From this article you will learn:
- what is periodontitis - symptoms, photos,
- anti-inflammatory therapy regimen,
- modern methods of treating periodontitis.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
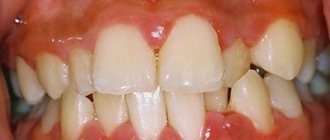
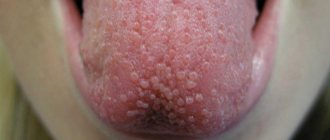
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the gums, which is accompanied by increasing destruction of the attachment of teeth to the bone tissue and soft tissues of the gums, which over time leads to tooth mobility. Periodontitis can appear in the area of only 1-2 teeth - in this case it is called localized, or it can be generalized (in the area of most teeth).
Most often, patients consult doctors with chronic generalized periodontitis, in which the gums of almost all teeth are inflamed. As a rule, most of these patients have a long history of self-medication of sore and bleeding gums (ie, symptoms of catarrhal gingivitis). Moreover, it is ineffective treatment or no treatment at all for gingivitis that leads to its gradual transformation into generalized periodontitis.
Periodontitis: generalized (Fig. 1) and localized (Fig. 2-3)
The causes of the localized form of periodontitis are local traumatic factors. This could be an overhanging edge of a filling or an artificial crown that injures the gums in the interdental space. The reason may also be “premature contacts” between the upper and lower teeth, which can appear either from natural causes or if the filling on the chewing surface or the crown is made a little higher than necessary.
Another common reason is when a dentist, when restoring a damaged tooth with a filling, incorrectly forms a contact point between the teeth in the interdental space. The lack of tight contact leads to constant food getting stuck in the interdental space and the development of inflammation. In the localized form (as opposed to the generalized form), symptoms of periodontitis occur only in teeth exposed to the traumatic factor.
Nature of the disease
Periodontitis is an acute inflammatory reaction in the gum tissue, and periodontal disease is the internal depletion and thinning of the periodontium.
Causes of diseases
Periodontitis occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the gum tissue. This can be caused by poor oral care, non-compliance with hygiene rules, mechanical damage to the jaw, teeth and gums, or incorrectly installed dentures and implants.
The causes of periodontal disease are more difficult to establish: it may be a hereditary predisposition, the consequences of trauma to the gums and teeth, vitamin deficiency, and impaired vascular function in the tissues surrounding the teeth. Periodontal disease also develops against the background of chronic diseases of the body (for example, diabetes, diseases of the digestive system, etc.), and also often appears during pregnancy.
Symptoms of periodontal disease depend on the stage and characteristics of the disease.
The first stage is characterized by a complete absence of complaints and symptoms, despite the fact that pathological changes are already slowly beginning to occur in the periodontal structure. The second stage is manifested by a decrease in the interdental septa. The patient complains of blood, itching and unpleasant pain, and possible food debris getting stuck between the teeth. The third stage is the complete and irreversible destruction of the periodontal space. The main complaints are severe bleeding even with minor mechanical impact, pain, the appearance of ulcers and erosions, pathological mobility of teeth progresses, and possible tooth loss.
The course of periodontitis and periodontal disease
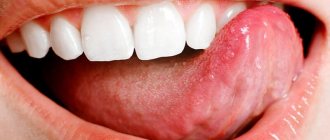
Periodontitis clearly manifests itself in the first weeks and is acute: the gums bleed, hurt, and swell, so the disease is easy to recognize immediately. However, if immediate attention is not paid to treatment, the inflammation penetrates deeper, affecting the periodontal ligament - the tissue that connects the teeth. The destruction of the ligaments leads to the formation of a periodontal pocket - the detachment of the gum from the tooth, creating an environment for the formation of tartar, the accumulation of plaque on the teeth and gums, and the proliferation of bacteria. During this period of the disease, pus is often released from the gums, there is bad breath, and tooth sensitivity increases. The result of periodontitis is rotting of the gums, adjacent tissues, and exposure of the roots. The teeth become loose, the chewing function of the dentition is impaired, and a feeling of gaps appears between the teeth. The disease leads to the decomposition of the jaw bone tissue and the loss of one or more teeth.
The main difference between periodontal disease and periodontitis is that bacterial damage (periodontitis) more often affects teeth one at a time or affects several adjacent units. The disease spreads to neighboring teeth if it is not stopped in time. Periodontal disease spreads and progresses evenly throughout the entire jaw and dentition. Bone decomposition during periodontal disease does not immediately manifest itself as clear symptoms, and this is the danger of such gum disease. For a long time, tissue destruction occurs without obvious symptoms and often without pain. Visual signs of periodontal disease are tooth mobility, receding gums, exposed roots, thinning of the dentition and cracks in the enamel.
The resulting space - pockets - is attractive for the growth of bacteria, and often it is periodontal disease that becomes the cause of rapidly progressing periodontitis in several areas or in the entire oral cavity at once.
Periodontal disease itself slowly progresses and leads to the loss of the entire dentition after 10-15 years. This disease is much less common; people suffering from immunodeficiency are at risk.
Note!
Periodontitis is often called periodontal disease, without suspecting that completely different diseases are hidden behind similar names. Doctors strongly do not recommend treating periodontal disease and periodontitis at home, because only an experienced dentist can distinguish gum disease, and the methods of treating periodontal disease and periodontitis are different.
Medical treatment of gums is a long and complex process. Folk remedies for the fight against periodontal disease are ineffective, and you cannot resort to strong pharmaceutical remedies without the advice of a dentist - self-medication can aggravate the situation, ruin teeth and damage other organs.
How is periodontitis treated?
Successful treatment of periodontitis can only be achieved in a well-coordinated team of “doctor plus patient”. Much depends on the doctor, but even more depends on the patient himself. The doctor is responsible for the treatment, and the patient is responsible for maintaining the result, because periodontitis is a chronic disease.
Treatment methods for periodontitis are divided into medicinal and surgical. In case of minor inflammation caused by dental plaque, the doctor thoroughly cleans the teeth, eliminates conditions that contribute to the retention of microbial plaque, polishes the surfaces of the teeth and applies a therapeutic bandage with medication to the inflamed area. If a deep periodontal pocket forms and severe pain occurs, the patient may be prescribed antibiotics. When treating severe periodontitis, it is necessary to resort to more serious (surgical) procedures, such as curettage and flap operations. But in any case, periodontitis requires complex treatment, including professional hygiene, drugs for local and internal use, and, if necessary, surgical procedures.
There is also a hardware method for treating periodontitis - Vector. The method involves using ultrasound in combination with medications aimed at fighting microbes and stimulating healing. The Vector device is used both as an independent technique and in combination with surgical treatment.
Treatment of periodontal disease
It is rarely possible to cure periodontal disease completely: the cause of the disease lies in the weakened state of the body and the improper functioning of organs. This is why older patients most often suffer from gum disease.
However, proper treatment stops the development of the disease, prevents it from progressing, and damaged teeth and tissues can be restored.
The first stage of periodontal disease treatment is examination.
Without high-quality diagnostics and analysis of gums and teeth, it is impossible to cure periodontitis. To establish the causes of the disease, it may be necessary to examine not only the mouth, but the entire body.
At the LeaderStom clinic, examinations are carried out using modern equipment, which accurately determines the cause and extent of the lesion:
- An orthopantogram and an x-ray of the oral cavity will show how deeply the disease has penetrated and what tissues it has affected;
- Analysis of periodontal tissue (gum tissue) will reveal the presence of pathogenic bacteria and the concentration of microorganisms in the mouth.
The result of an in-depth examination of the oral cavity is a comprehensive gum treatment plan.
Diagnostics
The presence of at least one of the above symptoms should be a reason to contact the clinic, where a more thorough examination will be carried out. Doctors at our clinic only need a simple examination to make a preliminary diagnosis. A comprehensive diagnosis of periodontitis includes a number of diagnostic procedures that are necessary to clarify the extent of the disease and differentiate it from other diseases. Diagnostic procedures:
- Probing of periodontal pockets.
- Orthopantomogram is necessary to assess the degree of destruction of the jaw bones.
- Calculation of periodontal indices.
- Bacterial culture or PCR of the detachable gingival pocket.
- Schiller-Pisarev test.
To clarify the cause of periodontitis, you may need the results of other examination methods: biochemical and general blood tests, glucose level testing, and others. Gastroenterologists and endocrinologists are often involved as consultants, since without adequate treatment of somatic pathology, the treatment of periodontitis is very difficult.
Treatment of periodontal disease in the early stages
When periodontal disease has not yet destroyed bone tissue, it is easier to cure teeth and gums. To begin with, ultrasonic cleaning of the oral cavity is carried out, which removes plaque, tartar and deposits.
Afterwards, drug treatment of periodontal disease is prescribed:
- General therapy includes taking hormonal and immunomodulating drugs and antibiotics. The exact selection of medications for periodontal disease is made by a dentist; the treatment method depends on the cause of the disease. This is why doctors do not recommend self-medicating without consultation and resorting to traditional medicine - these ineffective remedies create the illusion of treating teeth and gums while the disease progresses.
- Strengthening the immune system. Drugs that boost immunity actually help the body cope with the destruction of gums, tooth roots and bone tissue faster, but only a doctor can prescribe them, and only after conducting a series of tests that will show what substances the body lacks. Contrary to popular belief, special diets do not help get rid of periodontal disease, but dentists recommend excluding spicy, fatty and fried foods - such foods irritate damaged gum tissue and negatively affect the microflora of the oral cavity. It is recommended to eat more fruits and vegetables, because they strengthen the immune system.
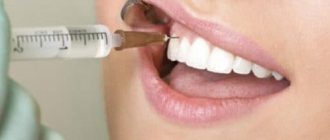
- Local therapy. Injections into the gums for periodontitis, gels, painkillers and disinfectants. The main goal of such treatment is to prevent the return of plaque or inflammation.
What are the causes of periodontitis?
Understanding the causes of the disease is a very important point, which helps the doctor correctly determine how to treat gum periodontitis. The disease can be triggered by both general and local factors. Common causes include diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diseases associated with pathology of the endocrine system, some gynecological and urological diseases, sexually transmitted infections, and a weakened immune system. Local, or local, factors are missing teeth, malocclusion, incorrectly installed fillings or crowns, which mechanically irritate the gums and create conditions for the accumulation of bacterial plaque. A significant role is played by the specific microbial flora of the oral cavity, which occurs in some patients and causes periodontitis. But the main factor in the development of periodontitis is poor oral hygiene.
How to treat periodontitis with complications
If gum disease was not noticed immediately and has already manifested itself through external destruction - receding gum tissue, wedge-shaped changes or tooth mobility, treatment of periodontal disease will be much more difficult:
- After the examination, the dentist will indicate which teeth cannot be restored and must be removed, and will also clean the oral cavity from plaque, tartar and microbes.
- The next step in the treatment of periodontitis is splinting. The purpose of the procedure is to bind the remaining teeth and prevent further loosening and loss. A horizontal groove 1-1.5 mm deep is drilled into each tooth, into which a fiberglass construction tape is poured. A light composite is applied on top, which returns the teeth to their natural aesthetics.
- If periodontal disease has been advanced, teeth can only be restored with the help of prosthetics - making a bridge. The prosthesis not only creates an aesthetic effect, restoring the beauty of the smile, but also replaces the chewing function of lost teeth, and also strengthens and does not allow the remaining teeth to decay.
Treatment of periodontal disease is accompanied by strengthening the immune system and drug therapy. Dentists at the LeaderStom clinic will definitely tell you about caring for your teeth during and after periodontal disease treatment.
Is it true that periodontitis can be cured with implantation?
Implantation is a method of combating not periodontitis itself, but its consequences. At a later stage of the disease, teeth become loose and fall out, so they have to be replaced with implants. It should be understood that dental implantation for periodontitis has its own difficulties and limitations, since bone tissue is absorbed in this disease. Its sufficient volume is the main condition for successful installation of implants. If periodontitis is in an advanced stage, implantation can be very difficult or even impossible due to a lack of bone volume. That is why patients should begin treatment as early as possible in order to do everything possible to preserve their teeth, and if they are lost, do not miss the opportunity to restore them with implants.
In any case, before installing implants, it is necessary to transfer periodontitis to the stage of remission (stabilization) or, if possible, eliminate the cause of its occurrence.
Treatment of periodontitis: the new Vector procedure will strengthen the gums and eliminate bleeding
Seeing blood on your toothbrush and in the sink while brushing your teeth every day is not pleasant. You can solve the problem of bleeding gums in just one visit with the help of deep mouth cleaning using the Vector device.
This procedure does not provide visible aesthetic results: the teeth do not become noticeably whiter or straighter, so patients tend to classify it as a minor procedure. This is a fatal mistake, because it is with tartar, bleeding and periodontitis that serious problems with teeth begin: loosening, exposure of roots and loss of dentition units.
The Vector device fights gum problems, strengthens tissue, cleans out inflamed pockets, destroys germs, saving gums from infection. The complex effect of Vector restores the adherence of the gums to the teeth, closing periodontal pockets that are attractive to infections.
The revolutionary principle of longitudinal movement of the Vector Paro Pro!
- Non-traumatic
- Antibacterial
- Strengthening method
It is the tartar deposited in the pockets that is the main cause of bleeding gums, since when you press on this place with a toothbrush or while eating, the gums are injured, wounds appear, into which pathogenic bacteria enter - the cause of inflammation of the oral cavity.
Prevention
To prevent such serious problems with soft tissues, it is best to stick to simple and accessible methods of prevention. Dentists recommend:
- avoid stressful situations;
- eat well and strengthen the immune system;
- do not cause general diseases;
- if even one unit falls out, install prostheses;
- lead a healthy lifestyle and give up bad habits;
- try not to damage soft tissues with sharp objects, avoid traumatic situations;
- treat any diseases in a timely manner and eliminate the first symptoms;
- Brush your teeth daily with a medium-hard brush, in circular motions, for at least five minutes;
- If a malocclusion is detected in childhood, it is better to correct it.
- do not forget about the importance of solid products that stimulate metabolic processes in the gums and naturally cleanse the surface of plaque;
- visit the dental office every six months for a thorough examination and detection of the first signs of any abnormalities, as well as for professional cleaning of plaque and tartar.
In addition to these general tips for maintaining health and maintaining good oral hygiene, you can also periodically massage your gums. To do this, apply light pressure on both sides with clean fingers. It is not difficult, and the whole procedure lasts no longer than 5-10 minutes. As a result, metabolic processes in periodontal tissues will resist the proliferation of bacteria.
Why is it important to choose Leaderstom for the treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease?
LeaderStom is the ideal price-quality ratio for dental services: treatment of diseases of the teeth and gums is performed by highly qualified periodontists. Dentistry is developing every day, which is why our doctors undergo advanced training courses, get acquainted with new methods and devices that restore health to teeth and gums. The use of innovations, rich experience and modern methods of therapy and prevention together give a 100% result - to get rid of periodontitis in one visit to the dentist.
The doctor begins therapy only after a complete examination of the oral cavity, since some gum diseases can be the cause of other serious disorders in the body: hypovitaminosis, malfunction of organs or infectious diseases. If there are no other diseases, the periodontist performs probing (penetrating examination of the gums and teeth), based on the data of which the treatment tactics are determined.
Our main principle in treatment is adherence to high quality standards at all stages of treatment: from examination to recommendations for rehabilitation and dental care, the doctor takes care of the patient. We understand that neglect of any stage of treatment leads to relapse of the disease, which means that money for the treatment of teeth and gums was wasted. Even with the most conservative estimates, the cost of a periodontist’s work is high: from 4,000 thousand rubles. However, you cannot delay treatment - the later you start treating your gums, the higher the price for periodontitis treatment will be, and the more often you will have to visit a periodontist.
Periodontitis: what is this disease?
Before moving on to considering treatment methods for periodontitis, it is worth finding out what kind of dental disease it is and why it appears. In dentistry, periodontal tissue is the tissue that tightly surrounds the roots of the teeth and holds the tooth itself in its socket. When an infection penetrates into the periodontium, an inflammatory process begins in the tissue, which leads to the occurrence of periodontitis. Treatment of periodontitis should be started immediately, however, the disease cannot always be recognized in a timely manner and independently, since it can develop completely asymptomatically. It is for this reason that it is recommended to undergo regular examinations by a dentist: a specialist will determine the signs of periodontitis and treatment of the disease will be as effective as possible.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
The main cause of periodontitis is pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate into the deep layers of the periodontium, however, there are factors that contribute to the appearance of the disease and accelerate the process of its development. These factors include:
- Untreated or advanced gingivitis;
- Autoimmune diseases (diabetes mellitus, HIV);
- Bite defects;
- Increased tone of the jaw muscles;
- Injuries to soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- Poorly performed dental procedures: prosthetics, fillings;
- Stressful and depressive conditions, the presence of bad habits;
- Poor or irregular oral and dental hygiene;
- Some gastrointestinal pathologies.
The listed factors will complicate the treatment of periodontitis, and therefore it is recommended to eliminate them before starting a course of therapy, which means that for effective treatment of periodontitis you will need to visit not only the dentist, but also specialists in other areas of medicine.
Rehabilitation after treatment of periodontal diseases.
The importance of a doctor’s recommendations cannot be underestimated, because the effectiveness of even the most modern treatment of periodontal disease and periodontitis largely depends on proper oral hygiene. Only daily brushing of teeth and caring for gums will help get rid of plaque and avoid the appearance of tartar. Massaging with the right toothbrush will have a beneficial effect on your gums, and using medicated toothpastes recommended by your doctor will protect against irritation. The periodontist at the LeaderStom clinic will tell you in detail about toothbrushes, how to choose the right toothpaste and what products to use to reliably protect the gum tissue.
If dental health is important to you and you dream of a snow-white, dazzling smile, feel free to contact Leaderstom: prices for treatment of gums, teeth, periodontitis and periodontal disease will invariably please you, and doctors will make the treatment procedure comfortable and painless. We will conduct a preventive examination, advise and help you choose oral care products, perform professional teeth cleaning and cure gum disease. New products in the field of dental equipment and doctors who have many years of experience, advanced training courses and thousands of treated teeth and gums will help with this.
Prosthetics for periodontitis
Prosthetics for periodontitis are necessary in cases where a person has no dental units in his rows. Carrying out prosthetics allows you to prevent the displacement of teeth in rows and completely restore the correct chewing load in the oral cavity. Prosthetics is the final stage in the conservative treatment of periodontitis and must be carried out before surgery (if the operation is planned in the general treatment plan).
For prosthetics in the treatment of periodontitis, it is extremely important to choose the right prosthesis. It must be of high quality and modern, otherwise it will not be possible to stop the process of bone atrophy.
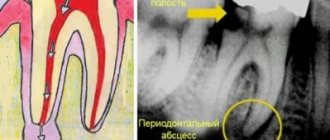
First you need to understand what “periodontal” is and what part of the oral cavity we are talking about.
In fact, the teeth are not permanently attached to the jaw, i.e. they are attached to the bone using various soft tissues and ligaments. These include: the gums, the jaw bone itself (the bony alveolus or “socket”) and the periodontal ligament of the tooth.
If you depict it in the figure, it will look like this (in this question, the elements highlighted in red are important to us):
Now let's move on to the issue of defining periodontal disease itself.
Periodontal disease is a disease in which intensive loss of bone tissue, gums and tooth ligaments occurs.
It is very important to distinguish “Periodontal disease” from “Periodontitis”; what is the difference?
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the tissues surrounding the tooth. It most often occurs as a result of poor oral hygiene. Symptoms of this disease include bleeding, swelling and pain in the gums, and tooth mobility.
Periodontal disease is a non-inflammatory disease, which means there will be no redness, bleeding or pain in the gums.
The occurrence of periodontal disease is interpreted in different ways. They are divided into systemic (i.e., arising indirectly from diseases) and local (arising due to factors acting directly on the periodontium).
The most common common causes of periodontal disease:
- Atherosclerosis (narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels due to deposition of lipid granules in the walls)
- Disruption of the endocrine glands (such as thyroid, pancreas, hypothyroidism)
- Gastrointestinal dysfunction (eg, gastritis, ulcers)
- Changes in the body's reactivity, i.e. appearance of allergies
The cause of periodontal disease and its development
Periodontal disease is a complex disease and has many causes.
The most basic reason is sclerosis (narrowing of the lumen) of blood vessels. Next, tissue trophism begins to be disrupted, i.e. there is insufficient blood supply, delivery of oxygen, nutrients and then a decrease in the number of tissues.
As a result, due to insufficient tissue nutrition, gradual resorption of bone tissue occurs, a decrease in the amount of gums, and exposure of the roots.
Factors that can lead to the development of periodontal disease include:
- Elderly age
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Diabetes
- Nervous system diseases
How to carry out early diagnosis of periodontal disease. Observation of which specialists is important for this disease. Who is at risk?
Periodontal disease is a rather difficult disease to diagnose.
But, as a rule, people experience the following symptoms:
- Reduced gums and decreased bone tissue (the most important symptom!)
- Increased sensitivity of the necks of the teeth
- No gum inflammation
- No periodontal pockets
- Stable position of the tooth in the socket, even with severe gum recession
- Diseases of various body systems that indirectly indicate periodontal disease
Observation by a dentist, i.e. preventive examination once every 6 months. Then you will be referred to a highly specialized doctor - a periodontist. Also, in a regular city clinic, observation by a regular local physician is necessary so as not to miss the onset of any systemic disease.
The main risk group for development is older people. Also people exposed to constant stress, overwork, smokers, etc.
How to identify the cause and what examination methods exist.
There are quite a lot of examination methods.
- Methods for assessing the condition of bone tissue
- The X-ray method of examining teeth with periodontal disease is the most common and simplest. This method makes it possible to assess the degree of bone tissue loss and its quantity. The most common and accessible methods are: intraoral contact radiography, orthopantomogram (OPTG). The disadvantage of this method is the limited field of study.
- An orthopantomogram (OPTG) allows you to assess the condition of the alveolar processes of both jaws in one image. The disadvantage of this method is distortion in the area of the front teeth.
- Computed tomography (CT) is the most preferred research method. Thanks to it, you can build a 3D model of the human dental system. When using CT, there is practically no distortion, unlike OPTG.
- Method for assessing tooth mobility
- Palpation (without the help of special instruments)
- Periodontogram (done using a special apparatus, and then a table is filled in where the periodontal strength of various teeth is determined)
This symptom is important in periodontal disease, but can also occur in other periodontal diseases. The essence of this method is thermal diagnostics (using hot or cold water, i.e. irrigating the tooth from a syringe or by applying a cotton ball to it).
In clinical practice, there are three degrees of hyperesthesia:
- The first is that tooth tissues react to temperature stimuli (a person feels hot or cold water, but does not experience discomfort)
- Second - a person feels pain from the irritant
- Third – pain from any irritants or even without them
Removal of supra- and subgingival dental plaque. Oral hygiene
Removing supra- and subgingival plaque is essential to maintaining both periodontal and overall oral health. This is the main goal of professional oral hygiene. Tartar does not play a significant role directly in the development of periodontal disease, but indirectly it can aggravate the situation with periodontitis (see above the differences between periodontal disease and periodontitis).
There are two ways to remove hard plaque: manual and hardware.
The manual method involves the use of various hand tools to remove tartar.
These tools are different and perform different functions, respectively: scalers, curettes, excavators, smoothers, chisels, rasps.
The hardware method is more common and involves the use of a special device. These piezoelectric devices have a frequency from 25 to 45 kHz. Using these frequencies, the tip attachment breaks the contacts between the molecules of the tartar and allows you to simply wash it off with water or clean it with a special brush and paste.
Main representatives: scalers from EMS (Switzerland), Amdent Boitrol (Sweden), Satelec (France), Siroson L (SIRONA).
After treating the teeth with an ultrasonic scaler, sandblasting is carried out (if there is dark plaque) if necessary, and mechanical cleaning of the teeth with a brush and paste to remove remaining dental deposits, for example, Detartrine. Further, after such an aggressive effect on its structure, it is necessary to restore the mineral composition. To achieve this, fluoridation is carried out in various ways: varnishes, gels, etc.
After professional oral hygiene, it is necessary to replace the old toothbrush with a new one. This is necessary because an old toothbrush contains many microorganisms that can lead to an exacerbation of the same diseases that existed.
During and after treatment, oral hygiene is required 2 times a day and replacing the toothbrush once every two months.
The optimal set of dental products for periodontal disease:
- EZSH (electric prophylactic toothbrush) – if a person has the opportunity to use an EZShch, then this is better than having a manual one. An electric toothbrush should be characterized by: a round head, two-level bristles, indicating bristles (degree of wear), a timer.
- Manual protective shield (if it is impossible to purchase an electrical protection shield) – medium degree of hardness, multi-level bristles, rounded bristle tips, microtextured polymer coating, indication of the degree of wear of the bristles, rubber-plastic in the handle, comfortable grip, non-traumatic. If hyperesthesia occurs, it is possible to replace the brush from medium-hard bristles to soft ones.
- Therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste - should contain anti-inflammatory oils and plant herbs, it is possible to introduce fluoride compounds to prevent carious lesions, should not contain strong antiseptics, and should contain a moderate abrasive. Also, if hyperesthesia occurs, it is recommended to switch to a “Sensitive” type paste.
- Therapeutic and prophylactic mouth rinses - an anti-inflammatory component in the form of extracts of herbs and plants, without strong antiseptics, with sweeteners is also possible. Regular use is required.
- Flosses (dental floss) are two-component, regular use after each meal is mandatory.
- Irrigator – if you have the opportunity to use an irrigator, then this is very good. There are 2 modes: shower and jet.
Irrigator
Treatment algorithm for periodontal disease
First, it’s worth making a reservation: is it possible to cure periodontal disease? In the early stages of the process - yes, later we are talking about stabilizing the process and stopping further bone resorption. This is done to preserve the teeth for as long as possible.
Treatment for periodontal disease includes several stages:
- Consultation with a periodontist - this doctor specializes in such problems, so he will review images and other research methods and then come up with a plan for further treatment.
- Professional oral hygiene with removal of supra- and subgingival dental plaque. I wrote above about the need for this procedure.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy - includes local and general.
- With local anti-inflammatory therapy, drugs are applied directly to the gum and have a local effect through the capillaries of the gum. Typically this treatment includes the following drugs:
- Rinse with Chlorhexidine 0.05% immediately after brushing your teeth (in the first minute)
- Applications with “Cholisal” or “Solcoseryl” gels. It is carried out after applying chlorhexidine and drying the gums.
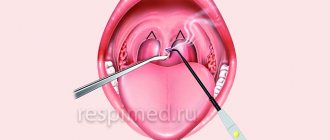
- Closed curettage: the purpose of this method is to completely clean out periodontal pockets of possible microorganisms that cause infection. This method is used for mild periodontal disease. It is carried out using special curettes, which, under infiltration anesthesia, are introduced into the periodontal pocket and all dental plaque is removed there manually. The regime after surgery is important: do not eat for the first 2 hours after surgery, then for several days use only crushed, non-hot food and perform hygiene only with liquid products. It is better not to use a toothbrush for the first 2–3 days.
- Open curettage: performed for moderate to severe periodontal disease (depth of periodontal pockets more than 5 mm). Methodology: under infiltration anesthesia, the gum is dissected and detached. This access allows you to completely open the periodontal pocket and clean the tooth root from dental deposits. Then treatment with antiseptic drugs and application of drugs that stimulate osteogenesis (bone growth) are carried out.
- Transplantation of the soft tissue component. This operation is used when the tooth root is exposed. A patch taken from the palate is sutured onto the affected area.
- Gingivectomy is the removal of affected, inflamed, hardened gums by excision.
- Tooth extraction is a radical method, but it is necessary in cases of severe mobility, bleeding and the impossibility of restoring tooth function.
Non-traditional methods of treating periodontal disease
As an independent treatment, this type of treatment will be ineffective, because... Doctors' intervention is necessary to adequately assess the condition of the oral cavity.
And only with the permission of a doctor can unconventional methods be approved.
For example, herbal poisons that have a local anti-inflammatory effect.
Is implantation possible for periodontal disease?
Yes, this method of treatment is possible, but do not forget that no one will give you implants right away.
First, you need to undergo long-term treatment with bone restoration and only then should you talk about implantation.
{jlcommentspro}