- Indications for the use of a core inlay made of zirconium dioxide
- Contraindications
- Materials for the manufacture of stump inlays
- Inlays for chewing and front teeth
- Pros and cons of stump inlays
- Stump tab or pin?
- Manufacturing process
- Single-channel and multi-channel tabs
A zirconium dioxide inlay is one of the many methods in modern dentistry that is used to restore damaged teeth. When wanting to restore a dental unit damaged by caries or trauma, many patients encounter a number of difficulties that prevent them from using one or another method. A variety of techniques - provide variability, but do not exclude the presence of shortcomings in each of them. Each clinical case is individual.
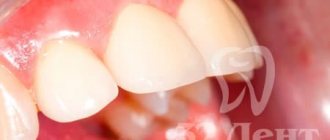
The zirconium stump inlay consists of several parts. The first is immersed in the root, the other is located on the surface and serves as the main one, onto which a crown is installed using special cement. In cases where most of the tooth is destroyed - 2/3 or about 50-70%, this method of restoration is the most effective and safe.
General information about designs
Zirconium dioxide inlay - what is it? You need to understand that inlays in dentistry belong to the field of prosthetics, or more precisely, microprosthetics. That is, these are small-sized prostheses, which come in 2 types:
- restorative (or coronal): independently restore the integrity of the tooth,
- stump (or pin): serve as a support for another prosthesis - a crown, bridge, removable orthopedic structure.
Both restorative and pin inlays are made from zirconium oxide1 - we will describe below what each of these zirconium inlays is and what it looks like. It is worth noting that zirconium dioxide is a very strong material in compression and bending (more than 1400 MPa), in this it can even be compared with metal alloys. However, zirconium dioxide is more often called ceramics - more precisely, metal-free ceramics, since purely externally the material is white, like your own teeth.
%akc72%
Indications
As mentioned above, a zirconium core inlay is indicated for large or even complete tooth destruction; if thin walls remain, restoration is also possible, the main thing is the presence of a strong root that has been preserved.
If the root is lost 1-2 mm below the gum level, in some cases, inlays are used. By first performing an osteotomy
. All this is at the discretion of the doctor.
That is, indications for stump inlays for a crown are cases when:
- support for a crown or bridge is required;
- splinting of loose (moving) teeth due to periodontal damage;
- to remove a defect in the supragingival area;
- aesthetic correction of teeth (irregular shape, location).
Restorative microprostheses - features and advantages
Restorative inlays made of zirconium dioxide are small-sized microprostheses. They are fixed on a natural dental crown, provided that it is destroyed by no more than 50%. You can compare restorative ones with fillings (only very strong ones). Because both are installed in a dental cavity cleared of caries and restore the integrity of the tooth. However, if the filling is formed directly in the tooth during 1 visit to the clinic, then the microprosthesis is made only in the laboratory using impressions (casts) taken in advance.
In most cases, restorative ones are installed on the chewing surfaces of the teeth in the lateral sections of the row - on premolars (“fours” and “fives”) and molars (“sixes”, “sevens”, less often - on “eights”, i.e. wisdom teeth) . In size, microprostheses can be small - inlay, or almost completely cover the top of the crown along with chewing tubercles or cutting edges - onlay, overlay, pinlay varieties.
Stump tab or pin?
Why do people often get pins immediately, without even being offered the option of making an inlay? It’s surprising, the average person might think, because the tab is more expensive and the doctor could earn more. The only problem is that many dentists believe that it is better to see many patients and put pins on them than to bother with each one for longer, and even in two appointments. Companies that make pre-fabricated pins also do their best to promote the idea that their products are the answer to everything.
Orthopedic dentists are very familiar with the statistics on the use of post restorations. They know that the service life rarely exceeds 3 years. Why do they continue to make a mistake, knowing about it? Because no warranty on a pin seal exceeds its service life. They have nothing to fear. The warranty period has expired, and then it’s not their problem anymore. Then people come to their colleagues whose teeth, restored in this way, simply fell apart. Everything would be fine if we were talking about single teeth, but often these are impressive bridges that have lost one of their important supports.
Features of stump microprostheses
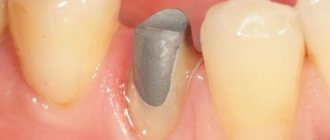
A stump or pin inlay, unlike a restorative one, is not an independent prosthesis. But it is used as a kind of microprosthesis, which is installed in the tooth under a crown or bridge. In essence, the stump is a support, and a very reliable one. The upper part of the stump is an analogue of a ground natural crown, and the lower part is analogous to miniature roots that are inserted into the root canals of the tooth.
Stump microprostheses can be one-piece or dismountable. Solid ones are installed in teeth with 1-2 roots, and collapsible ones are installed in teeth with 3 or more roots. After all, the canals in the roots diverge at different angles, and inserting a solid tab on three or four supports simply won’t work. If we consider single-channel and multi-channel tabs, then single-channel ones are always solid, and multi-channel ones can be either solid (for 2 channels) or collapsible (for 3 or more channels).
A prerequisite for prosthetics is if your own crown is destroyed by 70% or more, if only 1 wall is preserved, if the crown is completely broken at the root. But with all this, the roots must be healthy and intact. Stump zirconium inlays are placed on both the front and chewing teeth.
Pros and cons of stump inlays
This method has many advantages. For example, the tab is fixed inside the canal much better than pins. The load on the teeth (especially chewing teeth) is uniform and natural. If you damage the crown, the inlay does not need to be replaced. They will simply make a new crown for you based on an existing impression.
Tabs are a universal solution. They can be used in cases of complex shape and obstruction of root canals. The product is cast, i.e. the crown and root parts will not split in half, and the upper part will not fall out. Disadvantages include prices and timing. Although the second point is controversial. Two visits within a week is, of course, longer than a one-time placement of a filling, but much faster than six months of suffering during implantation. Also, some people believe that to install such a tab, too much dentin has to be removed. But we all understand perfectly well that it is installed when there is significant destruction of the tooth crown, when other methods are not effective.
Are there any complications? Theoretically possible if the tab was placed in a tooth that was not pulpless. Its secondary caries and pulpitis are possible. Sometimes patients complain that their tooth hurts. If such symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor for help. You may need to take a photo to determine what is causing your symptoms.
Advantages of microprostheses made of zirconium dioxide
If the question arises, which is better - a zirconium restoration inlay or a filling, then the first has the following advantages:
- more reliable: it is made of the strongest zirconium dioxide, and the filling is made of liquid composite or cement. In the future, these factors seriously affect the service life,
- more durable: a microprosthesis made of zirconium dioxide can last more than 20 years, and a large filling - on average 3-5 years, maximum about 7 years,
- tighter fit to the walls of the cavity: the microprosthesis is created in the laboratory using special equipment, and in exact accordance with the dimensions of the cavity - therefore it adjoins it without gaps. And over time, the tab, unlike a filling, does not peel off from the walls,
- does not wear off or sag during use: let us remind you that the material is extremely durable, which cannot be said about the filling - it begins to wear out and sag within a year after installation.
There are 2 moments when the filling wins. The first is if the cavity is very small, i.e. the microprosthesis will not be qualitatively fixed in it. The second is the front teeth, since they have a very thin cutting edge instead of an extensive chewing surface (like premolars and molars). More often, front teeth with small defects are restored with fillings or veneers - they, by the way, can also be made of zirconium dioxide. Restorative (pinlay varieties) in some cases can be placed on the lingual surface of an incisor or canine.
Patients often ask which inlays are better – fiberglass or zirconium? You need to understand that the fiberglass pin is not a tab, but a thin rod (just like a metal pin). Let's see what important advantages zirconium dioxide core inlays have over conventional pins:
- made individually for the patient, so they fit tightly to the root canals,
- very durable: while fiberglass pins are less durable, metal pins are thinner, so they often break,
- do not shine through the prosthesis: because are white in color, and the metal pin is visible through the filling material,
- qualitatively transfer the load to the root and jaw bone due to the anatomical shape of the microprosthesis,
- serve for about 15-10 years: and the maximum service life of a conventional pin is 5 years, because it leads to overload and destruction of the tooth root.
Materials for the manufacture of stump inlays
Various materials are used for manufacturing; the choice in favor of one or the other depends on a number of reasons:
- From the position of the tooth in the oral cavity. For example, metal inlays cannot be used to reconstruct the front teeth (in the smile area), since they are very noticeable and will stand out from under the crown.
- Patient's financial capabilities.
- Allergic reactions. Materials are classified as hypoallergenic or not. Metal inlays may cause allergies in the patient, but are much more durable. Ceramic inlays, on the contrary, are much safer for patients with allergies, but may not withstand mechanical stress.
In connection with the above, the best option for most patients is the use of metal-ceramic inlays. They also have sufficient strength, which is why the risk of breaking them is significantly lower, aesthetic appeal - it is almost impossible to visually distinguish such inlays from natural teeth, and will not cause an allergic reaction in patients with hypersensitivity.
The metal-ceramic inlay contains zirconium dioxide. The service life of such a tab is up to 10 years. Installation is carried out in 2 stages, which is also a significant advantage of this procedure. In addition, the material does not change its shade during use, which means the teeth will not lose their aesthetic appeal years after installation.
According to many experts, one of the best options when choosing a metal/alloy for stump inlays is gold. Moreover, this is not at all the 585 alloy from which rings and earrings are made. In this case we are talking about 750 sample and above, with the addition of 10% platinum. This makes it possible to process the material much more accurately, resulting in an excellent edge seal. Silver and silver-palladium alloys are also used. The gold tab will last 15 years or more.
Among the inexpensive metal options, chrome-cobalt and chrome-nickel alloys, titanium and surgical steel are popular.
On the one hand, doctors recommend silver-based materials, because it has bactericidal properties. On the other hand, it has one drawback, which is expressed in the staining of the gums. The pigmentation is noticeable enough to cause concern and dissatisfaction among patients.
The alloy with nickel shrinks and is harmful to health. Cobalt-chrome is better, but more difficult to process. Titanium is more convenient in this regard, but in some cases it turns out to be too fragile. After all, more massive products are usually made from it.
The simplest and cheapest is the composite tab. Essentially, this is the same photopolymer filling, the only difference being that it is formed not directly in your tooth, but in advance, in a dental laboratory. The disadvantages are the same - low strength and durability. If it falls out, then there is usually no warranty with a free replacement. And it can fall out quite quickly. Statistics show that for many people, such a tab falls out within a year or two. That is, there is no point in installing it. Composites are used for restorative inlays. Photopolymer materials are not suitable at all for stump inlays.
What is known about the shortcomings
According to reviews from some patients, a zirconium inlay (restorative or stump) has only one drawback - its high cost. Another disadvantage is the time spent on prosthetics - it takes about 2 weeks to complete the treatment. Although, for example, CEREC technology allows you to make a restorative microprosthesis in 15-20 minutes - and it will be installed on the day you go to the clinic. However, such equipment is not available everywhere.
Read on the topic: what is CEREC technology - when does the dentist and patient need it, its pros and cons.
Another disadvantage is the pure white color of zirconium dioxide (several shades lighter than natural enamel) and its opacity. But dental technicians solve this problem by applying liquid ceramic, colored in the shade of enamel, to the upper part of the zirconium restorative microprosthesis. Or you can use alternative prosthetic options (more on them below).
Indications and contraindications
Indications for the use of a stump inlay as a prosthetic method are severe destruction of dentin, in which its restoration is impossible with composite materials and pins. The crown on the core tab will hold quite firmly and at the same time not exert strong pressure on the root. Stump inlays are also used to create a high-quality foundation for the installation of dental bridges.
However, like any other medical procedure, the installation of stump inlays has not only indications, but also a number of restrictions on its implementation. These restrictions include:
- The patient has an individual allergic reaction to the material used to make the stump insert.
- Identification during examination of cysts and other formations in the root system.
- Excessively thin dental walls, abnormally short roots of the dental unit.
The procedure for installing a stump inlay for periodontitis, as well as poorly treated dental canals, is not carried out. Depending on the individual characteristics of the case, the dentist may offer the patient different types of stump inlays for installation. The cost of the stump tab and tooth restoration services using it will depend on the type of structure.
Stump tab
from 5400 rub. More about prices
We have been working since 1994
we are one of the first to open private dentistry in Moscow
Best materials
only new and modern equipment for dental treatment
Free
consultation with a dentist
Payment options
- cash
- plastic cards
- cashless payments
Doctors' experience
- with great experience
- graduated
- conference participants
Indications for prosthetics
Restorative and core microprostheses made of zirconium dioxide are indicated for installation in adult patients, less often - in adolescents with permanent teeth (such prosthetics are not performed on dairy patients). Let's look at the readings in more detail in the table below.
| Factor | Restorative microprostheses | Stump microprostheses |
| Installation location | On a natural crown | To the root canals |
| Initial preservation of the natural crown | 50% or more | Less than 70% or complete destruction to the root |
| Root condition | Healthy, no cracks, cysts or granulomas | |
| Presence of dental nerve (pulp) | As a rule, the pulp should be healthy | Subject to mandatory removal, root canals are filled |
| What teeth are they placed on? | Mainly for chewing | Stump inlays can be placed under chewing and front teeth |
| Fixing another prosthesis on top | Not required | Mandatory |
When choosing a core microprosthesis made of zirconium dioxide and the patient wants to put a ceramic crown on the front teeth, the dentist can tell you why zirconium inlays are dangerous in this case. The aesthetics of the restoration will certainly be high. But the fragile ceramics of the crown will quickly become unusable - it will simply crack on a strong support. Therefore, it is better to give preference to a zirconium crown.
Don't know what type of prosthetics to choose?
We will help in the selection, advise where to read more information and compare types of prosthetics.
Consultation with an orthopedic doctor in Moscow clinics is free! Call now or request a call
Working hours: from 9:00 to 21:00 - seven days a week
Single-channel and multi-channel tabs
If the tooth is multi-rooted, then the question arises: should I make a solid core inlay or a collapsible one? If the channels run parallel, solid blanks can be used. It is possible to determine how to proceed further only if the doctor has photographs of your tooth and sees how the canals pass. Some experts, in addition to standard diagnostic methods, recommend doing a CT scan. With the help of computed tomography you can see:
- condition of the root part;
- shape of root canals;
- the presence of periodontal and bone pathologies that require treatment. After all, you may have a cyst under your root that you didn't know about.
Overall, a multi-root stump is an excellent solution. Being held in several channels at once, it creates an even load on the entire tooth, is securely held and ensures that the root does not break. A crown based on such an inlay can be attached to a bridge without fear of damage or destruction.
Contraindications for installation
A contraindication to fixation of a restorative microprosthesis is extensive destruction of the natural crown. If, for example, more than half of it is missing due to caries or injury, or there is a very large cavity inside, surrounded by thin walls.
“I had a zirconium core inlay and the same crown made by my dentist. Probably 6 years have passed, but the tooth feels great and looks like a real one. Before this, I constantly had to change the filling - but in chewing ones, the fillings are large and not very beautiful, they fail over time.” Tatyana P., review from the woman.ru forum
It is contraindicated to install a stump if the dental nerve is preserved, if there are cracks in the root or if a pin/instrument fragment is stuck. Also considered a contraindication is the presence of inflammatory processes under the roots, formations (granulomas, cysts). It is also not recommended to install core microprostheses on teeth with pronounced mobility.
Zirconium dioxide: criticism and facts
Peter Yanev, dental technician (Plovdiv, Bulgaria)
I will try to explain why zirconium dioxide has become my favorite material when it comes to solving complex aesthetic problems using prosthetics. We will also consider examples of critical statements in relation to this excellent material and try to figure out whether such assessments coincide with reality.
I will briefly list the properties and advantages of zirconium from the practical side:
- Biological compatibility is a property that hardly needs detailed explanation. To date, there have been no reports of any allergic reactions caused by zirconium dioxide;
- Exceptionally high strength - with this material we can successfully produce the same work that we do with metal;
- Aesthetics - these days it is no longer enough for a patient to “just have something to chew.” Patients are paying more and more attention to appearance.
Zirconium dioxide is a material that successfully combines all these qualities and meets modern requirements. How do I choose zirconium in my daily practice? Let's start with the "foundation" and gradually move towards the "roof".
Stump inlays
Can we use zirconium dioxide to make them? Definitely yes. Thanks to its strength and transparency, we obtain both a strong and highly esthetic basis for the subsequent all-ceramic restoration (Fig. 1).
Figure 1a
Figure 1b
Figure 1c
There have been critics who argue that, due to its relatively reduced modulus of elasticity, the zirconia inlay can cause cracks and fractures in the root of the tooth being restored, acting like a wedge on the more flexible natural hard tissue. In fact, it is the reduced elasticity combined with the exceptional strength that makes the zirconia core inlay strengthen the tooth root. Of course, to achieve this, proper preparation of hard tissue is necessary: sufficient thickness (at least 1/3 of the total root cross-section) and pin length (at least 2/3 of the total root length). It is also necessary to provide a circular platform in the cervical part of the root, to which the coronal part of the core tab will fit tightly, thus limiting the wedging effect on the underlying tissues (dentin, cement).
Abutments for implants
Another area of application in which zirconium dioxide has proven itself, especially when it comes to restoring the frontal group of teeth (Fig. 2).
The zirconia abutment is the basis for a highly esthetic result. Excellent biocompatibility and polishability have made zirconia a particularly suitable material for the manufacture of superstructures.
Figure 2
Frameworks for crowns and bridges
This is the main application of zirconium in my daily work (Fig. 3). It is in this area that there are most of the unfounded fabrications on the part of opponents of this excellent material.
Figure 3
Questionable strength (chips and fractures)
The origin of the zirconium blocks plays an important role here.
Famous manufacturers bring to the market only certified high quality products.
However, many “suitcase merchants” (as we call them in Bulgaria) have appeared who offer goods of unknown origin, without a guarantee of quality or any documentation, and at a dubiously competitive price.
Designing the future frame
It is necessary to take into account all factors that may affect the final strength of the prosthesis: the size of the structure, the number and volume of the intermediate/cantilever part of the bridge; thickness of the caps; cross-section of connections between frame elements.
Another factor influencing the strength of the product is the process of milling the zirconium frame itself and its subsequent machining. If the technician does not have his own ZrO2 milling system, he must carefully choose who to entrust the production of zirconium frameworks to. Here the responsibility lies not only with the equipment, but also with the operator who operates it. After all, the operator is the person who sets the parameters of the equipment, the one on whom the final appearance, precision of fit and quality of the prosthesis largely depend. From the CAD/CAM center we receive a frame ready for subsequent manipulations, which requires almost no additional mechanical processing (Fig. 4).
Figure 4a
Figure 4b
Unfortunately, our practice is replete with examples of unsatisfactory results resulting from insufficiently well-trained operators operating CAD/CAM systems (Fig. 5). In this case, serious additional processing of the zirconium frame is required, which wastes time and negatively affects the quality and strength of the finished work.
Figure 5
Of course, the correct additional processing, namely the use of burs for zirconium, the absence of overheating of the material during milling, and mandatory subsequent firing, may well minimize the risk of cracks, chips and fractures.
Connection with ceramic layer
Recently, there have been a lot of critics who unanimously say that there is no chemical bond between zirconium dioxide and the ceramic coating and therefore chipping or splitting can occur. The strange thing is that in my practice and in the practice of colleagues with whom I know, there have been no such cases. Where is the truth? After careful scientific research, it was found that the bond between the zirconia framework and the ceramic is stronger than the similar bond between the metal and the ceramic (which is both mechanical and chemical). The reason is simple: the metal, unlike zirconium, has a significantly higher modulus of flexibility compared to the flexibility of sintered ceramics. Even minimal bending of the metal frame leads to the formation of cracks in the ceramic precisely because of the extremely low, almost non-existent elasticity. Zirconium dioxide, in turn, thanks to its exceptional strength and reduced elasticity, provides a stable and healthy base for ceramic veneers.
It is necessary to follow the rules for processing the material:
- avoid the presence of sharp edges and corners on the surface of the frame;
- provide space for a relatively uniform layer of ceramics;
- observe slow cooling after firing (up to 600 °C), especially for large structures.
Such ceramics can be separated from the finished prosthesis only by sawing/milling.
Unsatisfactory aesthetic results
Many critics argue that zirconia does not have good optical properties: transparency is insufficient and there is almost no fluorescence. Recently, it has been very fashionable to talk about the transparency of certain ceramic materials. But how much transparency do we really need? This depends on the type of structure, volume of material and area of prosthetics. If we are talking about a classic veneer, 0.3-0.5 mm thick, then we choose a material with better transparency, and this is due to the fact that it is mainly the enamel layer that is being restored. When it comes to bridge frames, things are different: the total thickness of the material (frame + ceramic) will be 1.2-2.5 mm. It must be remembered that the greater the transparency of an object, the more light passes through it and the less is reflected. But we see an object precisely thanks to reflection. The same is true for color rendering and perception. Thus, the transparent object is less noticeable and appears gray and colorless in the mouth.
Have you heard of a patient who would love this?
Another advantage is that due to the optimal transparency of zirconium, we can hide any defects in the tooth core (discoloration, metal pins) by using different frame colors and varying the thickness of the caps.
Thus, there is no need for maximum transparency: for the manufacture of frameworks, we need a material with optimal translucency close to natural dentin, which is what modern zirconium dioxide gives us.
What else does aesthetics depend on?
From the choice between white and colored zirconium, which is directly related to the ceramic system you use. In some ceramic systems, a special layer is necessarily applied on top of zirconium dioxide - bonding (often such masses have quite significant opacity), which worsens the optical properties of the finished prosthesis. The ceramic manufacturer usually recommends that owners of such systems work with white zirconium frames (Fig. 6).
Figure 6
I use only colored zirconium because the Vita VM9 ceramics I use do not require a special bond type material. When using VM9 as a bonding agent, a thin layer of Wash BASE DENTIN is applied to the surface of the zirconium framework (Fig. 7). After firing, no loss of transparency is observed.
Figure 7a
Figure 7b
Fluorescence
Zirconia does exhibit reduced fluorescence, but this is not a problem with modern ceramic systems. Most ceramic materials have varying degrees of fluorescence depending on their intended use. The kits contain specially developed fluorescent masses, thanks to which we have complete control over the fluorescence, since we are able to recreate it to the level we need. In Figure 8 we see zirconium caps on teeth 13 and 12. The cap of tooth 11 is coated with fluorescent material EFFECT LINER; 21, 22 and 23 are coated with the aforementioned Wash BASE DENTIN.
Figure 8
The esthetics of each all-ceramic prosthesis depends to a certain extent on the choice of cement. The market offers a wide range of luting cements, which I do not intend to dwell on in detail. From an aesthetic point of view, cement must be selected based on its transparency, degree of brightness and color in each specific case. It should be noted that, unlike thin veneers, prostheses with a zirconia framework are less sensitive and allow some freedom in the choice of cement. The correct choice of material for fixation allows you to correct minor color discrepancies in the finished structure. On the other hand, the “wrong” cement (often with a high degree of opacity and light blocking) is quite capable of ruining a perfect job.
In conclusion, if the fundamental principles of proper planning, fabrication and fixation are followed, zirconium is truly an excellent material for making frames. It allows us to fully control every stage of creating a precise, durable and highly aesthetic orthopedic design.
How are dentures made and installed?
The processes of preparation for prosthetics, creation of a zirconium dioxide microprosthesis and its fixation consist of the following stages:
- Stage 1 – diagnosis: also at this stage, contraindications are excluded, the condition of the tooth itself, as well as neighboring and opposite ones, is studied,
- Stage 2 – preparation: the dentist-therapist removes all carious tissues, if necessary, depulps the tooth and fills the root canals, leaves a cavity for a classic restorative inlay or forms it inside the roots,
- Stage 3 – taking impressions (impressions): for example, using wax or silicone (this depends on the type of future prosthesis), the color of the restoration is selected. In clinics with modern equipment, digital impressions of the oral cavity can be made using an intraoral 3D scanner - this is fast, convenient and very accurate,
- Stage 4 – modeling: a real model of the prosthesis is created based on impressions in a dental laboratory, and a virtual model is created in a computer program based on digital impressions. But the real model will also need to be digitized and worked out in a CAD/CAM system for the next stage,
- Stage 5 – manufacturing: production occurs by milling on a machine, because the material is so strong that it will not be possible to create a prosthesis by hand. Usually the workpiece is made 20-25% larger than the actual size, because After milling, it is baked - in this case, the material “shrinks” to the required parameters. If necessary, the microprosthesis is covered with a layer of colored ceramics. Next, the product is sent to an orthopedic dentist,
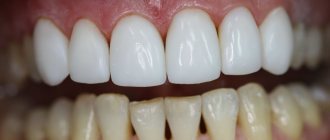
- Stage 6 – fixation of the zirconium inlay into the patient’s tooth.
Manufacturing process
The procedure is quite complex and is carried out in several stages. First you need to prepare the tooth itself. Excess tissue is removed from it. Then, if required, each channel is processed to achieve parallel processing. The prepared surfaces are treated with Vaseline. Now liquid plastic is poured into the tooth for modeling. After this, special ashless pins are installed in each channel.
Next, the tooth is limited using a matrix so that plastic can be added in height. Now the model freezes, it is removed and checked for defects. If there are none or it is possible to eliminate them, the cast is brought to perfection. During this time, a temporary filling is placed in the tooth. The impression is sent to a dental laboratory, where an inlay is made from it.
Inlays are installed using direct and indirect methods. Direct is the simplest. The doctor makes an impression and then an inlay is made. In indirect, the patient’s bite is taken into account, so an impression is made of both jaws. It's more expensive, but more reliable. It is also possible to use computer technology. Specialists create a 3D model of the jaws to calculate how comfortable it will be for the patient. After all, an error of a few tenths or even hundredths of a millimeter significantly affects the bite.
Service life and care features
The service life of zirconium dioxide is very long - 15, 20 and even 25 years. Such long-term operation will depend both on the quality of preparation of the tooth for prosthetics and the accuracy of the fit of the orthopedic structure, as well as on compliance with the rules of wearing and caring for prostheses. What is needed for this? Do not forget about regular brushing of your teeth in the morning and evening, avoid hard and stretchy products (so that the denture does not come off). Ideally, you should also visit your podiatrist twice a year for a checkup.
Recommendations for caring for the oral cavity after the installation of a stump inlay
Most often, immediately after installing the core inlay, a temporary acrylic crown is put on the tooth, which will protect the structure itself and the tissues in the area of manipulation from the negative effects of external factors. However, if for some reason a temporary crown was made, then before installing a permanent prosthesis, the following rules should be followed when caring for the oral cavity:
- After eating, be sure to rinse your mouth thoroughly;
- When brushing your teeth, do not touch the stump with the brush;
- Do not eat excessively solid foods.
You should also treat the area of the procedure daily with special anti-inflammatory gels. A specialist must give you detailed advice on oral hygiene immediately after completing all procedures.
Cost of prosthetics in Moscow and other cities
How much does a zirconium inlay cost? Its price is 18-20 thousand rubles. Moreover, prices in the capital and other cities are approximately equivalent, because the basis is the cost of the material (which is purchased from the same manufacturers or suppliers).
1Zinovenko O.G., Shinkevich M.V., Sadovskaya I.V. Aesthetic prosthetics using zirconium dioxide, 2014.
Author: Sambuev B. S. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
Installing a dental inlay under a crown
The production and subsequent installation of dental inlays can be carried out by a doctor in one of the following ways:
- direct method, when work on the formation and modeling of a microprosthesis is carried out in the patient’s mouth;
- indirect method, in which a microprosthesis is made from an impression in the laboratory from metal or pressed ceramic mass;
- CEREC technique, in which the design of a microprosthesis is modeled and manufactured using dental computer technologies (milling from zirconium dioxide).
The choice of manufacturing technique depends on the materials used and the clinical situation. After drawing up a treatment plan, the doctor explains to the patient why it is worth choosing one or another restoration technique and which dental inlays are best done in this case. Before starting orthopedic treatment, the dentist assesses the destruction and condition of the remaining root on which the structure is planned to be placed. For a comprehensive diagnosis, it is necessary to take an appropriate targeted photograph or orthopantomogram. At the next stage, preparation is carried out to remove unnecessary hard tissue, selection and preparation of the root for installation of the future prosthesis. Impressions are taken for indirect laboratory production or the formation of a dental inlay in the oral cavity. To fix the finished microprosthesis, a pin with cement previously applied to it is inserted into the prepared root.
The installed structure, depending on the type of defect, can serve as a support for an artificial single tooth crown or a bridge. If the permanent crown is still in the manufacturing stage at the time of installing the dental inlay, a temporary crown can be placed to restore aesthetics and chewing. Such an artificial tooth can also be made using a direct clinical method, which is done on the day of treatment.
Stump inlay for a crown for bruxism
Bruxism is a condition in which there is periodic (mostly nocturnal) involuntary active contraction of the masticatory muscles, causing clenching, clenching or grinding of the teeth. Among the causes of pathology, the following factors can be identified:
- chronic stress, overwork;
- occlusal disorders;
- hereditary predisposition;
- mental illness.
In case of pathological abrasion, reconstruction with metal inlays for crowns is used to restore hard tissues. Prosthetics and bite restoration are helped by the use of dental core structures with crowns made of highly wear-resistant material; therefore, for this pathology, composite or ceramic prostheses are not used.
Bruxism is a rather difficult neurological disease to treat, requiring careful diagnosis and long-term complex therapy. Restoration of dental tissues is advisable when achieving a reduction in symptoms leading to occlusal overload of the teeth. An interdisciplinary approach should be taken to choosing the optimal prosthetic technique for pathology; after installation of the prosthesis, individual aligners are used.
Indications for installation
The installation of dental inlays is indicated in the following cases:
- fracture of the coronal part;
- carious destruction of the crown;
- anomalies in the location, shape or size of the tooth;
- low tooth crown;
- production of a bridge structure, when a pin stump inlay for a tooth is placed as a supporting element;
- need for splinting.
The strength of fixation, the quality of the structure and how long the product will last depend on the condition of the tooth root when a microprosthesis is installed into it. The root should not wobble, should be without curvature in the upper third, with passable, well-sealed canals and walls of sufficient thickness for prosthetics. The use of a stump structure is not recommended in the following cases:
- damaged circular ligament;
- resection of the root apex (temporary relative contraindication), as well as inflammatory processes in which the gums or peri-root tissues may hurt;
- poor hygiene;
- incomplete obturation of the canals;
- mobility 3 degrees.
In each clinical case, the decision on the advisability of installing a stump structure is made by the attending orthopedic surgeon together with related specialists, taking into account all the advantages and disadvantages of using this reconstruction. If there are relative (temporary) contraindications, before prosthetics, therapeutic treatment or surgical correction, as well as replacement of failed orthopedic structures, can be carried out.