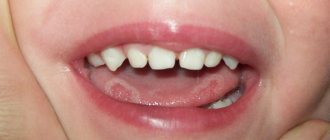
Why do ulcers appear on the gums, and is it always dangerous?
There are many possible reasons. To understand how dangerous the appearance of certain lesions on the gums is, you need to look at additional accompanying symptoms:
- in case it is trivial mechanical damage. The gums can be damaged by hard food, a toothbrush, or a foreign object. These lesions may resolve in 3-5 days. If a person does not brush his teeth, then infection is added to these damages, and healing may take several weeks.
- Sometimes ulcers can appear as a result of wearing orthodontic structures, braces or removable dentures.
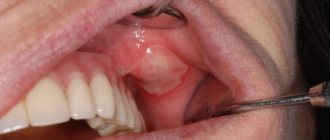
How can a fistula on the gum be cured?
Of course, we treat it, we deal with it, we work for it. In order to cure a fistula on the gum, first of all, we should eliminate the reason due to which the fistula occurred. We should not
fight the pimple itself, smear it with various ointments and lotions, but must eliminate the cause of its occurrence.
We must
eliminate the chronic inflammation itself that led to this fistula.
The first treatment option for a fistula is endodontic
For such treatment, we provide the patient with high-quality endodontic treatment under a microscope when:
- the tooth canal itself is visible,
- its branches are visible
- and you can see if there are cracks in the tooth canal.
Our doctors perform minimally invasive treatment procedures under a microscope at a high level. Treatment of processes that led to a fistula, to a fistulous tract on the gum, to complications of various periodontitis. In the video - endodontist of the Scientific Research Center, winner of many international competitions in endodontics and dental restoration Melikov Azer:
In the clinics of the German Implantology Center, special materials are used that seal the apical part very well and for a long period, which are biocompatible with the tissues surrounding the tooth and which give a very good result.
That is, we have a therapeutic method of treatment - this time
. When highly qualified endodontists, using microscopes, special equipment and special materials, carry out canal therapy and eliminate the cause of the fistula.
The second treatment option for fistula is mixed
Second method
- This is a mixed treatment, when treatment is carried out jointly by a therapist and a surgeon. If the lesion is already quite strong, lysis of a certain part of the root apex has occurred, when the process has already been going on for quite a long time, then the therapist cleans the canals:
seals the apical part of the root with a special material, and the surgeon opens, makes surgical access and polishes the apical part of the tooth root.
We do not perform dental resections when the tooth is cut down in half. You often think, I often have patients come to me who have had a resection and you think the person has had ⅔ of the root cut off and this tooth is no longer tenable, it can barely hold on, and why did it have to be done? We do it minimally invasively. We polish the apical part of the root with special ultrasonic tips after the therapist has carried out the treatment, and we get very good long-term results.
The third treatment option is surgery.
There is also a surgical method - this is the third method
treatment when the inflammation is already chronic according to the principle “No tooth - no caries, no periodontitis, no nothing.”
That is, the tooth is removed
, the source of inflammation is removed:
and an implant is placed
:
Subsequent rehabilitation of the patient takes place on the implant.
The fourth treatment option is autotransplantation.
Autotransplantation is a type of third, surgical treatment option. But the patient’s own donor tooth acts as an implant. As a rule, wisdom teeth, which are not involved in the process of chewing food and are actually the body’s reserve for such cases, are excellent for this role. Wisdom teeth transplantation is suitable for posterior teeth and premolars (fourth, fifth, sixth and seventh teeth).
Advantage
This method of treatment is that the patient’s own tooth is transplanted, the patient’s own tissue, which is not foreign to the body, even in conditions of the inflammatory process with a fistula, significantly reduces the risk of tooth-implant rejection.
The specialists of the German Implantology Center have accumulated many years of clinical experience in such operations. You can see how the autotransplantation operation takes place in the following video. There, at the end of the film, the patient shares his impressions of the dental transplant (this is a review 1 year after
the transplant operation):
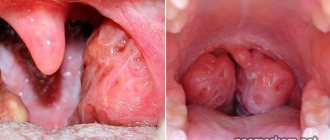
The most common diseases of the oral cavity in which ulcers appear
- ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis. The cause of this disease is bacteria that multiply when immunity decreases. Extensive ulcers appear on the gums, regional lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise
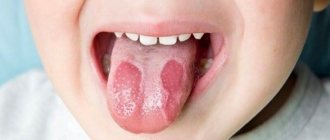
- chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Up to 4-5 white spots first appear in the mouth, which later turn into ulcers. There is no temperature or other problems related to well-being. If such symptoms appear 1-2 times a year in small quantities, then there should be no cause for concern. Frequent occurrence is associated with weakened immunity and possible intestinal diseases, as well as allergies.
- acute herpetic stomatitis. Herpetic stomatitis occurs in a child when he first encounters the herpes virus. Many bubbles appear on the gums, which, after bursting, turn into ulcers that merge with each other. The gums are always bright red, and the ulcers themselves are very painful, the temperature may rise
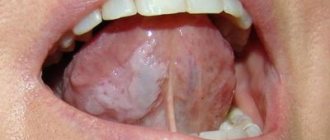
Stomatitis: what kind of disease is it, the mechanism of appearance of stomatitis ulcers
Scientists have not yet fully studied the mechanism by which stomatitis occurs on the mucous membrane in a person’s mouth. The manifestation of symptoms of the disease is associated with the specific reaction of a person’s immune system, which he exhibits in relation to irritants present on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
Bacteria, fungi, viruses and other microorganisms act as irritants. Normally, they are always present on human mucous membranes in one quantity or another. But when a person’s immunity is weakened, or other reasons provoke an increase in the number of microorganisms and the development of infectious diseases in the mouth (staphylococcal, streptococcal, candidal, etc.), this fact can trigger a stomatitis reaction.
Ulcers on the human mucosa, which are stomatitis in nature, are formed as a result of the fact that lymphocytes (white blood cells of the human immune system) begin to attack molecules that they cannot recognize. This reaction of the body is similar to that which occurs in the case of organ transplantation. As a result of such a lymphatic attack, stomatitis ulcers are formed on the oral mucosa, which usually go away on their own in one to two weeks without scarring.
First aid
If the temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic drug. In the future, before visiting a doctor, nothing should be done. Do not take antibiotics yourself or try to get into the ulcer with any object.
How to relieve symptoms of ulcers
- do not eat sour and salty foods
- food should be warm, no hot dishes or drinks
- Care should be taken to ensure that the child does not put dirty hands in his mouth
- teeth should be brushed, but make sure that the bristles do not touch the gums with ulcers
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal solutions (oak bark, chamomile) 3-4 times a day
You should be careful when using antibacterial solutions. They must be prescribed by a doctor. If such solutions are used incorrectly, they can provoke the development of thrush. The antibacterial agent will “kill” the beneficial microflora, which can result in a fungal infection.
Prevention of ulcers
- professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year
- Regularly replacing your toothbrush
- Proper brushing of teeth at least 2 times a day
- using additional hygiene techniques such as irrigators, dental floss, and tongue scrapers
- Children should be monitored for bad habits such as putting dirty fingers and other objects into their mouths
- It is important to treat your teeth in a timely manner. Microbes that are found in carious teeth and rotten roots can serve as a source of infection for ulcers
If you have problems in the oral cavity, contact the specialists of the Center for Family Dentistry!
Treatment of pericoronitis
Treatment by a dentist and surgeon should be aimed not only at eliminating the symptoms of the disease, but also at eliminating its causes. As a rule, for wisdom tooth pericoronitis, drug therapy and surgical intervention are used.
Drug treatment is the fight against microorganisms that caused the development of the infectious process. The doctor also prescribes medications that reduce pain and inflammation symptoms.
As a rule, the following groups of drugs are used to treat wisdom tooth pericoronitis:
- antiseptics, mouth rinses. The products reduce the microbial load and wash away bacterial and purulent particles.
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Ibuprofen, Ketorolac.
- antimicrobial, broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Azithromycin.
Surgical intervention for wisdom tooth pericoronitis usually involves excision (removal) of the gum hood over the wisdom tooth. This tactic is chosen in case of frequent relapses of the disease, pronounced pain syndrome, and spread of the purulent process to surrounding tissues. When an area of soft tissue is excised above the surface of the crown, plaque stops accumulating, which prevents infection and progression of the disease.
Excision of the hood takes no more than 10-15 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia.
If removing the hood and conservative treatment does not lead to an improvement in the condition, it is possible to remove the wisdom tooth. Removal is also carried out in case of incorrect tooth position or significant deviation of the “figure eight” from its physiological axis. In rare cases, not only the wisdom tooth is removed, but also part of the bone tissue. After removal, in almost 100% of cases, the patient recovers completely.
It is worth noting that many patients often insist on maintaining the “eight”. Many believe that in the future a wisdom tooth may be useful if prosthetics are needed. However, such an opinion is wrong. The wisdom tooth is located the farthest away and does not bear a significant functional load, taking only 2% of the total load on the dentition. When installing a crown, the wisdom tooth will not withstand the pressure, and the prosthesis will have to be replaced very soon.
What happens if the fistula is not treated?
If the fistula is not treated, then nothing good will end. The tooth will need to be removed, and what’s more, the bone surrounding the tooth suffers greatly, and the vestibular cortical plate suffers. When the tooth is not treated, when the cause of the fistula is not dealt with, the cortical plate is quite destroyed. Large cavities are formed in the bone, as exudate is formed, all this rots and the bone decomposes, softens and becomes infected, lyses, and exits through the fistulous tract.
Therefore, in addition to, as I said earlier, there is a fairly strong load on the body, since a fistula is a constant open source of infection in the oral cavity.
What is white plaque on the wound after tooth extraction?
A few hours after the tooth is removed, a dark clot appears in the socket - bluish, black, red or brown. This clot is blood, and it is the primary protection of the socket from bacteria or pieces of food entering it. On the 2nd - 4th day, the patient may see that a coating appears on the clot - yellowish, gray or white. The deposit looks like pus and, together with the resulting bad breath, can alert the patient. However, there is no need to be alarmed - this plaque is not a sign of wound decay and indicates a normal healing process. This special protein compound is fibrin.
A milky plaque (fibrinous) can be very dense, hard or soft. This is no cause for concern. If you come to the dentist with this question for an unscheduled appointment, the specialist will tell you that everything is in order and there is no need to remove the film.
If the film is not removed and the wound is not disturbed, active processes will occur underneath it:
- the blood clot will begin to dissolve;
- the hole will begin to decrease in size;
- young cells, osteoblasts, will begin to move from the edge of the wound to the center;
- The gums will begin to close the wound.
Fibrinous plaque after tooth extraction is a natural stage of gradual recovery of the body, in which it is better not to interfere.