How to use prosthetic teeth for periodontitis and periodontal disease
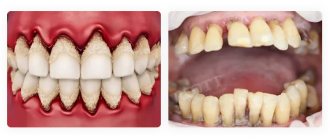
Periodontitis and periodontal disease are gum diseases with different origins. The first pathology occurs due to pathogenic microorganisms, and the cause of the second is a metabolic disorder in tissues. The processes in both cases lead to loose teeth, so it is much more difficult to prosthetize teeth. However, modern dentistry can cope with such situations and return the aesthetics of a healthy smile to the patient.
Periodontal measures for moderate disease
If the disease has become moderately severe, selective therapy is added to the above measures. It is aimed at grinding the surface of teeth that have undergone occlusion, removing deposits under the gums, applying therapeutic dressings and compresses. Along with this, questions are being resolved about whether it makes sense to remove roots or individual teeth, and whether it is worth carrying out splinting and orthopedic therapy. Local anti-inflammatory procedures are usually complemented by general therapy.
Differences and characteristics of diseases
Periodontal disease occurs when there is a metabolic disorder, which leads to a failure in the process of renewal of gum tissue. This, in turn, causes loose teeth. In the early stages, the pathology is almost impossible to detect, since there is no pain or bleeding. Other signs include:
- bad breath is noticeable;
- gums become pale;
- the roots of the teeth are exposed.
Important: without treatment, the patient may completely lose teeth.
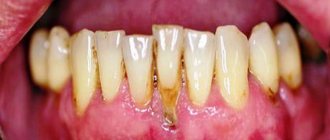
Periodontitis is different in that it is caused by gum inflammation and in most cases it is a consequence of bacterial gingivitis. The disease has characteristic symptoms:
- swelling and severe pain;
- bad breath;
- redness of the gums.
The acute form is manifested by bleeding and constant pain. Without treatment, gum tissue erodes and cannot hold teeth in place. These pathologies have several treatment options, which are prescribed by the dentist. Advanced stages definitely require one of the prosthetic methods.
What is periodontium, its features
In dental practice, the term “periodontium” is used. It includes a whole complex of tissues surrounding the teeth. They all have a common nerve origin and a single blood supply, therefore they are closely related to each other. The periodontium forms several constituent elements: gums, bone tissue, periodontium, cement of the root system of the teeth. Its functions include providing support, maintenance, and protection of the entire dental system. Pathologies associated with periodontal damage include conditions such as gingivitis, periodontal disease, tumors, and periodontitis.
How to choose a denture for periodontal disease
The disease cannot be completely cured at the moment, but medicine can achieve stable remission and a stable condition. If the disease is detected at an early stage, then therapeutic methods are used. If the condition is neglected, the teeth will need to be completely removed and replaced with dentures.
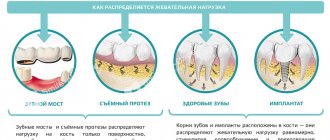
In any case, dentists carry out treatment to achieve remission of periodontal disease and stop the loss of bone tissue. Only after this, a prosthetic option is selected, using removable or non-removable orthopedic structures:
- zirconium crowns, which are placed on your own ground teeth. Usually they are placed in the smile zone;
- bridges fixed to crowns or abutment teeth. This solution is suitable only for the initial stages of pathology;
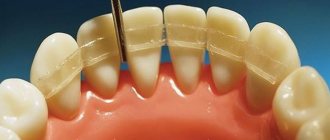
- splinting clasp dentures. This is a conditionally removable option that has minimal impact on the oral mucosa;
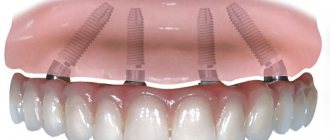
- implant-supported dentures (to avoid the risk of rejection, it is important to regularly treat periodontal disease).
The choice of orthopedic design depends on the clinical case and general health. If the patient still has his own teeth, the doctor will recommend a removable denture. In difficult clinical situations, two methods are suitable: installation of splinting clasps and implantation with immediate loading.
Features of the chronic form of generalized periodontitis
Any other oral disease can be a provoking factor in the development of the disease. Gingivitis, neglect of personal hygiene rules, mechanical damage - all these are obvious reasons for the development of a chronic form of pathology. It occurs in two stages:
- exacerbation, accompanied by throbbing pain in the gums, excessive bleeding, pus discharge, abscesses, fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes (such symptoms often make themselves felt against the background of pneumonia, stressful situations, ARVI);
- remission, which occurs during therapeutic measures; during this time, symptoms do not appear, and nothing bothers the patient.
The further the pathology develops, the longer the exacerbation lasts, and the time of remission gradually decreases.
Orthopedic systems for periodontal disease
Before selecting the optimal option, it is necessary to evaluate the supporting teeth to see whether they can withstand the chewing load. They must not be allowed to fall out or become loose after prosthetics.
Important: before taking impressions, the gums should not be inflamed due to periodontal disease, otherwise the finished prosthesis, crowns or inlays will be uncomfortable to wear. In addition, the risk of root infection will increase.
The most commonly used constructions are:
- Zirconium crowns.
For this pathology, metal ceramics are contraindicated and porcelain is not used. Therefore, the patient is offered products made from zirconium dioxide. They are more expensive than other crowns made from other materials, but are biocompatible with gum tissue and provide excellent aesthetics.
- A bridge that is used only in certain cases.
Its peculiarity is that installation requires supporting teeth, inlays or implants. The gums and other tissues experience pressure from such a prosthesis, which gradually leads to bone atrophy, so the system does not last long, about 5 years.
- Implantation, which is possible even in one stage.
Previously, it took time for artificial tooth roots to heal, and only six months later permanent crowns were fixed on them. The one-stage method involves making a small puncture into which a titanium base is inserted and the prosthesis is almost immediately put on. The method is also called momentary loading implantation.
- Clasp prosthesis.
Option suitable for periodontal disease and periodontitis. It does not have high aesthetics, but returns functionality when eating. With the help of a prosthesis, the load on the bone is distributed evenly. Abutment teeth will be required for installation.
Orthopedic treatment of periodontal diseases
Periodontal disease is a fairly common, frequent and difficult to treat problem in modern dentistry. It requires an integrated approach and multi-stage therapy, one of the points of which is orthopedic treatment of periodontal diseases. Since problems with periodontal tissues also affect teeth and there is a high risk of their loss, any emerging defects in the dentition will need to be replaced. And the remaining teeth need to be strengthened and “saved” from falling out. This is where orthopedics is needed.
Orthopedic treatment of periodontal diseases solves several important problems at once: they help relieve inflammation, eliminate pathological mobility of teeth (and thereby improve local blood circulation), normalize occlusion of the dentition, and correctly redistribute chewing loads.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Today, orthopedic dentists use the following methods of orthopedic treatment of periodontal diseases:
- Selective grinding . It is used for pathological abrasion of dental surfaces, possible deformations of the dentition due to partial edentia, the formation of interdental gaps and rotation or tilting of teeth. Allows you to “stabilize” problematic incisors, canines and molars, and also prevent their further movement.
- Splinting. It is used to eliminate developing pathological tooth mobility. There are several types of splints (temporary, removable and non-removable), which are used depending on the clinical situation - the orthopedist himself decides which is best to use for a particular patient.
- Temporary prosthetics . Temporary dentures are used to stabilize the dentition and replace defects. They allow you to replace cosmetic defects, as well as restore functionality and correctly distribute chewing loads.
- Permanent prosthetics . After the inflammatory process has been eliminated and the periodontal tissues have been treated to the extent possible, it is possible to replace the temporary dentures with permanent ones. Permanent structures are more reliable, aesthetically pleasing and durable than temporary structures, so it is better not to delay their installation.
Prosthetics for periodontitis
Before choosing one of the methods, the specialist conducts training. It will be approximately the same for periodontitis and periodontal disease. The set of activities includes:
- elimination of caries;
- cleaning gum pockets and teeth from stone and plaque;
- antibacterial and physiotherapy;
- removal of loose teeth.
Until recently, many types of prosthetics had contraindications for periodontal tissue diseases. The problem is that pathologies lead to thinning of the bone and loosening of the teeth.
But now prosthetics have become possible subject to certain conditions, including:
- installation of certain types of systems;
- stabilization of the pathological process;
- use of special materials.
As with periodontal disease, bridges are used at the initial stage. To restore chewing and aesthetic functions, clasps and prosthetics on implants are more often used.
Help: there is also the option of a complete denture (densary jaw) made of acrylic or nylon, but it, like the “bridge,” is rarely used because it does not prevent bone loss.
Treatment of moderate periodontitis: possible options
If the disease is of moderate severity, therapy will take longer. In addition to these procedures, the complex should include the removal of decayed teeth and the use of steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory compounds. Also, to improve the general condition, doctors prescribe physiotherapy procedures:
- exposure to affected areas through short-wave ultraviolet radiation;
- carrying out a special massage of the gums, which can be vacuum, vibration, etc.;
- darsonvalization procedures;
- local hypothermia;
- electrophoresis.
Upon completion of treatment, it is necessary to make a follow-up visit to the doctor so that he can assess the general condition and make a prognosis.
Stages of prosthetics using implants
After preparing the oral cavity, classic one-stage or basal implantation is performed. The first option involves immediate installation of an implant after tooth extraction. Then the abutment is screwed onto it and a crown or prosthesis is put on. The procedure is different in that it does not require an incision in the gum and detachment of the periosteum; a small puncture is sufficient. After six months, instead of a temporary crown, a permanent crown is fixed; during this period, the implant should take root.
If the tooth has been removed a long time ago, tissue volume is increased or the basal implantation method is used. It lies in the fact that the artificial root is not implanted in the place of the previous one, but where there is enough tissue volume, that is, in a deeper layer (basal). Likewise, it requires no incision, just one puncture. This type of prosthetics is used most often when several adjacent teeth are missing. Immediate load on the bone will improve blood supply to the tissues, which will have a beneficial effect on periodontal diseases.
Diagnosis of generalized periodontitis
In identifying the disease, a special role is played by the clinical picture and the “age” of the disease. If there are concomitant diseases, the doctor can refer the patient for examination to other doctors - an endocrinologist, therapist, gastroenterologist, immunologist, rheumatologist, etc. When analyzing dental status, the doctor should pay attention to the following criteria:
- the amount of deposits on the teeth;
- their character;
- general condition of the gums;
- depth of the vestibule of the oral cavity;
- features of bite;
- condition of the bridles;
- degree of tooth mobility;
- formation of periodontal pockets.
As part of the initial examination, a Schiller-Pisarev test is taken and the periodontal hygiene index is determined. The doctor also examines scrapings from the gum pocket using PCR diagnostics and saliva chemiluminescence. Among additional diagnostic methods, it is recommended to conduct a biochemical analysis of blood fluid for glucose and CRP. Of no small importance is the determination of IgA, IgM, IgG indicators.
To identify the stage of development of the disease, the following is used:
- orthopantomography,
- x-ray of the intraoral cavity,
- biopsy of gum tissue.
Doctors pay special attention to differential diagnosis with pathologies such as gingivitis, periodontal disease, periostitis, and osteomyelitis. Like therapy, diagnosis must be comprehensive and include several examinations to make the most accurate diagnosis.
Causes of gum recession
Quite often, gum recession is one of the manifestations of periodontitis (periodontal disease). In this case, as a result of poor circulation in this area, gum atrophy and exposure of the tooth root occurs.
As a rule, this condition is diagnosed in middle and older age, although there are exceptions - for example, juvenile periodontitis.
Gum recession due to periodontitis
Chronic mechanical trauma to the gums - for example, from an overhanging edge of an artificial crown or filling, which happens very often, trauma from a removable denture or its fixing element - a clasp, which, due to the rapid development of implantology, is much less common today. The presence of tartar is also a risk factor for the development of gum recession.
Chronic gum trauma with wide crowns
Acute trauma to a tooth, leading to its displacement towards the lip or cheek.
Acute trauma – tooth dislocation
Anatomical features of the structure of the alveolar process - a thin layer of cortical bone located on the anterior surface of the alveolar process or the so-called “thin gum biotype”.
In the latter case, the problem is not the thickness of the bone, but rather the thickness of the gum covering the bone along the anterior (vestibular) surface. However, in both cases, the problem is associated with insufficient blood supply to the area.
Gingival recession as a consequence of thin biotype
Incorrect (low on the upper jaw or, conversely, high on the lower jaw) location of the frenulum of the lip or frenulum of the tongue.
Gingival recession of the lower incisor due to a labial frenulum
If in the case of a lip frenulum, the recession will be located on the front surface of the tooth root, then in the case of a lingual frenulum, the posterior (lingual wall) of the tooth will be exposed.
Another cause of gum recession can be orthodontic treatment, which can result in thinning of the vestibular bone.
And, of course, oral hygiene can also cause recessions and wedge-shaped defects. Moreover, oddly enough, too thorough brushing of teeth is not at all a good thing, because as a result of excessive mechanical action, both the gums and teeth suffer, in the cervical area of which wedge-shaped defects are formed, which we wrote about above.
Is it possible to cure chronic generalized periodontitis?
In the process of getting rid of generalized forms of severe periodontitis, surgical manipulations are added to the listed methods. As part of these procedures, teeth with 3-4 degrees of mobility are removed, patch surgery is performed, abscesses are opened, etc. Based on the available indications, plastic surgery of the vestibule of the oral cavity and frenulum is performed. If the disease is accompanied by a particularly severe course, systemic anti-inflammatory therapy, immunomodulatory treatment, and vitamin intake are mandatory measures.
Physiotherapy takes part in complex therapy. In particular, the doctor prescribes electrophoresis, darsonvalization, laser treatment, hirudotherapy, herbal medicine, and apitherapy. Activities must be carried out under the supervision of a treating specialist in compliance with all his instructions. Violation of the treatment regimen is fraught not only with a lack of effect, but also with a complication of the general condition.