Dental crowns in our clinic
Specialists from the Beryozka clinic will help you place strong dental crowns based on an individual impression. Our doctors work according to the most modern treatment protocols, which ensures maximum similarity of the artificial crown with the real one. High-tech materials ensure long-lasting wear even with intensive use of the crown.
Making a crown based on an individual impression ensures the most comfortable use. And budget prices allow you to restore the beauty and functionality of the jaws to a person with any income.
Free consultation!
You can get acquainted with the specialists of the Beryozka clinic and decide on the need to install a crown at a free consultation. Our doctors are confident that the patient, once in their hands, will definitely return for treatment. This is facilitated by the beautiful and comfortable environment in the offices, friendly and polite staff, as well as the high professionalism of the dentists.
What will result from untimely replacement?
People are reluctant to visit dental offices, but if you experience discomfort from a crown, you should immediately contact a specialist. Untimely replacement of the prosthesis threatens the following negative consequences:
- Root destruction - a cap not only allows you to restore the function of a damaged tooth, but also protects its root from further deformation. Over time, the supporting part is negatively affected. The bond is gradually destroyed by the action of saliva, which ultimately contributes to the accumulation of food debris and microbes. It is impossible to remove them with a toothbrush, so the process takes a long time and is asymptomatic. As a result, the root is destroyed, which may subsequently lead to the need to remove it.
- Development of inflammatory processes - inflammatory processes can develop in the gums, which not only cause discomfort, but also lead to more serious consequences. If the prosthesis (especially a low-quality one) is not replaced in a timely manner, you can lose all adjacent teeth.
A dentist, whose visits should be regular, will help you make sure that you need to replace the crown. It is important to understand that it is almost impossible to determine this on your own and, as a rule, patients turn to a specialist already too late.
What is a dental crown
The visible part of a natural tooth is the crown. It is most often destroyed due to caries, trauma or the process of demineralization. It can be restored with an artificial prosthesis - a dental crown. It can be temporary - for the period of treatment, or permanent - for every day. In some cases, crowns are used to correct the shape of implants when they are damaged.
Prosthesis replacement technology
If the need to replace the prosthesis is identified, then the procedure involves performing the following actions:
- Removal of the old crown and production of a temporary prosthesis. It is made using a silicone key.
- Assessment of tooth condition. If the root is in order, then it must be cleaned, processed to give it the correct shape, and also remove possible caries.
- Impressions are taken to make a new crown and sent to a dental laboratory. The duration of production depends on various factors, but in any case, the patient does not walk without a prosthesis. On the same day, a temporary cap is installed.
Upon completion of the crown, the doctor informs the patient about this. At the appointed time, the new prosthesis is installed. All types of products (even the most expensive ones) have a certain resource, so it is important to understand that sooner or later there will be a need to replace them. It is especially important for people with crowns to monitor the condition of the oral cavity and regularly visit the dentist for preventive examinations.
Contraindications
Like any medical procedure, the installation of crowns has contraindications. Cases in which the procedure is not performed:
- advanced periodontitis;
- bruxism - teeth grinding;
- fragile enamel;
- teeth are small and poorly positioned;
- pathological bite, when the incisors overlap one another.
Sometimes the age of the patient may be a contraindication to installing a crown made of a certain material. Then he is offered another way to restore the integrity of the dentition.
Metal ceramics or zirconium?
Many patients wonder: what is better – zirconium crowns or metal-ceramics? Roughly speaking, both structures are metal-ceramic, but zirconium is a so-called “white” metal that does not shine through ceramics, as happens with ordinary metal. Therefore, today ceramic crowns on a zirconium frame are close in aesthetic qualities to all-ceramic crowns, but at the same time they have the same strength as metal-ceramics. However, the prices for such prostheses are higher than for metal-ceramic structures.
What are they: materials
Crowns are made from different materials: some are more durable, others are only suitable as a temporary measure. Their cost, complexity of manufacturing and installation also depend on this.
Metal ceramics
The product has a metal frame and is covered with ceramics on top.
| Pros: | Minuses: |
| High strength. | Contraindicated for people under 18 years of age. |
| Aesthetics. | Not suitable for gum recession. |
Metal-ceramic crowns are suitable for installation only in adult patients.
Metal composite
The crown frame is made of an alloy of chromium and cobalt. From above it is covered with a photopolymer composite: while it is soft, it is given a shape, after which it is fixed with UV rays.
| Pros: | Minuses: |
| High strength. | Coloring from products with pigment. |
| Thin and invisible edges. |
People with metal-composite crowns need to follow a diet to prevent artificial teeth from changing color. It is not recommended to consume drinks with dyes and foods with a high pigment content.
Golden
The oldest material for making crowns is gold.
| Pros: | Minuses: |
| Hypoallergenic. | Lack of aesthetics. |
| They do not damage neighboring healthy teeth. | Rapid abrasion due to the softness of the metal. |
It is best to install gold crowns on the back teeth, where they will be almost invisible.
Zirconium dioxide
Modern material for crowns is zirconium dioxide. It is durable, aesthetic, does not cause allergies and lasts a long time. But it has a fairly high cost, so it’s not suitable for everyone’s budget.
Metal-free
Modern synthetic materials can completely replace metal in the composition of the crown. They are no less durable, and look as close as possible to natural teeth.
Ceramic
The best way to choose the color of a crown is when it is made of ceramic. They do not look artificial, as they are quite transparent.
They are great for replacing incisors. But for chewing teeth, ceramic crowns are too fragile and cannot withstand such a load.
Porcelain
Porcelain crowns are not so popular, but are gradually becoming more and more in demand. They are easily and firmly fixed, which reduces the risk of loosening. Porcelain products last a long time, do not deteriorate due to temperature changes and are not stained by food. In this case, the crown can be made in an anatomical shape, repeating the relief of the tooth as accurately as possible, which ensures comfortable wearing. They look very aesthetically pleasing and are also hypoallergenic.
One of the disadvantages is their loose fit to the tooth, which can cause cervical caries. Crowns are quite fragile and can destroy adjacent healthy teeth. The product is not suitable for patients with thin enamel. In addition, the cost of such crowns is quite high, which is not affordable for everyone.
Combined
By combining several materials, it is possible to create crowns that combine their best properties. The product is suitable for use on front and back teeth: they look aesthetically pleasing and can withstand chewing loads. But such crowns are short-lived because they quickly wear out and sometimes become deformed. But their installation does not cause a blow to the budget.
Plastic
Plastic crowns are used as a temporary measure. They are manufactured on site and installed on the same day in place of the extracted or treated tooth. The cost of such crowns is low. But it is impossible to use them as permanent ones, since they cannot withstand prolonged chewing load.
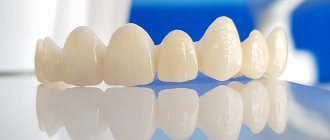
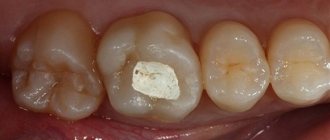
Dental crowns: types, installation, care, problems, service life
Dental crown - This is a “attachment” in the shape of a tooth, which is placed on top of it in order to cover the tooth, restore its shape, size, strength, and improve its appearance.Once cemented, crowns completely enclose the entire visible portion of the tooth located at and above the gum line.
Why do you need a dental crown?
A dental crown may be needed in the following situations:
- To protect a weakened tooth (for example, by caries) from decay, or to hold together parts of a decaying tooth;
- To restore an already damaged tooth, or a tooth that has been severely worn out;
- To isolate from the external environment and strengthen a tooth with a large filling in cases where there is too little dental tissue left;
- To hold a dental bridge in place;
- To cover a tooth that has lost its natural shape or has largely lost its natural color;
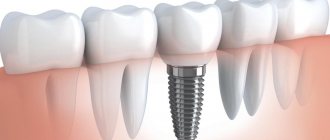
- To cover a dental implant;
- To change the appearance for aesthetic purposes.
For children, crowns can be installed on their first (baby) teeth in order to:
- Save a tooth that has been so damaged by caries that it cannot support a filling;
- Protect the teeth of a child at high risk for dental caries, especially when the child has difficulty maintaining daily oral hygiene;
- Reduce the frequency of use of sedatives and general anesthesia in children who, due to age, behavioral characteristics, or medical factors preceding treatment, are unable to fully meet the requirements for the behavior of dental patients.
In such cases, your pediatric dentist will likely recommend a stainless steel crown.
What types of dental crowns are offered?
Permanent crowns are all-metal (they are made, for example, from stainless steel, gold, gold-based alloys), they are also made from porcelain fused with a metal base, solid rubber and ceramics.
- Stainless steel crowns are prefabricated and placed on permanent teeth, usually as a temporary measure. Such a crown protects the tooth or filling for the period during which a permanent crown is made from another material. For children, stainless steel crowns are usually installed on previously prepared baby teeth. The crown covers the entire tooth, protecting it from further development of caries. When a baby tooth falls out to make room for a permanent tooth, the crown naturally falls out with it. Typically, stainless steel crowns are placed on children's teeth because they do not require multiple visits to the dentist for fitting, and therefore are not as expensive as custom crowns and the preventive services needed to keep teeth healthy without a crown.
- Crowns made from other metals are made using gold alloys, as well as palladium alloys and base metal alloys (such as nickel or chromium). Compared to other types of crowns, installing metal crowns requires the removal of less tooth tissue, and wear on adjacent teeth is minimized. Metal crowns can withstand the load applied when biting and chewing well and, perhaps, are more durable than all others. In addition, metal crowns rarely chip and rarely break. The main disadvantage is their metallic color. But metal crowns are a good choice for molars because they won't be visible to other people.
- Porcelain crowns with a metal backing can be matched to the color of adjacent teeth, unlike metal crowns. However, when wearing these crowns, adjacent teeth are subject to more wear and tear compared to metal or rubber crowns. The porcelain portion of the crown may also chip or fall off. Metal-porcelain crowns are very similar to natural teeth; in this regard, they are superior only to all-ceramic crowns. However, sometimes the metal underneath the porcelain can show up as a dark feature, especially near the gum line. This effect increases as the gum volume decreases. These crowns can be a good choice for both front and back teeth.
- Solid rubber crowns are cheaper than other crowns. However, over time they wear out and are more susceptible to cracks than metal-porcelain ones.
- Crowns made from solid ceramic or solid porcelain provide the most natural appearance and are best suited for people with metal allergies. However, they are not as durable as porcelain-metal ones, and they wear down adjacent teeth a little more than metal or rubber ones. All-ceramic crowns work well for front teeth.
- Temporary or permanent ? Temporary crowns can be made in the dentist's office, while permanent crowns can only be made in a laboratory. Temporary crowns are made from acrylic or stainless steel and can be used until the permanent ones are made in the laboratory.
Preparing a tooth for a crown?
Preparing a tooth for a crown usually requires two visits to the dentist. During the first, the tooth is examined and prepared, and during the second, a permanent crown is placed.
First visit: examination and preparation of the tooth
During your first visit to prepare for a crown, your dentist will take several x-rays to examine the roots of the tooth that will receive the crown and the surrounding bone. If a tooth has significant decay, or there is a risk of infection or damage to the tooth's pulp, root canal treatment will have to be performed before a crown can be placed.
Before the crown process begins, your dentist will administer anesthesia to numb the tooth and surrounding gum tissue. Then the tooth on which it is planned to install a crown will be ground from the chewing surface and on the sides to make room for the crown. The volume of dental tissue to be removed depends on the type of crown that is planned to be used (for example, all-metal crowns are thinner and therefore require the removal of less dental tissue than all-porcelain or metal-porcelain crowns). If, on the other hand, a significant amount of tooth structure is missing (due to decay or damage), the dentist may use a filler to “fill in” the tooth, giving it the ability to support a crown.
After adjusting the shape of the tooth, the dentist will take an impression of the tooth, which is necessary to give the correct shape to the dental crown. Impressions of the teeth above or below the tooth receiving the crown will also need to be taken to ensure that the crown will not affect your bite. The impressions are sent to a laboratory where the crown will be made. It is usually sent to the dentist's office in two to three weeks. If the crown is made of porcelain, the dentist will also select a shade that most closely matches the color of the adjacent teeth. During this first visit to the dentist, he will make a temporary crown to cover and protect the prepared tooth while the permanent one is made. Temporary crowns are usually made of acrylic and held in place with a limited-lasting cement.
Second visit: obtaining a permanent dental crown
During the second visit, the dentist will remove the temporary crown and check how the permanent crown fits on the tooth and how well it matches the color of the adjacent teeth. If both of these issues are resolved positively, the dentist will apply local anesthesia to numb the tooth, and the new crown will be placed in place, secured with a permanent cement.
Caring for a temporary dental crown
Because temporary dental crowns are exactly what they say - a temporary solution that only works until the permanent crown is ready - most dentists offer few precautions when handling them. These include the following:
- Avoid sticky and chewy foods (such as hard candy) and chewing gum, as they can grab the crown and pull it off the tooth.
- Try to chew as little as possible on the side of your mouth where the temporary crown is installed. Transfer the main effort of chewing to the other side of the mouth;
- Avoid chewing hard foods (such as raw vegetables) as this may cause the crown to become dislodged or broken;
- When flossing your teeth, pulling it outward, do it not sharply, but smoothly. By sharply pulling the floss from between the teeth in a normal manner, you can rip the temporary crown off the tooth.
What problems can arise when wearing a dental crown?
- Uncomfortable sensations or sensitivity . Your tooth that has received a new crown may become more sensitive immediately after the procedure, when the anesthesia used for it begins to wear off. If the tooth that has been crowned still has nerve in it, you may experience some sensitivity to heat and cold. Your dentist may recommend that you use a special toothpaste for sensitive teeth. The pain and sensitivity experienced when biting usually means the crown is too high for the tooth. If this is the case, contact your dentist - he can correct this problem.
- Breakage of crowns . Crowns made from solid porcelain sometimes suffer mechanical damage. If the chip on the surface of the crown is small, it can be repaired with a rubber-based composite material, leaving the crown in the mouth. If the crown has suffered extensive damage, it will have to be replaced.
- Loosening of the crown . Sometimes the cementitious substance is washed out from under the crown. This not only loosens the crown, but also allows bacteria to enter, causing decay in the remaining tooth under the crown. If you feel that your crown is starting to loosen, contact your dental office.
- Crown loss . Sometimes crowns fall out. This occurs due to improper fit, insufficient cementitious substance, or too little dental tissue to support the crown. If this happens, you should first clean the crown and front side of the tooth. You can temporarily put the crown back on using dental adhesive or a limited-life cementing agent available in stores. Contact your dental clinic immediately. The dentist will give you specific instructions on how to care for the tooth and the fallen crown for the day or two before he or she examines you. The dentist may be able to reattach the crown in place; otherwise you will have to make a new one.
- Allergic reaction . Since crowns are usually made not from pure metals, but from their alloys, including porcelain, an allergic reaction to the metals or porcelain used in the production of crowns may occur. But this happens extremely rarely.
- A dark stripe that is visible in the crown and runs adjacent to the gum line. A dark line running through the crown adjacent to the gum line is normal, especially if your crown is made of porcelain with a metal backing. This dark line is simply the metal component of the crown that is visible through the porcelain.
What are three-quarter onlays and crowns?
Onlays and three-quarter crowns are types of dental crowns. The difference between these and other crowns, which we have previously discussed, is the way they cover the tooth. A “traditional” crown covers the entire tooth, while onlay and three-quarter crowns only partially cover the tooth.
How long do dental crowns last?
On average, dental crowns last from 5 to 15 years. The lifespan of a crown depends on the degree of wear, oral hygiene and the patient’s personal habits. You should get rid of habits such as teeth grinding, clenching your teeth, you should not chew ice, bite your nails, or open packages with your teeth.
Does a tooth with a crown need special care?
Although a tooth with a crown does not require special care, remember that having a crown on a tooth does not mean that it is protected from tooth decay or periodontitis. Therefore, continue to maintain good oral hygiene, including brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing them daily. You should pay special attention to the area surrounding the crown, where the gum meets the tooth. Rinsing the mouth with bactericidal solutions will also help.
How much do crowns cost?
The cost of crowns varies depending on what region you live in and the type of crowns. For example, porcelain crowns are typically more expensive than gold crowns, and gold crowns are typically more expensive than porcelain-metal crowns. Typically, crowns cost from 12,000 to 25,000 rubles each.
Source: dentaldaily.ru
Types of crowns
The number of missing teeth, the presence of dentures and other individual characteristics of the patient determine what type of crown is suitable for him. It is impossible to determine this in absentia, since it requires an examination by a specialist.
Bridges
Suitable for people who have lost more than one tooth. The prosthesis is made for all missing units, and its parts are connected by a metal bridge. To secure the crowns, you need healthy chewing teeth. Only complex prosthetics are performed in this way.
Implant supported crowns
If the patient has implants, the crown can be secured to them. This will prevent the destruction of healthy teeth, which can occur due to excess stress. But the method is only suitable for those who already have implants installed.
Crown for one tooth
If one tooth is destroyed, a crown can be installed only on it. This usually happens after deep caries or injuries. Before installing a crown, the condition of the periodontium, jaw and gum tissue is assessed. Sometimes additional operations are performed to build up the bone plate.
Fixation with a pin
The rarest method of prosthetics is installing a crown on a pin. It is quite traumatic and carries a risk of complications, so it is almost never used. If other methods of prosthetics are not available to the patient, the crown is installed on a pin, but this is done in several stages under the supervision of specialists at each of them.
What are the consequences of untimely crown replacement?
1. Destruction of the tooth under the crown with its subsequent loss.
The main function of a crown is to restore a badly damaged tooth and protect it. The first time after installation, the crown performs its function perfectly. But after a certain time, changes occur. The gingival margin rises, saliva and gingival fluid affect the cement that “secures” the crown. Over time, this cement can be partially washed out (dissolved), a microscopic gap is formed between the crown and the tooth, and the tooth begins to deteriorate under the influence of microbes and oral fluid. The most insidious thing is that these signs occur asymptomatically and unnoticed by the patient, since they are painless. Therefore, replacement of crowns often occurs untimely, when the tooth is destroyed too much and becomes simply unreliable.
Associated with this is the myth that teeth under crowns are destroyed. The truth is that crowns are simply replaced at the wrong time, but too late.
This can be prevented by timely replacement of the orthopedic structure.
2. Inflammation of the tissues around the crown . This means the gums, tooth ligament and bone tissue. A poor-quality crown can lead to the formation of a chronic inflammatory process in the gums (gingivitis, periodontitis), which is manifested by redness, bleeding when brushing teeth, aching pain in the gums and an unpleasant odor. If such a crown is not replaced for a long time, the underlying tissues become involved in the inflammatory process, which may lead to the formation of bone pockets, disruption of the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, and local periodontitis, which in severe cases leads to tooth loss.
Photo 2.1. Inflammation of the gums near teeth under crowns, associated with inaccurate marginal fit of the crown to the tooth and with a violation of the biological parameters of tooth restoration.
Important! Make it a rule to visit the dentist for a preventive examination at least once a year, if you have any dentures, in order to notice their failure in time and prevent or correct the problem.
Methods for making a crown
Orthodontic products can be manufactured using several methods. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Cast products
Strong and durable crowns are made using casting. For this, a single piece of metal is used. The method is not suitable for all materials.
Stamped
More affordable, but less durable prostheses are made by stamping:
- a mold is placed into the dental anvil;
- using rubber rings a stamp is obtained;
- the crown is made using special hammers that differ in shape and size;
- The product is given its final shape using small tongs.
Such crowns last less than cast ones, but are much cheaper to produce.
What to do with old gold crowns
If gold crowns fall out, are worn out or become unusable, you can order other jewelry from them or take them to a buyer (there are buyers who specifically buy “ dental gold ”). Many people are confused by the fact that there is cement left inside, which was used to attach the gold shell to the tooth. Is it possible to completely remove it from gold crowns? Here's how to do it correctly:
- 1st method. If you can go to a specialized dental store and buy a solution for disinfecting impressions, it will dissolve the hardened cement.
- 2nd method. You can clean gold crowns from teeth using home remedies by mixing ammonia, household detergent, and hydrogen peroxide. Pour this mixture over the crowns, heat everything up, keep it in the mixture for a few minutes, brush with a toothbrush, rinse under water, and wipe dry.
- 3rd method. Remove the frozen solution from gold crowns by crumbling it using a small, light hammer. If there are plastic teeth left inside, they are burned out with a gas burner, after which they can be easily pulled out with tweezers. After the procedure, leave the crowns in 15% hydrochloric acid for complete cleansing. It is undesirable to carry out such a procedure at home because the process is dangerous, harmful to health, and difficult to remove the remaining odor from the room.
- 4th method. Boil and cool water, cut a lemon and squeeze the juice into the water, stir. Place the old crowns, keep them in the solution for up to 12 minutes, and rinse. Instead of juice, citric acid is also suitable.
- 5th method. The most convenient option is to seek the services of a dental technician in a dental clinic with a license to work with precious metals. He will carry out firing and bleaching in hydrochloric acid.
This way, you can profitably hand over old crowns that have been lying around in a box for a long time at a gold buying point.
Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
How a tooth crown is made
Before starting to make the prosthesis, the size and shape of the product are determined. To do this, the patient undergoes:
- examination by a doctor;
- general and targeted x-ray diagnostics;
- 3D - visualization on a computer screen of the entire jaw and a specific tooth.
Then the doctor selects the material from which the crown will be made. It depends on which tooth needs to be replaced, the age of the patient and his financial capabilities.
To accurately manufacture the prosthesis, an impression of the jaw is taken. For this, gypsum or a similar synthetic material is used. The resulting model is sent to the laboratory.
What determines the service life of a crown?
- The service life and the need to replace the structure greatly depend on the accuracy of manufacturing at all stages. Precision work means that the crown fits to the tooth without gaps, without steps, without voids, oral fluid and food do not get under it, the gums around it do not become inflamed, it is no different from the “native” tooth. It is the precision of manufacturing that determines the quality of work, and therefore is the key to a long service life of the crown. For example, I had to deal with a situation where the crown was made only a year ago, and upon examination, strict indications for its urgent replacement were revealed (due to poor quality, namely inaccurate manufacturing). And vice versa, when examined, the crown meets all the requirements, all parameters are normal, there is no need to replace it, and it has been standing for 10 years (which means it was manufactured very accurately and in a timely manner).
- We have repeatedly mentioned that accuracy, and therefore quality, is at the forefront. If we take quality as a given, then the material and method of fixation come to the fore. So, the service life also depends on the material from which the crown is made and, accordingly, on the method of fixing it to the tooth . Classic metal-ceramics and zirconium dioxide-based crowns are attached to a special “cement,” that is, an intermediary between the crown and the tooth, and do not enter into a “chemical” bond with either this cement or the ground tooth. Namely, this cement is “destroyed” and “washed out” over time, leading to a violation of the seal of the entire structure. Crowns based on lithium disilicate (also called “E-max”) are fixed without an intermediary: using the adhesive (“glue”) method, that is, they are glued to the tooth tissue, which leads to a very strong connection between the crown and the tooth. Accordingly, the service life of such structures is longer than the 5-7 years described above, which means that a crown change will not be required soon.
- In addition, the service life is greatly influenced by the condition of the tooth for which the crown was made. If a patient hesitates for a long time to adequately restore a damaged tooth, he comes for prosthetics at an untimely rate, in particular when the tooth is destroyed by a carious process to the level or below the level of the gum, becoming “soft” and unreliable. In such conditions, the doctor is no longer able to make an accurate marginal fit; such a structure will never be completely sealed, which means the tooth under such a crown will be destroyed. In such conditions, neither good materials nor the method of fixing the crown will help. And if the doctor nevertheless undertakes the restoration of such a tooth, this will be the last crown on it, since it will be impossible to repeat the restoration.
Important! Dear patients, do not delay the restoration of damaged teeth, do not deprive yourself of the opportunity to save your own tooth faster, more reliably and cheaper!
By clicking on the “Make an appointment” button, I consent to the processing of my personal data.
I have read and agree with the conditions for processing personal data set out on the website ds-chocolate.ru.
Consent to the processing of personal data
Preparing for installation
A crown cannot be placed on an unprepared tooth. He must be completely healthy. If you have inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, they need to be cured before installing a crown.
Then the teeth are ground down. It is performed under anesthesia, so the patient does not experience any discomfort. This procedure is carried out to ensure that the denture fits perfectly and no food remains get stuck under it. It also allows you to equalize the width of the neck and middle of the tooth. This way the prosthesis will be firmly fixed, which will prevent loosening.
Only 1-2 mm of enamel is removed. The depth of treatment depends on the selected crown material: metal-ceramics require more space, and ceramics are quite thin; a very thin layer is removed to install it.
In some cases, depulpation is performed. The patient is warned about its need in advance.
If the tooth is severely damaged, a core inlay is installed. It separates the internal tissues from the crown, allowing you to avoid pain while wearing it.
Upon completion of all manipulations, a temporary crown is installed on the tooth. It is made in the dentist's chair. The design protects the prepared area and restores its aesthetic appearance.
If you still have to remove the crown...
Sometimes you can hear very strange complaints from patients: “The dental crown hurts.” In fact, it is the tooth under the crown that hurts, because the crown itself is not living tissue. The question also arises: why should there be pain if the tooth is devoid of a nerve? Inflammation can also occur in the gum tissue, and it can already manifest itself as pain. Sometimes it happens that you just feel an unpleasant smell from under the crown, but there is no pain. But this is also a reason to remove dental crowns.
When dismantling such structures, it is important what dental crowns are glued to. Knowing this, you can try to dissolve the material with a substance that will not damage the tissue of the teeth and gums. After this, it will be much easier to remove the crown with forceps. It is often necessary to additionally break up the cement with a drill and a special bur so that the crown can be removed easily. The removal of the crown begins with a Kopp apparatus, a device that can make pushing movements, and ends with crown removal forceps.
There are also devices that work with compressed air. This is, for example, cronaflex. The procedure is more expensive due to the high cost of the device, but the crown is not damaged and can be reused.
If you use other methods, such as sawing, you will have to remove the dental crowns and install new ones after dental treatment. This will result in greater costs for the patient and will also take more time.
Once we know how dental crowns are removed, it remains to be seen whether the patient experiences pain during the process? If the reason for coming to the dentist is only the smell from under the dental crown, then when removing it there may not be any unpleasant sensations at all. After all, the smell may be a consequence of food and saliva getting under the crown, and not the development of caries under it. When a patient is brought to the clinic by a toothache, the dentist must first administer anesthesia, and only then get to work. Pain clearly indicates inflammation.
Whether a tooth hurts under a crown or not depends not only on its quality, and not always on how well the dentist installed it. Often, even the best dental crowns can fall off or the tooth underneath them begins to ache. This happens due to the poor condition of the gums and the sluggish inflammatory processes occurring in it. As soon as chronic inflammation worsens, pain symptoms may immediately appear.
This is why many doctors advocate long-term treatment before placing a crown on a tooth.
Installation process
The crown is installed in several stages. The number of visits to the doctor depends on the condition of the teeth and the chosen prosthetic method.
Laboratory stage
A cast of the patient's jaw is sent to the laboratory to create a plaster model of the jaw. After complete drying, the desired part is cut out. Using it, a wax prototype is made.
The model is fixed on the base and filled with a special mixture. It goes into the oven for 4-5 hours. The resulting mold is immediately filled with the alloy while it is hot. The future crown is left in this form until it hardens completely. The piece is then polished and sanded to achieve the perfect shape.
Removing the temporary structure
When the permanent crown is ready, the temporary structure is removed. It only takes a few minutes, after which prosthetics can be applied.
Installing a crown on a tooth
Before fixing the crown, a fitting is performed. If it is uncomfortable or the enamel color is not suitable, it is sent for revision. When the crown is perfect, it is secured with cement. The strength of the fixation must be checked after the material has hardened.
Monitoring the situation after installation
After fixing the crown, the doctor checks how correctly it is installed. To do this, an x-ray is taken. Only after his assessment can the patient go home. If you experience strange sensations, you should call your dentist to clarify your condition and the need for a second visit.
Our advantages
At the Beryozka clinic, the material for the crown and its type are selected individually. Each patient is given an approximate treatment estimate so that he can clearly see what he is paying for. A transparent work system, professionals, the latest equipment and materials ensure the ideal result of prosthetics at the Beryozka clinic. A polite attitude and the ability to quickly get an appointment are the key to pleasant emotions from visiting a dentist.
Omerelli Emir Romanovich
Specialization: maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist Work experience: more than 13 years Place of work: Works at the RUTT clinic on Proletarskaya First category doctor.
Candidate of Medical Sciences. He was one of the first to use the method of single-phase dental implantation with instant loading in Russia. He is a member of the Open Dental Community (ODC), where he took part in the development of the ROOTT implant system.
Every day he performs operations on classical dental implantation and implantation with immediate loading for complete and partial edentia.
Pros and cons of crowns
All medical procedures have both pros and cons. Before you decide to install crowns, you should compare the pros and cons.
Advantages
The advantages of using this method of prosthetics are much greater than the disadvantages. The advantages of installing crowns include:
- preventing the destruction of pulpless teeth;
- preservation of a living tooth even with partial destruction;
- restoration of the ability to chew food normally;
- restoration of an aesthetic appearance while smiling;
- prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which can be caused by insufficient chewing of food;
- restoration of the ability to speak clearly.
Due to the large number of advantages, the procedure has become so popular among patients.
Flaws
The procedure for installing crowns has its disadvantages. Flaws:
- the need to grind healthy parts of the tooth;
- limited period of wearing a prosthesis;
- inability to carry out the procedure with a damaged root;
- the need for regular visits to the dentist for monitoring.
The disadvantages of the procedure are offset by its advantages. Therefore, crowns remain the most popular way to restore the integrity of the dentition.
Which crown is better: rating
Below we will talk about the best options for prosthetics of chewing teeth in different clinical situations. In Table 1 you can see which crown is better in situations where only single crowns are needed, or when we are talking about restoring a missing tooth with a bridge. The types of crowns in the table are listed from best to worst.
Dental crowns: which ones are best for chewing teeth (Table 1) –
| Single crown | Bridge prosthesis | |
| 1. | pressed ceramic E.max | made of zirconium dioxide |
| 2. | made of zirconium dioxide | combined bridge * |
| 3. | metal ceramics | metal ceramics |
| 4. | solid crown | solid bridge |
* This prosthetic option involves a combination of metal-ceramic and solid-cast bridge prosthesis. So, if from the table it has already become clear to you which crown is best to place on chewing teeth, then below you will find a detailed description of the pros and cons of the above types of crowns in various clinical situations.
1) Crowns/bridges made of zirconium dioxide –
Zirconium dioxide is a metal-free ceramic. This type of ceramic has very high strength (more than 900 MPa), which is comparable to the strength of metal, as well as a higher level of aesthetics - compared to metal ceramics. If you need to make a bridge on the chewing group of teeth, then a zirconium dioxide bridge will be the best option. But if you need to make a single crown, then zirconium is inferior to pressed glass ceramics E.max.
Pressed glass ceramics E.max has: 1) better aesthetics, 2) it has a lower risk of chipping the ceramic mass, but it cannot be used to make bridge-like prostheses resting on the distal chewing teeth. Therefore, if at least one of 6-7-8 teeth must act as supports for a bridge, the only ceramic option will be zirconium dioxide. If you need a single crown, read the next section about E.max ceramics.
Important: Most often, zirconium dioxide crowns/bridges consist of two layers. First, the zirconium frame of the future crown/bridge is milled on a computer-controlled machine (similar to the metal frame of metal-ceramics). After firing in the kiln, layers of porcelain in different shades are applied to this frame to match the color of the adjacent teeth.
The second manufacturing option is that crowns/bridges are made from monolithic zirconium dioxide (without subsequent application of porcelain layers). This option has a big advantage - there is absolutely no risk of ceramic chipping, but the aesthetics will be worse. According to statistics, when making zirconium crowns with surface application of porcelain, ceramic chips occur in approximately 10% of patients after 6 years of using such crowns.
At the same time, studies show that the risk of ceramic chips in metal-ceramic crowns is approximately 2 times lower (than in zirconium crowns with a surface layer of porcelain). And the risk of chipping with pressed E.max glass ceramics will be even lower. Therefore, to the question: which crowns are best placed on chewing teeth, the answer is that bridges are best made from monolithic zirconium dioxide, and single crowns from E.max.
→ Cost of zirconium dioxide crowns/bridges
2) Crowns made of pressed ceramics E.max –
Two single crowns from E.max – before and after photos
E.max glass ceramics are the best option for metal-free ceramics if you have the highest demands on the aesthetics of your crowns. This type of ceramic has a high strength of 400 MPa (which is less than that of zirconium dioxide), but this is more than enough for prosthetics of posterior teeth with single crowns. But for the manufacture of bridges supported by 6-7-8 chewing teeth, this strength will no longer be enough, and therefore bridges from E.max are made more often for the front teeth.
E.max comes in two main types. Firstly, this is the “E.max PRESS” material, intended for the manufacture of crowns/bridges using the pressing method at high temperature and pressure. Let's say right away that this material is much better and somewhat cheaper than the second one. Secondly, the “E.max CAD” material, which is intended for the manufacture of crowns using the milling method (CAD/CAM technology, which is also used for the manufacture of zirconium crowns).
Important: E.max crowns/bridges can be (as well as zirconium) made either monolithic or consist of 2 layers - a pressed frame on which porcelain mass will be applied. Monolithic structures have the lowest risk of ceramic chipping, while layered structures have the best aesthetics. Not long ago, a new material “E.max PRESS Multi” appeared, which makes it possible to make very aesthetic monolithic structures, from which we recommend making all single crowns for chewing teeth.
→ Cost of crowns/bridges from E.max
3) Metal-ceramic crowns/bridges –
A more budget-friendly option is metal-ceramic prosthetics. Its main aesthetic disadvantages are more modest aesthetics (compared to metal-free ceramics), the development of cyanosis of the gums around the crown, and also, over time, gum recession with exposure of the metal edge of the crown. But on the other hand, chewing teeth are not visible when you smile, which, given a limited budget, makes metal-ceramics a good choice.
Below we have posted examples of prosthetics for missing chewing teeth using metal-ceramic bridges (before and after photos).
But aesthetics should not be the only selection criterion. The fact is that for metal-ceramics, teeth are ground on different sides by 2.0-2.5 mm, and for metal-free ceramics - only 1-1.5 mm. Thus, ceramic prosthetics allows you to preserve more hard tooth tissue under the crown, which increases its service life. The cost of one metal-ceramic crown starts from 8,000 rubles (for the most budget-friendly manufacturing option, using the cheapest materials made in Russia and Belarus).
On average, for a budget option using imported economy-class materials (for example, Duceram ceramic mass, Germany) - it costs from 10,000 to 12,000 rubles for 1 crown. If the issue of aesthetics is important to you, then the production of metal-ceramics using high-quality and expensive ceramic masses Vita (Germany), Noritake (Japan), Ivoclar (Liechtenstein) will cost at least 15,000 rubles for 1 crown. It is also worth considering that the indicated price does not take into account some additional costs.
→ Calculation of the cost of metal ceramics
4) Solid crowns/bridges –
Crown bridges on the back teeth (which do not fall into the smile line) do not have to be white and beautiful. There are metal cast crowns that are made of chromium-cobalt alloy. Such crowns have the color of polished metal, or by spraying they can be given a “gold” color. They have a long service life, and besides, the teeth under them are ground to a lesser extent than under metal-ceramics.
→ Calculation of the cost of cast crowns
5) Combined bridges –
If you need to make a bridge of 3 crowns on the chewing teeth (for example, supported by the 5th and 7th teeth), the design can be made in an unconventional way... The first 1-2 crowns that fall into the smile line can be made metal-ceramic, and the distant ones 1-2 crowns can be made solid and look like polished metal. This will be somewhat cheaper, and besides, it turns out that the abutment tooth for a cast crown will be ground down to a lesser extent.