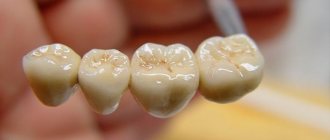
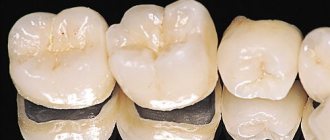
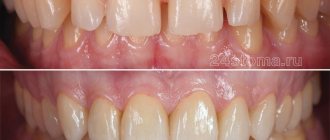
Today, dentists have a lot of options for prosthetics - restoring a damaged or missing tooth. One of the most effective solutions is metal ceramics - it is reliable and aesthetic. With its help, you can restore one or more teeth, and the structure is supported by implants or the patient’s own teeth.
Metal-ceramics are orthopedic structures - crowns and bridges, which are made by spraying or casting ceramics onto a metal base or frame. This method of prosthetics is in great demand, since the material used to restore the shape and function of the tooth does not cause allergic reactions. Metal-ceramic prosthetics are more often performed for the masticatory region, since in this case the strength of the structure is a priority, but this does not at all deprive artificial teeth of their aesthetics. Such designs closely replicate the structure and color of natural teeth.
Structure and types
Metal-ceramic dental prosthetics got its name due to the structure of the structures: inside it has a cast metal frame with a thickness of 0.3-0.5 mm. The material of manufacture is cobalt or nickel-chromium alloys. In some cases, alloys of precious metals - platinum or gold, palladium and others in different proportions - can be used. Crowns are divided into corresponding types according to this parameter.
The use of gold has an undeniable advantage - due to the natural yellowness of the precious metal, it is possible to achieve a natural shade of the structure, which is especially in demand when it is necessary to replace the front teeth.
The metal frame is covered with ceramics. The base is veneered using manual layer-by-layer application of ceramic mass. The structure is fired in a kiln after each layer is applied - this allows for the best connection between metal and ceramics.
As for the structure of the structure, the following types of metal-ceramics in dental prosthetics are distinguished:
- Actually single crowns. They are widely used to restore teeth in the lateral zone when they are more than ⅔ destroyed.
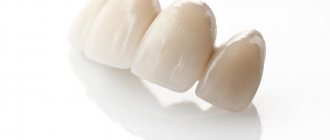
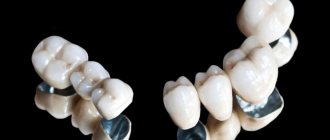
- Bridges. They are designed to restore several missing teeth in a row. The most reliable design is considered to be two crowns for supporting teeth and 2 artificial teeth between them.
General overview and features
Conventional crown models are equipped with a metal rim in contact with the gum. The metal element shines through the gum tissue and reduces the aesthetics of the smile. Because of this disadvantage, metal-ceramic prostheses are not used for reconstruction of the frontal zone of the dentition. The shoulder mass (ceramic composition) disguises the rim and eliminates the aesthetic defect.
Installation of a metal-ceramic crown certainly requires a tooth preparation procedure and the formation of a circular ledge. Due to the high strength of the structures, it is recommended to use them for the reconstruction of chewing units.
Advantages and disadvantages of metal ceramics
Compliance with manufacturing standards and installation technology almost completely eliminates possible harm from installing the structure. The use of modern materials eliminates the release of toxic substances, but it is important to remember that an individual reaction may occur.
The ceramics itself, used in the manufacture of artificial teeth, does not cause allergies - a possible reaction is provoked by the metals in the frame of the structure. For example, chromium-nickel alloys can provoke an allergic reaction to nickel, and the use of base metals under the influence of saliva can be susceptible to oxidation reactions. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- burning in the mouth;
- metallic taste;
- swelling of the gums in the area of contact of soft tissues with the crown.
If such symptoms occur, it is important to consult a dentist - you will probably need to replace the structure with an all-ceramic crown or use another prosthetic method.
Other disadvantages include the possibility of exposing the metal frame in the event of receding gums. It is worth noting that structures made of zirconium dioxide are not subject to this phenomenon. In addition, the technology of metal-ceramic dental prosthetics involves grinding the tooth under a crown and removing the pulp in many cases, which is also a disadvantage.
The advantages of metal ceramics include high strength and long service life. Today, metal-ceramics are used for both single crowns and bridges - it is in demand when it is necessary to replace teeth with a significant chewing load. The frame made of aluminum dioxide or zirconium is strong enough, so the dentures can withstand heavy loads.
A long service life - 10-12 years for alloys of base metals and about 15 in the case of using a gold-platinum alloy - is a key advantage of the designs. This is only relevant for those prostheses that are made using individual casts. It is also important to follow the doctor’s recommendations for care - in this case, the prosthesis will last as long as it should. This is necessary because one of the common reasons for premature crown removal is the development of secondary caries at the junction of natural and artificial tissues, so it is very important to visit a doctor in a timely manner.
To summarize, we can say that the advantages of metal ceramics are as follows:
- comfort of wearing structures;
- functionality - function is restored due to the flawless modeling of masticatory hillocks;
- strength;
- long service life;
- acceptable aesthetics;
- biological compatibility - in the absence of allergic reactions to metals;
- the possibility of prosthetics for both anterior and chewing teeth;
- shade fastness - ceramics are not susceptible to the action of dyes;
- comparative cheapness;
- the possibility of restoring the structure without removing it in the event of minor chips.
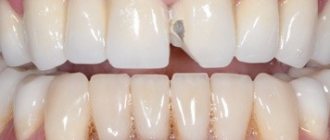
Color of metal-ceramic structures
Separately, I would like to note the advantage of metal-ceramics, due to which many patients prefer it - ceramics, which is used for the manufacture of structures, allows you to imitate the shade and structure of your own tooth enamel. Therefore, the prosthetic tooth is similar to the patient’s natural teeth. The shade is selected according to the Vita scale - the selected color will remain that way throughout its entire service life, since ceramics are not subject to darkening and do not tend to absorb dyes from drinks and food.
The only thing that can change the shade of an artificial tooth is pigmented plaque, which is easily removed with professional oral cleaning.
Indications for metal-ceramic prosthetics
A doctor may recommend this method of tooth restoration for the following indications:
- severe tooth decay as a result of caries or injury - the impossibility of restoring it with fillings;
- anomalies of dental development that disrupt the function and aesthetics of the dentition;
- the absence of 2 or more teeth in a row and the presence of supporting teeth on the sides of the dentition defect (cermet bridges can be used here);
- inability or unwillingness to use other prosthetic methods.
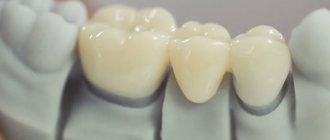
Crowns for chewing teeth
The main load when chewing falls on the back teeth. This is associated with increased strength and reliability requirements for crowns on chewing teeth.
Due to the large width and extent of the chewing surface and the correspondingly larger contact area of the upper and lower teeth, a decrease in pressure per unit surface can be assumed.
In simple terms, the risks of chipping the ceramic surface in the crowns in question are not great, and the only special requirement is that there is a certain relief on the contact surfaces of the upper and lower teeth, the so-called cusps, the presence of which ensures effective chewing of food during various lateral movements of the lower jaw.
Contraindications
This prosthetic method cannot be used for:
- periodontal disease;
- bruxism (in this case, it is important to first correct the condition or cure the disease, otherwise the structure may damage the teeth that come into contact with the crown when the jaws close);
- malocclusion;
- allergic reactions to metals and alloys;
- shortened crown parts of teeth;
- periodontitis is a temporary contraindication that requires preliminary treatment of the disease.
Stages of metal-ceramic prosthetics
The process of dental prosthetics with metal-ceramics can be divided into two large stages: preparation and prosthetics itself. An initial consultation with an orthopedic dentist allows you to determine the scope of work to be done, assess the condition of the oral cavity, and discuss options for restoring the shape and function of the tooth. According to the drawn up treatment plan, the patient is sent for diagnostics.
Preparing teeth for metal-ceramic prosthetics consists of the following:
- Performing X-ray diagnostics. It allows you to determine the absence of inflammatory changes in the periodontal tissues and evaluate the quality of filling if endodontic treatment was previously carried out (the pulp was removed and the root canals were sealed). If the canals are sealed poorly - not completely or, conversely, with the filling material extending beyond the apex of the root, the doctor will unseal them and carry out repeated treatment.
- Professional teeth cleaning and caries treatment, replacing old fillings, if necessary.
- Depulpation - removal of a nerve. If the damaged tooth has not been depulped previously, the doctor performs this procedure in the following cases:
- the presence of inflammation at the apex of the tooth, pulpitis;
- the need for prosthetic replacement of a single-rooted tooth - the pulp must be removed.
If prosthetics of a multi-rooted chewing tooth is required, the pulp can be left intact - but the final decision on this is made by the dentist, taking into account the individual characteristics of the condition of the oral cavity and the structure of the dental system.
In order to determine how dental prosthetics are done with metal-ceramics, it is necessary to take into account the degree of tooth destruction. Thus, a stump inlay for a metal-ceramic crown is made in cases where the tooth’s own crown is destroyed by more than half - at the root, or if only thin walls remain.
And if a larger volume of tissue is preserved, a pin can be used - it is screwed into the root canal, and an artificial crown is installed on it.
The actual stages of dental prosthetics with metal-ceramics are as follows:
- Tooth preparation - grinding. The question of whether teeth are anesthetized during metal-ceramic prosthetics, as a rule, is not raised - of course, the specialist performs preliminary anesthesia to eliminate the patient’s discomfort during the procedure.
The doctor grinds the teeth and then takes impressions - this is necessary for the further production of artificial structures according to individual parameters. Turning is carried out in one of two ways:
- with a ledge - the orthopedic dentist forms a circular ledge along the lower edge, which protects the gums from contact with the metal frame and reduces the likelihood of possible complications - swelling, irritation from contact of tissues with metal. This method also allows the use of metal ceramics with shoulder mass - it is applied in the area of the ledge to increase the aesthetics of the structure, and makes it possible to hide a strip of metal that can be visible through the ceramics at the base of the structure. Turning with a shoulder also makes it possible to extend the life of the structure;
- without a ledge - this method is outdated, so it is rarely used today. It has significant disadvantages - it does not provide enough space for a crown and can disrupt the contours of the gums. A space is formed between the structure and the gum tissue, in which dental plaque accumulates, and the edge of the denture looks quite unaesthetic. The design may cause irritation to soft tissues.
When contacting the clinic, find out how dental prosthetics are done with metal-ceramics - using the first or second method. This will avoid possible troubles with further wearing of the structure.
- Making an impression. Using impression material, the doctor takes impressions of the ground teeth. In order to accurately reproduce the parameters of the teeth, the gums are shifted using rings or retraction threads.
- Installation of a temporary crown. Due to the fact that the production of a permanent structure takes a certain time - about 1-2 weeks, the doctor installs a temporary crown made of plastic. This is necessary to protect the tooth core from food and saliva, as well as to ensure aesthetics. While the patient wears a temporary crown, a metal frame is made in the dental laboratory, onto which ceramic mass is subsequently applied layer by layer.
- After the permanent crown is made, it is installed using temporary cement after preliminary fitting of the structure. If it does not cause discomfort, the doctor will fix the crown using other, permanent materials.
Advantages and disadvantages
A metal-ceramic crown with shoulder mass in SPB has numerous advantages:
- durability;
- tight and precise fit to the ledge;
- strengthening the edge of the prosthesis;
- eliminating the risk of developing inflammation in the mucous membrane;
- preventing blackening of the gums in the neck of the tooth.
Thanks to the shoulder mass, the metal strip on the tooth is not noticeable at all. It is impossible to distinguish a denture from a natural dentition.
Most dentists provide installation services for such prosthetic structures. The doctor performing the installation procedure must have special knowledge and experience. The manufacturing technology of the product is complex and requires extreme care and skill from the dental technician. Another disadvantage is the high cost of prosthetic products.
How is a crown made?
Many patients wonder how long it takes to have metal-ceramic dental prosthetics. It is important to understand here that the procedures for preparing the teeth and the installation itself are carried out quite quickly, but the manufacture of the structure takes longer. As a rule, 1-2 weeks are enough to make a metal-ceramic crown. Based on the casts created, specialists make a plaster model - it is cast according to the impression after a preliminary assessment of its quality.
Then a dental laboratory specialist models a framework for metal-ceramics using wax. The finished frame is fixed on a plaster model and sent to an orthopedic doctor so that he can try it on in the patient’s mouth.
Then ceramic mass is applied to the frame. Before this is done, it is fired in a kiln and sandblasted - this allows for better adhesion of the metal and the ceramic mass.
The opaque is applied first - this is an opaque composition, then the structure is covered with a dentin layer (more transparent), and then with an enamel layer. This technology makes it possible to recreate the natural appearance of a tooth, taking into account the individual characteristics of the color of the enamel of your own teeth.
After the patient has tried on the design, glazing and final firing are carried out - then the crown is installed.
Types of alloys in metal ceramics
Gold-platinum alloy
The classic version with which orthopedic dentistry began. The first crowns were made from gold at the end of the 19th century.
Nowadays, many materials have appeared that, along with solving the problem of restoring chewing function, are quite durable and at the same time meet high aesthetic and cosmetic requirements. But gold, as a material for the manufacture of frames for metal-ceramic prostheses, is still relevant today.
Only a noble alloy can adhere so precisely to the treated tooth, which practically eliminates disintegration and recurrent caries. Gold almost never causes allergies.
The disadvantage of using a gold alloy is the limitation on the length of the intermediate (located between two supports) part of the metal-ceramic bridge (in the manufacture of metal-ceramic bridges), as well as the price: the cost of such a crown is from 10,000 rubles.
Sometimes, to improve color rendition, on a metal frame cast from other metals. a thin layer of gold is applied, which illuminates through a layer of ceramic mass with a warm yellowish color.
Nickel alloy
Most often, nickel-based alloys are used to cast the frame, which is the most accessible of the metals that can be the basis for metal-ceramics. With nickel alloys there are no problems when casting and fitting in the patient's mouth.
However, despite all the advantages, nickel has a serious drawback. This metal is a strong allergen.
Our body's daily need for nickel is thousandths of a gram, and the production of one metal-ceramic crown requires 2 grams of an alloy containing 1.3 grams of nickel. Thus, the metal is in contact around the clock with the oral mucosa, tooth tissues, and jaw. The result is allergic reactions and weakened immunity.
In Germany, they abandoned the use of nickel in dental prosthetics 10 years ago (as well as stainless steel back in the 30s).
Cobalt-chromium alloys
The most optimal option taking into account biocompatibility and cost.
In cost, they are only 1.6 times more expensive than allergenic nickel alloys. The biocompatibility of the cobalt alloy is 36% (for the gold-platinum alloy it is 42%, and only one’s own teeth are 100% biocompatible), they are non-toxic and do not cause allergic reactions. Cobalt alloys are durable, and metal-ceramic bridges of fairly long length can be made from them.
Chromium alloys are not dangerous; only some of its salts are poisonous, but they cannot form in the oral cavity.
Molybdenum
A non-toxic metal, it is added to dental alloys in very small quantities to improve casting properties.
Beryllium
This metal is a carcinogen. It causes granuloma (a type of malignant tumor) in the lungs, liver, spleen and heart. Upon contact with beryllium, skin diseases develop and a severe weakening of the immune system is observed. In Russia, its use in dental alloys is prohibited.
Features of caring for metal ceramics
Everyday hygiene measures do not differ from normal procedures - it is important to brush your teeth twice a day, and also rinse your mouth, if possible, after eating.
Cleaning the teeth should be carried out as follows: using sweeping movements, you need to go over all the teeth in the direction from the gums to the cutting edge. You should not ignore the use of dental floss, or better yet, an irrigator.
You can clean metal ceramics in the same way as regular teeth - a toothbrush should be purchased in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations (the degree of stiffness of the bristles is determined by individual characteristics), the toothpaste can also be selected based on your needs.
Remember that it is better to protect metal-ceramic structures from mechanical damage. It is not recommended to bite into hard foods - this can result in cracks and chips, and subsequent breakage of the prosthesis.
Warranty for metal ceramics
A good dental clinic provides a guarantee for metal-ceramic dentures - its period, as a rule, is less than the service life of the structure. If the prosthesis breaks before the warranty period expires, the clinic provides restoration or replacement services free of charge.
Restoration is carried out in case of mechanical damage to the crown - for example, chips. In this case, the prosthodontist assesses the extent of the problem and determines whether the framework of the structure is exposed. Restoration of a small chip that does not expose metal is carried out using composite materials. However, restoration when the frame is exposed may be impossible; the optimal solution here would be to remove the structure and re-prosthetics. In order to prevent unpleasant situations (chipping, crown loss), it is important to promptly replace metal-ceramics after their service life has expired.
It is important to make a choice regarding the type of metal-ceramic structure, taking into account how long you plan to wear the structure. Of course, the best can be considered to be made from a gold-platinum alloy; its service life reaches 15 years, and zirconium dioxide crowns can last even longer with proper care. However, the cost of such solutions will vary.
Cost of metal-ceramic crowns
| Name | Price, rub.) | Additional Information |
| Metal-ceramic crown | 2950/3950/4950 | Made in Germany, Japan |
The price of a crown, as a rule, consists of the cost of the crown itself, as well as fixation of the crown with permanent cement and impressions. Unfortunately, advertising often uses tricks in which the price is indicated, and then it turns out that it is necessary to add to it, for example, “the work of a doctor” and other similar elements that increase the price of the original price by two or more times.
But patients are interested in the final cost, the so-called turnkey price. And it is right. Because when comparing prices for metal-ceramic crowns in Moscow, it is fair to rely on the final real costs of identical work in different clinics.
Let's take a look at pricing at Amazing Price Dentistry. At a price of 2,950 rubles for a crown made from German-made materials, you need to add 1,200 rubles for impressions and 300 rubles for fixation, that is, one metal-ceramic crown will cost 4,550 rubles. It seems that the price is less than the minimum prices in Moscow (6,000 rubles) by only 1,450 rubles.
But if you calculate, for example, 2 bridges of 4 units with two supports in each, it comes out to 23,600 for crowns, 1,200 for fixation and 1,200 for casts. Only 26,000 for 8 teeth, that is, 3,250 rubles each!
Thus, the price of a turnkey metal-ceramic crown made of German material at Amazing Price Dentistry is almost half the minimum price (6,000 rubles) in Moscow for similar work.