Flux on the gums is an extremely unpleasant, but quite common phenomenon, which is an inflammatory process in the periosteum area. The word “flux” is of German origin and is translated as “flow, flow.” Today, this term is not commonly used in professional circles. Instead, experts use the scientific name of the disease - odontogenic periostitis. In most cases, it overtakes the most patient patients who diligently avoid visiting a professional dentist for a long time. As a result, due to laziness or fear of the dentist, the patient receives severe swelling of the gums, constant dull pain, and in some cases, high fever.
Despite the fact that the phenomenon in question cannot be called a rarity, this does not make it any less harmless. The advanced form of periostitis is quite dangerous, so the health of the oral cavity and teeth should be taken as seriously as possible, and at the first signs of inflammation you should consult a specialist as soon as possible.
Causes of the disease
Patients often blame the careless work of dentists for the development of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. Thus, “flux after wisdom tooth removal” is one of the most discussed topics on dental forums. In fact, the most common causes of periostitis are gum trauma and untreated tooth decay. Often the situation is complicated by the patient’s reluctance to visit the dentist in a timely manner. As a result, food debris inevitably accumulates in places of damage, which eventually begin to rot. Further, the pus accumulates and then begins to rapidly spread, affecting healthy tissues of the oral cavity.
The most common causes of gumboil are damage to the gums, poor oral hygiene and caries.
Treatment of flux on the gums with folk remedies cannot guarantee a high-quality result. Most often, self-prepared medicinal products can only suppress the pronounced manifestations of the disease, and not eliminate the causes of its occurrence. For this reason, when the first symptoms of periostitis appear, it is important to undergo high-quality flux treatment in dentistry, which can guarantee complete relief of the inflammatory process.
How to prepare a child for tooth extraction
If tooth extraction is unavoidable, try your best to minimize the child’s stress. For example, tell him a fairy tale about how one tooth began to behave badly and interfere with the others, so it needs to be “pulled out.” Before going to the clinic, you can also discuss some pleasant event with your child, be it going to the movies, the circus, or buying a toy, which you will do immediately after removing a capricious tooth. The main thing is not to panic, and then the confident and calm attitude of the parents will certainly give the child the strength to courageously endure this frightening but necessary procedure.
You can avoid tooth extraction surgery in children if you carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity throughout the entire period of dentition formation, monitor the quality of hygienic procedures and regularly take children to preventive appointments with the dentist.
Symptoms of gumboil
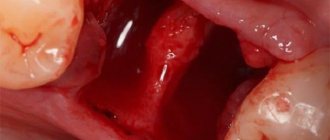
Symptoms are expressed in the appearance of a purulent sac or thickening of the gum area. The photo shows a clear example of gumboil on the gum. It is this infiltrate that is the main sign of the development of the disease. Experts distinguish two main forms of periostitis:
- The acute form is accompanied by severe toothache, severe tissue swelling, and swelling of the cheek. As the disease develops in the lower jaw, inflammation of the lymph nodes and swelling of the chin may occur. Often the advanced form of the disease causes elevated body temperature.
- The chronic form of the disease proceeds slowly and imperceptibly, which is its insidiousness. Often there is thickening of the jaw bone in the affected area. Despite the fact that there are practically no pronounced symptoms in this case, the consequences of this form of flux are no less dangerous.
What is flux
Flux is a somewhat outdated name that is common only in everyday communication. In modern dentistry, this pathology is called periostitis, which reflects the essence of the disease.
Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum that covers the bone of the upper or lower jaw. As the pathological process develops, the lesion ceases to be local in nature and spreads to other tissues - an abscess appears on the surface of the gum.
Diagnostics
Before proceeding with dental flux treatment, the doctor must conduct an appropriate diagnostic examination. The exact diagnosis is determined based on data obtained during a clinical examination and x-ray diagnosis. Laboratory tests allow you to accurately determine the stage of the inflammatory process. Only after making an accurate diagnosis will a specialist be able to decide what to do with gumboil and which method of treatment in this particular case will be optimal.
How to treat flux?
If your tooth hurts and gumboil appears on your cheek, you shouldn’t panic and look for something to rinse your mouth with. “Grandmother’s” treatment methods really help get rid of acute pain and relieve some swelling, but they have not yet helped anyone cope with purulent compaction, which is the main danger. How and with what to treat flux? How to remove gumboil in case of gum inflammation? Only a qualified dentist can give detailed answers to these and other questions.
Self-medication with folk remedies will only help dull the pain and relieve swelling a little. Only a qualified dentist can completely remove pus and eliminate the cause of inflammation.
How is flux treated in dentistry? Currently, there are two main methods of treating gumboil on the cheek:
- Opening the pus sac, in which the doctor removes the accumulated pus through a small incision. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. After removing the pus, the specialist installs a drainage at the site of the incision - a special rubber strip that ensures the outflow of pus and prevents the wound from healing ahead of time.
- Cleaning an abscess through a root canal is necessary if the inflammation is a consequence of caries or a crack in the tooth.
Often in advanced stages of the disease there is a need for tooth extraction. Typically, this procedure is carried out when there is deep destruction of the causative tooth or if there is a large infected area between the tooth and the gum. Removal is also used if there is a sufficiently large crack in the tooth that cannot be treated.
Typically, the doctor begins by making an incision into the periosteum or lining of the mouth. The causative tooth is usually removed gradually, that is, in parts. For this, a special dental saw or laser is used. Modern equipment has made it possible to make the procedure for tooth extraction quick and completely painless, so there is no need to be afraid of treatment. After the operation, the sharp edges of the incision are smoothed, which is then washed with peroxide or other antiseptic agents and fixed with sutures.
Where does the abscess come from and what is its danger?
In the vast majority of cases, an abscess on the gum is associated with a tooth, often with a milk tooth. The most amazing thing is that the tooth may appear healthy from the outside, it may have a beautiful filling, and the tooth may not hurt. Why does pus still appear?
Baby teeth are less resistant to infection than permanent teeth; they are designed for a short service life, although they, like permanent teeth, have a nerve and roots. However, the roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve after five years. Caries in such teeth spreads much faster. Within three months, a cavity can form in the tooth, reaching the nerve. If caries is not treated, all pathogenic bacteria enter the dental nerve, and then, through the nerve, the microbes enter the bone. Bone is quite comfortable for microbes. They multiply there, dissolve the bone, which is accompanied by the formation of pus. If the tooth is open, there is a hole in it, pus comes out into the oral cavity. If food particles, fragments of destroyed enamel get into the tooth, or the tooth is covered with a filling without adequate treatment, pus can no longer flow freely. If the pus cannot flow out through the tooth cavity, it begins to look for another way out. The pus melts the bone and comes out under the gum. The outer covering of the gum, under which the pus has come out, swells and takes the form of a lump. Over time, the lump may burst and pus leaks out.
Once the pus is released, the lump may disappear and the gums may heal until the pus collects in large quantities again. The danger of such “bumps” is as follows:
- there is always an infection in the body (you should never forget that the abscess is not just on the gum, but in the head);
- the pus that is in the jaw dissolves the bone and can damage the growing permanent tooth.
The disappearance of an abscess next to a tooth never means recovery.
Symptoms that appear along with an abscess
- redness on the gum;
- tooth pain (optional);
- There is a hole in the tooth or there may be a filling on it;
- enlarged lymph nodes (dense “balls” appear under the lower jaw).
Sometimes a lump is discovered by chance, and the child may not be bothered by anything at all. The parent should periodically examine the child's mouth independently.
Antibiotics for flux
As noted above, flux is a consequence of a bacterial infection, which is often treated by taking antibiotics. Many, at their own peril and risk, try to cope with inflammation by independently taking quite strong medications that can cause serious damage to the health of the entire body. Effective and at the same time safe treatment of flux with antibiotics can only be prescribed by a qualified specialist.
Antibiotics for flux are prescribed by a doctor individually. Self-use of strong medications is fraught with serious consequences for the entire body.
Antibiotics, like anti-inflammatory drugs, are used in dentistry for flux as part of complex maintenance therapy. The only way to stop the inflammatory process and remove the pus is surgery. Antibiotics are usually prescribed at the very beginning of treatment if the disease is in the earliest stages of its development, but identifying such inflammation at the initial stage can be quite difficult. As a rule, the dentist is able to detect the very first signs of periostitis by accident, for example, during a routine examination of the oral cavity. The specialist prescribes antibiotics for flux individually, depending on the characteristics of the patient’s body and the general clinical picture.
Flux - treatment in children
If a child has flux, you should never give him medications on your own, and especially antibiotics. Only a dentist can prescribe a medicinal course of treatment. Antibiotics destroy both pathogenic and beneficial bacteria that help fight infection, so the unauthorized use of such serious drugs can lead to negative consequences for the child’s entire body.
Treatment of gumboil largely depends on the causes of its occurrence. So, this process is not much different from the treatment of periostitis in adult patients. As a rule, to begin with, the specialist makes a small incision in the area of the inflammation and ensures the outflow of pus using a special drainage system. The treatment then continues at home under the supervision of parents. Most often, a complex of medications is prescribed, but in some cases, a specialist may allow you to limit yourself to rinsing with special decoctions and solutions.
Removal of permanent teeth
Removal of a permanent tooth in a child is carried out only in the following situations:
- Caries.
If the doctor sees that a decayed tooth cannot be treated, most likely he will suggest removing it. - Fracture.
A tooth fragment can injure the mucous membrane; it can either be restored or removed. - Crowding.
When installing braces or plates, it is sometimes necessary to remove one tooth to allow others to develop freely. - Complications after treatment.
Sometimes, after poor-quality dental procedures, problems arise that can only be solved by getting rid of the tooth.
How not to cause harm?
What to do if flux appears? Some patients mistakenly believe that swelling and severe toothache can be relieved on their own with the help of warming compresses, herbal infusions and other folk remedies. Unfortunately, such health experiments often end very badly. Thus, in order not to inadvertently harm yourself and provoke further development of the disease, the following contraindications should be observed:
- No warming compresses that contribute to the spread of periostitis.
- Never take painkillers less than 3 hours before visiting the dentist. Otherwise, you can significantly complicate the diagnosis process.
- After opening a purulent lesion, you should not take aspirin. It can provoke bleeding, especially since it is completely useless as a pain reliever in this case.
- If your condition has not improved 12 hours after surgery, you should see your doctor again.
What to do after removal or opening?
After opening the flux, you should not wait for the swelling to disappear immediately. Many patients feel that the flux does not go away after tooth extraction, although this is not the case at all. In some cases, the swelling may increase slightly after the procedure. Approximately on the third day after surgery, the patient should make a dramatic recovery, but the infiltration may remain for quite a long time. Within a few hours after the operation, the toothache in the area of the lesion should disappear and the body temperature should decrease.
Usually the swelling goes away only a few days after opening the purulent focus. Do not be alarmed if the swelling increases slightly after surgery.
The specialist installs a special rubber drainage in the incision, which you should never try to fix yourself. Otherwise, the recommendations are the same as for regular tooth extraction. You should not eat for several hours after the procedure. During the day, try to avoid hard and rough foods, as well as hot drinks. Regarding the use of medications in each individual case, the specialist gives individual recommendations.
How many days does tooth flux last?
Waiting for the flux to disappear on its own is, to say the least, naive. Some patients believe that if the flux bursts and pus comes out of the wound, then further treatment may not be carried out at all. This is a big mistake, since complete removal of pus requires special drainage, as well as complex therapy and subsequent treatment in the dentist’s chair. With timely and correct treatment, the flux disappears on average in 12-14 days; rehabilitation after severe periostitis can take more than a month.
Treatment prices
The cost of flux treatment largely depends on the severity and severity of the disease, as well as on the method of therapy chosen by the specialist. It is worth noting that modern medicine offers all the possibilities for quick, effective and completely painless elimination of the causes and consequences of periostitis. In addition, the price for flux treatment is influenced by factors such as the level of prestige of the dental clinic, the cost of the equipment and materials used, and the level of qualifications of the practitioners.