Defects in the development of the jaw are a common phenomenon, occurring in nine cases out of ten. Often, deviations do not cause significant discomfort to patients, since they do not affect the aesthetics and functionality of the teeth, being limited to slight unevenness in the position of individual units of the row. However, there are also pronounced anomalies in which the closure of the upper and lower jaws is noticeably impaired and worsens not only the appearance, but also the general condition of the apparatus. One of the variants of such manifestations, included in the orthodontic classification, is a deep bite - what it is, what it threatens, what forms and signs it has, and how to correct the situation, we will understand in this article.
What is a deep bite?
People strived for a perfect smile back in ancient times, evidence of this is found in mummies from Ancient Egypt, which had ropes obtained from animal intestines entwined around their teeth.
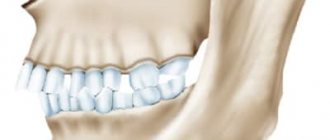
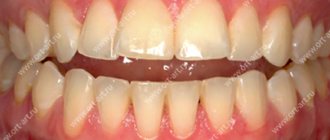
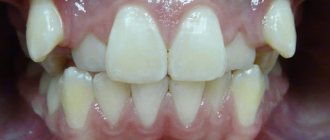
They played the role of modern dental wires for braces. Now it is much easier to correct a deep bite. To achieve faster and more effective results, you need to start treatment from childhood. A deep bite is an anomaly that manifests itself in the form of overlap of the lower dentition with the upper one. The defect can be diagnosed when there is an overlap of more than 1/3 of the height of the crowns. The “lucky” one with a deep bite experiences discomfort while chewing food, speech impediments, and injuries to the gums and palate.
Treatment methods in adults
In adults, correction of deep bites is carried out using braces of any type. If the patient is unwilling or unable to wear an orthodontic structure, the patient can have veneers installed, which only cosmetically eliminate the defect.
Also, prosthetics using implantation is considered as an alternative, but expensive method. This procedure has a lot of contraindications, but effectively eliminates abnormal bite development.
Duration
The longest method is correction using braces . To obtain visible results, the patient will have to wear braces for about 6 months .
2 to 3 years to achieve final correction .
Retention period
After removing the system, in order to consolidate the effect obtained, it is necessary to use retainers for as long as the braces are worn.
For this purpose, two types of retainers are used:
- Individual mouthguards of removable type.
- Fixed arc , fixed to the problem area using special glue.
Causes of deep bite
Such an unpleasant phenomenon as a problem bite can appear both in childhood and in older age. In dentistry, there are several reasons that can lead to the development of pathology:
- birth defects associated with facial deformation;
- genetic inheritance of the specific structure of the dental system;
- improper dental prosthetics;
- delay in prosthetics.
Also, the causes of a deep, incorrectly formed bite can be constant finger sucking and lip biting. Even a pacifier can lead to the development of occlusion. The pathology does not go away on its own, but fortunately orthodontics is now very well developed, making it possible to effectively eliminate the manifestations of deep bite.
What is the pathology characterized by?
Deep bite is a type of disocclusion, which is characterized by excessive overlap of the upper teeth with the lower ones.
This type of violation has other names:
- deep incisal occlusion;
- declining;
- traumatic;
- deep incisal (frontal) overlap.
Occasionally, excessive overlap is detected on the side of the lateral teeth. It is believed that in infancy, up to 80% of babies have a similar disorder. In some of them, as they grow and develop, this anomaly disappears by the time the permanent bite is formed. The rest require orthodontic correction. The baby should be regularly shown to the dentist in order to identify the need for it in time.
Classification of deep bite
According to the nature of origin, a deep bite can be:
- Primary – develops for reasons of irregular structure in the facial skeleton and dentition. The anomaly is most often represented by a deep blocking bite, which is manifested by limitation of jaw movements other than closing and opening. This pathological occlusion comes in two forms: dentoalveolar and skeletal deep bite.
- Secondary. The main reason for the formation of such a bite is due to previous diseases of the dental system. This could be periodontal disease, tooth loss, etc.
There is also a classification of deep bite according to the type of interaction of the lateral dentition:
- Distal - with this form of bite, the upper row of teeth overlaps the lower row by the length of the crown. The pathology is characterized by an underdeveloped lower jaw, a slightly sloping chin, a shortened face, and exposure of the crowns to the neck when smiling.
- Neutral - with such a bite, there are no pronounced defects in the skeletal structure of the face, its lower part is slightly shortened, and the chin is of a normal shape.
The stages of development of deep bite are divided into initial, progressive and traumatic.
Prices for bite correction
Orthodontic correction using a brace system.
Indirect fixation of one jaw. 5,300 rub.
Orthodontic correction using a brace system. Inspection and activation of the bracket system.
RUB 3,180
Orthodontic correction using a brace system. Re-fixation of the 1st bracket.
RUB 1,590
Orthodontic correction using a brace system. Fixation of the 1st bracket.
2,100 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 1st degree of complexity
RUB 109,180
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 1st degree of complexity, initial stage
53,000 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 1st degree of complexity, final stage
RUB 15,900
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 1st degree of complexity, scheduled visits
RUB 37,100
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 2nd degree of complexity
RUB 125,080
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 2nd degree of complexity, initial stage
53,000 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 2nd degree of complexity, final stage
RUB 15,900
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 2nd degree of complexity, scheduled visits
RUB 54,060
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 3rd degree of complexity
RUB 140,980
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 3rd degree of complexity, initial stage
53,000 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 3rd degree of complexity, final stage
RUB 15,900
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 3rd degree of complexity, scheduled visits
71,020 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 4th degree of complexity
RUB 155,820
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 4th degree of complexity, initial stage
53,000 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 4th degree of complexity, final stage
RUB 15,900
Orthodontic correction using braces on two jaws, 4th degree of complexity, scheduled visits
RUB 87,980
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 1st degree of complexity
RUB 50,880
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 1st degree of complexity, initial stage
26,500 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 1st degree of complexity, final stage
RUB 7,950
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 1st degree of complexity, scheduled visits
RUB 18,550
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 2nd degree of complexity
RUB 62,540
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 2nd degree of complexity, initial stage
26,500 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 2nd degree of complexity, final stage
RUB 7,950
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 2nd degree of complexity, scheduled visits
RUB 27,030
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 3rd degree of complexity
RUB 67,840
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 3rd degree of complexity, initial stage
26,500 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 3rd degree of complexity, final stage
RUB 7,950
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 3rd degree of complexity, scheduled visits
RUB 32,330
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 4th degree of complexity
RUB 78,440
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 4th degree of complexity, initial stage
26,500 rub.
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 4th degree of complexity, final stage
RUB 7,950
Orthodontic correction using braces on one jaw, 4th degree of complexity, scheduled visits
RUB 43,990
Orthodontic correction using braces. Treatment with partial braces.
RUB 21,200
Deep bite in children
The cause of deep occlusion can be birth trauma, a long period of sucking a pacifier or finger, late loss of baby teeth, calcium deficiency, or trauma to the dental system. In 15% of schoolchildren, a distal deep bite is diagnosed - the upper jaw is strongly pushed forward. It can develop against the background of impaired nasal breathing, adenoids, enlarged tonsils, frequent colds, and rickets. Also, improper formation of the bite can be caused by the removal of teeth at an early age, or the habit of propping up the chin.
Etiology
Factors predisposing to the formation of a deep bite are hidden in the prenatal period. Hereditary predisposition, infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy, mechanical injuries and chronic diseases (for example, anemia) can cause such negative consequences.
Causes of deep bite:
- Prenatal: toxicosis,
- intrauterine infectious diseases,
- multiple pregnancy,
- reduced oxygen content in the body.
- protein-energy malnutrition,
- late teething,
Symptoms of deep bite
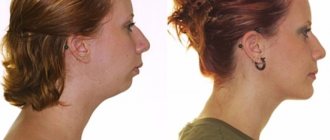
Externally, improper closure of teeth is manifested by shortening of the lower third of the face, the formation of a pronounced supramental fold, and turning of the lower lip outward. Among the oral signs:
- overlap of the lower frontal dentition with the upper one by the size of the crown;
- inflammatory process of the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- rapid erosion of tooth enamel, which leads to the development of caries;
- excessive overhang of the upper jaw over the lower jaw;
- decrease in the depth of the vestibule of the oral cavity.
Also, with malocclusion, secondary symptoms appear that develop against the background of the primary ones: problems with diction, breathing, deformation of the cranial vault, pain while chewing food.
How to determine mesial bite?
- By the face. Mesial occlusion can be determined by the structure of the face even without looking at the smile. The profile is concave - the middle third of the face falls back slightly, especially relative to the lower third. The chin protrudes forward and looks massive and disproportionate to the face and upper jaw. At the same time, the lower lip looks thicker, and the upper lip sinks. The facial expression seems angry.
- By posture. The temporomandibular joint is directly connected to the spine, so its malposition (as a result of malocclusion) affects the posture and balance of the entire body. Those with complex forms of mesial occlusion are characterized by a slight deviation of the body backwards. If you draw a straight line through the entire body in profile, the head will be tilted slightly back, and the pelvic bones will be pushed forward.
Concave profile with mesial bite
Poor posture with mesial occlusion - By smile and teeth. The clinical situation in which the lower incisors are in front of the upper ones is called reverse incisal overlap. This is the most characteristic intraoral sign of progeny. It is also characterized by: gaps between the teeth, dystopia (improper position) of the teeth, tilting of the lower teeth into the oral cavity.
Diagnosis of deep bite
Occlusion can be determined by external signs, but not all forms of improper closure of teeth are pronounced, so additional diagnostics are required. The specialist examines the patient’s medical history and conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity. The following activities can be carried out:
- taking an impression with alginate mass, followed by making diagnostic models and measuring them;
- photo of the face in profile and front;
- X-ray examinations;
- measurement of dental arches, apical base;
- performing an occludogram.
When making a diagnosis, data obtained from the results of electromyography, orthopantomography and teleradiography play an important role.
Surgical method
This method is used when others do not give results and the bite needs to be corrected in a short time. Surgery is used in very severe cases.
This method allows you to very noticeably transform a person’s face. The patient's external contour is transformed and becomes more attractive.
Surgical intervention is used:
- with an open bite in the area of the front teeth;
- with irregularities in the shape of the chin;
- in case of violation of facial symmetry as a result of an accident;
- with a deep bite, which appeared as a result of inheritance from parents.
The surgical operation is complex and difficult to perform, and expensive.
Consequences of deep bite
Elimination of deep occlusion is necessary not only to achieve an aesthetic result, but also to treat phenomena that bring a lot of discomfort in everyday life. Teeth that do not fit properly can cause the development of speech defects, facial asymmetry, and various aesthetic deviations. Besides:
- a large load on the front teeth provokes increased sensitivity and rapid abrasion of the enamel, which leads to caries;
- Loose teeth and frequent inflammatory processes in the gums appear against the background of their constant injury.
The pathology also leads to a decrease in the height of the bite, headaches, tooth wear and subsequent loss of tone of the masticatory muscles.
Complications
Reduced bite is a rather dangerous pathological condition. If nothing is done, serious complications arise.
The following problems begin:
- violation of diction;
- high load on the incisors;
- facial disproportions;
- inflammatory pathologies of the gums;
- pathological mobility of teeth;
- trauma to the oral mucosa;
- breathing and swallowing problems;
- headache;
- dysfunction of the maxillary joint;
- pathological abrasion of incisors.
All these complications can provoke numerous complexes in the child and complicate his relationships with peers.
Treatment of deep bite
For deep bites in adults, braces are usually used. A very interesting fact is that for the manufacture of certain types of braces, nickel-titanium is used - a material created by NASA for use in space. Clear aligners can also be used, which are more aesthetically pleasing. In addition, they are convenient, as they can be removed when eating or brushing your teeth. It takes at least 12-14 months to correct improper closure. The effectiveness of treatment and its duration depend on the degree of pathology and the correct choice of orthodontic design. To achieve a good result, it is important for the patient to comply with the rules established by the treating dentist. Treatment of deep bite in children is simpler, since the dentition is not yet fully formed; the course of occlusion can be influenced by the following methods:
- the child needs to be accustomed to solid food in order to create optimal stress on the teeth;
- it is important to cure dental caries;
- during the change of baby teeth, plates or other orthodontic structures (Frenkel, Bruckle, trainers) are installed on molars;
- At the age of 12 years, vestibular and lingual braces can be installed.
The iOrtho network of clinics selects the most effective treatment method taking into account the specific situation. We provide high-quality services and a modern treatment method using Invisalign aligners. Book your consultation now to enjoy a beautiful smile in just a few months.
Treatment errors
When turning to inexperienced specialists, you may be faced with the selection of the wrong treatment method. If there is a mistake in choosing devices such as occlusal pads, crowns, mouthguards for children, their large molars and incisors may become separated. This leads to rapid erasure of the cusps on the antagonist teeth located in the lateral row. In the anterior part, on the contrary, there is a sharp separation of the teeth and their protrusion forward, worsening the incisal overlap.
Deep bites in adults and teenagers can only be completely corrected if there is enough space underneath. Once the jaw has formed, some teeth will need to be removed to gain sufficient space. You also need to take into account the fact that when removing tooth protrusion in the anterior part of the dentition, the incisal overlap increases.
The effectiveness of treatment using the Herbst apparatus
Deep overbites are often corrected using the Herbstat appliance, a permanent orthodontic appliance. To correct the occlusion, it must be worn for at least 3-12 months. Its main task is to restrain the growth of the upper jaw, correct the lower jaw, and rebuild the functioning of the muscles of the dental system. The choice of this treatment method allows you to accurately predict the result and achieve it in a short time. The device does not interfere with eating or talking.
Symptoms and signs
In patients with this type of malocclusion, the periodontal tissues are most often the first to suffer, which is expressed in loose teeth, gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), as well as chronic trauma to the oral mucosa by teeth.
With a deep bite, facial signs are usually characterized by an unsightly lip position and a somewhat shortened lower part of the face. Patients with this anomaly may have difficulty chewing and biting food. In addition, there may be an increased load on the teeth in the front row and some speech disorders (“speech through teeth”).
Also, a deep traumatic bite can cause a decrease in the oral cavity, which, in turn, contributes to the development of improper breathing and swallowing. At the same time, some patients with this diagnosis also experience increased tooth wear, leading to changes in the tone of the muscles responsible for chewing, and as a result, to disorders in the temporomandibular joint. This consequence of deep incisal overlap is expressed by the fact that patients experience clicking and crunching in the joint, slight pain during movements of the lower jaw, and sometimes frequent headaches.
Forecast and prevention of deep bite
The prognosis of a deep pathological bite when choosing the right treatment method is always positive. It is possible to correct incorrect teeth closure even in adulthood, but in order for the result to be of better quality, treatment must begin in the first stages of its development. Prevention is also important, it is necessary to control the loss of baby teeth and the correct growth of molars, monitor the position of the child’s head during sleep, protect him from bad oral habits, in particular prolonged sucking of a pacifier and thumb, it is important to promptly treat ENT diseases and other pathologies that can cause the development of a deep bite.
These include:
- prolonged sucking of a pacifier and foreign objects (pencil, finger);
- bad habits (biting your lip, resting your chin on your hand);
- early loss of molars;
- pathology of ENT organs;
- abnormalities of the musculoskeletal system;
- severe caries of molars;
- skull injuries;
- malignant tumors of the skull bones;
- consequences of rickets;
- inflammatory diseases of the jaw bones;
- untimely teething;
- defect in the attachment of the frenulum of the lips and tongue;
- congenital anomalies of the facial skeleton.
It is necessary to identify the cause of the development of the pathology; corrective measures depend on this.
Types of mesial occlusion
By form:
- Dentoalveolar form. Malocclusion as a result of incorrect position of the teeth.
- Gnathic or skeletal form is an abnormal bite formed by a pathology of jaw development.
A more complex form of malocclusion, sometimes requiring surgical intervention. Often, clinical cases of mesial malocclusion combine both forms - incorrectly positioned teeth and abnormal jaw sizes.
For reasons of occurrence:
- Congenital abnormal jaw sizes: macrognathia of the lower jaw - a large or elongated lower jaw; micrognathia of the upper jaw - underdeveloped, small upper jaw.
- Prognathia of the lower jaw is a forced position when individual teeth interfere with the normal closure of the jaws and jaw growth. This type of bite occurs in children on their baby teeth due to fangs that cling to the lower teeth and prevent the lower jaw from taking a normal position.
- Retrogression of the upper jaw is the posterior position of the upper jaw relative to the proportions of the face. Unlike micrognathia, in this case the jaw is of normal size, but incorrectly positioned.
- Abnormal tooth sizes: macrodentia - large teeth on the lower jaw, microdentia - small teeth on the upper jaw.