Trismus is a spasm of the chewing muscles or their involuntary contraction. As a result of trismus, the jaws become closed and it is extremely difficult to open them. Usually the problem lies in impaired muscle function and tone, and this, in turn, can be associated with various diseases. It is very difficult to get rid of spasms of the jaw muscles on your own, so it is important to seek help from a dentist - he will assess the condition and refer you to specialists if necessary.
The mechanism of trismus occurrence
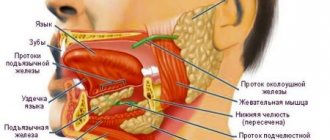
The chewing muscles set our jaw apparatus in motion. A sudden muscle contraction, accompanied by a strong closure of the jaws, limitation of the movement of the lower jaw, temporary loss of the ability to speak and eat, is called trismus. Strong clenching of teeth often causes breathing problems.
Excessive muscle tension leads to hardening. The disease can become a factor in a significant decrease in the quality of life and deterioration of the psycho-emotional background. A person’s appearance changes, the digestive tract organs suffer, so it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Without timely help, your general health may deteriorate, and it is also necessary to find out the causes of spasms.
Ask a Question
Video: Myoarthropathy
Psychosomatic and neurological disorders
Disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system often provoke functional disorders of organs and vital systems of the body. Psychosomatic and neurological disorders provoke groundless spasms against the background of prolonged emotional stress. When the muscles relax, numbness occurs.
At first, a person does not attach serious importance to his feelings, without thinking about why, in a state of anger, the face, neck, shoulders, torso are tense, and fear fetters the legs and abdomen so that it becomes difficult to breathe. This happens on a subconscious level and signals possible danger.
You can help yourself by trying to relax your jaw with soft massage movements.
Other manifestations
There are cases when, against the background of muscle spasms of the jaw apparatus, a person complains of stuffy ears. Such clinical symptoms require consultation with a specialized specialist and most likely indicate the following diseases:
- chronic tonsillitis;
- lesions of the soft tissues of the larynx;
- tumor formations in the nasopharynx of various origins;
- neuralgic attacks.
Sometimes a headache is added to cramps and ear congestion.
Those who observe these complex manifestations in themselves should give up the habit of resting their chin with their hand, as well as communicate on a mobile phone, pressing the device between the neck and the auricle.
Types of trismus and diagnostic methods
There are two main types of spasm of the masticatory muscles:
- Unilateral. Most often it is associated with an inflammatory process or injury to the mandibular joint and adjacent tissues. The result of unilateral pathology is a displacement of the lower jaw to the side when opening the mouth, as well as facial asymmetry.
- Bilateral. The cause of the disease is neuralgia and common infectious diseases. With this type of trismus, the jaws close together with a slight movement of the lower jaw back. There is an inability to open the mouth, difficulty speaking and eating.
To diagnose trismus, the doctor will find out information about previous diseases, operations, injuries, collect anamnesis, and listen to complaints. External examination is supplemented with radiography and other methods of clarifying the diagnosis.
Who usually experiences muscle cramps?
This trouble is familiar to everyone: men and women, children and the elderly, athletes and office workers. Only some people get to know her for natural reasons and rarely encounter her, while for others she becomes a frequent companion.
The risk group includes:
- children under 3 years of age who have experienced a rise in temperature above 38 degrees;
- elderly people suffering from vascular diseases and muscle atrophy;
- men engaged in heavy physical labor;
- athletes (football players, swimmers, runners);
- people who abuse alcohol and often experience hangovers;
Predisposes to muscle spasms and pregnancy. In mild cases, they are caused by a lack of vitamins due to changes in the body; in severe cases, they are caused by eclampsia.
Causes of trismus
The problem of spasm of the lower jaw can be associated not only with damage to nerve endings and reflex contraction, but also with other factors:
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
- previous injuries;
- unsuccessfully performed anesthesia of the teeth of the lower jaw;
- arthrosis of the mandibular joints;
- pathologies of ENT organs;
- irritation, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- purulent processes, etc.
In addition, trismus can be a consequence of pseudobulbar palsy, meningitis, epilepsy, calcium deficiency, etc. Symptoms may first appear after injury, temperature changes, or sudden hypothermia. Sometimes the jaw cramps after opening the mouth wide, for example, after removing a wisdom tooth.
Symptoms and manifestations
Trismus of the masticatory muscles is accompanied by limited mobility of the joints responsible for closing the jaw. The inability to unclench them can be of a different nature - from partial to complete immobilization. The mouth may open 40, 20, or 10 mm or less, depending on the severity of the condition. Spasmodic contractions can worsen your overall health, cause headaches and other consequences.
One of the manifestations is inflammatory processes due to jamming of the jaws, in this case there is an alternating reduction of the sides of the face. Less commonly, trismus is associated with tumor processes, accompanied by a noticeable increase in formation and increased symptoms. With viral infections, elevated body temperature is often observed.
Treatment methods
Patients with hypertension should receive help as soon as possible, since trismus can accompany a hypertensive crisis. It is also important to call an ambulance if you suspect rabies and tetanus. In the absence of severe concomitant pathologies, you can consult a dentist.
Knowledge of how to relax the jaw muscles on your own is necessary for self-help directly during spasm - but in the future, examination and consultation with a specialist is necessary. A warm compress can help with spastic jaw closure. Its use is not recommended if there are foci of inflammation in the oral cavity, for example, with pulpitis, periodontitis, periostitis, or suspected abscess. A light massage of the muscles can also help to relax, but remember that the movements should be light, and in no case should you put any force on the muscles.
The approach to the treatment of trismus includes a detailed analysis of the condition and a search for the causes of the disease. To eliminate the causes, it may be necessary to remove the inflamed tooth or surgical treatment of purulent inflammation. In case of a fracture, the doctor will immobilize the jaw.
Physiotherapeutic methods are widely used as a supplement. Laser, ultrasound therapy, electrophoresis with the use of painkillers can be used.
Antibacterial therapy is used for the inflammatory nature of spasms, for example, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
Treatment of spasm of the masticatory muscles often includes the use of sedative medications if the pathology was caused by diseases of a neurological nature. However, a neurologist prescribes such drugs.
Also, if muscle tone disorders are suspected of being infectious, vaccination is mandatory. Infection with the rabies virus requires immediate attention.
Why does pain occur in the upper jaw?
Injuries
Damage occurs as a result of household, street, sports, automobile, and industrial injuries.
The bruise is characterized by moderate pain that goes away after a few days. Fractures of the upper jaw are accompanied by extremely intense acute pain, rapidly increasing swelling, facial asymmetry, and stepped dentition. In case of fractures of the alveolar process, lacerations are visible on the mucosa, and sometimes the end of the displaced bone fragment is determined. The occlusal contact is sharply impaired, the teeth are mobile. With an isolated fracture of the walls of the maxillary sinus, severe aching pain in the upper jaw, infraorbital area, significant swelling, and hemorrhages is observed. Nasal breathing is difficult. With combined damage to the bone walls of the sinuses, a clinical picture of a concussion and profuse nosebleeds are revealed. Perforation of the maxillary sinus occurs during dental procedures. If the damage was not detected, swelling of the cheeks, a nasal tone of speech, pressing or bursting pain in the jaw, and projections of the sinuses subsequently appear.
In some cases, radiating pain in the jaws is detected in victims with subluxation of the cervical vertebra. Irradiation to the back and shoulders is also possible. The clinical picture includes a forced position of the head, neck pain, muscle tension, and sometimes dizziness, weakness, convulsions, and paresthesia in the arms.
Dental reasons
Discomfort and mild pain may be associated with the use of removable dentures and orthodontic structures. Pulling, pressing, aching pains occur in children due to malocclusion, including those caused by deformation of the upper jaw with a cleft lip and cleft palate. Some soreness is normal after tooth extraction, especially molars and wisdom teeth.
With the development of alveolitis, the pain disappears, and then reappears 3-5 days after tooth extraction. Intense pulsating sensations are noted in the projection of the socket, intensify as inflammation progresses, and sometimes cover the upper jaw and half of the face. Attacks of severe pain spreading along the trigeminal nerve are characteristic of acute diffuse pulpitis. More local pain is observed in acute periodontitis.
Upper jaw pain
Purulent processes
Intense tugging, tearing, bursting pain occurs with purulent inflammation of the upper jaw and nearby soft tissues. Combined with hyperthermia, deterioration of general condition, intoxication syndrome. The most striking clinical picture occurs in acute osteomyelitis. The disease begins suddenly, the symptom progresses quickly, and the temperature rises to high levels. A foul odor emanates from the mouth, and pus accumulates in the gum pockets.
Periostitis has less severe symptoms. With a high intensity of pain, the general condition is slightly disturbed, the temperature is subfebrile. In patients with a perimandibular abscess, the abscess is limited, located in the soft tissues, the condition is moderate or closer to satisfactory. With perimaxillary phlegmon, the infection spreads quickly, twitching, shooting pains intensify with the slightest movements of the jaw, the condition is serious.
With abscesses of the salivary glands, the first symptoms are dry mucous membranes and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Hyperthermia up to 40°C is noted. Maximum pain is determined in the projection of the affected salivary gland, complemented by pronounced swelling. Irradiation is noted in the upper jaw, neck, and ear.
Neuralgia
With ganglionitis of the pterygopalatine ganglion, a clinical picture of neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve is observed in the zone of innervation of its 2nd branch – n.maxillaris. An attack of intense shooting pain develops spontaneously, often occurring at night. Pain sensations predominate in the upper jaw, eye, hard palate, and at the base of the nose, spreading to nearby anatomical zones. The episode lasts from several minutes to several hours, complemented by autonomic disorders: lacrimation, profuse salivation, hyperemia of half the face.
Atypical facial neuralgia, which is more often detected in middle-aged women, is considered as another possible cause of the symptom. Pathology is provoked by dental procedures. The pain is dull, sometimes burning. They do not reach the intensity typical of other neuralgia. They quickly transform from paroxysmal to permanent.
Diseases of the ENT organs
In otolaryngology, the manifestation is more often provoked by odontogenic sinusitis against the background of injuries, dental diseases, and endodontic treatment. The acute form is characterized by heaviness, bursting unilateral pain in the upper jaw, intensifying when lowering the head, and throbbing headache. There is a sharp pain when chewing food, a subjective feeling of lengthening of the teeth. For chronic sinusitis, the clinic unfolds gradually. The symptom is also combined with a headache, radiating to the forehead, temple, and orbit.
Radiating pain in the upper jaw, orbit, and temporal region can be observed in acute purulent otitis and is caused by irritation of the trigeminal nerve during infiltration of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity. Supplemented by severe pain in the ear, intoxication syndrome. A similar irradiation is found in mastoiditis, which develops simultaneously with otitis media or a few days later, manifested by profuse suppuration from the ear, throbbing pain behind the ear.
Tumors of the upper jaw
Against the background of benign neoplasia of the upper jaw (fibromas, cementums, osteomas, osteoblastoclasts), the pain is usually mild, dull, and aching. They do not occur in all patients. They grow slowly over a long time in parallel with the growth of the tumor. Sometimes they are complemented by progressive facial asymmetry. An exception is osteoid osteoma, which is characterized by intense pain that worsens when eating and at night.
With malignant tumors of the upper jaw (cancer, sarcomas), pain appears in the early stages. At first periodic, dull, aching or pressing. They quickly intensify, become permanent, acute, painful, unbearable. They radiate to adjacent anatomical zones. They are supplemented by tooth loss, infiltration of nearby tissues, decay with the formation of ulcers, and enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Other reasons
Aching, initially paroxysmal, then constant pain in the upper and lower jaw is observed with bruxism and myofascial syndrome. In both cases, the cause is constant excessive load on the masticatory muscles. In patients with Horton's disease, the symptom is caused by irradiation and is combined with a dull headache that gradually increases over several weeks, more pronounced in the temporal region.
Measures to prevent trismus
To prevent trismus, it is important to sanitize the oral cavity in a timely manner: remove teeth that cannot be restored, treat caries and inflammatory gum diseases. If prosthetics are necessary, you should contact only qualified specialists, and orthodontic structures should be replaced in a timely manner. The presence of neurological diseases requires constant monitoring by a neurologist.
If you have trismus, you can get advice from dentists at STOMA clinics. If pathology of the temporomandibular joints is detected, experienced specialists will prescribe an additional examination and give recommendations aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease. You can make an appointment for an examination by calling the specified phone number or using a special form on the website.
What to do if a muscle is severely cramped
It is not always possible to easily endure such an attack by limiting yourself to rubbing the affected area. The pain can be unbearable. It can be removed with a sharp impulse.
For cramps due to a hangover, the patient should be placed in a horizontal position and the legs should be raised to reduce blood flow to the extremities. At the same time, it is important to make sure that we are not talking about an epileptic attack (they are not uncommon in alcohol intoxication).
In older people, involuntary muscle contractions are often a warning sign of stroke. Convulsions may give way to paralysis. Timely treatment is important here, so it is better to call an ambulance immediately.