Most dental patients want to have not just a healthy, but also an attractive smile. Unfortunately, not everyone can boast of this.
Back in 1984, some components that are necessarily inherent in a “beautiful smile” were identified:
- The smile should expose almost 100% of the coronal part of the tooth and the gingival papillae, while the gum itself should not be visible (otherwise, when the gum is exposed, we are talking about a “gummy smile”).
- The gingival contour should be symmetrical, smooth, the edges of the gums at the central incisors and canines should be located at the same level, and at the second incisors - 1-2 mm lower.
- The length of the tooth crown should not be less than 11 mm, and the width should correspond to the “golden ratio”.
- The gum contour should be in harmony with the smile line.
If the patient's smile does not fit into these standards, then it can be significantly improved by changing the edge of the gingival contour and increasing the length of the dental crown.
What is lengthening of the clinical crown of a tooth?
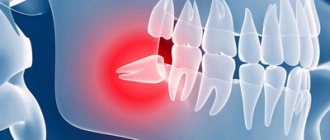
Lengthening the crown of a tooth is a tooth-preserving dental intervention, as a result of which the required amount of subgingival tooth tissue is exposed and a new gingival contour is formed.
A radical alternative to this manipulation is to remove the problematic tooth and install an implant of the required length in its place, forming the most aesthetically pleasing gum contour. But do not forget that not a single most beautiful artificial tooth can compare in functionality with your real teeth, so resorting to such a radical method is only in exceptional cases.
Causes
causes of row lengthening are:
- pathological change in respiratory function with oral predominance;
- disruption of the swallowing process with the formation of the infantile type;
- pronounced articulation of the tongue during conversation;
- the presence of bad habits with the manifestation of obsessive movements: sucking a finger, pacifier or tongue, chewing a pencil and other objects;
- macrodentia, with the formation of several abnormal teeth;
- remote or abnormal position of the buds, with the growth of which a trema or diastema is formed between the teeth.
Several anatomical factors can be identified, for example, the eruption of supernumerary teeth during the primary dentition period or the failure of teeth to fall out during a change in occlusion.
In what cases is it necessary to lengthen the clinical crown of a tooth?
Lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth may be prescribed to a patient for the following reasons:
- Aesthetic
- "Gummy" smile.
- Violation of the gum contour of one or more teeth.
- The natural crowns of the teeth are too short - after eruption the gums did not rise and remained “lowered” on the tooth.
- Under-eruption of one or more teeth in the dentition.
- To improve dental hygiene.
- Tooth-preserving
- The need to restore the length of teeth that was lost as a result of pathological abrasion (bruxism, increased tone of the masticatory muscles can lead to this).
- The presence of caries in the subgingival part of the tooth, i.e. below the gum line.
- The need to carry out and maintain high-quality tooth restoration using any of the methods, because to maintain periodontal health, such restoration should not go below the gum level.
- For high-quality prosthetics, in case of complete destruction of the tooth crown, for reliable “full” capture of the hard tissues of the tooth and to prevent future problems with the crown.
- As one of the components of complex surgical treatment of periodontal diseases for the removal of periodontal pockets.
Diagnostics
When visiting a dentist, a patient expects comprehensive care, healthy teeth and comfortable dentures, but, unfortunately, not all dentists can do this. A small dental office, where a private doctor works, does not have complex diagnostic equipment (for example, an orthopantomograph or a computed tomograph), and does not use a microscope, since this is also too expensive for a private doctor. Another problem of small clinics or private offices is that when situations arise when surgical intervention or complex treatment of tooth canals is required with retreatment, extraction of fragments, etc., the doctor suggests removing the tooth as hopeless, since he can cope with it on his own. problem, and doesn’t want to lose the patient by sending him to another clinic. It would seem that what problems - the tooth was removed and an implant or bridge was installed - the problem was solved. But if there is hope of saving your own tooth, even the root of it, it is better to turn to an experienced doctor who will save the tooth.
At Family Dentistry, when a question arises whether to treat a tooth or remove it, a decision is made only after a comprehensive examination and analysis of the situation. This is possible thanks to the availability of modern X-ray diagnostic equipment in the clinic, including a computed tomograph, and the well-coordinated work of specialists - endodontists working with microscopes, surgeons, prosthetists, dental technicians - who are able to find a joint solution in the most difficult cases.
This work reflects only one part of the complex treatment that was performed by Dial-Dent specialists to put all of this patient’s teeth in order. There were a lot of problems, but the peculiarity of Family Dentistry is precisely the solution of complex cases that require complex treatment. In the near future, other stages of treatment will be described: dental implantation and prosthetics on implants, aesthetic prosthetics, dental restoration, caries treatment.
For general diagnostics, a panoramic photograph of the teeth was taken. In a fragment of a panoramic image, arrows show the teeth considered in this work at the top left. Existing problems:
- Voids inside previously treated canals - which indicates unsatisfactory quality of treatment.
- An overhanging edge of the crown that catches food.
- A pin in a tooth made of unknown material.
- Crowns combined into one design.
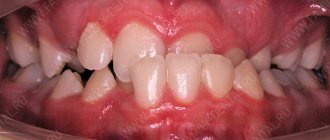
The appearance of old crowns is unsatisfactory (the teeth in question are shown with arrows). Upon examination, it is clear that the edge of the crown hangs over the gum, food gets stuffed under it, which leads to injury and inflammation of the gums, the crowns are made in the form of a combined structure, which is extremely unfavorable for the roots of the teeth, as they become loose, as well as for the interdental papilla of the gums - the combined structure led to its inflammation:
It was decided to redo the crowns, so the old crowns were removed. Under the crowns there was severe inflammation of the gums (1), one tooth was reinforced with a metal pin (2), the teeth had caries, and one of the teeth had an old filling that went under the gum, which complicates treatment (3).
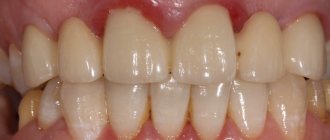
View of teeth from the inside:
External view of teeth:
Methods for lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth in modern dentistry
In modern dentistry, there are 4 methods of lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth:
- Orthodontic – involves “pulling” a tooth from the bone using a brace system, which can be installed on several teeth or on the entire jaw. This method is used when there is free space between antagonist teeth, mainly to lengthen the crown of one “under-erupted” tooth, the length of which differs from the rest. The disadvantage of this method is the need to wear braces, a long treatment time - 2-3 years, and the presence of a retention period.
- Surgical - is an operation to remove part of the gum and/or bone and give a new shape to the gingival contour. The main types of surgical intervention are gingivectomy or gingivoplasty, as well as bone resection.
- Orthopedic - involves building up the crown of a tooth using orthopedic structures - veneers/lumineers or dental crowns, due to the installation of which the bite is raised, i.e. the tooth is lengthened from the cutting edge, without involving the gingival zone. This method of lengthening dental crowns is used in the presence of an erased cutting edge and in the restoration of significant defects in damaged and chipped teeth. The doctor will also choose this technique if the patient has short teeth, but at the same time an ideal gingival contour.
- The therapeutic method is composite augmentation of the incisal edge. Effective for minor chips and chips on single teeth.
This technique is used to “raise” the gum level when correcting a gummy smile, and before caries treatment and restoration that need to be performed below the natural gum level.
What does a patient need to know about lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth?
In order for the tooth crown lengthening procedure to be successful, it must be carefully and comprehensively planned - this applies to all methods of its implementation. In planning such treatment, depending on the chosen intervention technique, several specialists will take part - a periodontist, a dental surgeon and/or an orthodontist, a dental therapist and/or an orthopedic dentist.
When planning to determine the volume and type of intervention, the following are taken into account:
- Current and future health status of periodontal tissues.
- The proportions of the tooth itself, the aesthetics of the patient’s smile.
- The structure of the roots of the tooth and the ratio of the length of the root and crown. It is IMPORTANT that its root part is no less visible.
- Condition of the jaw bone.
- Biological width is the distance from the bottom of the gingival sulcus to the crest of the tooth-bearing bone, and in order for the tooth to be stable in the future, its value must be at least 3 mm.
Therefore, lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth requires a very careful diagnosis, because the procedure should not disrupt the stability of the teeth on which it will be performed.
Diagnostics before tooth crown lengthening includes:
- Assessment of periodontal condition (diagnosis by a periodontist).
- Diagnosis by a surgeon – if a surgical lengthening method is proposed.
- Consultation and diagnosis with an orthopedist – in case of need for extensive restorations, prosthetics or the use of an orthopedic lengthening method.
- Consultation with an orthodontist and orthodontic diagnosis, if the crown will be lengthened by installing a brace system
One of the mandatory studies during diagnosis will be a 3D CT scan - computed tomogram, to determine the length, location of the tooth root and the condition of the jaw bone tissue.
Preventive recommendations
After surgery, the rehabilitation period is at least two weeks. During this time, the specialist prescribes the patient to take painkillers and mouth rinses. During the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to minimize the load on the gums, avoid eating solid foods and foods that require thorough chewing, carefully brush your teeth, and stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
When installing braces, you must follow the rules of oral hygiene so that food particles do not accumulate between the elements of their design and do not provoke infection of the gum tissue or the proliferation of harmful microorganisms. When choosing this method, you need to regularly visit the doctor on the appointed dates so that he can regulate the braces and monitor the rehabilitation process.
What awaits a patient undergoing a clinical crown lengthening procedure?
Read about the orthodontic, orthopedic and therapeutic method of lengthening the crowns of teeth in the relevant sections - on orthodontics (installation of braces), prosthetics with crowns and veneers, and restoration. In this article we will focus on surgical lengthening of the crown of one, and more often, several frontal teeth.
Basically, in this case, they resort to gingivoplasty - a surgical operation during which part of the gum is removed along the gingival contour, often this intervention also requires the removal of part of the bone.
This manipulation is performed by a dental surgeon in a surgical office, on an outpatient basis, under local anesthesia and, sometimes, sedation.
Such an operation is prescribed after a thorough diagnosis, in most cases - as a stage in complex treatment and the formation of an aesthetic smile.
- Before any surgical intervention, professional hygiene and sanitation of the oral cavity are carried out to reduce infection in the oral cavity and speed up healing.
- The patient is given anesthesia.
- After which, if resection (removal) of a part of the bone is required, the mucoperiosteal flap is peeled off and an osteotomy is performed. A new gingival contour is formed, which is located above the previous one.
- The wound is sutured and a gum bandage is applied.
- In the postoperative period, for a speedy recovery, the patient is prescribed antiseptic rinses and painkillers, and a course of antibiotics may be prescribed. It is necessary to limit physical and chewing activity.
- The stitches are removed after about 7-10 days.
- Immediately after the wound has healed, a temporary restoration or prosthetics is performed, and after a few months the temporary structures are replaced with permanent ones.
- Complete restoration of the new natural gum margin occurs in 1-3 years.
The perfect smile of Hollywood stars
Dental services in America are noticeably expensive. For this reason, more aesthetic and image prosthetics are carried out there, and medical procedures often remain in the shadows. The new teeth of famous personalities are often displayed like an expensive car. Unfortunately, the Hollywood smile is not for everyone. Perhaps you have noticed how comical teeth sometimes look in some photos.
The effect of “artificial dentures” is not at all what modern aesthetic dentistry strives for. Your smile should be natural and healthy, highlighting your individuality. A harmonious, attractive smile, what is it like according to the majority of our compatriots?
Contraindications to lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth
In some cases, after weighing all the pros and cons, the dentist may refuse to lengthen the patient’s dental crowns.
The following reasons may serve as the basis for this:
- After tooth crown lengthening, the appearance and health of adjacent teeth will deteriorate.
- Regardless of the lengthening, restoration of this tooth is still impossible.
- Insufficient biological width.
- A tooth with a short crown has a short root.
- During orthodontic lengthening, there is no space between the tooth that is planned to be lengthened and the opposing tooth.
- The ratio of the effort required to lengthen the crown of a tooth and its value is not in favor of preserving the tooth.
- The patient is unable to maintain the required level of periodontal health.
We create a unique, beautiful smile
A beautiful smile is not a privilege, but a requirement of our dynamic times, as well as a significant part of the image of every business person. But what makes a smile unique? First of all, it is the harmony of color, size, shape and position of the teeth. In addition, your teeth should have an optimal relationship with your facial structures.
Today, a technology has been developed for calculating the correct height of the tooth crown. It combines a mathematical calculation and a biological component, in this case the color of the iris.
Taking into account the biological characteristics of each person, beauty salon specialists will form a smile that will give the patient maximum self-confidence.