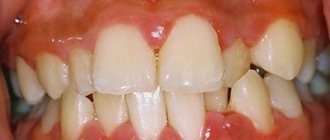
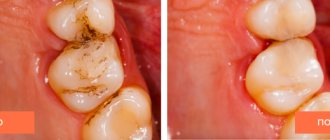
Inflammation of the nerve of the tooth is characterized by:
- Pain from temperature stimuli;
- Very severe pain that radiates to the ear, temple or larynx;
- Night pain.
In the first stages, pain appears rarely and quickly subside, but as pulpitis develops, pain appears more often and more severely. The pain becomes more severe and throbbing when pulpitis becomes purulent.
When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor, because pulpitis is dangerous due to its complications. Treatment of pulpitis consists of removing the dental pulp (nerve) under anesthesia or using arsenic paste, mechanical and medicinal treatment of the canals, filling them and placing a filling, if necessary, using pins.
To perform high-quality work in root canals, qualified doctors at our center use modern treatment methods. The work is carried out with “four hands” (doctor-assistant), which improves the quality of the doctor’s work and the patient’s comfort.
Treatment of tooth pulpitis from 6,500 rubles.
Gum diseases
Pulpitis
Pulpitis is an inflammatory disease of the soft tissues of the tooth, of an infectious nature, which is the most common consequence of untimely or poor-quality treatment of carious lesions, characterized by acute pain and a sharp reaction to temperature stimuli.
Pulpitis is not so much an independent disease as a consequence of improper treatment of dental diseases or lack of treatment as such. The mechanism of development of the disease is simple: in the presence of carious lesions left unattended, the destruction of hard tooth tissues can reach the root pulp, as a result of which microorganisms and their metabolic products begin to penetrate into the vascular bundle located in the center of the tooth. The ingress of pathogenic agents is accompanied by a response accompanied by acute pain, a sharp, time-long reaction to cold or hot - this is inflammation. In addition to caries, pulpitis can be caused by tooth trauma - loss of part of the tooth or crown, fracture, crack.
Symptoms of pulpitis are varied and depend on the form of the disease. There are acute and chronic forms of the disease. Acute pulpitis is characterized by periodically occurring pain in the tooth, occurring suddenly and disappearing on its own. Most often, pain occurs in the evening and at night. At the initial stages of the development of the disease, pulpitis may not bother the patient much, but over time, attacks of pain become more frequent and intensified, the pain becomes pulsating in nature and is expressed with greater intensity. Sometimes the pain radiates to the jaw, ear, or nearby areas, which can cause a migraine or headache attack. Subsequently, the pain becomes unbearable, excruciating and cannot be relieved with painkillers.
Chronic pulpitis manifests itself somewhat differently. This disease in its chronic form makes itself felt with any thermal changes - painful sensations occur when the temperature changes, for example, when moving from a cold room to a warm one and vice versa, eating very cold or very hot. As the thermal factor is eliminated, the pain gradually subsides. Spontaneously occurring causeless pain is not typical for chronic pulpitis.
Treatment of pulpitis involves removing the pulp and installing a filling on the damaged tooth. If pulpitis is not treated, a number of complications and consequences may develop. The most common include: periodontitis, periostitis; osteomyelitis, etc.
What tools and equipment are used in our clinic?
First and most important
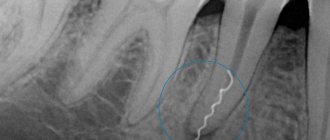
when treating tooth canals and treating pulpitis, this is an opportunity to quickly and effectively conduct an X-ray examination (radiovisiography). It is necessary for: making a correct diagnosis, determining the length and location of the canals, and monitoring the quality of their filling.
The advantage of a radiovisiograph is that the radiation exposure to the patient is 10–20 times less than when using a conventional X-ray machine.
Second
, the presence of an apex locator allows the doctor to know exactly in which part of the canal the instrument is located.
Third
, the presence of an endodontic motor allows you to work with advanced nickel-titanium instruments to expand and taper the canal. This allows you to efficiently clean and seal the canals.
Fourth
, the presence of optics allows the doctor to see the hidden mouths of the canals.
Fifth
, our clinic uses the latest advances in dentistry in canal treatment - three-dimensional obturation of root canals with hot thermoplasticized gutta-percha. During heating, gutta-percha becomes very plastic, due to which the tooth canal system is tightly sealed. This material is introduced on a special carrier made of a denser, modified gutta-percha - Gutta Core, preheated in a special oven. The tightness of the material virtually eliminates the risk of developing an infection in the tooth. Gutta-percha does not dissolve over time and does not irritate the tissue surrounding the tooth.
This method is very effective, it involves sealing and filling the entire system of lateral tubules, but it requires a highly qualified doctor and considerable financial and time costs.
What is pulpitis
Dental pulpitis is an inflammation of the dental pulp that occurs as a result of untreated cavities or trauma. The main symptom is unpleasant pain. The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical data and the results of radiological studies.
Depending on the damage to the pulp, the condition may be reversible or irreversible, and symptoms range from mild tooth sensitivity to tooth loss due to nerve death.
The following types of dental pulpitis are distinguished:
- Reversible is mild temporary inflammation of the nerve. Swelling is caused by changes in the pH of the tooth, eating excessively sour or sweet foods, or eating very cold or hot foods. Likewise, teeth whitening usually has some sensitivity in the tooth, which is temporary and only lasts for a month while the treatment is taking place. In these cases, when the patient experiences reversible pulpitis, the discomfort disappears as soon as the irritant that caused it disappears.
- Irreversible. In cases of more advanced pulpitis, discomfort persists for a certain period of time even after the irritant disappears. The reason is that the inflammation of the nerve is so severe that it is impossible to return it to its previous condition.
- Pulp necrosis (complete or partial). Occurs when pulp inflammation is not treated promptly or when the blood supply is cut off due to injury and can put the tooth at risk.
Pulpitis complicated by periodontitis usually occurs in children aged 6 to 9 years and indicates reduced immunity.
Reasons for the development of pulpitis
One of the most common causes of dental pulpitis is caries, but this is not the only factor that triggers the disease. Tooth decay and periodontal disease (such as pyorrhea) can damage tooth structure, leaving the dental pulp exposed, but there are other possible causes of pulpitis.
Due to this, factors such as tooth erosion, cracked or broken tooth due to injury, or even age and alcohol consumption may be associated with the occurrence of this condition.
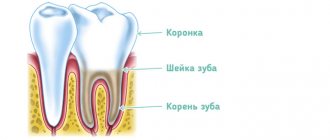
Periodontitis
Enamel
Dentine
Pulp
Periodontitis (inflammation at the root apex)
Periodontitis is a process of inflammation that occurs in the bone tissue in the area of the tooth root. Infection from a carious cavity penetrates into the root canal, and from there enters the tissues surrounding the tooth root, destroying them. Periodontitis can have serous and purulent forms. If periodontitis occurs without pain, then the bone around the root of the tooth is reabsorbed, a granuloma appears (a sac at the apex of the root), which over time can turn into a cyst.
Dental granuloma is an inflammation of the periodontium, which is a small round-shaped formation located in the area of the tooth root. This disease, like a dental cyst, is characterized by a long asymptomatic course. Granuloma is aggravated under the influence of certain factors, which, as a rule, do not differ from the factors that cause exacerbation of dental cysts.
During therapeutic treatment, canals require filling not only to preserve the tooth, but also to prevent infection of the body as a result of the decay of dead tissue.
Acute periodontitis is manifested by sharp and severe pain in the tooth area, aggravated by touching it. There may be swelling of the lips, cheeks, bad breath, and sometimes fistulas on the gums. The tooth becomes mobile.
Chronic periodontitis develops slowly and does not cause characteristic pain. In the chronic form of periodontitis, the symptoms are less pronounced, but swelling and redness of the gums and increased temperature may occur. In some cases, a fistulous tract forms on the gum.
Diagnostics
To diagnose periodontitis, it is enough for an experienced dentist to examine the patient’s oral cavity. The presence of fistulous openings, inflammation of the gums around the tooth and the presence of symptoms typical of periodontitis will help to recognize the disease. To differentiate pathology from pulpitis and periodontal disease, use:
- X-ray of the tooth - the images will show rarefaction of the periodontium, the presence of a purulent focus, granuloma or cystic neoplasm at the root apex;
- CT is a more informative method of radiation diagnostics, which allows you to obtain a three-dimensional detailed image of the tooth and its surrounding tissues, on which the boundaries of periodontal inflammation will be visible, and its sources will also be determined.
Treatment of periodontitis
In order to save a tooth with periodontitis, complex and lengthy professional treatment is necessary. In case of chronic periodontitis, the canal of the affected tooth is first treated: infected tissue is removed and the canal is disinfected. Then anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial medications are injected into the canal, and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed if necessary. To assess the success of treatment of such a tooth, a control radiovisiographic study is prescribed after 6 months. In very advanced forms of periodontitis, it is sometimes necessary to remove a tooth.
In case of acute periodontitis, the tooth is first left open for the outflow of inflammatory fluid and antibiotics are prescribed, and when the process subsides, treatment is continued according to the same scheme described above. Under X-ray control, root canals are filled using modern filling materials.
Depending on the degree of destruction, the tooth can be restored in different ways:
1. made of composite filling material directly in the mouth. With this type of tooth restoration, titanium or fiberglass pins are used to better fix the filling;
2. restore the missing part of the tooth using a post and a crown.
Treatment of periodontitis from 8,000 rubles.
Methods and stages of treatment
Treatment of periodontitis is divided into several stages. The first and most important is tooth depulpation - removal of necrotic tissue from the root canal, its mechanical treatment and expansion, treatment with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Important! If a tooth affected by periodontitis was previously filled, the doctor will have to remove the filling materials from the canal and re-process and prepare it.
In the future, conservative or surgical treatment of periodontitis is carried out.
Conservative therapy
To conservatively eliminate periodontitis, local agents are used, which the doctor places into the prepared root canal. Most often these are long-acting pastes with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect, “Kalosept” or “Metapex”. They are left in the canal for 2-3 weeks, and in case of extensive tooth damage, they are periodically renewed for 2-3 months. Additionally, antibiotics are prescribed, rinsing the mouth with antiseptic (chlorhexidine, Miramistin, etc.) or saline solutions, herbal decoctions, etc.
Important! During the treatment, photographs are taken that will show the dynamics. If the inflammation is stopped, treatment can be completed with a filling.
Surgery
Surgical methods of treating periodontitis are resorted to in the absence of positive dynamics, a large focus of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (more than 10 mm in diameter), and when it is impossible to depulpate and clean the root canals (previously installed gutta-percha, stump inlays, etc.).
Several methods of surgical treatment of periodontitis are used:
- resection of the apex of the tooth root - cutting off a third of the root with granuloma through an incision on the gum;
- hemisection - removal of the entire root with tissues surrounding the root;
- root amputation - removal of the root while preserving the crown;
- separation - removal of the root along with part of the crown;
- replantation is the removal of a tooth and its subsequent treatment outside the oral cavity, and its subsequent implantation in its original place.
These methods allow you to save a tooth for a certain period of time. If they are impossible due to the destruction of most of the crown, perforation of the roots, rapid spread of infection and necrosis of bone tissue, a radical tooth extraction is performed, followed by treating the hole with antiseptics, scraping out the granuloma and filling the cavity with agents that stimulate the formation of bone tissue.
Other
Treatment of dental cyst
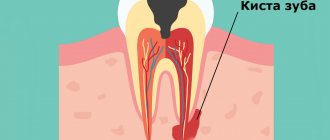
A dental cyst is the last stage in the development of chronic periodontitis. It is a cavity of various sizes, which is formed in the thickness of the jaw and is connected to the root of the tooth. This cavity is lined with a membrane and filled with liquid. When microbes enter, the contents of the cyst suppurate. Usually the cyst grows for a long time without any subjective sensations or clinical manifestations. The first symptom that attracts attention is the deformation of the jaw in the form of a protrusion at the site of the growing cyst.
Tooth cyst
If the cyst does not suppurate, then it can reach a significant size without causing any reaction from the general condition of the patient and without causing him pain.
Types of cysts according to their causes:
- Eruption cyst – most often occurs in children aged 7 – 10 years.
- Paradental (retromolar) cyst - appears when there is difficulty in the eruption of a wisdom tooth and its chronic inflammation.
- A follicular (tooth-containing) cyst is formed due to infection of a tooth germ or an unerupted or supernumerary tooth.
- Primary cyst - is formed when the development of a tooth is disrupted from the remains of dental tissue.
- Radicular cyst - a cyst that forms on the root of a tooth and usually develops due to chronic periodontitis
- A residual cyst appears in the bone after tooth extraction.
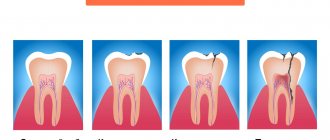
Types of carious process
Initial caries - carious spot
Visually, initial caries can be seen by the appearance of light spots of various shapes and sizes on the tooth enamel. At this stage there is no pain. Treatment of carious spots involves remineralization of the enamel using fluoride and calcium-containing preparations. caries is not treated , the spots will darken and a carious cavity will form.
Superficial caries
This is a lesion of the tooth tissue within the enamel. Superficial caries is characterized by significant losses of calcium in tooth tissues. With superficial caries, pain can appear when exposed to sweet, sour, salty foods. Treatment of superficial caries involves filling the cavity with a composite or compomer, a special polymer material.
Medium and Deep caries
This defect affects the tooth enamel and part of the dentin. Pain can occur from sweet, salty, cold and hot foods. Medium and deep caries require more serious and thorough caries treatment. The affected tissue is removed, the carious cavity is treated and disinfected, then the tooth crown is restored with filling material. At the final stage, the filling is polished.
Signs and symptoms of a dental cyst
Often the development of a cyst is completely asymptomatic or with barely noticeable symptoms: rare slight pain when biting on a tooth or mild pain when pressing on the gum. In this case, the cyst is detected completely by accident - on x-rays during the treatment of other teeth.
The main signs of a cyst begin to appear already at a late stage of development. Main symptoms of a cyst:
- Aching or nagging pain that only gets worse all the time. It is difficult to get rid of it with the help of simple analgesics and folk remedies. Initially, pain may occur when chewing on the causative tooth.
- The appearance of edema. When a cyst occurs, the gums around the diseased tooth become red and swollen.
- High temperature due to associated infection.
- Suppuration, flux and fistulous tract are external manifestations of an already formed cyst.
- X-rays and tomography are necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
Why is a dental cyst dangerous? Consequences of the disease
A cyst that is not detected in time grows, which leads to the destruction of bone tissue and its replacement with connective tissue formations. As a rule, at this stage complications appear that lead to tooth loss. Possible complications with a dental cyst:
- Purulent inflammation of the cyst.
- Melting of the jaw bone due to cyst growth.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- The appearance of chronic sinusitis due to the growth of a cyst into the maxillary sinus.
- The appearance of osteomyelitis or periostitis.
- Formation of an abscess on the gum or cheek.
- Formation of phlegmon of the neck due to prolonged purulent inflammation.
- The development of sepsis - blood poisoning.
- Spontaneous fracture of the jaw, which appears due to the growth of the cyst and thinning of the bone.
Therapeutic treatment of cysts
If the size of the cyst does not exceed 8 millimeters, drug treatment is necessary. The entire treatment process takes place in several stages:
Opening of the causative tooth, instrumental and thorough medicinal treatment of the canals. The tooth canals are filled with medicinal paste, which has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Periodically, the medicinal paste must be changed, so the tooth is opened again, and the cavity is filled with a new portion of medicinal paste. The number of repetitions depends on how successful the treatment is. The doctor monitors the condition of the cyst using x-rays.
- If the treatment is successful, as evidenced by a decrease in the size of the cyst, the dentist decides to permanently fill the canals and takes measures to restore the tooth.
- The process of further reduction of the cyst and regeneration of bone tissue is monitored for two years. To do this, it is necessary to take a photo every few months, since if the treatment is insufficiently effective, timely measures must be taken.
The only drawback of conservative therapy is its duration. During treatment, regular visits to the dentist are necessary, and further observation by the attending physician is necessary.
Advantages of contacting PROFI-Dent
The main objective of the PROFI-Dent clinic is to provide a full range of dental services at the highest level of quality.
Our advantages:
- modern equipment that allows you to avoid diagnostic errors and act precisely on the affected area;
- a full range of services, including tooth-preserving operations;
- absence of pain and discomfort even during the most invasive procedures;
- use of the latest materials and new generation drugs;
- attractive price.
Treating tooth pulpitis in PROFI-Dent dentistry means solving the problem quickly and as efficiently as possible!
All our regular clients can undergo a free preventative dental examination once every 6 months!