A common reason for visiting a dentist is a lump on a child’s gum. Upon examination, the doctor discovers a round formation of varying degrees of density, painless or with a mild pain symptom.
In most cases, in the area where the pathological element occurs there is a dilapidated or filled tooth. But sometimes the tooth turns out to be intact (undamaged), and the surrounding gum has a normal color. The reasons for the appearance of a lump can be varied. To determine them, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible.
Where does the abscess come from and what is its danger?
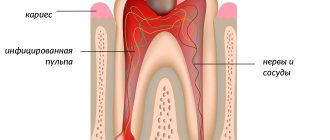
In the vast majority of cases, an abscess on the gum is associated with a tooth, often with a milk tooth. The most amazing thing is that the tooth may appear healthy from the outside, it may have a beautiful filling, and the tooth may not hurt. Why does pus still appear?
Baby teeth are less resistant to infection than permanent teeth; they are designed for a short service life, although they, like permanent teeth, have a nerve and roots. However, the roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve after five years. Caries in such teeth spreads much faster. Within three months, a cavity can form in the tooth, reaching the nerve. If caries is not treated, all pathogenic bacteria enter the dental nerve, and then, through the nerve, the microbes enter the bone. Bone is quite comfortable for microbes. They multiply there, dissolve the bone, which is accompanied by the formation of pus. If the tooth is open, there is a hole in it, pus comes out into the oral cavity. If food particles, fragments of destroyed enamel get into the tooth, or the tooth is covered with a filling without adequate treatment, pus can no longer flow freely. If the pus cannot flow out through the tooth cavity, it begins to look for another way out. The pus melts the bone and comes out under the gum. The outer covering of the gum, under which the pus has come out, swells and takes the form of a lump. Over time, the lump may burst and pus leaks out.
Once the pus is released, the lump may disappear and the gums may heal until the pus collects in large quantities again. The danger of such “bumps” is as follows:
- there is always an infection in the body (you should never forget that the abscess is not just on the gum, but in the head);
- the pus that is in the jaw dissolves the bone and can damage the growing permanent tooth.
The disappearance of an abscess next to a tooth never means recovery.
Symptoms that appear along with an abscess
- redness on the gum;
- tooth pain (optional);
- There is a hole in the tooth or there may be a filling on it;
- enlarged lymph nodes (dense “balls” appear under the lower jaw).
Sometimes a lump is discovered by chance, and the child may not be bothered by anything at all. The parent should periodically examine the child's mouth independently.
Causes of Teething Cysts in Children
During teething, a hematoma is formed; it occurs due to the fact that the tooth cannot break through the mucous membrane and thereby injures the gums and ruptures blood vessels. The longer the formation is in the oral cavity, the larger its size; in addition, the amount of swelling will depend on the group affiliation of the tooth.
The main causes of the tumor:
- pulpitis;
- caries;
- periodontitis;
- improper tooth treatment or lack thereof;
- eruption injuries.
The baby’s body tries to limit the source of infection, which is why a dense protective capsule is formed, which eventually develops into a cyst. The occurrence of such formations is quite common. An infection caused by carelessness, an unsuccessful attempt to chew hard food, a fall that led to a tooth injury - all this can serve as a starting point for gum inflammation and further development of a cyst.
Another fairly common mistake parents make, which can lead to the appearance of a tumor during teething, is negligence in caring for baby teeth.
It is generally believed that you should take serious care of your dental health after changing them. Since there is no point in treating non-permanent baby teeth - they will soon fall out. In fact, not taking things seriously leads to many problems. Any gum diseases and oral infections should be eliminated in a timely manner, regardless of how many teeth the baby has and whether they are permanent or not.
Never do
You should never heat your gum or cheek, no warm compresses or salt or other “folk remedies”! It’s better not to do anything at all before going to the doctor. After warm compresses, pus may spread not only in the jaw, but also in the cheeks, throat, and neck. Situations arise that are dangerous not only to health, but also to life.
Contraindicated
- refusal to brush teeth;
- independent opening of the abscess;
- taking medications without the consent of a doctor (except for painkillers).
Complications with cyst growth
Tooth trauma, advanced caries, nasopharyngeal or periodontal disease, dental malformations - one or more of these factors can lead to the development of a cyst. The danger is that the cyst grows unnoticed. It usually does not hurt and at the initial stage does not cause discomfort or reaction of the lymph nodes. With further development, suppuration and various unpleasant sensations may appear. But even if there is no pus, the cyst is very dangerous. Therefore, do not delay treatment.
A cyst can lead to intoxication of the body due to the fact that waste products of harmful microorganisms enter the blood. The consequence of this can be headaches, high fever and, in the worst case, sepsis.
In addition, complications are caused by local problems - phlegmon, abscesses, osteomyelitis. These complications are inflammatory in nature and often occur when the cyst suppurates. The spread of pus can lead to destruction of the jaw bones, damage to the internal organs of the digestive system, liver, and heart.
It is impossible to avoid the appearance of a cyst, but if you properly care for baby and permanent teeth and treat infections in a timely manner, you can reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. In addition, periodic visits to the dentist will allow you to notice the problem at an early stage, when treatment will be as simple and easy as possible for the body.
Treatment
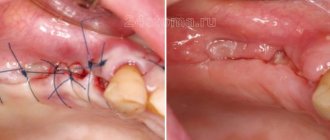
Depending on whether a permanent or baby tooth caused a lump on the child’s gum , the doctor carries out appropriate treatment. If a permanent tooth is damaged, seek help immediately while there is a chance to save the child’s tooth. The doctor will have to remove the nerve and fill the canals. In this case, adult dental treatment is a necessity, because if high-quality treatment and appropriate treatment are not carried out, the child may lose a tooth.
Milk teeth are removed immediately - their root system has not yet had time to form, and it is impossible to properly fill the canals. In addition, if a diseased tooth is left, the molar may grow back with defects (stains, damage.
At the Family Dentistry Center, you can remove a child’s tooth without pain or fear. All procedures in the clinic are performed under medical sedation. While the baby is sleeping peacefully and does not feel pain or discomfort, the doctor can carry out all the necessary procedures. Being able to treat your teeth while you sleep is a great way to cope with dental phobia.
Why gums may turn blue
Experts identify a large number of factors that can affect the condition of the gums.
Reasons for discoloration of gums in a child:
- Eruption of baby or molar teeth. Due to strong mechanical pressure on the soft tissue vessels, a blue hematoma appears.
- Bruise or cut. Due to mechanical trauma to the gums, a blood clot accumulates at the site of the bruise, causing the gums to turn blue.
In an adult, soft tissues may change color for the following reasons:
- Improper functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Kidney diseases;
- Problems with the thyroid gland;
- Inflammatory diseases of teeth and gums: gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, herpetic and candidal stomatitis, which are accompanied by increased accumulation of bacterial plaque on the enamel.
- Carious formations localized in the cervical area of the tooth.
- Errors in orthopedic treatment. An incorrectly made crown or denture reduces blood flow along the gingival margin, which causes the periodontium to turn blue. In this case, the color change occurs due to a violation of the blood supply to the soft tissues.
- Surgical interventions. After tooth extraction, the soft tissue in the area of the formed hole may turn blue.
- Burns (regular thermal or chemical burns). A chemical burn can occur due to contact with the mucous membrane of an aggressive substance that is used in the treatment of root canals.
Prevention
There are no special unique ways to prevent dental disease in children. Ulcers on the gums are the result of untreated caries. Therefore, all preventive measures are aimed at preventing caries:
- oral hygiene (make sure your baby brushes his teeth properly);
- balanced diet;
- rinsing your mouth every meal;
- preventive procedures (remineralization, fluoridation; fissure sealing);
- timely dental treatment;
- preventive examinations at the dentist 2 times a year (some experts recommend once every 3 months if the baby already has treated teeth).
Timely dental treatment for children and proper hygiene will help avoid many dental problems. Teach your child to take care of the health of their teeth and beautiful children's smiles will delight you every day!
Main reasons
Why can one or more teeth turn blue? There may be several reasons for this; sometimes there is nothing dangerous to health in this process, and sometimes this is a reason to urgently seek advice from a dentist. A change in shade is possible due to poor quality nutrition or adherence to a strict diet. This can also happen if you eat a lot of fresh berries, such as blueberries, blueberries or blackberries.
Newly installed fillings may differ in color from natural tissues. A pulpless, that is, dead tooth can also change its color. This is explained by the fact that when the pulp is removed, nutrients stop flowing to the tissues.
If a seemingly healthy tooth begins to turn blue, this may indicate that there are problems with the root system. This is usually preceded by serious dental diseases. In addition, the cause of blue enamel may lie in the patient’s body; this phenomenon may be caused by the presence of chronic diseases or problems with the digestive system. Another common reason is the use of low-quality water with high levels of iron.
Causes of blue gums in adults
The reasons may be different, the most common include:
- problems with the cardiovascular system;
- thyroid diseases;
- kidney pathologies;
- stomatitis;
- inflammatory periodontal diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis or periodontal disease;
- caries and its complications;
- improper orthodontic treatment;
- incorrectly selected or incorrectly manufactured orthopedic design.
- a consequence of surgical intervention (blue discoloration of the periodontium can occur after tooth extraction);
- chemical (exposure to the mucous membrane of an aggressive substance used in the treatment of root canals) or thermal burn (exposure to high temperatures on the gums).
How to make teething easier
While the teeth are just getting ready to appear, the baby experiences a lot of unpleasant sensations, which, of course, causes a lot of trouble for the parents. During this period, the child needs care and affection, as well as plenty of fluids. It is recommended that infants be breastfed more often, and children on artificial nutrition should be offered more warm water.
There are many ways to relieve discomfort. Two most popular:
- Give your child special teethers - these are soft silicone toys filled with liquid. Cool the toy slightly in the refrigerator before use. This will help relieve swelling and reduce pain. The textured surface of the teether will give the baby the opportunity to thoroughly massage and “scratch” the gums. The bright design of the toy will attract attention to it and amuse the child.
- Use topical medications - pain-relieving gels and ointments for gums, designed specifically for children. These remedies act very quickly and help the child forget about discomfort for several hours.
When to see a doctor
When a child is teething, his immune system is weakened. Symptoms that parents attribute to teething may be hiding a viral or bacterial infection. Don't wait for it to go away on its own and see a doctor if:
- the child has a temperature above 38.5℃;
- he became lethargic and drowsy;
- refuses food;
- Vomiting and diarrhea began.
So:
- When teeth are being cut, the baby’s gums may be painful and swollen; this is a normal phenomenon; otherwise the tooth cannot pass through the tissues of the jaw and gums;
- When the gums erupt, they look swollen, reddened, then they turn white, and a hole forms in the place of the future tooth;
- You should not use a gel to relieve pain in your baby’s gums unless absolutely necessary; if the pain bothers the child greatly, then choose gels without anesthetics or combination drugs;
- If, against the background of teething, the child has a high fever, he is very restless or, on the contrary, lethargic, refuses to eat, if vomiting or diarrhea begins, consult a doctor.
(0 ratings; article rating 0)
Share Share Share
Treatment of blue teeth
If during diagnostics it is determined that the cause of blueness of all teeth is the use of special products, the dentist or hygienist may prescribe a professional cleaning of the oral cavity. Quite often the patient requires enamel polishing; this allows for the best results.
If after such manipulations the blue discoloration does not disappear, you can try other methods.
First of all, the doctor should send the person for an X-ray examination of the jaw, this will make it possible to make a correct diagnosis, as a result of which the treatment will be as effective as possible. It may also be necessary to remove previously installed fillings and caries-infected hard tissues. If necessary, treatment of the annals and root system of the tooth will be prescribed.
There are several methods to restore the original whiteness of your teeth. One of the most common options is the installation of a composite filling, that is, direct artistic restoration of a row. A more expensive procedure is the production of an artificial crown or special onlays - veneers (indirect restoration).
Why do my gums hurt when teething?
To appear on the surface, the tooth needs to pass through the jaw bone and gum tissue. Although this is a natural process, it can be painful, because the tooth “grows” through the gum and violates its integrity. The gums become sensitive during tooth eruption, and pain may occur when pressing on them. These unpleasant sensations go away as soon as the tooth moves apart the gum and looks out.