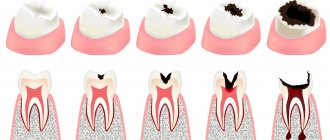
Sterilization is the process of complete disinfection of instruments, during which all microorganisms, as well as their spores, are killed.
Everything that comes into contact with the patient’s biological fluids and is used repeatedly is subject to sterilization. Human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B and C, malaria, typhus – this is an incomplete list of diseases that are transmitted through blood. Sterilization is necessary to prevent their spread.
At the Karmen-Med clinic, all instruments are subject to mandatory sterilization. Regardless of the manipulation performed, the dentist always has only clean instruments in his hands. Our patients do not have to worry about their health.
Sterilization methods used in dentistry
Sterilization is the general name for any disinfection process, regardless of the method of removing microorganisms. There are several such methods:
- Mechanical – removal of microorganisms by mechanical action. For example, liquids are passed through special filters that retain particles of certain sizes. Microorganisms can be mechanically removed from objects or surfaces by cleaning, wiping, and sweeping. The method is unreliable and is used in medicine only as a preliminary step.
- Biological - sterilization with antibiotics, is rarely used because it does not affect all pathogens.
- Chemical is a method of disinfection by applying special solutions or gas treatment. Gaseous ethylene oxide or formaldehyde is used as the latter. Acids with oxidizing agents, detergents, halogens and aldehydes are used as solutions. Most are known antiseptics, such as chlorhexidine or betadine. Used for processing cabinets, surfaces, and apparatus.
- Microwave - in this case, disinfection occurs in a special microwave sterilizer. Microorganisms die under the influence of an electromagnetic field. The method is rarely used in medicine.
- Physical - a method that includes exposure to temperature, pressure or ionizing rays. The most commonly used sterilization is high temperatures (in a dry-heat oven) or high temperatures and pressure (autoclaving). Most tools and materials can be cleaned using these methods. Ionizing radiation is used in factory conditions in the manufacture of sterile products.
Clinical examples. Video
Minimal invasion: micro-mirror
Initial situation: missing 3.6 tooth, preparatory stage before implantation, sanitation of the oral cavity. A carious change in the tissues of the proximal surface of the 3.5 tooth was revealed (Fig. 10-11).
Fig. 10. Clinical situation
| Fig. 11. Revision of the proximal surface of tooth 35 using a micro-mirror |
Preparation: It is not possible to prepare only the proximal surface with a conventional handpiece, since there is not enough space to accommodate the collet and bur.
The use of an ultrasonic nozzle and a micro-mirror allows for minimally invasive treatment of the approximal class II cavity without bringing the preparation to the occlusal surface (Fig. 12-15).
| Fig.12-15. To remove carically damaged tissues, ultrasonic approximal attachments are used; for visual control of the cleanliness of the preparation - micro-mirror MEGAmicro (HAHNENKRATT, Germany) |
Direct restoration: surface etching with 37% H3PO4 followed by adhesive treatment (Fig. 16, 17); applying a flowable composite to the bottom of the cavity using a special nozzle (Fig. 18, 19); layer-by-layer application of a dual-curing composite, activation of light polymerization and finished composite restoration of 3.5 teeth (Fig. 20-22). Visual control is carried out through a micro-mirror.
| Fig. 16, 17. Etching with 37% H3PO4 and adhesive preparation of the cavity of the 35th tooth | |
| Rice. 18, 19. Special nozzle for applying flowable composite |
| Fig.20. Adding composite | Fig.21. Light polymerization |
Fig.22. Finished restoration
To learn the technique of minimally invasive caries treatment using a micro-mirror, watch the video
To see or not to see? Mirror EverClear
When carrying out various dental procedures (especially when working with ultrasound instruments), it is a great inconvenience to have to constantly interrupt the treatment process in order to restore a clear view of the surgical field and clean the mirror from water splashes and debris (Fig. 23 a-c).
| Fig.23 a-c. Increasing low visibility of the surgical field |
The special EverClear mirror from I-DENT provides dental practitioners with continuous visual control during any treatment procedure, which is especially important when using ultrasonic instruments (Fig. 24). Accordingly, reception time is reduced and work productivity increases.
Fig.24 a, b. EverClear mirror features:
|
Clinical demonstration: preparation of a deep carious cavity of tooth 1.6 using an EverClear mirror (Fig. 25 a-c).
| Fig.25 a-c. Maintain a clear view of the surgical field | ||
To compare the quality of visual control over the work process when using a splash-proof mirror, watch the video
Stages of sterilization
Before proceeding directly to sterilization, it is necessary to carry out preliminary preparation. Tools and materials are washed, cleaned, dried - and only then sterilized. The processing steps for the toolkit are as follows:
- Disinfection. At this stage, the items to be disinfected are placed in a disinfectant solution. Exposure time depends on the solution and type of instrumentation.
- Washing. Tools and materials are removed from the solution, washed under running and then under distilled water. Some instruments can be cleaned mechanically using brushes. If the instrument has nicks or nicks, it is recommended to disinfect it and wash it in a special apparatus under ultrasound.
- Drying. The instrument is treated with steam and waited until it dries completely.
- Final sterilization. The stage depends on the method of processing the tools. Items are placed in a special package or container and then sterilized. There must be an indicator near them that will show that the required temperature or pressure has been achieved. After all stages, the instruments are stored under ultraviolet lamps or in individual packages so that they remain sterile.
Magnification and lighting
Dental treatment using a magnifying glass or head-mounted optics (Fig. 1) has significant advantages over the “naked” eye. In endodontics, Harry Carr was the first to propose the use of an operating microscope: in addition to magnification, the microscope illuminates the object better than a traditional dental lamp (Fig. 2).
Fig.1. Zeiss glasses
Fig.2. Optimizing object lighting
Today, microscope-oriented practice (Fig. 3) is the main priority and the main trend in the development of modern dentistry, the main principles of which are preventive and minimally invasive methods.
Fig.3. OPMI pico microscope from Carl Zeiss equipped with a beam splitter, video adapters and a camera
Carrying out endodontic and restorative manipulations using an operating microscope (Fig. 4, 5) increases the likelihood of successful treatment and optimizes the dentist’s work process.
Ergonomics: • Comfort for the eyes. • Comfortable position. Video!
| Rice. 4, 5. At a dental appointment in microscope-oriented practice, 90% of manipulations are carried out indirectly | |
Watch the video!
Features of working with different dental instruments
In dental practice, working with instruments involves distinctive features of sterilization. Instruments vary among dentists of different specializations.
- Endodontic instruments. Most endodontic instruments cannot be sterilized. They are disposable. After use, they must be disinfected and disposed of as biologically hazardous waste. Disinfection is necessary to ensure that pathogenic microorganisms cannot penetrate from the instruments to the surfaces with which they will come into contact. For example, they did not contaminate the soil when dumping hazardous waste. For each patient, they take their own individual disposable instrument. Packages are usually opened in the presence of the patient.
- Therapeutic dentistry. Instruments undergo all stages of sterilization. The only difference is the sterilization of dental handpieces. They cannot be soaked in a disinfectant solution. Therefore, the tips are manually washed with a solution, dried, lubricated, packaged and sent to an autoclave.
- General purpose kits. The disposable components of such kits are used personally for each patient, then disinfected and disposed of. But most tools are reusable. They are processed according to all stages of pre-sterilization treatment, and then placed in a dry heat or autoclave. Metal tools are usually heat treated. Objects with non-metallic parts - by pressure.
New requirements for dentists registered as individual entrepreneurs.
According to the requirements approved by Order No. 786n dated July 31, 2020, individual entrepreneurs will not be able to implement the equipment standard because do not have the right to hire specialized personnel (radiologists and x-ray laboratory technicians) and will not be able to obtain a sanitary and epidemiological certificate for working with sources of ionizing radiation.
To continue operating from January 1, 2022, all individual entrepreneurs will need to register a Limited Liability Company and obtain an X-ray license (license to operate in the field of using ionizing radiation sources).
To obtain an x-ray license you must:
- prepare a project for calculating the radiation protection of the X-ray room;
- purchase an X-ray machine and install it;
- obtain an expert opinion on activities with sources of ionizing radiation;
- obtain a technical passport for the X-ray room;
- obtain a sanitary and epidemiological certificate (SEZ) for activities with sources of ionizing radiation.
Changes for existing dental clinics registered as LLCs.
If a dental clinic already uses the legal form of a Limited Liability Company in its work and has a functioning X-ray room, according to the updated requirements of the X-ray room equipment standard, it must contain not only a radiovisiograph, but also a panoramic X-ray machine. Previously, the office could only be equipped with a radiovisiograph.
At the same time, it is not enough to simply purchase the necessary equipment; you will need to comply with safety standards for the installation and operation of X-ray equipment. To do this, redevelopment and installation of additional x-ray protection may be necessary, after which it is necessary to re-issue a technical passport for x-rays. Failure to comply may result in license revocation.
At the same time, it is not enough to simply purchase the necessary equipment; you will need to comply with safety standards for the installation and operation of X-ray equipment. To do this, redevelopment and installation of additional x-ray protection may be necessary, after which it is necessary to re-issue a technical passport for x-rays. Failure to comply may result in license revocation.
From January 1, it will become mandatory to have a pharmaceutical refrigerator in a dental surgeon’s office. They also added a requirement to have one defibrillator per department/office. Instruments, etc. were practically eliminated.
Order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated July 31, 2020 N 786n was registered on October 2, 2020 with the Russian Ministry of Justice. Full version of Order N 786n dated July 31, 2020.