Many still remember the time when a visit to the dentist resembled a sophisticated execution. The most vivid impressions were obtained when a nerve was removed from a tooth, and special horror was associated with the word “arsenic.” Modern painkillers relieve toothache quickly and effectively. This allows you to carry out the most complex procedures without physical suffering. Why, against the backdrop of the new generation of painkillers, do dentists still use the good old arsenic?
Tooth hurts after arsenic
Painless removal of a nerve from a tooth: how it goes and consequences
Many people are familiar with the procedure of removing a nerve from a tooth, which was accompanied by the mandatory placement of arsenic. Previously, this method took several days, during which the substance killed the nerve, after which the doctor removed the pulp and installed a filling or crown. Modern methods make it possible not to resort to arsenic, using more effective and painless methods. The pulp or neurovascular bundle performs important functions; it nourishes and protects tooth tissue from infection. Without it, the enamel changes color, hard tissues are destroyed faster, but in some situations, removal of the nerve is necessary.
What is a root canal
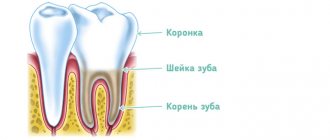
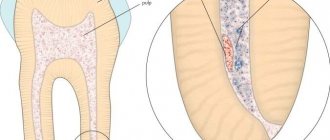
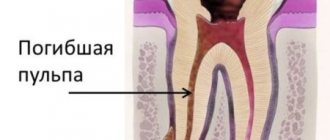
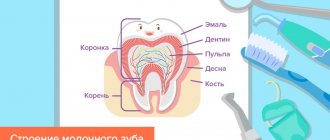
In addition to enamel and dentin, any tooth has a fairly large internal cavity. Its main part is called the pulp chamber. Thin tubules extend from it. They are located along the entire length of the roots. These are root canals. The number of roots varies among different groups of teeth. Accordingly, the number of channels is also different. The front teeth have only 1 canal. Side groups can have from 2 to 4.
Dental tubules are narrow tubes with many branches. They originate at the top of the root. This place is called the apical foramen. From here, neurovascular tissue passes to each root. If it is inflamed or dead, it is removed during endodontic treatment. Next, the resulting cavity is cleaned of its residues, disinfected and sealed.
Causes of dental pulp damage
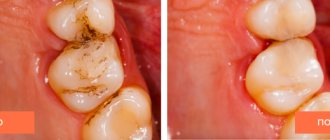
The dentist is often visited because of caries - damage and destruction of enamel, which at the initial stage causes aesthetic discomfort.
Important: if the disease is started, the process affects the deeper layers of the tooth and pulpitis develops, that is, the neurovascular bundle becomes inflamed.
Pathologies arise due to the rapid proliferation of microbes, but in addition, the pulp can be damaged for the following reasons:
- gum disease, in which the neck of the tooth is exposed, the bone tissue is destroyed and harmful bacteria penetrate inside;
- trauma, as a result of which part of the tooth can break off, and then microbes enter the resulting cavity;
- mistake by the dentist who installed the filling or crown. If some actions were incorrect, then the nerve will make itself felt after a while.
These are the main causes of pulp damage. The symptoms of this condition will be acute. The pulp will begin to react to cold, hot, too spicy, sweet foods. Removing the nerve in such situations is a necessity, despite the fact that minerals and nutrients will stop flowing to the tooth.
Modern methods of endodontic treatment
In the treatment of tooth canals today there are two approaches: therapeutic and surgical. Let's look at them in more detail:
Therapeutic treatment. With this method, it is possible to preserve the entire pulp or at least part. The drug is placed into the cavity. The pulp chamber is isolated using a special gasket, then the tooth is filled. The drug can also reach tissues through dentin. To do this, special bandages with antibiotics are applied to the tooth. This therapy is used only in the initial stages of the inflammatory process.
Surgery. In this case, the pulp is completely removed, the canals are cleaned, disinfected and sealed. There are the following methods for filling cavities:
- Classical. The canals are filled with conventional filling material.
- Vertical filling. A special filling composition is administered as an injection.
- The use of thermophiles. A special heated composition on a carrier is placed into the cavity.
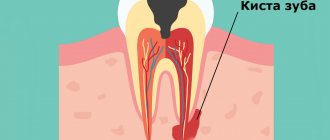
Sometimes, in order to cure the canal, you have to remove the tip of the root. This measure is necessary for cysts, granulomas, perforations, fibroids and other problems.
Why do you need to remove the pulp?
We talked about the main reasons why nerve inflammation occurs, but most often pulpitis becomes a consequence of advanced caries. Therefore, it is very important to visit a dentist, even if nothing bothers you. The decision to remove the pulp is made in the following situations:
- pulpitis has passed into the stage of periodontitis, when inflammation affects the whole complex of connective tissue in the tooth;
- large area of carious lesion;
- the infection spreads through the apex of the tooth root;
- the appearance of unbearable, prolonged pain;
- spread of infection under an artificial crown;
- consequences of improper treatment.
The nerve can be removed either completely or partially, it all depends on the degree of tissue damage. Depulpation will prevent the spread of the inflammatory process under the crown and preserve the natural tooth, which is a priority for endodontic therapy.
The mechanism of interaction between the drug and dental tissues
Arsenic as a poison has been known to mankind since time immemorial. In ancient times, arsenic poisoning was punishable by a severe death penalty: for men - wheeling, for women - drowning after torture. This toxin is still used to kill rats and mice today. For humans, the dangerous dose is 5 mg or more.
Arsenic
Dentists work with a paste whose formula is based on arsenic anhydride. Other ingredients include:
- antiseptics in the form of thymol and camphor, neutralizing microorganisms and disinfecting the pulp;
- anesthetic substances such as lidocaine, novocaine, dicaine, tannin;
- astringent components that provide a prolonged effect of the drug;
- fillers to maintain the required amount.
Arsenic paste
When the chewing organ is painful, this means that the destruction has already affected the soft tissues where the neurovascular bundle is located. This is the last stage of caries, which means that pulpitis or periodontitis develops in the dental tissues, when the exposed nerve reacts sharply to an uncomfortable temperature environment or mechanical irritants.
Advanced caries
The cytotoxic properties of arsenic are used by doctors to kill the sensitivity of the neurovascular bundle. As a result of this procedure, the blood supply to the pulp stops and necrosis occurs, blocking the transmission of nerve impulses in the dental core.
Modern medicine has many options for extracting the dental nerve, but there are only two main methods:
- removal of pulp contents without additional devitalization of the neurovascular bundle. This means that the doctor has come to the conclusion that soft dental tissue must be removed immediately, and such a decision cannot be delayed. The doctor uses local anesthesia and performs all manipulations without killing living tooth tissue. This option is less common;
- Usually, before the procedure, the dentist opens the pulpal contents of the masticatory organ and treats it with a special paste designed to devitalize soft tissue. Popularly the name “arsenic” was assigned to this product. The method of anesthesia using arsenic-based paste is still popular.
Arsenic in the tooth
Diagram of a tooth with arsenic applied
Why do doctors choose the old proven technique? With the right approach, permissible doses of this toxin reliably anesthetize the tooth depulpation procedure without the use of other drugs. The patient only needs to wait a certain time until the unnecessary nerve dies, so that it can be removed without any problems. Many patients are concerned about the question: should they panic if, after adding arsenic paste, the problematic chewing organ begins to hurt? Is he obliged to get sick, and what pain is normal and what is pathology?
How does the pulp removal process work?
We mentioned the method using arsenic at the very beginning. Some dentists still use it. The disadvantages of this treatment include its duration and pain. Before administering arsenic, the doctor must widen the root canal and place the substance into it. He then seals the area with a temporary filling. After two days, the arsenic kills the nerve, then the dentist cleans the substance from the tooth cavity and removes the pulp.
Important! Arsenic should not remain longer than expected in the oral cavity, as it is a poison and can be destructive to tissue.
There are more modern ways of performing the procedure, which are both safer and more painless. Before any action, an x-ray is required, which shows the vitality of the pulp, the length of the canal and other features.
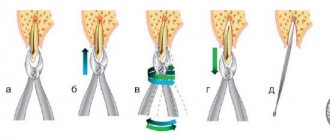
Pulp removal is carried out using the vital and devital method. The first option is used for patients of any age. Its stages are as follows:
- the tooth is exposed;
- the pulp is removed with a special tool - a pulp extractor;
- a filling is installed.
In some situations it may be temporary and after a few days it changes to permanent.
Note: all stages of treatment are performed under anesthesia, so they will not be painful or uncomfortable for the patient.
The devital method is similar to what was used ten or more years ago, only instead of arsenic, a non-toxic substance is installed in the tooth cavity. The main method of pulp removal in modern dentistry is the vital method, when in just 1 visit to the doctor you can undergo complete painless dental treatment.
Important: temporary pain after a dental procedure is considered normal, as tissue intervention has occurred. If severe pain does not go away within 3 days, you should consult a doctor.
Arsenic-free pastes
With pastes without arsenic, the situation is much simpler: even with prolonged use, periodontitis does not occur so quickly, although you should not exceed the time prescribed by the doctor!
Arsenic-free pastes are even used to treat children. Thus, the treatment is intermittent and the child does not have to stay in the chair for a long time. And also, which is very important, it is possible to do without injections.
For the adult population, root canal treatment is successfully carried out under anesthesia, on average in 1-3 visits, depending on the complexity of the situation.
In what situations should a nerve not be removed?
We are talking not only about contraindications, but also about cases in which the pulp can be preserved. The procedure is not performed if the patient has:
- any infectious disease;
- one of the forms of stomatitis;
- psychoemotional disorders;
- acute pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- unsatisfactory condition of the oral cavity with suppuration and inflammation.
The nerve is preserved if it is not subject to inflammation due to caries or other pathologies and injuries. The dentist’s task is to save the pulp and remove it only in case of emergency.
Important: you cannot endure a toothache and hope that the pain in your nerve will stop. Inflammation can become chronic and show almost no effect, but any provoking factor will affect the development of a purulent abscess. In this case, the minimal consequence will be tooth loss, and the possible consequence will be the spread of infection to other tissues.
Consequences of nerve removal
If the treatment was carried out by a professional and experienced dentist, then apart from slight pain the patient will not be bothered by anything. Otherwise, there may be such complications:
- a fragment of the instrument remains in the dental canal;
- the nerve was partially removed;
- incorrect or poor-quality filling of the canal;
- mechanical damage to the root or wall;
- rapid darkening of the enamel;
- suppuration due to poor disinfection.
Important! Depulpation at the Crystal clinic is carried out with the minimum possible complications, since all procedures are carried out by certified doctors with extensive experience using high-tech equipment and tools.
After depulpation, it is recommended not to eat for 2-3 hours, not to eat cold, hot, hard or other foods that irritate the mucous membrane. Your doctor will tell you in more detail about the necessary actions after removing the nerve.