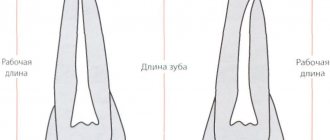
The choice of dental instruments and materials nowadays is very wide. This is primarily due to the fact that using them, dentists perform a variety of medical procedures, from filling teeth to prosthetics. Secondly, in recent decades, many new instruments and materials have been created that significantly expand the capabilities of dentists. Despite this, not a single tool, not a single material can be called absolutely perfect and ideal; there are always some limitations and requirements that no invention can satisfy at the same time.
Types and purposes of dental instruments
The work of a dentist uses both a universal set of medical devices and specialized instruments necessary to perform highly targeted manipulations. There is a generally accepted classification of dental instruments:
- for examination of the oral cavity;
- for treatment and filling of teeth;
- for the preparation of filling and other compositions;
- for removing teeth and their roots;
- for removing dental plaque;
- for processing fillings and root canals.
The listed devices are universal and necessary for general dental procedures. In addition to them, dentistry uses ordinary and surgical instruments intended for highly specialized dentists: orthodontists, orthopedists, periodontists, hygienists, and technicians.
Orthopedic instruments
This type of dental instruments is represented by metal and plastic spatulas made of different materials, from plastic to metal. They can be flat or curved and are used for processing impression materials and mixing impression materials.
Orthopedic instruments also include impression trays for making plaster models, both perforated and regular, ideally repeating the shape of both rows of teeth and accurately depicting the desired area of the dental system.
Also indispensable in the work of an orthopedist are pliers for plaster and tweezers for soldering, coronal forceps, occlusal retainer, coronal removers and coronal scissors, a micrometer, tweezers for articulating paper and other types of dental instruments necessary for a specialist to professionally perform his duties.
At the same time, the better the quality, and therefore the more convenient and reliable the instruments, the more effective the doctor’s work will be and the safer and more comfortable the patient’s treatment will be.
Dental instruments for oral examination
Diagnostic devices are included in the basic kit that every dentist needs. Their main purpose is to examine the patient’s oral cavity to identify problems and find further ways to solve them. In addition, they are necessary in the process of treatment and removal of teeth, during prosthetics.
Every dentist should have in his arsenal:
| Tool name | Photo |
| A tray in which utensils are placed. | |
| A dental mirror that magnifies the problem area and is necessary for tapping the tooth surface to assess the degree of pain. | |
| Dental tweezers, the working part of which has a curved shape and allows manipulation in hard-to-reach places. Also, using this device, the stability of the diseased tooth is checked. | |
| A dental probe that performs a number of functions: identifying irregularities and other defects on the surface of teeth, assessing their condition (density, depth, size, degree of pain). | |
| A dental spatula used to move the cheeks, tongue, and lips to the side to provide access to the damaged area. |
Dental instruments for dental treatment
Tools for dental treatment are varied. They differ in names, functional purposes, and the material from which they are made. The choice of the right tools depends on what problem the patient came to the doctor with. The same instruments can be used by a dentist to treat a wide range of diseases.
In addition to the basic set of instruments used in the treatment of diseased teeth, dentistry uses a number of additional devices for carrying out highly targeted actions, for example, prosthetics.
Dental instruments for prosthetics
Prosthetics of any complexity requires an individual approach and takes a lot of time. Each stage of the procedure uses its own set of instruments.
| Name | Photo |
Impression (impression) trays designed for taking impressions from the jaw. They are classified into several main types that are used for taking impressions:
If it is necessary to make an impression of the entire dentition, large spoons are used. For impressions of individual dental units - small. Sometimes, along with standard spoons made in production, the medical technician uses special ones, selected individually. | |
| Burs and discs used for tissue preparation. | |
| Spatulas for stirring solutions. | |
| Devices used for removing, cutting, filing installed crowns. | |
| A micrometer that determines the thickness of the crown. |
Dental instruments for filling teeth
The filling procedure using cement or amalgam requires the use of special instruments, with the help of which:
- The tooth cavity in which the filling will be placed is prepared.
- The future tooth is modeled.
In modern dental practice, the following instruments are used for filling teeth:
| Name | Photo |
| A spatula is a small device in the form of a short flat spatula with a handle. Designed for introducing medication into the dental cavity, forming temporary and permanent fillings, eliminating excess material from which the filling is made. | |
| A spatula is a metal handle with flat elongated blades on both sides. Used in the preparation of pastes for filling canals and medications. | |
| A plugger is a device whose working part is a round, cylindrical or pear-shaped head. It is used to seal the filling in the dental cavity. | |
| An excavator is one of the most common devices in dentistry. It is a handle with sharp spoons along the edges facing in different directions. The main purpose is to remove excess filling material, soft plaque, temporary filling, and tartar. | |
| Handpieces for drills. They secure dental burs and abrasive materials and transmit rotation from the drill. |
During the filling process, not only the main, but also auxiliary devices can be used: matrix holders, channel fillers, strips.
Dental materials, requirements and classification
The main requirements for such materials are: biocompatibility, long-term and reliable connection with the tooth base, good resistance to the environment in the oral cavity, appearance.
Depending on their use, there are five main groups of materials used in dentistry.
- Toothpastes, teeth whitening products, sealants, i.e. everything that serves to prevent dental diseases;
- Restorative materials: filling, adhesive, materials for bases and gaskets;
- Materials used in orthopedic dentistry for treatment after tooth loss (both complete and partial);
- Materials used to treat malocclusion and dentition anomalies. These are materials for braces, metal wire, archwires, etc.;
- Materials from which dental implants are made and used to restore facial tissue;
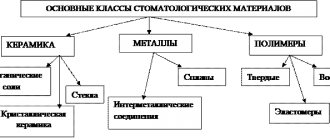
Depending on the chemical composition, dental materials are divided into ceramic, polymer, metal and their alloys.
Metals perfectly withstand significant mechanical loads and conduct heat well, but the appearance of, for example, dental crowns made from them is not everyone’s cup of tea.
Ceramics and polymers are ideal for reproducing the natural appearance of teeth, and due to their low thermal conductivity, they are also used to protect teeth from sudden changes in temperature.
Often materials with different chemical natures are used in combination with each other, which makes it possible to minimize their undesirable properties and achieve the desired combination.
Dental surgeon tools for teeth removal
Tooth extraction is one of the most common procedures faced by patients in dental clinics. The tools of a dental surgeon are extremely diverse. The main ones among them are elevators and tongs.
| Name and description | Photo |
| An elevator is a tool for removing teeth and their roots. There are three varieties: straight, angular, bayonet-shaped. Direct elevators are effective in removing roots in the upper jaw. Angular (lateral) ones are used to extract roots removed from the lower jaw. Elevators in the form of a bayonet are necessary for pulling out dental units in the lower jaw. | |
| Dental forceps that perform various functions. To remove teeth from the upper and lower jaws, permanent or temporary, the doctor uses different types of forceps. The most commonly used are wire cutters. | |
| A curette is a medical device shaped like a spoon with sharp edges. It is used in surgery to remove damaged tissue and suppuration from the bone. | |
| A surgical scalpel used to cut soft tissue. | |
| Surgical scissors for various manipulations related to the application or removal of sutures during surgical interventions. | |
| A syringe for administering an anesthetic drug. |
In addition to all of the above, when removing incisors, canines and molars, you may need tools for separating the gums from the jaw, tweezers for transferring and holding dressing material, needles of various thicknesses and lengths, clamps and forceps for holding a surgical needle.
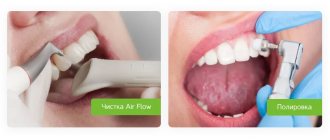
Tools for removing plaque from teeth
Very often, patients turn to the dentist who want to get rid of deposits on the surface of their teeth and gums. For these purposes, tools are produced under the following names:
- Curettes. Instruments that have different shapes, which facilitates their penetration into any part of the oral cavity.
- Hooks of different shapes and sizes. Used to clean the tooth surface and gums from deposits.
- Excavators. Necessary for removing temporary fillings, pieces of food, as well as deposits that form above or below the gum, in the periodontal canals.
- Attachments for pneumatic or ultrasonic scalers. Effective in removing deposits above the gums, as well as in cleaning the area between the teeth. A device such as a scaler should not be used in the presence of subgingival deposits.
- Enamel knife. Used for polishing and giving the ideal color to tooth enamel.
- Root file. A dental instrument used in the final stage of a dental plaque removal procedure. It is used to grind the surface of the root.
It is not so easy to list all the main dental instruments used in modern medical practice. The number of devices that every specialist should have in their arsenal is steadily increasing, as treatment methods are constantly being improved, new approaches to practical activities are being developed, and the quality of services provided is growing. It is important to correctly navigate and understand the variety of existing tools, using new technologies and developments.
How to Choose Good Quality Dental Instruments
Price
High-quality dental instruments are distinguished by their price, which, in turn, depends on the material from which the instruments are made. For example, dental instruments made of stainless steel are highly wear-resistant, can withstand repeated sterilization and, accordingly, last a long time. Is it worth buying inexpensive dental instruments? This is a rhetorical question. But only if we are not talking about the deliberate acquisition of instruments that do not require sterilization, that is, disposable ones.
Brand
In this case, you should be even more careful about the quality of the product you choose. When choosing, you can rely on the name of the manufacturer and, again, on the cost. This approach to business is guaranteed to provide you with a reputation as a true professional, and the patient will feel great both during treatment and after it.
Material of manufacture
But what else says about the quality of dental equipment? If we recall cutting instruments - the role of which is very significant and great in dental practice - then, of course, it is worth mentioning abrasive materials. They are both natural and artificial. The coarse grain size of diamonds always guarantees high speed of tooth surface preparation. This advantage allows the doctor to easily and quickly cut the silicone, apply longitudinal grooves, open the cuvettes, and generally perform the required amount of work without much effort.
Durable alloys such as titanium and stainless steel, as well as steel with chromium, nickel and molybdenum, are a real guarantee against corrosion.
Sterilization
Such instruments must be able to withstand the necessary sterilization treatments of various types (steam, air or chemical). This factor is direct evidence of the high quality of the product.
Comfort
It is convenient for a doctor to work with instruments when they do not slip out of their hands, have a good grip, smooth contours that do not dig into the hand. Comfort is the most important criterion when choosing dental instruments.