Kids are in a hurry to explore the world around them, they are interested in everything, they are inquisitive and are distinguished by special motor activity. However, often it is this curiosity and restlessness that lead to various bruises and injuries - dental injuries in children are no exception. According to statistics, trauma to baby teeth in children accounts for about 30% of all visits to the dentist. Most often, children succumb to such injuries at the ages of 2-4 and 8-10 years. As for gender, they are predominantly boys.
We divide all dental injuries of children
- Bruise - characterized by only minor damage, a crack in the enamel, hemorrhages in the pulp chamber, swelling, or bruising on the gums may be observed.
- Subluxation - a damaged tooth is displaced, its ligamentous apparatus and neurovascular bundle are partially damaged, and tooth mobility is noted.
- Luxation - incomplete and complete - the tooth protrudes significantly from the dentition, barely maintaining connection with the socket, or even falls out of it. The integrity of the neurovascular bundle and ligamentous apparatus of the tooth is compromised.
- Fracture of the crown of the tooth.
- Tooth root fracture
Further in the article we will tell you how acute injury to baby teeth in children is characterized by an impact, how to recognize an injury to the front teeth, and how to treat any tooth injury in a child.
Emergency and long-term treatment strategies
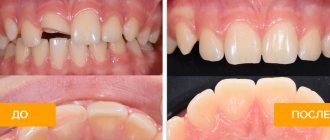
When a child knocks out a tooth or significantly damages it, the question arises of what to do. In many cases, the tooth can be saved completely or partially. For any injury, consultation with a pediatric dentist is required. And in cases where a tooth falls out or is broken, you need to see a specialist immediately. If you preserve a splinter or a fallen tooth in an isotonic environment - saline, milk, saliva - then it can be used for restoration or returned to its place in the socket [1]. Water is not suitable for transportation. If the child is old enough, you can place a clean, washed tooth or part of it behind the cheek while traveling to the doctor. Special containers are also sold, which significantly increase transportation time [4]. It is sometimes possible to reliably determine whether the pulp has been damaged only 6 months after the injury [2]. But in some cases, when crowns and roots are fractured, pulp damage is obvious. It is necessary to assess their degree in order to choose the right treatment: partial or complete amputation. For very minor damage, the dentist will suggest direct pulp capping with biocompatible materials. For minor fractures, cosmetic restoration and tooth augmentation are used. Modern composite materials imitate the missing parts of the tooth so well that it is almost impossible to visually notice the difference. However, the extension and restoration of teeth impose certain restrictions: the impossibility of teeth whitening, contraindications to solid foods.
installation of crowns and veneers will be offered as treatment In many cases, aesthetic treatment will be conditionally divided into two periods: temporary and permanent, since children’s teeth grow over many years and the bite takes its final shape closer to 20 years. Until this period, your doctor will suggest a temporary alternative.
Trauma to the front teeth in a child
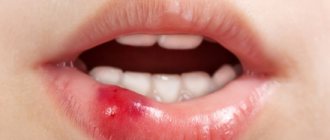
The front teeth in children are most often injured. And while injury to other teeth may go unnoticed, injury to a child’s front teeth quickly attracts the attention of parents. An ordinary bruise, in which only a barely noticeable crack in the enamel can be visually seen, may not bother the child in any way. In some cases, there may be discomfort or pain during chewing, or mechanical stress, and slight swelling of the soft tissues.
It’s another matter if, as a result of an injury, a subluxation, dislocation, or even fracture of a tooth occurs. Then the injury to the child’s front teeth is primarily visually noticeable. In the case of subluxation or dislocation, parents may notice an atypical position of the tooth, its slight displacement relative to other teeth. In addition, with this type of injury to the front teeth, bleeding, swelling of the soft tissues, inflammation, severe pain, and mobility of the injured tooth will be noted.
Children often experience fractures of their front teeth. It will be characterized by a violation of the integrity of hard tissues, chipping of a part of the tooth, pain, bleeding, swelling of soft tissues, and hemorrhages in them.
Prevention of childhood dental injuries
In order not to encounter the situations described above, you should take care in advance of the safety of the baby’s oral cavity. Remember that some dental injuries can be prevented by using simple protective measures:
- An excellent protection against injury during active games or sports is a helmet that not only protects the head, but also the teeth.
- To protect your child's teeth, use a mouthguard. This simple dental product provides as much as 85% protection.
- Talk to your children about the importance of being careful when playing. But don't intimidate them.
- Teach your child to fall without injury. Demonstrate how to tuck to avoid head and neck injuries.
- Provide your baby with healthy nutrition with all the necessary vitamins and microelements.
- Teach your child to brush their teeth regularly and visit the dentist every six months.
If you still failed to protect your baby from injury, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible. You can get qualified help at Aesculapius dentistry. In our dentistry you will find first-class equipment and modern treatment methods.
Four specialists work in one shift and they know their job very well. We work with each patient on an individual basis and provide a guarantee for all services. Absolutely all clients are satisfied with the level of service.
Acute dental trauma in children due to impact
Acute tooth trauma in a child upon impact is characterized primarily by damage to the periodontium - parts of its fibers are torn, small blood vessels and nerves are damaged. The degree of damage directly depends on the strength of the mechanical damage and on what kind of tooth injury occurred in the child during the impact - bruise, dislocation, or fracture.
Almost any acute dental injury in children resulting from a blow is accompanied by severe pain, swelling of soft tissues and hemorrhages in them. Bleeding is also very common. The pain intensifies during mechanical stress and chewing. Often acute dental trauma in children resolves with the impact of the tooth root into the jaw. Then, in addition to the symptoms described above, a visual shortening of the injured tooth will be observed.
Symptoms
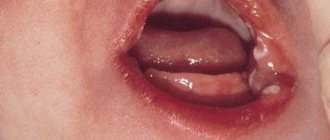
To suspect that a child has broken a front tooth is quite simple:
- Violation of the shape and integrity of the dental crown. Upon examination, you may notice a chipped tooth and a defect;
- Appearance of a crack. Characteristic of an incomplete fracture, part of the tooth may wobble, but not break off;
- Strong pain. The pain can be localized in the tooth, gum, or even spread to the entire jaw, depending on the severity and nature of the injury. Pain in the jaw occurs with impacted fractures, which are most often the result of trauma. Young children who cannot say what happened begin to cry and refuse food;
- Swelling, redness, bleeding of the gums. In some cases, the fracture is also accompanied by injuries to the soft tissues of the oral cavity. In severe cases, pathological mobility of adjacent teeth may appear.
What consequences may there be
A piece of teeth knocked out in childhood can lead to the following complications:
- malocclusion: neighboring teeth will shift, preventing the formation of permanent teeth,
- speech defects: their risk especially increases with the loss of incisors, which take an active part in articulation,
- diseases of the digestive tract: the inability to thoroughly chew food leads to its insufficient processing by oral enzymes, swallowing in pieces, which over time provokes gastrointestinal diseases.
Also among the negative consequences can be noted: violation of the aesthetics of the dentition, the appearance of problems in communicating with peers, an increased risk of pathologies in neighboring units, frequent inflammation even after successful treatment.
Where to put the knocked out tooth?
Make sure that the tooth does not dry out and call the clinic. Take the crown part without touching the roots, rinse in cold water. Do not use alcohol, antiseptics, hydrogen peroxide, or mechanically clean dirt.
Suitable for transportation:
- A container for lenses and the saline solution in it.
- A container with milk or a pharmaceutical preparation - glucose, 0.02% furatsilin, novocaine, sodium chloride.
- The victim's own saliva, if nothing is available.
Possible complications
Complex injuries can often have serious consequences, manifested in complications. It doesn’t matter which tooth was injured – the front incisor, the chewing tooth. After the examination, the doctor will decide how to save the child’s tooth. If you neglect the recommendations of a specialist, this can lead to more serious consequences, not to mention aesthetics.
Types of complications
1. Possibility of infection of the pulp area.
2. Increased tooth sensitivity.
3. The appearance of a bend in the tooth root.
4. Violation of occlusion.
5. Formation of cysts and granulomas.
You need to prepare for the fact that a damaged child’s tooth will begin to change the angle of development. And this leads to deformation not only of the damaged tooth, but also of its healthy neighbors. If it is necessary to remove a broken tooth, the space must be filled with an implant. If filling is not carried out, other teeth will begin to shift and move closer together, which leads to occlusion disorders - bite.
How are they treated?
The dentist determines treatment tactics depending on the severity of the injury and the condition of the tooth. The following methods are used:
- Tooth restoration. Suitable only in cases where a small piece of the tooth has broken off and the pulp is not involved in the pathological process. Various types of composite materials are used to restore the integrity and normal appearance of the tooth;
- Depulpation. This procedure is used for more severe fractures when the child has symptoms of pulpitis. The process removes the infected pulp, which allows you to save the tooth and prevent the child from developing a malocclusion;
- Delete. A radical measure that is used in cases where it is no longer possible to save the tooth.
Act quickly. The tooth can be saved
An injured tooth can be brought back to life if treated as soon as possible.
The work of a pediatric dentist at Idealdent is aerobatics:
- will restore a broken or dislocated tooth;
- splints the mobile group;
- will preserve the nerve so that the damaged dental unit grows and performs functionality.
View prices for pediatric dentistry
Now let's consider another situation. A wisdom tooth chipped into the gums - what to do?
If a tooth breaks or falls out, do not treat the area with peroxide, alcohol, touch the wound, or brush with a toothbrush. In a situation where there is a suspicion of not just a broken tooth, but also a broken jaw, she needs to be provided with peace and immobilized. To do this, you will need to make a bandage passing through the top of the head.
Severe trauma to the jaw can lead to nosebleeds. In this case, it is necessary for the child to lower his head and place a cold compress on the bridge of his nose. At the same time as these actions, someone should call the doctor.
After identifying the nature of the damage in the hospital using an X-ray, it will be possible to determine how damaged the surrounding tissues are, whether there are dislocations or subluxations.
First aid
If you see a small chip on a tooth, but nothing bothers your child, then make an appointment with the dentist as planned. Many parents do not know what to do if their child breaks a front molar. Your actions should depend on the child's condition. If there is bleeding from the gums and severe pain, then you need to immediately go to the nearest dental clinic to see a doctor. If there is slight pain, but overall health is not affected, then you can give an anti-inflammatory drug (for example, paracetamol) in an age-appropriate dosage and make an appointment with a doctor the next day.
Causes of dental injury
A large or barely noticeable gap in the teeth area spoils the entire appearance. To treat and restore a tooth, you need to know the main causes of dental injury. There are several of them.
1. Mostly, children receive mechanical injuries from a fall or bruise, when parents see, for example, that a front tooth has broken at the root.
2. Children's teeth are not yet strong enough to experience serious jaw load. Therefore, it is worth making sure that children do not get used to, for example, clenching their teeth tightly.
3. If half of the tooth crown is broken, it is due to a poor-quality filling.
4. The filling or inlay may pop out or break when it reaches the end of its service life.
5. Teeth with thinned enamel become a risk area.
6. Due to thinned enamel, the tooth may be destroyed due to carious formation.
7. The quality and properties of food also affect tooth decay.
Avoid giving children foods that are too hard or rough. Even seeds can cause a piece of a tooth to break off. To avoid all these unpleasant consequences, you will need to pay more attention to care, as well as the quality of food.
To strengthen tooth enamel, you need a sufficient amount of calcium in the body. To strengthen the structure, remineralization is required. The appearance of microcracks is due to the fact that the child receives food that is too contrasting. This affects the condition of the enamel, it becomes vulnerable. A weakened tooth may break at some point. This is the result of exposure to food and ingestion of hot and frozen drinks.