- general information
- Compound
- Advantages of the drug
- Flaws
- Mode of application
- Review of manufacturers
- Price
Almost all patients, having decided on artificial restoration of teeth through prosthetics, know little about the materials used during the operation. Perhaps very few people know that there are a huge number of cement composites, each of which is designed for a particular clinical case. What is glass ionomer cement, what are its features and advantages, manufacturing specifics and varieties - this material is dedicated to this.
General information about glass ionomer cement
Glass ionomer cements (hereinafter referred to as GIC) are the latest innovative mixtures characterized by a heterogeneous structural content, where the base part is aluminosilicate glass, and polyacrylic acids act as a polymer matrix.
GIC is the optimal solution for placing fillings on a temporary basis, as well as being used as insulating liners.
Initially liquid in consistency, the mass gradually hardens and takes on the desired state. This happens in several stages:
- dissolution – the process of formation of ions;
- gelation – creation of gel-polymer chains, increase in pH level. The duration of the transition to this state is about 5 minutes;
- complete hardening of the material occurs within 24 hours.
The mixture reacts well with hard tooth tissues, intensely releasing fluoride elements. It is characterized by an average degree of strength, interacts better with enamel than with dentin tissue, and has an inhibitory effect on previously formed caries manifestations.
General overview
From the point of view of the current classification, glass ionomer cement belongs to the category of materials based on the combined structure of a silicate system and a polyacrylic polymer of the thermoplastic group. The functional properties of the composition determine the rapid growth of its popularity - GIC can be considered as the next stage in the evolution of cement materials, replacing traditional zinc-based phosphate and polycarbonate compositions.
Differentiation of glass ionomer cements involves the use of three criteria:
- By area of application, they are divided into compositions for fixing prosthetic and corrective systems, treating and restoring the structure of dental tissue, securing fillings and onlays, as well as ensuring tightness and adhesion;
- Based on the form of release, there are powder materials, capsule modifications, as well as photopolymer cement paste that does not require pre-mixing;
- According to the mechanics of hardening, the already mentioned photopolymer compositions are divided, as well as materials that harden as a result of a chemical reaction with water.
Composition of glass ionomer cement
The filling component consists of standard elements for such materials - distilled water and powder mass. As a result of their interaction, they become solid from a liquid state - this is ensured by the influence of acidic processes.
Most often, alkene polymers are used to create GIC:
- maleic;
- polyacrylic;
- itaconic.
They help reduce the viscosity of cement, slow down the process of gelation of the liquid and bind all the elements into a homogeneous mass several times faster. These qualities have a positive effect on the service life of the composition.
The liquid part basically contains distillers or tartaric acid. Powder – calcium silicate glass and calcium fluoride drops.
Upon completion of the filling processes, fluoride ions begin to be actively released into the oral cavity, which is an excellent obstacle to the development of secondary caries manifestations. The silicate substance is necessary for proper acid reactions to occur. Mineral substances in contact with glass form a silicon film, which is subsequently impregnated with acidic masses. In this case, the processing time becomes shorter, and the hardening time, on the contrary, becomes longer. The same principle is used to ensure hygroscopic reduction.
Structure
The structure of primary and secondary cements is different.
- Primary (acellular) consists mainly of collagen fibers, as well as an amorphous adhesive substance.
- The secondary (cellular) structure is similar to coarse-fiber bone, only without blood vessels, and contains mainly cementocytes, cementoblasts and intercellular substance.
Unlike real bone tissue, cement is nourished diffusely through the periodontium. The chemical composition consists of organic substances, which make up 32%, and inorganic substances, which make up 68%.
Advantages of glass ionomer cement
Glass ionomers have the following advantages, in comparison with analogue filling materials:
- ease of use - cement fills the cavity in one or two portions. Its use does not involve the processes of preliminary etching of the area and bonding of dentin;
- the unique property of hardening even in a humid environment - this quality ensures the active use of the composition in the treatment of caries cavities in the cervical zone, elimination of wedge-shaped pathologies, as well as caries, the affected area is the area located below the gum level;
- connection of the component with the tissues of dentin and enamel according to the intermolecular principle - makes it possible to install fillings with excellent marginal fit and eliminates the need to create retention areas during the treatment of the organ;
- complete adhesion to compositions with clove oil - thus, GIC is used as insulating liners that protect fabrics from excessive attachment of composites to them;
- adhesion to metal components;
- the ability to release ion enzymes into the organ cavity for at least a year after the filling is installed;
- weak shrinkage during polymerization - at the moment of transformation into a solid state, cement slightly increases in volume, which partially compensates for shrinkage processes;
- no irritating effect on dentin and pulp tissue - their composition is not aggressive and not dangerous in the treatment of deep caries if cement is used as a spacer;
- the thermal expansion indicator corresponds to the coefficient of expansion of the organ tissue - in such a situation, the filling is fixed more reliably, lasts longer, and its marginal fit is an order of magnitude better. This is a good preventive protection against the formation of damage to the enamel surface - cracks, chips.
How to choose the right dental cement - dentists advise
You should not judge cement by such standards as the best cement for fixing crowns. Experts say that this concept does not exist. Each has its own pros and cons.
Against this background, it would be more correct to say that you need to make a choice regarding each individual situation.
How to choose the best cement for crowns?
When making this choice, you need to focus on a number of parameters in the form:
- Strength: i.e., how a frozen substance compresses and unclenches during eating or closing teeth for other reasons.
- Adhesiveness: here we are talking about how artificial cement bonds with natural dental tissues.
- Irritability : namely, whether the cement will cause an allergy, whether it will lead to rejection of the remaining natural teeth and gum mucosa.
- Removal difficulties : this parameter is important in a situation where there is a need to remove a permanent prosthesis, replace it with another, or if the doctor allows it to be defective at the stage of fixing it - and then quickly eliminate it.
- Aesthetics: when a prosthesis is installed in the smile area, both the retainer layer and its exact match to the shade of the product are taken into account.
Rate
—
Disadvantages of glass ionomer cement
The material is not without its shortcomings, some of which are quite significant:
- long maturation of the cement composition - it completely hardens only a day after installation, despite the fact that the first setting occurs within a few minutes;
- in the first hours the mixture is sensitive to a humid environment - it is at that stage that active leaching of ions occurs, which slows down the processes of final polymerization;
- poor resistance of the structural content to mechanical vibration - the material cannot be affected by a conventional drill immediately after installing the filling;
- etching of organ tissue is unacceptable;
- limited use for complex caries with a deep damaging effect;
- poor resistance to diametric tension, which completely excludes the use of GIC for the treatment of occlusal surfaces, as well as in clinical situations when the load on the tooth is distributed in different directions;
- shorter service life compared to conventional cement composite;
- average level of aesthetics, which limits its use on the frontal areas of the jaw row.
How are cementum, tooth sensitivity and periodontitis related?
Loss of cementum contributes to a number of dental problems, such as tooth sensitivity, loss of enamel, and gum recession . When cementum is lost, the dentin underneath is exposed, and this, in turn, can cause tooth sensitivity. The latter manifests itself as short-term or acute pain in the area of one or more teeth. If you've ever winced and winced painfully after taking a sip of cold water or juice, you know the feeling!
While cementum loss can trigger the development of some dental diseases, other dental diseases can trigger cementum loss. Such diseases include, for example, periodontitis. Cementum loss occurs when there is irreversible damage to the bone and connective tissue fibers that hold the tooth in place. Such damage to bone tissue and cement is characteristic of progressive periodontitis and leads to tooth mobility, which in some cases even has to be removed.
Method of using glass ionomer cement
The algorithm for using standard glass ionomer cements is as follows:
- thorough treatment of the working area with a conditioning liquid, which is washed off 20 seconds after application and the cavity is well dried;
- the damaged tooth is isolated from moisture and salivary secretions for the entire period of setting of the mass - about 5 - 6 minutes;
- the liquid and powder composition are mixed until a shiny, homogeneous thick mass is obtained;
- they place it in the organ cavity and form a filling, while ensuring dense condensation using a cotton swab or a special device with a spherical movable working tip;
- after giving the filling the desired shape, its relief is coated with varnish;
- after 1 – 2 days, treat with a drill. After this, the tooth can function normally.
General characteristics of the material
Dental cement
It contains powder and liquid, when mixed, a paste-like mass is formed.
Dental glass is used to mix dental cement .
An accompanying attribute is dental glass for mixing cement, available without a hole, with 1, 2, 3 holes
During the hardening process, the mass begins to harden and becomes like stone. Hardening occurs as a result of the components entering into a chemical reaction.
The main indicators that high-quality dental cement
, the following:
- mixing time;
- work time;
- curing time.
Mixing time refers to the period of time recommended for preparing the solution. Typically this figure is 90 seconds , and it is not recommended to exceed it.
The time during which the doctor must have time to apply the mixture to the tooth and model the filling is called working time. Each manufacturer of dental cement has its own characteristics, but the average varies from 4 to 10 minutes .
The period allotted for hardening of the cement mass also varies among manufacturers. Sometimes it can take a week for the ingredients to react and cause hardening. An important role in the setting of the material is played by the temperature and mixing proportions of dental cement.
with liquid.
Overview of glass ionomer cement manufacturers
Despite the fact that the composition of the GICs of the main manufacturers is almost identical, the following line of leading manufacturers are distinguished in the domestic market of dental materials, firmly holding the rating for a long period of time. It is advisable to consider the features in more detail.
Arde Kwik Tsem
It is a fluid hybrid mixture of a double solidification principle. Ideal for attaching veneers, bridge devices, and inserting pins during restoration with implants.
Thanks to its unique structural content and viscous consistency, it ensures the highest quality filling of the tooth cavity.
It has a serious disadvantage - it can provoke individual intolerance and cause allergic reactions of varying degrees of intensity.
Arde Fix
It is used for permanent fixation of orthodontic and prosthetic devices. Not prone to dissolution and oxidation in the oral cavity. If the composition is mixed correctly, side effects and complications are completely excluded. May cause a short-term decrease in the sensitivity of taste buds, which resolves spontaneously after some time. It does not tolerate the presence of eugenol elements in the work area.
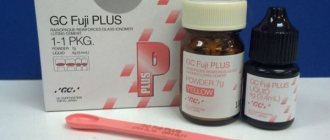
Fuji Plus
A distinctive feature of the mixture is its modification with a composite, which provides a number of advantages:
- stronger fixation;
- possibility of use when interacting with metal, non-metal, ceramic prosthetic structures of all types in the process of orthopedic manipulations.
The disadvantage is the weaker light reflectivity of the material in the solid state.
Ketak Tsem
The main advantage is simplicity and ease of use. Shorter time for manual mixing and bringing to the required consistency.
It has high aesthetic indicators - a matte, slightly silky surface, which is especially important when working on the frontal area of the jaw.
The disadvantage is sensitivity to low temperatures, which increase the hardening time.
Tsemion F
The composition has good radiopacity, withstands high mechanical loads in comparison with analogue products, and has a low solubility index.
Adhesive to enamel and dentin tissues.
Allows you to achieve a high level of marginal sealing, releases fluoride over a longer period of time, which helps strengthen tooth enamel. It has a low pain sensitivity threshold and causes virtually no discomfort in patients during the rehabilitation period after treatment.
Features of various cements for crowns
Table 1. Features of various cements for crowns
| Type of cement | Example | Characteristics | Application |
| Composite cement | High strength and adhesiveness, aesthetics. | Suitable for fixing not only ceramic crowns, but also veneers and lumineers. | |
| Zinc phosphate cement | One of the very first cements used. Easy to use. Has average strength and adhesiveness. May temporarily increase tooth sensitivity (up to 3 weeks). | Suitable for single crowns and small bridges. | |
| Glass ionomer cement | This aluminosilicate glass with a high fluorine content is an excellent caries prevention. High adhesion, but low strength. | It is used for increased risk of caries and high tooth sensitivity. | |
| Polycarboxylate cement | High biocompatibility, serves as additional prevention of caries. However, it has low adhesiveness and strength. | Used for fixing single crowns with high tooth sensitivity. | |
| Modified glass ionomer cement | Innovative material. Combines the advantages of composites and glass ionomers: high strength and adhesiveness. | It is used for installing both single crowns and bridges. Suitable for people with an increased tendency to caries. |
Glass ionomer cement price
Depending on the manufacturer, the cost of cement of various brands looks something like this:
Arde Kwik Cem - from 1,300 rub.
Arde Fix - from 1,420 rub.
Fuji Plus - from 1,520 rub.
Ketak Tsem - from 1,380 rub.
Tsemion F - from 1,240 rub.
Having placed a filling from the material discussed in this article, you don’t have to worry that after a short time it will crumble under temperature or mechanical influence. And although in some respects cement is inferior to more expensive mixtures, with proper use the tooth will retain its functionality for a fairly long period of time.
Fixation of dental crowns
At certain stages of orthopedic treatment there is a need to use temporary crowns. In such cases, temporary fixation of crowns with special cement or artificial resin is used. The main feature of these materials is that the temporary structure can be removed without difficulty. Adhesive materials are easy to clean and leave no residue.
There are two types of permanent fixation of crowns in dentistry: cement and screw. With the development of implantology, they began to separate fixation on their teeth and on implants.