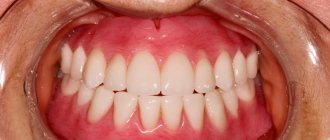
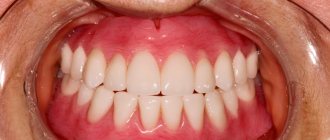
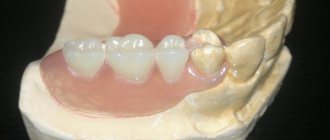
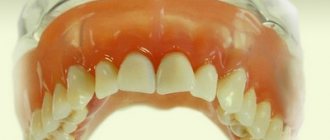
Reasons for chipping ceramics in metal-ceramic structures
At the junction of the metal frame of the denture and the ceramic coating, strong stresses often arise, which in stressful situations lead to the formation of cracks, chips or spalls in the ceramics.
The main reasons for ceramic chipping are:
- Mismatch between the thermal expansion coefficients of ceramics and the metal alloy from which the frame is made.
- Unreasonable choice of metal ceramics as a material for a fixed prosthesis in some patients (for example, those suffering from bruxism).
- If the intermediate part of a metal-ceramic bridge is too long, the frame of which is made of precious alloys (which have lower rigidity than non-precious alloys), chewing loads on it can lead to chipping of the veneer.
- Incorrect tooth preparation, for example, insufficient taper, can lead to stress in the framework of the metal-ceramic crown and subsequent chipping of the veneer.
- Chips often occur when performing orthopedic work (especially large-scale ones) without an articulator and a facebow.
- When fixing a metal-ceramic prosthesis with excessively thick cement, or when foreign bodies get between the tooth stump and the crown.
- Chips may be a consequence of incorrect modeling of the metal-ceramic frame of the future prosthesis:
- insufficient height of the frame, which necessitates the layering of an excessive amount of ceramics - unmodeled tooth relief - non-compliance with the technology of mechanical and chemical processing of the metal frame - holes in the metal frame, which technicians close with ceramics. Subsequently, after cementing the crowns, tension arises here, since the cement presses evenly on all walls and later a chip forms in this place and rapid decementing of the structure.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
- The cause of chipping may be stress in the ceramics or metal frame, resulting from non-compliance with technological rules for working with ceramics:
- overheating of the metal during firing of ceramics - violation of temperature relationships during successive firing and cooling of ceramics - violation of the rules for working with ceramic masses offered by manufacturers - non-compliance with ceramic processing technology.
- Careless or careless handling of the patient with prosthetic metal-ceramic structures. The fragility of ceramics under inadequate loads, and less often during sudden temperature changes, should be taken into account. We also recommend that you read the article about installing ceramic crowns at 32Dent dentistry.
Technological aspects of metal ceramics
In the process of manufacturing metal-ceramic structures, there are a number of key points that deserve special attention.
Tooth preparation for metal ceramics.
- The tooth must be prepared (ground) with a ledge at the gum level.
- The total thickness of the metal frame and the ceramic mass covering it is about 1.5 mm. As a result, if the tooth is ground without a ledge, we get the edge of the crown hanging over the gum and pressing on it. The crown presses against the blood vessels and a “bruise” forms. The metal frame comes into direct contact with the gum, and metal ions cause it to darken.
- In the case of preparation with a shoulder, the edge of the metal-ceramic crown rests on the hard tissues of the tooth without injuring the mucous membrane. This technology is quite labor-intensive, and its implementation requires a modern dental unit and, of course, the qualifications of a doctor and dental technician.
The intermediate part of the metal-ceramic bridge prosthesis should also not put pressure on the mucous membrane (gum), otherwise bedsores may form. Of course, in those places where it is visible, you have to make a compromise, but in any case the touch should be very gentle. And if food gets into a place where there is a loose seal, it will be much easier to remove it from there than in the case of the “full contact” option.
Many doctors “sin” by depulping (removing the nerve of the tooth) even healthy teeth under metal-ceramics, which is not always justified, since modern technologies make it possible in many cases to avoid this procedure. Depulped (dead) teeth cannot resist infection and often have to be re-treated. In addition, a pulpless tooth becomes more fragile and can collapse under a heavy metal-ceramic structure.
How to take impressions correctly?
If the mucous membrane was damaged when grinding the native crown, the procedure for taking impressions should be postponed until it is restored.
- In some patients, the injured gum can give recession - move away from the neck of the tooth and expose its root.
- Due to the presence of blood, the materials used to obtain impressions may not clearly depict the formed ledge.
As a result, the edge of the manufactured and installed crown will stick out above the gum, which will significantly reduce the aesthetics of prosthetic treatment of the front teeth.
Stages of manufacturing a metal-ceramic bridge prosthesis
The main indication for prosthetics using fixed bridges is the absence of one or more teeth.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Dental prosthetics using fixed metal-ceramic prostheses is one of the most common methods of treating violations of the integrity of the dentition and restoring chewing function. For this purpose, missing teeth are replaced with artificial ones, supported by adjacent teeth. The functional basis of such treatment is the reserve capacity of the dentition, which allows it to withstand additional load.
A fixed metal-ceramic bridge prosthesis is a structure consisting of one or more artificial (metal-ceramic) teeth rigidly attached to adjacent natural teeth using fixing elements - metal-ceramic crowns.
Typically, the number of supports in a bridge is two, but sometimes there is a need for three or more supports. Due to the fact that the supporting teeth experience pressure not only directly on them, but also on the intermediate part of the bridge, the number of replaced teeth cannot be too large. As a rule, this is 1-2 teeth.
The manufacturing process of a metal-ceramic bridge consists of clinical and laboratory stages.
Clinical stage
After the examination, if necessary, preliminary treatment is carried out: gum treatment, filling of supporting teeth and, if this is unavoidable, removal of the pulp and filling of root canals.
Then the teeth are prepared, on which the crowns that are part of the metal-ceramic bridge will be placed. This stage consists of grinding down their convex surfaces that prevent the crown from being put on.
After processing the teeth, an impression is taken and a plaster model of the missing dentition, along with data on the state of the bite, is sent to the dental laboratory.
Laboratory stage
In the laboratory, jaw models are made, on which the frame of the bridge is formed from wax, and then the metal frame is cast in a foundry.
Then the frame can be coated with a golden sublayer, which, due to the high gold content, allows the ceramic mass to be applied in an ultra-thin layer, through which the black or dark gray color of the oxide film covering the surface of the metal frame will not show through.
Next, the frame is covered with ceramic mass. The ceramic coating is applied in layers in accordance with the colors selected by the orthopedic surgeon. The “face bow” data is transferred to the articulator and the bridge is finally modeled in shape, taking into account the bite and relationship of the teeth during movement.
A bridge is a rather complex structure, so another intermediate visit is required - fitting of the frame. During the third visit, the final correction is made. The ceramics are covered with glaze, which gives the prosthesis a natural look, and with the help of special cement, the metal-ceramic prosthesis is fixed to the teeth.
Possible problems and complications
Installation of a metal-ceramic crown is a mini-operation in the oral cavity, with local anesthesia at the request of the patient, possible (but unlikely) problems. The more positive the clinic’s reputation, the lower the risk of complications, since this is based on the doctor’s mistake.
The most common occurrence is the development of caries under the crown. Causes:
- drying of the tooth if the nerve is removed;
- violation of tightness.
Prevention is considered to be proper dental care. Visiting the dentist once every six months will also prevent complications.
Although metal ceramics are considered biocompatible with the tissues of the human body, another complication that can appear both immediately after installation and several years after installation is toxic or allergic stomatitis. Without ulcers, but with swelling of the tongue, difficulty breathing, drooling, burning of the tongue. With toxic stomatitis, there will be a deterioration in health (pain, heaviness in the liver, kidneys), itchy skin, and urticaria. Please note: if the frame is made of gold or silver-palladium, cases of such stomatitis are rare.
Sometimes patients complain of chipping of the ceramic coating. Most likely reasons:
- incorrect frame modeling;
- improper processing of the area for ceramics (the surface is too smooth, poorly polished, without an oxide film, etc.);
- selection of materials without taking into account physical and chemical characteristics;
- violation of the technology of applying layers, firing and cooling;
- too many firings to change color or shape (ceramics shrink);
- uncorrected occlusal interlocking contacts;
- internal stresses in the metal part of the crown due to improper preparation of the supporting teeth and fitting of the frame.
If the ceramic part breaks off, you need to contact an orthodontist. If a piece is swallowed, it is advisable to immediately rinse the stomach.
Stages of manufacturing a metal-ceramic crown
The traditional manufacturing process of metal-ceramic crowns involves the following steps:
- Determination of tooth color, characteristic features, structure of enamel, dentin, determination of the transparent layer, the presence of individual characteristics (enamel cracks, staining of fissures in the chewing group of teeth, the presence of chalky stains, enamel abrasion, etc.).
- Next comes the removal of the destroyed dental tissue and the process of preparation (grinding) of the tooth, which takes a very long time. In order to ensure that after installing a metal-ceramic crown there is no effect of the so-called “blue” gum or compression of the gingival dental papilla by the crown, the doctor must very carefully grind the tooth to create a gingival ledge (the angle on which the crown will rest). Only with this method will the work be successful.
- An impression is then taken and sent to the laboratory.
During the production of permanent metal-ceramic structures, a temporary crown is placed, which hides the defect and eliminates psychological discomfort.
- After the metal frame is made, ceramic masses are applied to it layer by layer, recreating natural teeth as accurately as possible. Next comes the artistic design of the metal-ceramic crown, taking into account the individual characteristics of the tooth.
- Then follows the fitting of an almost finished metal-ceramic crown (a metal frame with ceramics already applied, but not glazed). At this stage, the color of the crown is finally determined, because You can still make changes.
Finally, at the last visit, the permanent crown is placed. The entire process of manufacturing a metal-ceramic crown takes on average up to 10 working days.
Indications and contraindications for installing metal ceramics
These dental crowns are used for aesthetic prosthetics. Main indications:
- Destruction of the natural crown of a tooth by caries, trauma, non-carious lesions, etc., which cannot be restored with filling.
- Traumatic tooth fracture.
- Darkening of color or hypoplasia of enamel.
- Dental abnormalities.
- Fluorosis.
- Restoration of the lower part of the face with pathological abrasion.
- How to fix a prosthesis (removable, bridge).
- When splinting teeth for periodontitis.
- Replacing dentures.
Contraindications for installing metal-ceramic crowns are relative (sometimes it is enough to carry out preliminary treatment):
- Age up to 16 years (intact pulp).
- Teeth with fragile, thin crowns (often this applies to the lower incisors).
- Blocking bite, when the lower incisors completely overlap the upper incisors.
- Pathological abrasion of teeth and a decreasing bite (will lead to breakage of the metal-ceramic crown if the bite was not corrected and myostatic reflexes were changed before installation).
- Parafunctions of the masticatory muscles (for example, bruxism).
- Diseases of marginal periodontium due to possible functional overload of teeth.
Allergy sufferers and people with gastrointestinal diseases need to be very careful when choosing a metal frame, since the constant presence of metal can cause a deterioration in well-being over time. For such patients, a gold base is recommended. Doctors also do not recommend nickel-chromium alloys even for healthy people, since there is a tendency for general immunity to decrease and a surge in autoimmune diseases and the gastrointestinal tract.
Materials used in metal ceramics
In metal-ceramics, a metal frame is used as a base, which solved the problems of excessive fragility of ceramics. Ceramic is applied layer by layer to the outer surface of the metal and held firmly in place by sintering. As a result, a metal-ceramic crown is reliable, durable and very beautiful. Plus, it looks like a real healthy tooth.
To effectively protect teeth from destruction under crowns, teeth are treated with a protective paste that releases fluoride into the tooth tissue. Modern dental cements are used to fix metal-ceramics, which makes it possible to achieve the strongest fixation. A high-quality metal-ceramic structure lasts for decades. The average service life of cermets on base alloys is 10-12 years. On gold-platinum alloy 15 years or more.
The nuances of installing metal-ceramic dentures: consultations with Berezki dentists
Patients who decide to restore the fullness of their dentition with metal-ceramic products should know that there are different types of structures. They differ from each other in terms of strength and reliability, aesthetic characteristics, service life and price.
You need to understand that to achieve a positive effect, it is not enough to simply choose the most expensive products. It is very important to carry out the preparatory procedures correctly and efficiently:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- treatment and filling of root canals if they are preserved;
- grinding of dental units.
After therapeutic manipulations, a control X-ray examination is required to prevent negative consequences. Only after making sure that the preparatory stage has been completed flawlessly does the doctor begin taking impressions from which the crown is made.
Ceramic lining in metal ceramics
The quality of a metal-ceramic prosthesis depends on many factors. Color accuracy is determined mainly by the quality of the ceramic mass. Imported ceramics convey color more accurately than domestic ones; in addition, they are more stable during processing and use - they do not change color when fired, and do not crack.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Applying porcelain mass to a metal frame is a long and painstaking job, since it is applied in layers and after each application the mass is fired in a special vacuum oven. Firing metal ceramics is a very important task. If the temperature or barometric modes are chosen incorrectly, the ceramics will crack and all the work will have to be done again. It is thanks to the layered application of porcelain that metal-ceramic teeth accurately convey the color and transparency of natural teeth. In addition, porcelain is intertwined with the tissues of the oral cavity and is hygienic.
Recently, ceramics have appeared in world dental practice, having a rigidity coefficient comparable to that of healthy teeth, which makes it possible not to injure or abrade antagonist teeth when chewing.
The use of the latest technologies allows you to give metal ceramics any color. Typically, the color of metal-ceramics is as close as possible to the color of the patient’s teeth. To do this, doctors use a set of small porcelain plates in the shape of a tooth (each plate has its own shade); Dentists call such sets a “color chart.” Depending on the specific situation, a metal-ceramic crown can be made so that porcelain covers only certain sides of it that are visible when smiling and talking, and the remaining parts of the crown are made completely metal.
The world leaders in the production of dental ceramics and porcelain are Ducera, Noritake.
One of the leading factors when choosing porcelain for ceramic cladding is the constancy of its coefficient of thermal expansion, which prevents the occurrence of cracks in the ceramic coating even during the manufacture of extended multi-unit structures. Some manufacturing companies produce porcelain, the coefficient of thermal expansion of which does not change during multiple firings, and is also little sensitive to the selected firing mode, therefore metal-ceramic products coated with such porcelain can be successfully fired in any dental furnace, starting from the simplest ones with a strictly specified heating rate , and ending with ultra-modern ones.
Another important criterion for choosing porcelain for metal-ceramic dentures is its strength. According to the international standard ISO 9693 “Dental metal-ceramics for dental prosthetics,” the flexural strength of porcelain must be at least 50 MPa.
Another pleasant distinguishing feature of some types of porcelain is their resistance to greening when applied to metal frames made of semi-precious silver-based alloys.
Types of alloys in metal ceramics
Gold-platinum alloy
The classic version with which orthopedic dentistry began. The first crowns were made from gold at the end of the 19th century.
Nowadays, many materials have appeared that, along with solving the problem of restoring chewing function, are quite durable and at the same time meet high aesthetic and cosmetic requirements. But gold, as a material for the manufacture of frames for metal-ceramic prostheses, is still relevant today.
Only a noble alloy can adhere so precisely to the treated tooth, which practically eliminates disintegration and recurrent caries. Gold almost never causes allergies.
The disadvantage of using a gold alloy is the limitation on the length of the intermediate (located between two supports) part of the metal-ceramic bridge (in the manufacture of metal-ceramic bridges), as well as the price: the cost of such a crown is from 10,000 rubles.
Sometimes, to improve color rendition, on a metal frame cast from other metals. a thin layer of gold is applied, which illuminates through a layer of ceramic mass with a warm yellowish color.
Nickel alloy
Most often, nickel-based alloys are used to cast the frame, which is the most accessible of the metals that can be the basis for metal-ceramics. With nickel alloys there are no problems when casting and fitting in the patient's mouth.
However, despite all the advantages, nickel has a serious drawback. This metal is a strong allergen.
Our body's daily need for nickel is thousandths of a gram, and the production of one metal-ceramic crown requires 2 grams of an alloy containing 1.3 grams of nickel. Thus, the metal is in contact around the clock with the oral mucosa, tooth tissues, and jaw. The result is allergic reactions and weakened immunity.
In Germany, they abandoned the use of nickel in dental prosthetics 10 years ago (as well as stainless steel back in the 30s).
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Cobalt-chromium alloys
The most optimal option taking into account biocompatibility and cost.
In cost, they are only 1.6 times more expensive than allergenic nickel alloys. The biocompatibility of the cobalt alloy is 36% (for the gold-platinum alloy it is 42%, and only one’s own teeth are 100% biocompatible), they are non-toxic and do not cause allergic reactions. Cobalt alloys are durable, and metal-ceramic bridges of fairly long length can be made from them.
Chromium alloys are not dangerous; only some of its salts are poisonous, but they cannot form in the oral cavity.
Molybdenum
A non-toxic metal, it is added to dental alloys in very small quantities to improve casting properties.
Beryllium
This metal is a carcinogen. It causes granuloma (a type of malignant tumor) in the lungs, liver, spleen and heart. Upon contact with beryllium, skin diseases develop and a severe weakening of the immune system is observed. In Russia, its use in dental alloys is prohibited.
Alloys in cermets
To make a metal-ceramic crown, the dental technician first makes a metal frame that exactly matches the contours of the tooth prepared for prosthetics. The frame is the most important part of the design of a metal-ceramic crown.
There is a saying: “the mouth is the beginning of the stomach, saliva is the first “stomach” juice.” Saliva is rich in a variety of enzymes. As a result of a chemical reaction, the metals that make up the alloy of the metal-ceramic prosthesis are “washed out” by saliva into the oral cavity in microdoses. Next, saliva with microdoses of metals is swallowed, absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and enters the liver. This causes slow poisoning of the body.
The ceramic layer covering the outside surface of the metal frame is a good barrier to saliva and is an excellent insulating material. The teeth are isolated from the metal with high-strength cement, which completely protects your tooth from harmful factors, but metal is still present in the structure, and no one can guarantee that subtle biochemical reactions between your body and the metal frame do not occur.
There is no “best alloy” that suits everyone; patients have different sensitivities to certain elements. The determining factor here is the degree of corrosion. The fewer components of the alloy are dissolved, the less danger there is of a pathological reaction of the body to metal-ceramics. It follows from this that the alloy should contain a minimum of base components, because they are more susceptible to corrosion compared to noble metals.
Determination of the allergic effects of the alloy is carried out using tests on animals. Direct transfer of results to humans is not shown, however, it is possible to establish the allergic potential of the alloy.
Stages of dental prosthetics with complete edentia
The production of a complete removable denture begins with an examination of the patient’s oral cavity, diagnosis of the condition of the dental system, and selection of a suitable design. The first impression is taken with a standard impression tray. Depending on which design is chosen, the impression mass is selected. The impressions are sent to the laboratory, where a dental technician casts plaster models and makes a wax base with occlusal ridges and custom impression trays.
On the second visit, using these trays, the doctor takes functional impressions, and using rollers, determines and fixes the occlusion. All information is transmitted to the dental technician. He makes the future prosthesis from wax with acrylic (plastic) teeth .
On the third visit, the structure in the oral cavity is checked, occlusion, fit, and the appearance of the patient’s face are assessed. The doctor makes the necessary notes and corrections and transfers the future design to the laboratory. The dental technician finally models the wax structure, plaster it into a cuvette where the wax is replaced with plastic. Next, he grinds and polishes the finished prosthesis.
At the next visit, the prosthesis is handed over. Finished structures are fitted, fit, occlusion and aesthetics are checked. The doctor will tell the patient how to use and care for the new prosthesis. During the adaptation period, additional corrections are possible.
Aesthetic properties of metal ceramics
Metal-ceramic crowns have excellent aesthetic qualities. Modern technologies make it possible to achieve any shade of ceramic coating color.
In the 60s and 70s, there was a fashion for the so-called “Hollywood smile”, to create which metal-ceramic dentures with straight white teeth were made. Despite its external attractiveness, the “Hollywood smile” is unnatural, lifeless and, with rare exceptions, does not match the remaining teeth.
Increasingly, patients began to express wishes that artificial teeth would not differ from the preserved natural ones. But the possibilities of materials for the manufacture of metal-ceramic dentures were then very limited.
This led to the emergence of a number of research projects aimed at developing dyes, effect masses, opalescent porcelains, etc. A revolutionary step in the development of materials for creating natural aesthetics in dentures was the creation of the internal coloring technique, developed by one of the world's most famous dental technicians, Hitoshi Aoshima. The principle of this technique is that all the characteristic features of the tooth are not drawn with dyes on the surface of the metal-ceramic prosthesis, but are modeled from the inside.
Luster (glossy) porcelain was also developed. Research scientists have come to the conclusion that tooth enamel, in its shine, resembles the surface of a pearl. To imitate the natural shine of enamel, scientists have created a new technology for producing opalescent materials. The surface of luster porcelain, thanks to the ultra-fine structure of the particles, resembles the enamel of a natural tooth in its relief, ability to transmit light and color.
If the metal ceramics nevertheless turn black, then the reason for this may be trivial - the patient forgets to brush his teeth. If the lowest layer of ceramic, opaque, does not sufficiently dampen the metal frame and allow chromium ions to pass through (in the case of a cobalt-chromium alloy), then they give the accumulated plaque an unpleasant greenish tint. Individual oral hygiene is very important for everyone, and especially for those who have metal-ceramic dentures.
Caring for metal and ceramic crowns
Metal ceramics do not require special care. Enough:
- brush your teeth regularly to remove food debris;
- rinse with rinses (for example, “One Drop Only”, “Paro Chlorhexidine 0.12%”), intended for daily care for gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis, as well as after surgical operations on the oral mucosa;
- rinse with warm decoctions of herbs (for example, chamomile, lemon balm, rosemary, sage, bloodroot, witch hazel), which reduce bleeding gums.
To care for the crown, it is better to purchase a toothbrush specially designed for people with implants, dentures, or orthopedic structures (especially if no ledge is created during preparation). They clean the interdental spaces, gingival areas of the teeth, and the space under the crowns well. The brushes are small, the working part is usually a bundle of fibers collected into a cone, or 1 row of bundles.
Caring for metal-ceramic crowns
The most popular orthodontic toothbrushes:
- "Antiplaque". The bristle profile is V-shaped. Designed for patients with various orthodontic structures (crowns, braces).
- Oral-B Interdental. There is a removal-fixation system with a “volcano-shaped” tip, which makes it easier to replace cone-shaped or cylindrical brushes.
- "StaiNo Interdental Brush" ("Sultan"). Aluminum oxide abrasive bristles are used. The brush cleans well the interdental spaces and the space around bridges and braces. The brush designs and color markings are different.
- Lacalut Interdental. There are 2 replaceable heads for cleaning interdental spaces and effectively processing orthodontic structures and bridges. Used without toothpaste.
The dental floss recommended by dentists for cleaning a metal-ceramic crown without the risk of damaging it is Oral-B Super Floss. This is a triple thread, which includes:
- a short, rigid tip for ease of entry into the interdental space and under the body of a bridge or orthodontic structure;
- A section of soft nylon fiber (sponge floss) cleans areas around and in wide spaces between teeth;
- regular floss removes plaque in the periodontal sulcus.
Superflosses are specially designed for patients who have permanent orthopedic crowns. It is not recommended to use regular threads.
Electric toothbrushes and irrigators cannot damage a high-quality metal-ceramic crown. However, if the manufacturing technology is violated, the supply of water under pressure, as well as pulsating or reciprocating movements can lead to microcracks.
When choosing a toothpaste, you should pay attention to products that provide the prevention of caries, periodontal diseases and oral mucosa. Remember: tooth ceramics are dense, not porous. There is no point in using special whitening pastes; you can continue to use the one you are used to.
Prosthetics with metal-ceramics
Advantages of metal-ceramic prosthetics
The following facts speak in favor of the use of metal ceramics:
- correspondence of artificial metal-ceramic teeth to natural ones in function and appearance
- the possibility of prosthetics for both frontal and lateral teeth, included and end defects of the dentition, the ability to combine removable and non-removable metal-ceramic structures.
- "hygienic" Microbial plaque settles less on metal-ceramic teeth than on natural teeth, which is especially important for patients with periodontitis.
- durability. Today, metal ceramics are one of the most durable structures used in dentistry. If a metal-ceramic crown is made using modern materials and techniques, then its service life is on average from 10 (on a non-precious alloy) to 15 (on a gold-platinum alloy) years.
- A properly made metal-ceramic crown will never cause unpleasant changes in the gums, such as bleeding, changes in color or contour.
Crown installation
After completion of the final heat treatment, the metal-ceramic crown is ready for fixation on the jaw. Before this, it is treated with an antiseptic consisting of ethyl alcohol and hydrogen peroxide - 97 and 3% of the composition, respectively.
as retainers - zinc phosphate, polymer, polycarboxylates. For final fitting of the prosthesis, initial fastening is carried out using temporary cement. If the anatomical shape of the product and its color meet the requirements, final installation is carried out.
The process of making dentures is relatively fast. This depends on the workload of the dental laboratory, but on average all stages of work require from 10 to 15 days. For comparison, prosthetics with implants lasts up to six months.