01.12.2019
Penetration of bones and tooth roots into the maxillary sinus indicates perforation of the latter. A similar complication may be accompanied by treatment at the dentist. Perforation of the maxillary sinus occurs quite often. From this article you will learn the causes of this pathology, signs of perforation, methods of diagnosis and treatment, as well as prevention. Photos of tooth roots in the maxillary sinus can also be seen in the sections of the article.
Reasons for the breakup
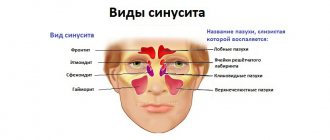
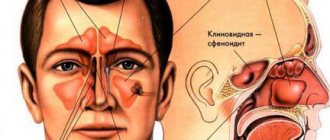
The sinus, called the sinus or maxillary sinus, is not characterized by tightness. It interacts with the nasal cavity through a small gap. As a rule, a sinus rupture occurs in the area of its lower part.
This happens due to the characteristic structural features and against the background of certain diseases, namely:
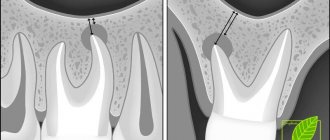
- The roots of molars and premolars are located very close to the sinus. In some cases, the bone layer is quite thick and reaches 1 cm. However, sometimes the barrier can be less than 1 mm in thickness.
- The first and second molars in the root part can be located directly in the sinus cavity and are separated only by the mucous membrane.
- Rapid thinning of the bone layer due to inflammatory diseases in acute or chronic form, including cysts, periodontitis and periodontitis.
- Thin trabeculae of bone in the maxillary tissues.
All these factors can cause a sinus rupture during dental treatment. In this case, there may be no violation of the technology of performing dental procedures. This may be a result of each patient's individual anatomy. Let's figure out why the tooth root penetrates the maxillary sinus.
CT scan for acute sinusitis in children
CT scans of the upper jaw are performed not only in adults, but also in children, since this is one of the most informative diagnostic methods.
Acute sinusitis in children in most cases is a complication of a viral infection. Infecting the nasal mucosa, the virus almost always penetrates the sinuses and causes inflammation in them. Maxillary sinusitis in a child can develop against the background of allergic rhinitis: upon contact with an allergen, the nasal mucosa swells, the outflow of secretions from the sinus worsens, and inflammation develops. Other predisposing factors include:
- nasal injuries;
- congenital anomalies (deviated nasal septum, etc.);
- inflammation of the nasopharynx;
- oral diseases;
- the presence of a chronic source of infection in the body;
- vascular disorders (as the blood supply to the maxillary sinuses deteriorates, local immunity decreases and susceptibility to disease increases).
To avoid unnecessary radiation in uncomplicated sinusitis, CT scans of the upper jaw and maxillary sinuses are rarely performed in children. A computed tomography scan is mandatory if intraorbital or intracranial complications are suspected and in preparation for surgery.
Frequent cases
Perforations of the maxillary sinus occur, as a rule, as a result of the dentist’s work during dental treatment. Tissue ruptures are typical for the following situations:
- Tooth extraction.
- Dental implantation.
- Endodontic therapy.
- Tooth root resection.
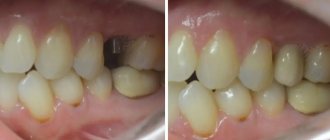
If perforation occurred during a tooth extraction operation, this may be a consequence of unskilled and excessively rough work of the dentist, as well as the individual characteristics of the structure of the maxillary sinus of the patient himself. If the dental roots are located directly in the sinus cavity, perforations during the removal of molars are almost inevitable.
One of the complications during endodontic therapy can also be perforation of the tooth root, which in most cases is associated with perforation of the sinus floor. This situation can occur as a result of excessive expansion of the root canals, as well as when using brute force when installing pins and compacting cement for fillings. In this case, most often not only the root of the tooth may be in the maxillary sinus, but also its fragments and particles of filling material. And this is dangerous for the patient.
When a rupture occurs during installation of an implant or during filling a root canal, as well as as a result of inserting pins into the root of a tooth, this in the vast majority of cases is a therapeutic error by a specialist. Sometimes you can find the roots of a wisdom tooth in the maxillary sinus.
No hospitalization required
Operations in our Center are performed by operating teams of experienced maxillofacial surgeons with ENT training in a sterile operating room. The treatment is as gentle and minimally traumatic as possible; a 24-hour hospital stay is not required; you will go home the same day .
The intervention lasts about an hour, under sedation. After completion, the patient quickly returns to clear consciousness without unpleasant consequences or risk of complications. After 30-40 minutes you can safely go home. For patients with concomitant cardiovascular diseases, a day hospital is provided . You can lie down for the time necessary for recovery under the supervision of our anesthesiologist-resuscitator.
Tooth root cyst in the maxillary sinus
Removal of the tooth root is considered the most effective method of treating cysts localized in the apex area. When the patient has not been carefully examined, and the dentist does not have information about the thickness of the bone tissue that separates the cystic wall from the sinus floor, and also in the case when it is necessary to remove a large amount of jaw bone, rupture of the sinus tissue quite often occurs.
Chronic sinusitis and sinus lifting
The chronic form of the inflammatory process is a relative contraindication for sinus lifting. In some situations, when it is not possible to use alternative methods, the operation is still performed. There is a risk of exacerbation of the infectious process after a sinus lift, but such a complication is rare.
If a patient has chronic inflammation in the maxillary sinus area, the dentist must carefully weigh the benefits and possible risks before setting a date for surgery. During the rehabilitation period, the patient must take strong antibacterial drugs to minimize the risk of exacerbation.
Exacerbation of sinusitis in the postoperative period can lead to implant rejection (if a closed sinus lift was performed). This complication is considered very unfavorable, since the deficiency of bone tissue worsens after removal of the structure. Doctors are not always able to restore bone volume after implant failure, so it is better not to risk the patient’s health again.
Symptoms
When perforation and entry of the tooth root into the maxillary sinus occurs during dental resection procedures, characteristic signs of rupture appear, including:
- Bleeding from the tooth socket with small air bubbles, the number of which increases when you try to exhale sharply through your nose.
- Bloody nasal discharge from the side of the ruptured sinus.
- A sharp change in the timbre of the injured patient’s voice, characterized by nasal sound.
If there is a tooth root in the maxillary sinus, the symptoms cannot go unnoticed. Sometimes, after resection, the patient begins to complain about difficult passage of air through the resulting hole, as well as pressure and heaviness in the projection of the maxillary sinus.
When perforation occurs during implantation or endodontic therapy, signs of such a complication include:
- Specific failure of the instrument or material for implantation after some effort to move it into the jaw.
- Changing the position of the instrument used in the resulting wound.
- The appearance of small air bubbles and blood discharge from the hole.
Perforation may not be detected and repaired immediately after a sinus rupture, which leads to infection of the sinus cavity and is accompanied by signs of acute sinusitis or sinusitis.
The following symptoms are typical for such pathologies:
- Acute intense pain in the sinus area of the upper jaw.
- Swelling of the nasal mucosa on the side of the injury, accompanied by difficulty in nasal breathing.
- Discharge of purulent secretion from the nose.
Systemic complications and symptoms of intoxication appear, which are characterized by chills, headaches, weakness and increased body temperature. But how to detect the root of a tooth in the maxillary sinus?
"ENT clinic of Doctor Zaitsev"
Our clinic specializes in the treatment of ear, nose and throat diseases. The most modern equipment, our own techniques and experienced specialists are the three components that will allow you to treat acute sinusitis quickly, safely and effectively. Regular clients of our clinic notice that our prices remain at the 2013 level!
When the first signs of sinusitis appear, please do not delay visiting a doctor. Call and make an appointment - we are always ready to help you!
Diagnostics
For an experienced dentist, specific testing may not be necessary to confirm a maxillary sinus perforation.
If we are talking about tooth resection, then such a complication as soft tissue rupture is accompanied by a typical clinical picture. If the dentist is in doubt when perforation occurs during endodontic treatment, the following additional examinations may be required:
- Probing the hole formed after tooth extraction, as well as the root canal. For this purpose, a thin probe is used. In this way, it is possible to establish the absence of a bone bottom in the wound. During the study, the instrument passes through soft tissues without hindrance.
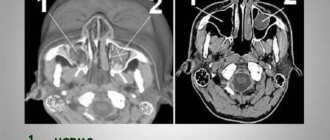
- Carrying out an X-ray examination of the sinuses. The resulting images will show darkening in the sinus cavity, indicating the accumulation of blood in this area, as well as filling material and fragments of teeth and implant. In some cases, contrast radiography may be required with the introduction of a special substance into the perforation cavity.
- CT scan. This diagnostic method makes it possible to detect ruptures and the presence of foreign bodies. In this case, the image is as accurate and informative as possible.
- If the perforation is old, it is recommended to donate blood for a general examination, based on the results of which it will be possible to draw a conclusion about the presence or absence of an infectious focus in the body.
After carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures and confirming the fact of a rupture of the maxillary sinus, the dentist will prescribe appropriate treatment. So, a person has a tooth root in the maxillary sinus - what to do?
Treatment
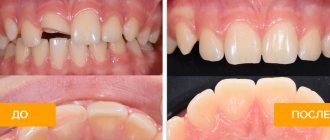
The choice of treatment for maxillary sinus perforation depends on the changes that occur as a result of the rupture. Non-surgical treatment seems possible in case of violation of the integrity of the tissues during tooth extraction, when the pathology was detected immediately, and according to the results of the radiographic examination it is clear that there is no infection of the sinus cavity and there are no foreign bodies in it. With such a clinical picture, the doctor, as a rule, tries to preserve the blood clot formed in the hole as much as possible. In addition, preventative measures are taken to prevent wound infection.
For this purpose, a small gauze swab soaked in an iodine solution is inserted into the hole. As a rule, the tampon is self-fixed in the wound cavity. However, sometimes it may be necessary to place a stitch in the gum. Treatment with an iodide solution should be carried out for 6-7 days until the defect disappears and full-fledged granulations are formed. It is not recommended to remove the tampon from the socket during treatment, as this can damage the clot and lead to infection of the wound.
When a tooth root is found in the maxillary sinus, everyone should know what to do. In some cases, the doctor decides to close the defect with a special plastic plate, which is secured to adjacent teeth with clasps. Thus, it is possible to achieve separation of the sinus and oral cavity.
Preventing inflammation
In addition to preserving the wound, preventive therapy is carried out aimed at preventing the development of the inflammatory process. Most often, antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. In addition, drops are prescribed for instillation into the nasal passages, which have a vasoconstrictor effect. Treatment can be carried out both on an outpatient basis and while staying at home.
If the examination reveals the presence of a foreign body in the maxillary sinus, then treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting. Therapy consists of surgical intervention to open the cavity and remove the tooth root from the maxillary sinus.
Types of pathology
There are several types of maxillary sinus cysts:
- Odontogenic. The inflammatory process forms in the root system of an untreated dental unit located on the upper jaw. As the tumor increases in size, it destroys the bone and grows into the sinuses. The contents of the cyst are purulent.
- Retention. The reason for the development is dysfunction and obstruction of the glands responsible for the production of mucus.
False cysts are classified into a separate category. In such formations there are no epithelial cells. The appearance of such formations is due to a violation of the structure of the maxillofacial apparatus.
Complications
Rupture of the maxillary sinus is a serious consequence of dental procedures, the treatment of which most often occurs in an inpatient setting. What is the risk if the tooth root has grown into the maxillary sinus?
Self-treatment of the problem using traditional medicine methods can lead to even more serious complications, including:
- Severe inflammatory process in the sinus cavity with further infection of adjacent tissues. Then osteomyelitis develops in the upper jaw.
- Transition of the inflammatory process to other cranial sinuses, including the sphenoid, frontal and ethmoid.
- Loss of healthy teeth located in the perforation area.
- Formation of foci of pus, phlegmon and abscesses.
Due to the immediate proximity of the brain, and the fact that the tooth root has gone into the maxillary sinus and the latter has ruptured, the occurrence of an infectious lesion of the meninges cannot be ruled out. The next stage of serious complications may be meningitis or meningoencephalitis, which are life-threatening for the patient.
Prevention
As for preventive measures regarding perforation of the maxillary sinus, they consist of following the following rules:
- A thorough and comprehensive examination of the patient before undergoing serious dental procedures, including tooth resection or implantation.
- Correct assessment of the anatomical features of the jaw structure of each patient.
- Strict compliance with all technological requirements for complex dental procedures.