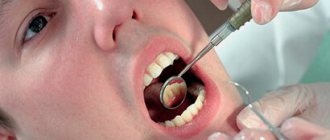
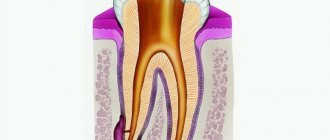
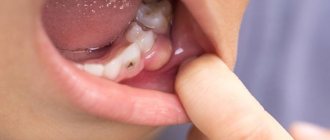
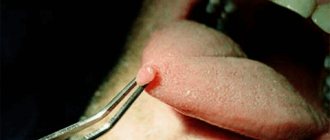
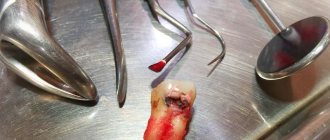
When a root canal infection occurs, a formation called a cyst may develop at the top of the tooth root, which appears as a pus-filled cavity with a fibrous lining on the inside.
A cyst, also often called a periodontal abscess, can gradually enlarge over time, causing serious discomfort to a person. The cyst located on the teeth of the upper jaw has the highest growth rate, which is facilitated by more porous bone.
If we look at the x-ray, then a strong darkening in the upper region of the root is a cyst.
Diagnosis of dental cysts
Since at an early stage the disease has practically no symptoms, it can be very difficult to determine. Nevertheless, there are certain diagnostic methods that allow you to identify a cyst:
- external examination, the task of which is to determine whether there is growth of the capsule in the gingival tissue;
- checking the integrity of existing fillings (if there are any violations in the root part, they begin to collapse, which is noticeable to the naked eye);
- X-ray;
- tomography of the jaw.
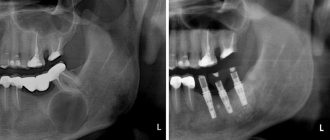
The surest way to make a diagnosis is an x-ray: the capsule filled with cystic fluid will appear as a bright white area (its shape can be round or oblong) located under the gum pocket.
Based on the location of the formation and the current stage of development of the disease, the doctor will be able to prescribe the most effective treatment.
Serous cystadenocarcinoma
Ultrasound reveals a complex cystic-solid formation in the left ovary, and another large complex formation containing both a solid and a cystic component in the right half of the pelvis
A CT scan of the same patient reveals a complex cystic-solid formation with thickened septa accumulating contrast in the right ovary, extremely suspicious for a malignant tumor. There is also bilateral pelvic lymphadenopathy (arrows). Histopathological examination confirmed serous ovarian cystadenocarcinoma (the most common variant)
CT scan and macroscopic photograph of serous ovarian cystadenocarcinoma.
Ultrasound (left) shows a large multilocular cystic formation in the right parametrium; Some of the chambers are anechoic; in others, uniform low-level echogenic inclusions are visualized, caused by protein content (in this case, mucin, but hemorrhages can also look similar). The partitions in the formation are mostly thin. No blood flow was detected in the septa, the solid component was also absent, and no signs of ascites were detected. Despite the absence of blood flow during Doppler ultrasound and a solid component, the size and multilocular structure of this formation allows us to suspect a cystic tumor and recommend other, more accurate diagnostic methods. Contrast-enhanced CT scan (right) shows similar changes. The formation chambers have different densities, corresponding to different protein contents. Histopathological examination confirmed mucinous cystadenocarcinoma with low malignant potential.
Types of cysts
To prescribe the most effective treatment, the dentist needs to determine the type of cyst and identify why it formed.
Cystic formations are:
- radicular (occur at the root of the tooth or in close proximity to it);
- residual (formed after tooth extraction);
- retromolar (formed as a result of problematic eruption of wisdom teeth).
Based on their origin, cysts are divided into:
- odontogenic (they are caused by various dental diseases);
- non-odontogenic (their formation is not associated with dental diseases).
Separately, it is worth highlighting follicular cysts, which contain the tooth germ: they are formed as a result of improper care of baby teeth.
Ovaries after menopause
Entering the postmenopausal period is defined as the absence of menstruation for one year or more. In Western countries, the average age of menopause is 51–53 years. In postmenopause, the ovaries gradually decrease in size and Graafian follicles stop forming in them; however, follicular cysts may persist for several years after menopause.
On a T2-weighted MR image (left) of a postmenopausal woman, the ovaries appear as dark “clumps” located near the proximal end of the round ligament. On the right, the tomogram also visualizes a hypointense left ovary, devoid of follicles. Although it is slightly larger than expected, overall the ovary appears completely normal. And, only if it is possible to detect an increase in the size of the ovaries compared to the initial study, the differential diagnostic series should first of all include a benign neoplasm, for example, fibroma or fibrothecoma.
Main symptoms of an abscess
A dental cyst may not reveal itself for a long time: a person may not realize that there is something wrong with his teeth and gums. Sometimes an abscess causes mild pain when biting or pressing on the gum. But barely noticeable and far from constant pain can force few people to go to the doctor: a cyst at this stage of development is discovered by chance when a person goes to the dentist about completely different teeth.
An infection in the abscess cavity can worsen if immunity decreases: the process of pus formation accelerates, severe pain appears, the cheek swells, the person feels weak and lacks strength, and the temperature rises.
Reasons for appearance
A coccyx cyst may not bother the patient at all throughout his life, but still certain prerequisites and factors can trigger its development. It can be:
- weakened immunity;
- injuries to the lower back and in particular to the tailbone;
- low level of physical activity;
- sedentary work that involves sitting in one place;
- infection of the body;
- lack of proper personal hygiene;
- inflammation of the follicles;
- severe hypothermia.
When exposed to unfavorable factors of the external or internal environment, the epithelial coccygeal duct becomes blocked
Sometimes the doctor does not detect any visible reasons for the development of such a cyst. And in some cases it does not begin to grow even with the combined influence of all factors.
Why does a cyst occur?
The main reason for the development of an abscess is the appearance of infection in the root canals. But there can be several reasons for infection:
- Advanced caries that has developed into pulpitis due to ignoring the need for its treatment. In the tissues on which the carious formation has appeared, pathogenic microorganisms settle, first entering the pulp, as a result of which its inflammation begins, then, if the pulpitis is not treated, penetrating beyond the boundaries of the tooth, resulting in a periodontal abscess.
- Unsatisfactorily filled root canals. Canal filling is a fairly common procedure that dentists have to perform during treatment. However, despite the routine nature of the operation for a dentist, not all specialists, due to lack of experience or due to inattention, carelessness and the desire to complete the work as quickly as possible, do it efficiently. The canal must be sealed along its entire length, since in the unsealed part there is a high probability of infection, which, just as in the case described above, will sooner or later go beyond the boundaries of the tooth and lead to the appearance of an abscess. Official statistics on poorly filled canals are depressing: in more than half of the cases, dentists make mistakes during the procedure, which subsequently result in the appearance of a cyst. In the picture, the unsealed part of the canal is always clearly visible. Sometimes it happens that the root canal is completely filled, but the material used for filling is loose, which is also not good.
Hormonal drugs
Conservative treatment is based on the use of various combinations of hormonal drugs. Gynecologists prescribe the following groups of drugs:
- If there is a deficiency or excess of hormones - “Duphaston”, “Urozhestan”.
- If it is necessary to reduce the level of the hormone that provokes the growth of formation - “Diane”, “Janine”, “Regulon”.
- To eliminate inflammatory processes - “Indomethacin”.
- To eliminate pathogenic microflora - “Vancomycin”, “Lincomycin”.
- To stimulate the immune system – “Timalin”.
To normalize hormonal levels and regression of education, specialists prescribe oral contraceptives. For treatment, a special drug regimen is developed. In some cases, COC therapy is combined with the use of gestagens, which block the pituitary gland and promote temporary replacement of hormones with artificial derivatives.
The drug Duphaston with the main active ingredient – Dydrogesterone – has proven itself especially well. The drug is actively used for the treatment of follicular formations and endometriosis. In the first case, it promotes the correct transition from the first to the second phase of the menstrual cycle, and in the second, it prevents the growth of the endometrium and the appearance of new capsules.
This drug is prescribed only by a doctor, who determines the dose and treatment regimen based on:
- Data obtained during the inspection.
- Nature of the pathology.
- Age.
- Analysis results.
In some cases, after taking large doses of the drug, side effects are observed, such as migraines, rashes, bleeding. But with proper treatment and dose selection, hormonal levels are normalized and the cycle improves.
If the inflammatory process or cyst formation is caused by pathogenic microflora, the doctor may prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics that can eliminate diseases of the reproductive system.
If the urinary system is disrupted, diuretics are prescribed, and if the formation is inflamed, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Additionally, agents that enhance immunity are used, for example, folic acid, vitamin C, E. To minimize pain, use Diclofenac or No-shpa.
To enhance the effect of medications, various physiotherapeutic treatment methods are prescribed. Most often used:
- Electrophoresis.
- Ultraphonoresis.
These procedures make it possible to enhance the effect of medications, normalize the function of the damaged organ, and prevent the development of inflammation. Physiotherapy is also used during the recovery period to reduce the likelihood of relapse, improve blood circulation and other factors.
Tooth cyst: treatment
Treatment can be divided into therapeutic (use of drugs) and surgical (gum incision and root resection).
Conservative treatment is justified if:
- no unsealing required;
- if the canal is unsatisfactorily sealed along its entire length;
- if the diameter of the cyst is large (over 1 cm), which is accompanied by pain and swelling noticeable even to a non-specialist.
Surgery is recommended when:
- there is a pin in the channel;
- there is a crown on the causative tooth;
- the root canals are unsealed at the upper part of the root for 1/3 of their length;
- The gums swell, which is accompanied by pain.
Endometrioid ovarian cancer
Bilateral cystic solid ovarian masses are suspicious for tumor and require further evaluation. The importance of radiological research methods is to confirm the presence of formation; however, it cannot be concluded with absolute certainty that it is benign or malignant. For patients who have epithelial tumors (a much more common group of ovarian neoplasms), even after surgical treatment, determining the exact histological type of the tumor does not affect the prognosis as much as FIGO stage, degree of differentiation, and completeness tumor resection.
The sonogram (left) shows enlargement of both ovaries, inside of which there is both a cystic and soft tissue (solid) component. A CT scan of the same patient reveals a large cystic-solid formation extending from the pelvis to the abdomen. The role of CT in this case is to stage the formation, however, based on CT (MRI) it is impossible to determine the histological structure of the tumor.
Description of therapeutic method of treatment
This method takes a lot of time, requiring a lot of patience from the patient (you will have to visit the dentist more than once), a lot of free time and significant financial expenses.
The process consists of a number of sequential stages:
- First, the doctor works with the canals. The dentist looks to see if they have been filled: if not, the pulp is removed, and the canals are processed using the instrumental method; if they were, then they need to be unsealed before proceeding with subsequent actions.
- The cyst contains pus, which is why after unsealing and getting rid of the pulp, repeated thorough rinsing of the canal with an antiseptic solution will be required.
- A potent medicine is removed from the apex of the root.
- The canal is temporarily filled with a paste that has an antiseptic effect.
- Since the medicine needs to be changed once every certain period of time, the patient will have to come to the dentist every time for this over the next couple of months. After the next change of medication, the canal is again filled with medicinal paste.
- From time to time, an x-ray is taken to monitor the progress of treatment and evaluate its progress. If the cyst in the picture becomes smaller over time, then this indicates positive dynamics.
- When the cyst shrinks, the doctor fills the canal with gutta-percha - this filling is permanent and periodic refilling is not required.
- Installation of a seal.
But even after placing a permanent filling, the patient still must visit the doctor for an image for another two to three months. It should show a reduction in the size of the existing abscess and restoration of natural tissue.
Drug treatment of dental cysts
If the size of the mass is less than 1 centimeter, your doctor may recommend trying medication.
The range of prescribed drugs usually includes:
- antibiotics (for example, azithromycin, amoxicillin, etc.);
- immunomodulatory agents (arbidol, dibazon);
- antihistamines (ketotifen, acrivastine, etc.).
Depending on the individual characteristics of the development of the disease, multivitamin complexes and antifungal drugs may be prescribed. On average, treatment takes about 2 weeks minimum; every 4 days it is advisable to visit a dentist, who, after an examination, will adjust the medication intake.
Removal of a tooth cyst
The operation is called root resection. It takes no more than an hour: the procedure time depends on the location of the damaged tooth (back teeth are easier and faster to treat, front teeth take much longer).
The operation consists of the following steps:
- A couple of days before the procedure, the canals are sealed (days, not weeks, otherwise early filling can cause purulent inflammation).
- Immediately before the operation, the doctor gives the patient a pain-relieving injection - local anesthesia (it does not hurt, the only thing is that it may hurt a little when the injection begins to “go away”).
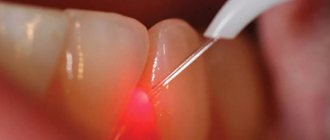
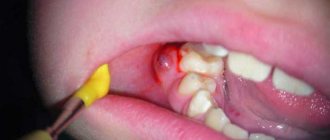
- The gum is cut, exposing the bone. A hole is made in the bone tissue near the tooth in which the cyst has formed, for which a drill is used (due to the anesthesia, the patient will not feel anything).
- The hole will allow the doctor to see part of the root and the cyst attached to it. This area of the root is cut off with a drill and removed from the resulting wound using tweezers.
- Since the cyst occupied a certain space in the tissue, after removal a cavity appears in its place. If the cyst is large, the doctor fills it with synthetic bone tissue, which stimulates the growth of normal bone.
- The dissected mucosa is sutured, and for a more effective outflow of the ichor, a drain is installed, which must be removed after a few days.
Resection in no way affects the lifespan of the tooth. The doctor’s task is to completely get rid of the cyst, since even leaving the slightest remnant of it can lead to its re-formation.
Removal or treatment of a dental cyst?
The question is of great importance for people who are afraid of dental operations.
Before deciding on a treatment method, you need to consider a number of nuances:
- if you treat the cyst with medication, it will take at least 3 months; in case of surgical intervention, you will have to visit the doctor only 3-4 times;
- Nowadays, in most surgical operations, a laser has replaced the scalpel, but in some cases it is still impossible to do without traditional incisions;
- if there are deep cracks on the tooth, you cannot do without surgical intervention - no modern medications will help in this case;
- Regardless of the chosen treatment method, the probability of cyst recurrence is about 10%.
In any case, the final decision regarding the method of treatment remains with the doctor, who, based on the analysis of the x-ray and other measures, can make the right choice about the development of the disease.
Malignant cystic ovarian tumors
Radiation diagnostic methods, such as ultrasound or MRI, are not intended to determine the histological type of tumor. However, with their help it is possible to differentiate benign and malignant neoplasms with varying degrees of certainty and determine further tactics for patient management. Detection of radiation signs of malignant tumor growth should direct the attending physician (gynecologist, oncologist) to further actively determine the nature of the cyst (surgery with biopsy, laparoscopy). In unclear and contradictory cases, it is useful to re-interpret the MRI of the pelvis, as a result of which you can get a second independent opinion from an experienced radiologist.
Get an MRI of the ovaries in St. Petersburg
Complications of a cyst on the root of a tooth
If the cyst was detected too late, complications cannot be ruled out. The following scenarios are possible:
- deformation of the dentition, which is fraught with the installation of removable orthodontic appliances to correct the situation;
- purulent inflammation that develops into abscesses and fistulas;
- pulp destruction;
- damage to healthy teeth;
- blood poisoning and further transfusion.
The only way to avoid complications is timely detection of the disease, so it is extremely important to visit the dentist at least once a year, even if there are no obvious reasons for this.
Is it possible to get rid of a cyst without visiting a doctor?
Dental treatment has long ceased to cause severe pain, which has become possible thanks to the development of medical technology, but many people still do not like the hassle of going to the dentist, delaying the visit until the last minute.
A person who notices a cyst often tries to get rid of it with the help of strong antibiotics, hoping that the drugs will eliminate pathogens and stop the inflammatory process. However, none of the most modern medications will change the situation for the better if you do not get rid of the infected tissue, treat the root canals with an antiseptic and do not seal them thoroughly. Yes, antibiotics are also needed, but they play the role of an auxiliary, not a primary remedy.
All other traditional methods of treatment (applying lotions, rinsing with various solutions, using homeopathy) bring temporary relief and do not solve the problem. The pain may subside, and the cyst may even decrease slightly for a while, but the inflammatory process will continue to progress.
An abscess is quite insidious because it can develop over a long period of time without any symptoms at all. Dentistry knows many examples when a cyst grew to enormous sizes, turning into a pus-filled sac 6 cm in diameter. In such advanced cases, saving the tooth becomes extremely problematic.
Functional neoplasms
When diagnosing functional formation, 90% use conservative methods. It uses hormonal drugs that affect the follicular and luteal capsules. Gynecologists most often choose progesterone-based tablets “Regulon”, “Janine”, which reduce the concentration of estrogen in the blood. After treatment, to stabilize hormonal levels, Duphaston courses are prescribed for up to 2 months.
Sometimes experts may recommend using traditional medicine methods. Most often this is brewing infusions of chamomile, calendula and other herbs that help activate the immune system and reduce pain. But traditional medicine methods are used exclusively in an auxiliary role and cannot replace drug treatment.
It is important to take into account that after 50 years, functional cysts do not form, which is due to physiological changes in the female body. At this age, the risk of malignancy of other types of formations is highest.
Prevention measures
To avoid cyst formation, you need to:
- brush your teeth twice a day, or better after every meal. If this is not possible, then it is worth purchasing an irrigator that will allow you to rinse the mouth;
- once a year take a photo of the jaws and maxillary sinuses;
- correct any dental disorders at an early stage, preventing their development;
- try not to injure the jaw;
- Visit the dentist twice a year to examine the condition of your teeth and gums.
Cystic metastases to the ovaries
Most often, metastases to the ovaries, for example, Krukenberg metastases - screenings of stomach or colon cancer, are soft tissue formations, but often they can also be cystic in nature.
A CT scan reveals cystic formations in both ovaries. You can also notice a narrowing of the rectal lumen caused by a cancerous tumor (blue arrow). Cystic metastases of rectal cancer are clearly visible in the recess of the peritoneum (red arrow), which in general are not a typical finding.
Choosing a clinic for cyst treatment
A large number of hospitals and dental offices have now opened, but not all of them provide truly high-quality services: situations where people, having parted with money for treatment, not only did not get rid of the disease, but ended up with an even bigger problem, are, unfortunately, not uncommon .
To avoid mistakes, you should try to find out the following information before your visit:
- how long has the dentist been practicing, does he have enough experience to perform surgical interventions;
- The clinic also has dental microscopes in its arsenal, which allow us to examine the affected area in as much detail as possible and efficiently fill the canal.
Choosing a professional doctor is the key to quality treatment the first time.