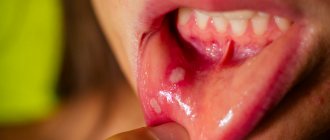
What is burnt alum
Burnt alum is a powdery substance that is obtained by heating a potassium-aluminum compound. After heat treatment, the substance is ground and sieved to isolate the hygroscopic powder. Burnt alum is white, odorless, and has a sour-astringent taste. Natural origin allows you to exclude perfume components, fragrances and artificially synthesized substances from the composition.
You can buy burnt alum in 50 g plastic jars. The instructions indicate that the product is intended for external use. It does not completely dissolve in water and tends to clump when left in the open air.
Manufacturers indicate only 100% crystalline powder of potassium alum in the composition.
Description
Burnt alum is a unique substance created on the basis of traditional potassium aluminum samples. To obtain them, the starting material is heated to 160 degrees Celsius, after which it is evaporated until 50% of the original volume is lost.
As a result, it is possible to obtain an absorbent, odorless, white powder, distinguished by its shape in the form of small crystals.
The finished product has the following effect:
- antibacterial;
- drying;
- hemostatic;
- cauterizing;
- enveloping.
In addition, alum quickly eliminates itching and other discomfort. As a result, help with stomatitis is guaranteed in every case.
How burnt alum works
When applied topically, the powder acts in several ways:
- relieves inflammation and disinfects;
- dries;
- relieves itching;
- prevents and eliminates unpleasant odors.
The substance does not irritate the skin at the site of application. After application, it forms a colloidal film that envelops the nerve endings. It relieves pain, itching and burning sensations, and discomfort from insect bites.
In what cases will burnt alum help?
According to the instructions for the drug, burnt alum is used in:
- combating excessive sweating. The ability to adsorb moisture and reduce the functioning of glands that secrete sweat and sebum is actively used by patients with hyperhidrosis. In addition, alum is able to disinfect areas with excessive sweating and get rid of bacteria and fungi that are sources of unpleasant odors; can be used as an antiperspirant;
- prevention of skin irritations, for treating minor scratches, including after using a razor;
- therapy of dermatological pathologies: dermatitis, diaper rash, eczema, neurodermatitis, fungal infections of the feet;
- gynecology and urology – for the treatment of vulvovaginitis, balanitis;
- dentistry - for the treatment of gingivitis, stomatitis;
- cosmetology - to narrow pores, increase elasticity, relieve inflammation. Added to powder or cream.
Burnt alum powder can be used to treat festering wounds and trophic ulcerations on the skin. As a result, the damaged surface of the skin will dry out and tighten, and bleeding will stop.
Lotions, rinses
The rinse solution is prepared as follows:
- take the following ingredients: a glass of boiled water, 4-5 g of burnt alum;
- mixing until the crystals are completely dissolved;
- store the solution for no more than two days in the refrigerator;
- The liquid must be stirred before use.
To cure stomatitis in a child, you can use the method of spot treatment of ulcers with a concentrated solution.
To obtain the working fluid, you need to take 10 g of alum per glass of water. The solution is applied using cotton pads and rubbing.
The resulting solution should be used every 3 hours by rinsing. Afterwards it is recommended to treat the ulcers locally.
How to use burnt alum powder
The manufacturer prescribes the use of the drug, if indicated, externally as a powder; the frequency of administration is not limited.
Wounds and ulcers are treated with a solution of powder. To prepare, take ½ teaspoon of the substance and add to 200 ml of hot water. The composition is applied to the wound surfaces the required number of times; a gauze bandage may be applied.
When used simultaneously with other drugs, the powder does not react with them.
Causes
The pathology is caused by numerous infectious agents, as well as oral injuries and allergic reactions. The reason for its development may be a lack of certain vitamins and microelements.
The following types are distinguished:
- viral (herpetic - present in 80% of all cases, the rest are represented by measles, chickenpox, influenza, rubella, mononucleosis, adenovirus, enterovirus, papillomavirus viruses);
- fungal – candidiasis is detected in the vast majority of cases in infants; in older children it occurs due to immunodeficiency, diabetes, or taking antibiotics;
- bacterial - most often it is caused by various types of staphylococci and streptococci; in rare cases, stomatitis is caused by pathogens of tuberculosis, syphilis, diphtheria, gonorrhea;
- allergic – often the pathology develops as a reaction to various products, components of toothpaste, chewing gum;
- autoimmune – in the occurrence of aphthous lesions, one of the leading causes is considered to be the presence of autoimmune problems;
- traumatic - in children, the oral mucosa is less stable than in adults; it is easily damaged under the influence of chemical and physical agents, or mechanical trauma.
The factor that caused this pathology determines the treatment tactics and what drugs will be prescribed.
There are factors that contribute to the development of the disease.
These include:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (duodenitis, gastritis, intestinal dysbiosis, colitis, enteritis);
- blood diseases;
- pathologies of the nervous and endocrine systems;
- helminthiases;
- prematurity;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- weak local immunity;
- lack of microelements, vitamins (B vitamins, selenium, zinc).
All these numerous factors cause and contribute to the development of stomatitis. In this regard, there is a significant difference in the treatment of different types of disease.
Recipes
A remedy to combat armpit sweating. To prevent the white powder from crumbling during application and to ensure that the composition gets directly onto the skin, it is better to prepare the composition:
- dissolve two teaspoons of burnt alum in 500 ml;
- add a few drops of essential oil with your favorite scent;
- pour the solution into a bottle equipped with a sprayer.
At first, the product must be used twice a day, then the composition can be applied to the armpit area once a day.
- For sweaty feet. In this case, dry alum is used. First you need to clean your feet with a pumice stone or a scraper. Then the surface is treated with alum. To enhance the effect, you can treat socks and shoes that are worn every day with alum. Already on the third day, sweat production decreases, cracks in the legs heal, and small wounds heal. To prevent the skin from drying out, the skin of the feet can be treated with cream.
- Face mask for enlarged pores. Ingredients you will need: one egg white, 5 grams of burnt alum powder, one teaspoon of almond or apricot oil. The protein must first be whipped into a foam, add other ingredients and mix. Apply to clean skin for half an hour. Then wash off with warm water.
Instructions for use
Alum is used as a mouth rinse for stomatitis.
To prepare the solution, add 0.5 tsp to a glass of boiled water. powder and stir it thoroughly.
In this case, the consistency of the solution becomes slightly viscous (like laundry starch), and the taste becomes sour. Should be used 5-7 rubles/day, duration of procedure is 1-2 minutes.
The use of the solution for the treatment of stomatitis in children is not prohibited, but the application pattern is modified: it is necessary to lubricate the oral cavity with a cotton swab 3-4 times a day and for 30-40 minutes. After the procedure, refrain from eating and drinking.
Reviews
According to customer reviews, burnt alum works well in treating skin problems, including complex wounds with suppuration and trophic ulcers.
However, the powder is mainly used in the fight against sweating and its consequences; it is applied instead of deodorant to the armpits, on the feet and palms, and in shoes to prevent unpleasant odors. The downside is that it stains clothes when applied.
Some buyers note that alum does not help overcome excessive sweating, but an unpleasant odor does not appear after application.
Stomatitis in a child - what to do?
In pediatric patients, stomatitis is the most common diagnosis, which occurs even in children during the neonatal period. The concept of stomatitis itself combines several diseases that are expressed by ulceration and/or inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity.
Causes of stomatitis in children
Stomatitis can develop for a number of reasons, but the most common are allergic and infectious. Inflammation of the oral mucosa in children can be caused by:
- Herpes, chickenpox, influenza and rubella viruses. The main symptom of the viral form of stomatitis is rapidly bursting blisters that transform into extremely painful oval ulcers covered with a yellowish coating.
- Bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci and others). Symptoms of bacterial stomatitis consist of the appearance of a putrid odor from the oral cavity, redness of the mucous membranes and the formation of superficial erosions on it.
- Fungi (candida, mycoplasma and others). The main symptom of candidal stomatitis is the formation of a dense cheesy coating on the inner surface of the cheeks, tongue and gums. The child's breath smells like sour milk.
- Mechanical damage, allergies in combination with infection of the mucous membrane (aphthous stomatitis). The symptomatic picture includes the formation of round, well-defined ulcers, covered with a dense white coating and surrounded by a pronounced rim (granulation).
The onset of the disease can be triggered by a lack of vitamins, a stressful situation, general hypothermia (even mild), immunodeficiency and an allergic reaction, anemia and dehydration of the body. However, most often stomatitis is diagnosed after a course of treatment with antibiotics and sulfonamides.
Symptoms of the disease in children
The first signs of stomatitis in children resemble a common cold and ARVI. They appear 4-8 days after infection. The most common symptoms are:
- temperature rise to 38-40 degrees;
- general malaise, tearfulness;
- increased gag reflex and nausea;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
Less commonly, children may be bothered by cough and runny nose, conjunctivitis. A day after the appearance of these symptoms, a gray, white or yellowish coating forms in the child’s mouth (depending on the type of pathogen), and later - ulcers or watery blisters.
Already at this stage, the child needs complex therapy, which can be started after detailed diagnosis. First, a culture is carried out to determine the causative agent of the disease, and its sensitivity to drugs is also determined. In addition, consultation with a pediatric gastroenterologist, allergist and endocrinologist may be required. Only after this can the doctor prescribe appropriate treatment.
Treatment methods for stomatitis in children
The tactics of therapeutic measures to combat stomatitis in children are determined by the diagnostic results and consist of a set of standard procedures, the action of which is aimed at reducing symptoms, and taking medications appropriate to the type of pathogen.
For viral and herpetic stomatitis, children are prescribed the following medications:
- antiseptic drugs - Stomatidin and Hexoral;
- anti-inflammatory and painkillers - Paracetamol, Nurofen, Ibuprofen;
- antiviral and antiherpetic drugs - Bonafton, Acyclovir, Viferon and Zovirax;
- healing preparations for treating ulcers - Vinilin, Karotolin.
Additionally, folk remedies can be used: sea buckthorn and rosehip oil, centenarian oil and decoctions of chamomile and sage.
For fungal stomatitis, drugs with antimycotic and healing effects are used:
- Pimafucin;
- Clotrimazole;
- Fukortsin;
- Candide.
Additionally, the mucous membranes are treated with Nystatin tablet powder. Children are advised to take Diflucan and Fluconazole tablets, Imudon and pain relievers (Nurofen, Paracetamol and Panadol).
For aphthous stomatitis, the set of drugs depends on the source of the disease:
- for the allergic nature of stomatitis - antihistamines in the form of creams, ointments and tablets (Loratadine, Cetrin);
- for an infectious nature - Hexoral and Lugol, as well as Iodinol;
- for stomatitis caused by gastrointestinal problems - Bonafton, Dekaris and others.
Treatment of ulcers in the oral cavity is carried out using boric acid, the drug Aekol, sodium tetraborate and Cholisal gel.
For stomatitis caused by the activity of pathogenic bacteria, treatment of the oral cavity with antimicrobial drugs Chlorhexidine and Miramistin, Furacillin and Metrogyl is recommended. In the case of a prolonged course of the disease or in the absence of a visible effect, antibiotics are prescribed orally. In childhood, the drugs Ampiox, Kanamycin, Gentamicin are indicated. At the same time, they strengthen the child’s own immunity with Interferon or Viferon and vitamin complexes.
Basic rules for treating stomatitis in children
In addition to regularly taking medications and daily treatment of the oral cavity with special solutions prescribed by your doctor, you must follow several general rules:
- Dieting. It is important to exclude spicy and salty dishes, coarse, too hot or cold foods from the child’s menu. You should also give up sweets.
- Oral hygiene. During an exacerbation of stomatitis, when the symptoms are most severe, brushing your teeth with brushes is not recommended. It is better to give preference to rinsing with disinfectant solutions and herbal decoctions.
- Personal hygiene of the child. It is better for the sick person to provide a separate set of dishes, which must be disinfected daily by boiling or special detergents. The same applies to the child's toys and personal belongings.
An equally important point in the treatment of stomatitis in children is strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations. Despite the abundance of drugs that help get rid of symptoms, their independent selection and use can lead to the transition of the disease to the chronic stage, or even aggravate the course of the disease with numerous complications.