, so the filling must be placed not only reliably, but also beautifully.
That is why the condition of the front incisors - teeth with a small chewing surface area - must be monitored especially carefully.
If caries affects the front teeth, due to the thin enamel and dentin, it very quickly passes into the middle and deep stage, affecting the sensitive pulp. If you do not know whether it is painful to treat deep caries of the front teeth and doubt whether you need anesthesia, we recommend that you definitely agree to an anesthetic injection. Of course, in the absence of contraindications to the anesthetic. Because treating caries on the front teeth is painful.
Anesthesia doesn't work
There are cases when the anesthesia does not work and the person feels pain. There are several factors why this happens:
- Alcohol. The chemical composition of ethyl alcohol can block the effects of the anesthetic. Therefore, it is not recommended to go to the dentist if you have recently consumed strong drinks.
- Using large amounts of painkillers. If a person is taking medications that contain painkillers, they should not be taken before seeing a doctor.
- A person may have individual immunity to certain anesthetics. This factor is very rare.
If the anesthesia does not work, then it is worth understanding the reason. Having received the result, the treatment is postponed to another day.
Indications and contraindications for anesthesia during dental treatment
Pain relief is indicated in the following cases:
- Low pain threshold and pain intolerance;
- Severe psychological discomfort, anxiety, fear during treatment;
- Serious surgical interventions, tooth extraction, treatment of deep caries, removal of plaque and tartar, dental implantation.
Local anesthesia has almost no contraindications, mainly due to individual intolerance to the components of the anesthetic;
Anesthesia is excluded in the following cases:
- Pregnancy (due to the negative effects of medications on the fetus);
- Allergic reactions to anesthesia components;
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- Mental disorders, epilepsy;
- Early childhood;
- Recent stroke, heart attack or traumatic brain injury;
- Acute viral disease.