What kind of disease is this
In general, a cyst is a benign formation, similar to a cavity, with contents inside the walls.
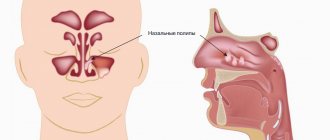
In addition to the maxillary, it is often found in the sinuses near the nose, but under no circumstances does it extend beyond these zones. The cyst can be of any size - from small formations in the initial stages to large ones that expand if treatment is started.
There are two mechanisms for the development of education:
- Retention , which occurs and develops if the excretory duct of the glands in the mucous membrane is blocked.
- Odontogenic , progressing as a dental pathology, i.e. due to diseases of teeth and gums.
Both single and multiple cysts can also be detected. In some people this formation is acquired, while in others it is present from birth.
This is a very common disease: according to statistics, in every fifth person, a detailed examination of the nose can reveal a small maxillary sinus cyst (MSC). Such formation does not make itself felt for a long time, or manifests itself in the form of pain and unpleasant symptoms.
The patient who has been diagnosed with a cyst is being monitored dynamically. If his condition worsens sharply, surgical intervention is possible.
ENT about a cyst in the sinus:
ICD code
There are two disease codes according to the ICD:
- 8
- K09
Each of them is assigned depending on how the cyst was formed and what type it acquired.
Comments
The other day I visited LORA, because... I'm worried about constant nasal congestion. HE examined and diagnosed “odontogenic sinusitis” and prescribed symptomatic treatment. He said that in order for everything to return to normal, you need to go to the dentist and look for the cause. No cyst was found. Explain what could be the reason and why this is dangerous?
Tanyusha (06/03/2020 at 17:53) Reply to comment
- Dear Tanyusha, the diagnosis of odontogenic sinusitis indicates that the problem should be looked for in the oral cavity. The cause of its development is often periodontitis, perforation of the sinuses during dental treatment, impacted and dystopic teeth. If the exact cause is not identified and eliminated, then the formation of a cyst will not take long to occur.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (06/08/2020 at 09:16) Reply to comment
Hello. Today I had an MRI about pain on the right side of my face. A cyst was discovered in the maxillary sinus on the right. Tell me where to run and what to do? Thank you.
Victoria (08/17/2021 at 04:57 pm) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Main symptoms
This problem makes itself felt with a whole range of symptoms.
| Symptom | Description |
| Nasal congestion | The primary symptom that signals clogged ducts. A person experiences difficulty breathing through the nose and discomfort in the upper jaw. Rapid irritability and poor performance appear. There is a risk of exacerbation of chronic sinusitis or rhinitis. Manifests itself in everyday life or during physical activity. People, for example, who go diving, may experience problems. When diving under water, they will feel unpleasant pressure and pain in the area where the cyst has formed. If swelling appears or fluid begins to leak out, this leads to the appearance of ENT diseases. |
| Headaches, cheek and eye pain | Symptoms characteristic of both cysts in one and two sinuses. All this affects the overall performance of a person, appetite, drowsiness, as well as the respiratory process. In special cases, the patient suffers from vision problems (double vision). Sometimes a cyst located on one side can manifest itself with unilateral symptoms. For example, headaches and nasal congestion are felt mainly on the side where the tumor appeared. Pain and swelling in the cheeks can spread to healthy teeth. There is a risk of unpleasant sensations in the forehead area. Regular headaches and intoxication of the body occur. Clogged sinuses cause severe pain when tilting the head. |
| Mucus and pus in the throat | The patient notices a strong discharge of clear yellow liquid from the nose. It can leak from one or two nostrils, depending on the location of the cyst. This phenomenon appears as a result of film rupture and leakage of a cyst-like formation. This will not last long, but the risk of contracting an infection during this period increases significantly. |
| Temperature | A natural reaction of the body, signaling the fight against an infection in the sinus. Cyst-shaped tumors take a long time to form, so elevated temperatures can also persist for a long time. |
Perforation discovered after the fact
If the patient suffered discomfort in the first 2-4 weeks and did not contact the dentist, who, in turn, did not identify the problem at the time of its occurrence, the perforated wound turns into a permanent fistula that is not prone to healing.
Typical signs of chronic sinusitis appear:
- the nose on the side of the fistula is constantly stuffy;
- the parasinus area gives off a dull pain, its waves can roll to the nearest eye and temple;
- pus is discharged from the nostrils and in the mouth (from the fistula);
- possible swelling of the cheek on the side of the fistula with visible deformation of the face.
In most cases, a fistula is felt as air passing between the nose and mouth while talking or sneezing. Pronunciation of a number of sounds becomes more difficult. Liquid food may enter the nose from the mouth. Therapy for an old fistula shows rather weak results, and relapse with such a problem is not uncommon. There is no alternative to surgical intervention - it is necessary to open the maxillary sinus, remove foreign objects and non-viable tissue. The fistula requires excision throughout its entire thickness, the defect is closed with healthy tissues of the patient. After the operation, an antibiotic course lasting one and a half to two weeks is prescribed; in parallel, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs must be used.
Causes
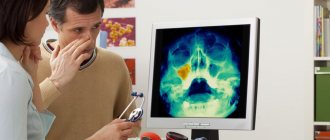
Maxillary sinus cyst on MRI
A cyst usually forms if the excretory ducts of the gland are blocked. If they are clogged, a special substance is released that stretches the walls of the duct, causing them to gradually fill with serous fluid. The substance inside the tumor continues to be produced. The longer they remain in this state, the larger the cyst becomes.
There are several reasons for the appearance of such formation:
- Injuries to this area, due to which the ducts are blocked (for example, due to blows to the face, falls, etc.).
- Due to hereditary predisposition, abnormal structure of ducts and bones in this area.
- The presence of sinusitis (chronic processes in this area).
- For problems with the upper teeth and gums (usually due to caries, periodontal disease, etc.).
- As a consequence of an allergic reaction.
- Due to the location of the roots of the teeth.
The last reason is related to the structure of the root system: the roots of the upper teeth (5 and 6 on one side or the other) can extend to the lower wall of the sinus, or be separated from it by a small partition.
If the pathology in this section has been neglected, ondogenic protrusions may form. There are two types of them: radicular (coming from the roots of the teeth) and follicular (formed when the tooth germ is displaced).
A neoplasm can also arise as a result of pathogenesis - when an infection enters this area and affects healthy tissues, as a result of which they are enclosed in a formation hidden by a membrane.
Such protrusions form in most of the population, but can safely resolve on their own. However, having reached a certain size, they begin to cause concern, and treatment is no longer possible.
How does a sinus cyst appear?
The mechanism of development of paranasal sinus cysts is quite simple.
Let's start with the fact that in the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses there are glands that produce mucus. Each such gland has its own excretory duct for secreting secretions, which opens on the surface of the mucous membrane of the sinus.
Under the influence of various unfavorable factors, the mucous membrane thickens and the excretory ducts become clogged. At the same time, the gland continues its work with the same force, mucus is formed, but the exit for it is blocked. Due to wall pressure, the glands begin to fill with mucus, stretch and form a cystic neoplasm. Approximately the same effect is obtained if you put an inflatable balloon in a water tap and open the tap - water will flow and inflate the balloon.
There are several UNFAVORABLE FACTORS that will contribute to the development of this process, namely changes in the thickness of the mucosa and blockage of the ducts:
- exposure to an allergen and the occurrence of allergic reactions,
- polyps,
- infectious diseases,
- chronic diseases developing in the nasal cavity (rhinitis) or in its paranasal sinuses (sinusitis: sinusitis, sinusitis, etc.),
- diseases of the teeth of the upper jaw, anatomical features of the structure of the nose.
Classification
Cysts are classified according to several criteria:
| Criterion | Varieties |
| Due to the occurrence | In medicine, there are three types:
|
| By content | Neoplasms may contain a number of substances inside:
|
| By location | It is formed in one or more places:
|
Alveolar cyst
We are talking about odontogenic neoplasms that are localized in areas near the alveolar bay. The negative impact of such a cyst, if left untreated, can damage the root system of the upper teeth. It can only be removed through surgery.
Maxillary sinus cyst
This variety practically does not manifest itself in any way. Only with a certain location and significant size can it lead to pain.
Most often, it is discovered by chance when the doctor suspects another disease. To do this, a CT, MRI, or x-ray is performed in the area of the maxillary sinus.
Cyst in the maxillary sinus and sinus lift
Many patients are interested in the question of whether it is possible to simultaneously extract a cystic formation and perform bone grafting of the upper jaw. The answer to this question depends on several factors, which include:
- The degree of severity of bone tissue atrophy at the site of the cyst (in some cases, the deficiency is so pronounced that sinus lifting becomes impossible, and patients can only hope for the installation of removable dentures);
- The presence of an active inflammatory process (cysts are often complicated by infectious pathologies, especially sinusitis, which are a direct contraindication for surgery);
- The size of the cystic formation (small cavities can be removed immediately before sinus lifting, but if the cyst occupies the entire space of the sinus, then bone grafting is out of the question);
- The location of the cyst (if it is located on the lower wall, then problems with removal during sinus lifting usually do not arise, but if the formation is located higher, the dentist simply will not be able to reach it without injuring the walls of the sinus).
Performing a sinus lift with preliminary removal of a cystic formation is performed quite rarely and only in cases where the process has just begun to develop and was accidentally discovered by instrumental studies. The doctor must correctly weigh the benefits and risks of future surgery. Most often, patients are transferred for treatment to ENT specialists, and the sinus lift is postponed to a later time.
Dimensions
The size of the cyst does not affect the severity of symptoms. Large formations may not cause inconvenience. It is much more important where exactly the tumor is located :
- Those located in the lower section of the sinus cause less discomfort.
- But even a small formation located in the upper wall can lead to complications and headaches.
This is due to the close location of the cyst to the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Recording of a webinar from a doctor of sciences on the topic:
Diagnostics
Typically, such a pathology is discovered by chance when a person is tested for the presence of another disease.
To do this, they go to a dentist (if the disease concerns the jaws and teeth) or an otolaryngologist, who then issues a referral for an x-ray or another type of examination. ENT specialists can be involved in the diagnosis.
Laboratory tests will not accurately evaluate a cyst.
The doctor may do the following:
- Examine your nose.
- Refer him for endoscopic examination.
- Prescribe an x-ray or computed tomography scan of the patient’s sinuses and skull.
X-ray
X-rays reveal blockage of the sinuses.
Large tumors will appear in black on the image. An odontogenic cyst is identified by adjusting the x-ray to a specific projection. The x-ray will show the size of the cyst:
- Light areas indicate the sinus.
- Dark ones signal a cyst.
Tomography
Currently it is the most effective diagnostic method.
Thanks to it, it is possible to determine with high accuracy where the cyst is located and what the thickness of its walls is, what substance accumulates inside it. Based on the tomography results, the doctor obtains a layer-by-layer section of the patient’s skull. This helps to assess the structure of the formation, which is especially important when selecting a further treatment method.
Puncture
The method involves puncturing the cyst.
The color of the fluid that flows from the wound determines the appropriate diagnosis. This method is only suitable for identifying large tumors. For this, local anesthesia is used. The procedure is not only diagnostic, but also therapeutic. After pumping out the fluid, the person’s breathing returns to normal. The cyst shrinks and the patient's condition improves for a while.
Sinuscopy
An accurate way to study clogged areas and determine their location. The doctor inserts an endoscope into the excretory anastomosis.
With its help, it is possible to examine the tumor in detail and study it for other pathologies.
conclusions
The most objective way to diagnose dense space-occupying formations of the upper jaw is computed tomography (CBCT or MSCT).
If signs of osteoma are detected in the cavity of the upper jaw, the patient must be recommended to undergo surgical excision of the formation. Morphological verification of the removed material is mandatory.
The combination of an endoscopic transnasal approach and navigation equipment in the removal of osteomas of the upper jaw is the most modern and optimal option for treating the pathology.
MestaMidin-nos has proven itself in local therapy as a means to prevent possible postoperative infectious and inflammatory complications. The use of MestaMidin-nos allows you to avoid a course of systemic antibacterial therapy.
The publication was carried out with the support of Solopharm in accordance with internal policy and current legislation of the Russian Federation.
Treatment
Since such a tumor is not malignant, it is easily and without consequences surgically removed.
As long as the cyst has not developed to a large size, it can actually be cured without surgery. But the doctor must determine the symptoms, then order an examination, based on the results of which he will select an individual course of treatment.
Medication (without surgery)
A good method of treatment if the cyst has not reached a large size.
In this case, after some time you can reduce the size of the formation. The patient is given an appointment:
- Saline solutions used to rinse a clogged nasopharynx.
- Drugs that increase the outflow of mucus from the ducts.
- Nasal medications aimed at narrowing blood vessels (use drops and sprays).
- Antibiotics (local and general use).
Only taking special medications is suitable. Prescribing physiotherapeutic procedures and a course of warming up the sinuses is strictly prohibited - such actions accelerate the growth of the cyst and cause side effects.
If there is a risk of developing acute sinusitis, the doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics. Plus, he recommends rinsing clogged sinuses and nasal cavity with antiseptic solutions.
How is the operation to remove a cyst performed?
Surgical intervention
An effective method, however, is resorted to only if it is impossible to overcome cyst formation with medications . An asymptomatic tumor does not need to be operated on - it is usually small and can resolve on its own with proper drug treatment and rinsing.
Reference! Only a doctor can give a referral to a surgeon. However, the procedure is prohibited if the disease has acquired a more acute form.
Operating methods
If the pathology can harm the patient’s health, the doctor decides to perform a surgical operation to remove it. The operating method is determined based on the size and location of the cyst:
| Method | Description |
Endoscopic removal | At the moment, endoscopy is considered one of the most modern and gentle methods. Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. No additional incisions are required and the risk of injury is minimal. Thanks to this, the patient undergoes a short recovery period. |
Puncturing | The area where the substance has accumulated breaks through. As a result, the accumulated liquid comes out. The procedure is risky and is used only for large formations that urgently need to be reduced. After the operation, you will need to comply with the conditions of the recovery period. In parallel, medications are used (mainly for general effects). |
Denker's maxillary sinusotomy | The most traumatic method of surgery, used when a tumor needs to be removed in a hard-to-reach place. The operation is performed only under general anesthesia: an incision is made under the upper lip, and then one of the walls of the cyst is opened. Then it is necessary to comply with the conditions of postoperative recovery - the patient must remain at rest for a week, after which the stitches can be removed. |
Caldwell-Luke operation | Gentle method of surgery: local anesthesia is used for removal. An incision is made under the gum to expose the walls of the cyst. The tumor is carefully removed so as not to harm healthy tissue. The infected mucous membrane along with damaged tissues is scraped out, after which the oral cavity is watered with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide. The incision is sutured and the sinus is temporarily packed. |
Consequences of deletion
For successful recovery after removal of the cyst, the patient is hospitalized. It lasts no more than 2 weeks:
- Every day the nose and sutures are treated and washed with an antiseptic.
- The patient takes antibiotics (broad-spectrum), antihistamines and, if necessary, painkillers.
- The patient will be offered to undergo a course of physical treatment aimed at resolving the swelling.
If the incision heals at a normal pace, the stitches will be removed after 7 days. But in general, rehabilitation will take up to 4 weeks.
During this period, the patient must follow a number of rules :
- Maintain oral and nasal hygiene.
- Rinse your mouth with plain water every time after eating.
- Do not pick your nose or put your fingers in your mouth.
- Reduce physical and thermal stress on the body. Therefore, stop playing sports for a while, do not bathe in hot water, and do not eat hot and spicy foods.
Important! At first, swelling of the lips and cheeks, numbness, and poor sensitivity in this area may persist. It happens that the sense of smell deteriorates for a while, breathing through the nose becomes difficult, and discharge appears. This is a temporary post-operative effect that will go away within a week.
Possible complications
Since this formation is not malignant and does not form metastases, it does not lead to disruption of the functions of other organs. Only a large tumor can lead to complications.
If the cyst has been damaged, then there is a chance of contracting ENT diseases, infections, purulent infection of oral tissues, bones, and also the loss of several teeth. Otherwise, with proper treatment and recovery process, the risk of relapse is minimal.
Could she burst?
If the size is significant and there is overload in this area, the tumor may burst. The liquid will begin to flow out and cause inconvenience.
When is anastomosis closure required?
Damage to the integrity of the voids of the appendages, which are located on both sides of the nose, can occur during the removal of a tooth from the alveolus in the upper jaw.
The channel occurs due to the following reasons:
- quick removal of a dental unit using surgical forceps;
- an operation to implant an implant into the jaw bone tissue;
- urgent treatment of a complex tooth with inflammation;
- chronic periodontitis, in which the ligaments and plate of bone that hold the tooth in the socket become thinner and flake off.
When performing manipulations in the upper row of the jaw, a cavity or fistula may form. The danger is the possible spread of purulent fluid. The problem is solved by surgery.
Preventive measures
During the postoperative period, it is better to eat non-solid food at room temperature, so as not to irritate the nervous system and not fully restored tissues.
After and before the course of treatment, it is allowed to use traditional medicine.
Here are a few of them:
- The leaf of any plant must be washed and placed in the refrigerator, keeping it there for at least 3 days. Then the juice is squeezed out of it, mixing the resulting substance with water and instilling 3-5 drops of the resulting mixture into the nostrils several times a day.
- 2 gr. mumiyo and 5 ml. glycerol dissolves in warm water. Place this solution in the nostrils 3-5 times a day.
- Make an infusion of eucalyptus, tea and honey (in equal parts). The nasal passages are instilled in the morning, afternoon and evening.
Their individual use will not give great results, but together with other methods they provide a significant effect, reducing the size of the tumor and clearing the ducts. Plus, they must be agreed upon with the attending physician.