MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
- Removal cost
- Indications
- Preparation
- Methods and steps
- Complications
- What to do after the procedure
- Our doctors
- Reviews
- To make an appointment with a doctor
In practice, specialists at Plomba dentistry periodically encounter cases of complete destruction of the crown of a tooth and infection of the root system, in which a purulent-inflammatory process occurs. Most often, this problem can be solved only by removing the root and remains of the tooth. But sometimes the root system can be preserved for subsequent prosthetics. How the removal will be carried out, what measures and tools will be used, the doctor will be able to decide after familiarizing himself with the clinical picture.
Indications for tooth root removal
- Complete destruction of the coronal (supra-gingival) part, affecting the root system;
- extensive purulent-inflammatory process at the root: cyst, abscess;
- longitudinal axial fracture;
- previous incorrect extraction - during removal, fragments remained in the hole, causing an inflammatory process that affected nearby tissues.
The damaged area of the tooth is easily identified visually. Additional symptoms of the need for urgent medical intervention and even possible removal of a diseased tooth are:
- twitching, throbbing pain;
- acute pain due to mechanical action - pressing, biting, chewing food;
- unpleasant odor;
- gum hyperemia;
- a purulent process is a direct indication of the need to remove the root of a diseased tooth;
- elevated body temperature.
If one or more symptoms are present, the destroyed units are removed. In some cases, incomplete removal is performed - resection of the tooth roots. This usually occurs when the root apex is affected by periodontitis, a small cyst, or granuloma. Often in such diseases the coronal part is preserved. In this case, the damaged part is removed through an incision in the gum. Subsequently, installing a crown solves the problem of restoring the chewing unit.
Preparing for tooth extraction
Removing a tooth or its roots is a rather complex surgical dental procedure, but it will not be difficult for the patient to prepare for it. If local anesthesia is planned to be used for pain relief, the patient should eat a large meal before visiting the dentist because:
- After removing a tooth or root, it is forbidden to eat for several hours;
- salivation after eating is significantly reduced, which will make the dentist’s work easier;
- after eating, blood glucose levels are normalized and the risk of loss of consciousness under the influence of local anesthesia is reduced
In the case of general anesthesia, on the contrary, it is necessary to abstain from eating for several hours before the removal procedure begins. Drinking alcohol before visiting the dentist is prohibited. Alcohol affects the structure of the blood and does not combine well with anesthetics, not to mention the negative impact on the human psyche and behavior.
Inflammatory and infectious diseases of any nature must be cured before surgery to remove a tooth or its roots. The dentist must be warned about the presence of allergies to certain medications, in particular to anesthesia drugs.
A normal pregnancy in general is not a contraindication to dental procedures. However, during this period the use of a number of drugs used in dentistry is prohibited, so information about pregnancy is entered into the patient’s dental record. Also, detailed information about the patient’s chronic diseases, especially heart pathologies, is recorded in the dental record.
Treatment
Depending on the picture and accompanying symptoms, the process of wisdom tooth removal is conventionally divided into simple and complex.
Easy removal
The operation begins with the administration of anesthesia.
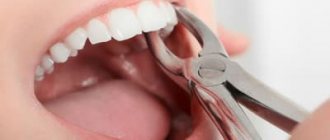
During removal, specialists use forceps and elevators. No incisions are made for this type of intervention. The process of extracting a tooth from bone tissue lasts 2 to 10 minutes, depending on the location of the roots.
The resulting wound is treated with an antiseptic. If it is large, stitches are placed to reduce the risk of infection in the wound. A bandage with an anesthetic is applied to the area of manipulation, this is done to reduce bleeding.
Difficult removal
In the case of a complex operation to remove wisdom teeth, the necessary data is also collected and analyzed, and anesthesia is administered.
The operation is accompanied by dissection of the gums with a scalpel. To remove the tooth itself, it is cut into pieces using a drill. This is done to make it easier to remove. After removal, the resulting wound is treated with an antiseptic and then sutured.
Depending on the location of the tooth, the operation can take from 15 minutes to an hour and a half.
After the manipulations, regardless of their complexity, the doctor must consult the patient on wound treatment and, if necessary, prescribe medication.
Removal using ultrasound
In some cases, and with the appropriate equipment, a tooth can be removed using an ultrasonic scalpel. It allows for contactless intervention. Wounds with these manipulations heal faster, and the risk of complications is reduced.
Excision of a dental pocket with preservation of the tooth
There is a disease of the wisdom tooth in which its removal is called into question. This is an inflammation of the dental pocket, which is caused by bacteria that get under the gums. With this pathology, the doctor dissects the hood without affecting the tooth itself. The area of inflammation is treated with antiseptics.
The process of tissue healing and restoration, as a rule, proceeds quickly and the need for removal disappears. If the so-called pericoronitis has reached the stage at which ulcers form on the mucous membrane, the wisdom tooth is removed.
Methods and stages of removing teeth or their roots
Most often in modern dentistry, only two methods of removing teeth or their roots are practiced:
- removing a tooth from the gum using forceps;
- rocking of the tooth and its rotation around its axis by elevators.
In cases where the roots are deep, the gum tissue can be cut with a scalpel. In general, the process of removing teeth or their roots is divided into the following stages:
- separation of the round ligament from the neck of the tooth (ligamentotomy);
- applying (installing) forceps to the tooth;
- advancing the fixing elements of the forceps under the gum;
- final fixation of the forceps;
- rotation (rotation) or luxation (swaying) of the tooth;
- extracting a tooth or its roots from the socket.
Preventive measures
In order to avoid serious complications after molar tooth extraction, you need to follow a number of recommendations:
- 20 minutes after the end of medical procedures, the gauze swab should be removed from the socket of the extracted tooth;
- In order for healing to occur faster, you should not drink or eat for the first 2-3 hours after surgery;
- for several days you should avoid eating solid foods, as well as spicy and hot foods and drinks;
- hot water procedures and physical activity are contraindicated until the hole is completely healed;
- You cannot wash the hole yourself or try to clean it with foreign objects that have not been disinfected;
- During the first 24 hours after surgery, you should not rinse your mouth;
- A cold compress on the right side of the cheek will help prevent swelling and reduce the likelihood of bleeding.
If the hole does not heal for a long time or it seems that there are remains of a tooth in it, then you should contact your dentist again and under no circumstances try to solve these problems yourself.
Common complications after tooth extraction
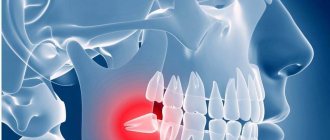
Tooth extraction is essentially a full-fledged surgical intervention. Symptoms such as pain and inflammation in the surgical area are considered normal for the rehabilitation period, unless they are too severe and are not eliminated 3-4 days after tooth (root) extraction. The rehabilitation period may also be characterized by increased body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes.
More serious clinical complications include:
- renewed bleeding from the socket after tooth (root) removal - methods for eliminating minor bleeding can be discussed by the dentist; in case of intense bleeding, it is necessary to urgently consult a specialist;
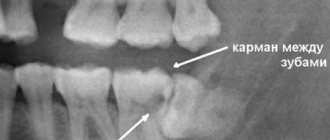
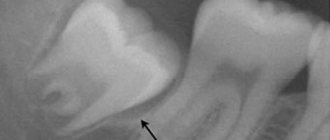
- incomplete removal of the tooth root - the presence of residues is diagnosed by x-ray and follow-up and quickly eliminated;
- alveolitis is a dangerous, but easily eliminated by antibiotics, inflammatory process in bone tissue, characterized by a significant increase in body temperature, swelling, severe pain, and requires immediate treatment, as it can lead to sepsis.
In the first hours after removal, the patient should not eat. Cotton swabs from the surgical area can be removed 30 minutes after completion of all manipulations. In the first days after surgery, it is not recommended to eat sour, sweet, salty, very chilled or hot foods. Short-term cold compresses can relieve pain in the first days after tooth extraction.
Tooth extraction is a last resort in modern dentistry. A qualified specialist must strive by all means to save the tooth even in the most difficult cases.
The final stage of restoring oral health is not the removal, but the replacement of teeth (except for wisdom teeth).
Wisdom tooth – “secret agent”
Few people know in detail what kind of tooth this is and what its “wisdom” is.
And everything is quite simple - he is called that because he/they appear much later than the others, at the age when a person’s mental development is considered complete, and the acquisition of wisdom begins. It does not have a “milk” predecessor, and it grows only after the final formation of adult bone tissue. In our time, it has been proven: the wisdom tooth, also known as the eighth tooth, is a rudiment, a relic of evolution. Unlike ancient humans, our jaw is shorter, and there is simply no room for it. That's why Western dentists insist: it must be removed as soon as it begins to appear. However, in any case, if the “eight” causes pain, your best assistant is the dentist! After looking at the x-ray, he will tell you what to do next. If everything is fine with the newly erupted tooth, the dentist will prescribe a course of treatment that will relieve inflammation.
what to do with the eighth teeth based on the patient’s complaints and clinical picture. Problems with even one or two elements disrupt the normal functioning of the entire dental system. Pain appears when opening the mouth and chewing, sometimes the bite and position of the incisors change.
So, if the eighth tooth is problematic, then the surgeon will perform an operation to remove it.
Wisdom teeth that have not erupted or are in the wrong position make removal more difficult and require the use of a complex extraction method.
We remove the nerve, save the tooth
Removal of the nerve - depulpation - is necessary when:
- As a result of injury, the tooth enamel is chipped so badly that the nerve is affected.
- pulpitis was detected. Inflammation of the nerve can begin as a result of advanced caries.
- you are preparing for prosthetics and installation of orthopedic structures.
Removing a nerve today no longer requires the use of arsenic, and modern anesthesia literally works miracles. Not only the capital, but also Samara can boast of modern clinics where you can get rid of the nerve without hassle and pain. How much does it cost? The prices are quite reasonable!
Yes, after removing the nerve, the tooth will lose sensitivity and blood supply. But when the nerve disappears, the painful reaction to all irritants, including sweets, cold and hot, will also go away.
In any case, the dentist advises removing the nerve only when it is no longer possible.
What to do after tooth extraction
The operation cannot be prescribed without an X-ray examination, which makes it possible to determine the amount and degree of root destruction and the extent of the inflammatory process. Before root removal, the patient is given anesthesia, after which the gum is separated from the neck of the tooth. The surgeon's further actions are determined by the clinical picture. Dentists call the most difficult operation the removal of the deep and often twisted roots of the “figure eight” – the eighth tooth in the dentition. But the specialists of the Plomba clinic successfully cope with this too.