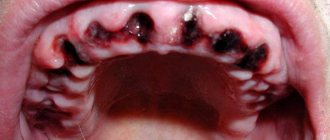
Most often, people turn to a periodontist for treatment of gingivitis and periodontitis. The main symptoms of these diseases are as follows:
- swelling of the gums occurs;
- their color changes;
- bleeding occurs;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- burning, itching, and soreness are present.
The doctor first examines the oral cavity to make a diagnosis, and then carries out treatment. As a preventative measure, he recommends maintenance therapy.
A little about periodontal disease
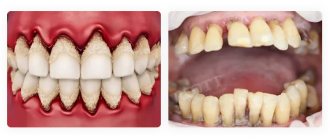
Periodontal disease occurs in approximately ten percent of patients with gum disease. There are a number of root causes that lead to damage to the oral mucosa. However, the topic has not been fully studied. Among the established causes of periodontal disease are the following:
- The presence of chronic diseases. These could be disorders in the endocrine system, problems with blood pressure, regular migraines, diabetes and many others.
Periodontal disease is accompanied by various unpleasant symptoms, if you notice them you should immediately consult a dentist. Among these symptoms, it is worth highlighting the most characteristic of this disease:
- teeth become very sensitive. They react to cold, to warmth, to rough food, to touch;
- gums become paler in color;
- gums bleed;
- gums itch;
- the root of the tooth may become exposed;
- in advanced forms of the disease, loosening of the teeth and an increase in the distance between them are observed.
Prevention of stomatitis in children
Irritative stomatitis can be prevented with good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups and proper nutrition. Because many adults and children carry the herpes virus and can transmit it even without symptoms, there is no practical way to prevent herpetic stomatitis. However, parents may discourage their child from kissing, eating, or playing in close contact with people who have an active herpes infection.
Ulcers can be minimized by teaching children to avoid injury, even minor trauma to the mouth. If our doctor determines that a child has a nutritional deficiency, parents can make sure the child is taking appropriate supplements and eating recommended foods. It won’t hurt to visit the dentist once every six months if we have previously discovered stomatitis in the child. Regular visits to our clinic will help prevent serious complications and detect the disease in time.
Dental diseases for which Levomekol is used
Levomekol is actively used for periodontal disease . Periodontal disease is a pathology of the tissues that fix the tooth. At the initial stage, patients often do not complain about changes. At first, gum disease may bleed, itch, and turn pale. As the disease progresses, the gum pockets become deeper (the teeth are less hidden by the gum). At the junction of the tooth and the gum, the enamel is very thin. When the gums recede and atrophy, the enamel begins to wear off.
Patients with periodontal disease often have inflamed gums. Gingivitis is manifested by severe inflammation, pain, and redness of the mucous membrane. In some cases, the addition of bacterial flora is possible.
Levomekol is used for gum fistulas. In this case, in patients, purulent discharge begins to drain from the fistula canal. The patient complains of severe pain, bad breath, and the taste of pus.
actively prescribed for fluxes . The disease occurs as a result of untreated caries. Flux is manifested by severe pain, swelling at the site of the lesion, and compaction. Pus accumulates in the area of the flux. Over time, the flux breaks through with the release of purulent exudate. Levomekol is approved for use for thermal burns caused by hot food and drinks. The medicine can also be used to treat necrotic damage to the mucosa if the inflammation has not been treated.
What problems may arise after tooth extraction?
Many patients experience swelling and pain in the gums during the first time after tooth extraction, but in most cases these problems quickly disappear. If the removal was traumatic, recovery may take longer. What factors influence the rate of wound healing?
- Her condition immediately after the operation, determined by the qualifications of the surgeon.
- The addition of a secondary infection, in most cases provoked by the patient himself.
- The patient has diseases that affect blood clotting and prevent the formation of a blood clot.
Therefore, it is so important to seek qualified dental care - in a reputable clinic, with an experienced surgeon who does not make annoying, unforgivable mistakes during surgery.
Salt treatment
One of the most effective and proven means for the treatment of periodontal disease is salt. It stimulates restoration processes in periodontal tissues, relieves inflammation and prevents the formation of tartar on the surface of the enamel.
When treating, it is better to use sea salt, which is rich in iodine compounds and fights the disease even more effectively.
To prepare the solution, dissolve 1-2 teaspoons of salt in a glass of warm boiled water and rinse your mouth for 2-3 minutes. The procedure should be repeated after each meal at least 3 times a day.
Salt massage has proven itself well. Lightly moisten a soft toothbrush with water and then dip the ends of the bristles in fine salt. Then massage the gums and teeth for 3-4 minutes, paying special attention to areas with periodontal disease. There is no need to rinse your mouth after the procedure. The massage must be repeated once a day before bedtime.
When used regularly, sea salt is a reliable remedy for preventing disease at home.
What happens in the mouth after tooth extraction?
A wound formed in the mouth creates problems:
- it can bleed for quite a long time;
- food can get into it and cause repeated injury;
- it can fester, infecting surrounding tissues.
How long does it take for gums to heal after tooth extraction under normal conditions? After the surgeon removes the tooth, the healing process begins, and the ligament surrounding the removed tooth begins to contract. A blood clot forms in the wound itself, which will protect it from infection. After a couple of days, granulation tissue begins to form, which over time is replaced by osteoid tissue. As a result, after 2–2.5 weeks the edges of the wound come closer together, and then young bone is formed, over which the gums take shape.
Fistula on the gum: main symptoms
The channel that drains fluid and pus from the source of inflammation is usually visible to the naked eye. It is simply impossible to ignore the hole that appears after the gums have suppurated and pus comes out. Thus, pathology is extremely easy to identify by visual examination. However, in addition to the obvious, the disease also has a number of other symptoms:
- the problematic tooth has become mobile;
- the gums are red and inflamed;
- there is discharge of pus;
- body temperature increased.
Nowadays, the most accurate results are provided by diagnostics using radiographic examination. However, most often there is no need to resort to it - a routine examination allows you to accurately make a diagnosis.
Why does a fistula form on the gum?
A fistula canal is evidence of a number of dental diseases:
- caries. It is an inflammatory disease in which the tooth rots, leading to the formation of a cavity. The cause of development is exposure to carious bacteria;
- pulpitis. It is a complication of caries, in which decay affects the pulp. Through it, bacteria can penetrate further into soft and bone tissues;
- periodontitis. A disease in which the tissues surrounding the tooth become inflamed due to infection. The cause of development may be caries, mechanical trauma, unqualified dental treatment;
- cyst. A neoplasm that appears at the apex of the tooth root. Most often it occurs if treatment of pulpitis is neglected;
- granuloma. A formation that somewhat resembles a cyst, but does not have a shell and is small in size - no more than 5 mm.
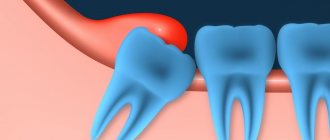
A fistula canal can appear not only with the above diseases. Quite often, the cause of its occurrence is inflammation that develops during the eruption of a wisdom tooth or the difficult eruption of baby teeth. The gums begin to swell and are damaged by the teeth. The opportunistic microflora present in the oral cavity is activated, which triggers the inflammatory process.
Types of stomatitis
Everyone is more accustomed to saying “stomatitis”, but it would be more correct to say “stomatitis”, since this is a generalizing concept for a whole group of diseases. Depending on the causes of stomatitis, it can be divided into several types, each of which has a number of characteristics.
Viral or herpetic stomatitis in children
One of the most common types of stomatitis in children is caused by the herpes simplex virus. Typically, a child becomes infected through airborne droplets. In addition, the virus is transmitted through dishes, toys, and household items. Most often, herpetic stomatitis appears in a child between the ages of one and four years. The disease begins with a cold, accompanied by lethargy and increased body temperature. Sometimes there is a runny nose and cough. Around the second day, small round or oval erosions of a light yellow color with a bright red border appear on the lips, tongue and inside of the cheeks. Swelling appears, the gums begin to bleed, and the child refuses to eat.
Traumatic stomatitis in a child
The disease is caused by mechanical trauma to the oral cavity. For example, burns from hot food, a too hard nipple, the habit of chewing a pencil. In addition, traumatic stomatitis often occurs in children with malocclusion due to frequent biting of the cheeks and tongue.
Candidal stomatitis
Appears in children under one year of age. The cause is Candida fungi. The main symptom is the appearance of a white coating in the baby’s mouth. It should be noted that this should not be confused with regular flowering after feeding. A cause for concern is if plaque persists and the baby refuses to eat.
Drug or allergic stomatitis in children
Caused by certain allergies or reactions to medications. If this type of disease is suspected, it is necessary to identify and remove the allergen, otherwise there is a risk of unpleasant consequences, including anaphylactic shock.
Each type of stomatitis is characterized by a certain childhood age. Young children often have candidiasis or fungus (thrush). At the age of “I want to know everything” in a child of 3-4 years, stomatitis is usually infectious in nature, when the infection is transmitted through dirty hands or objects. From one to four years, an acute herpetic form of the disease is often observed.
Contraindications and precautions
Doctors recommend conducting an allergy test before using Levomekol ointment for the first time. To do this, apply a small amount of the drug to the crook of the elbow, and the patient monitors for redness or irritation. The main contraindication is hypersensitivity to any component, severe allergy to chloramphenicol. It manifests itself in symptoms:
- hives;
- rash on the mucous membrane;
- The gums begin to itch very much.
The ointment can only be used externally. If it gets into your eyes or throat, rinse the area well with clean water. Dentists safely recommend Levomekol to pregnant women at any stage: it does not accumulate in the blood and plasma, and does not cause complications for the placenta and fetus.
In case of an allergy to chloramphenicol, the patient is replaced with a similar one with an anti-inflammatory effect: Salicylic-zinc ointment, Levosin, Levomethyl, Protegentin and Solcoseryl creams.
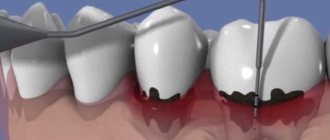
Conservative treatment of periodontal disease
Unfortunately, modern dentistry cannot guarantee complete relief from this problem, because periodontal disease is often detected when it acquires a chronic status. People often search until the last minute for some folk remedies and use widely advertised herbal rinses. Yes, they strengthen the gums a little.
However, a visit to a periodontist almost always turns out to be more effective than folk remedies combined and is even cheaper if you compare the costs of many years of suffering for all these dubious rinses.
At the first stage of treatment for periodontal disease, the doctor may ask the patient to undergo a complete examination of the body to rule out diseases leading to disorders. Then the dentist must perform professional oral hygiene. Today it is believed that bacteria and other pathogenic microorganisms do not play a significant role in the development of periodontal disease. But removing plaque and stones significantly improves the absorption of drugs by oral tissues.
To treat periodontal disease, the doctor prescribes special vitamin and mineral complexes that strengthen tissues and improve metabolic processes in the gums. Often, but not in all cases, antibiotics can be used: lincomycin hydrochloride, chloramphenicol, levovinisol, levomekol and levosin ointments. Physiotherapeutic procedures may also be prescribed:
- Gum massage. It is carried out with a special apparatus. After this procedure, blood flow to the gum tissue improves significantly. This leads to acceleration of metabolic processes and strengthening of tissues.
- Electrophoresis with calcium gluconate. Using a low voltage current, calcium is introduced into the soft periodontal tissues. Thanks to this procedure, gum tissue and tooth enamel are significantly strengthened.
- Darsonvalization and dynamic currents. These procedures have the same principle as massage.
Physiotherapeutic procedures saturate the tissues of the oral cavity with oxygen and nutrients. But, if the disease has acquired a severe form, then most likely it is impossible to do without surgical intervention.
Causes of stomatitis in children
In childhood stomatitis, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is affected: small, white or yellowish, fluid-filled pimples appear on its surface. In some cases, ulcers form.
Stomatitis is predominantly a childhood disease, although it can also occur in adults. The rash affects the inside of the cheeks, tongue and gums. The disease causes a lot of inconvenience: pimples hurt and itch, and their appearance is accompanied by a burning sensation in the mouth.
Among the main reasons for the development of stomatitis are:
- poor oral hygiene;
- mucosal injuries;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- burns of the oral cavity;
- pathogenic bacteria that enter the oral cavity with dirty hands, toys, etc.
Types of inflammatory and dystrophic gum diseases
Inflammatory manifestations include:
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
Dystrophic manifestations include:
Gingivitis: signs, causes and treatment
Gingivitis is the first stage of inflammation, in which the integrity of the periodontal junction has not yet been compromised. This disease can be identified by the following signs:
- Swelling of the gums.
- Blood while brushing teeth.
- Pain when eating cold, hot or solid foods.