Concept and reasons for origin
The term “small lower jaw” in dentistry and orthodontics has several interpretations with significant differences:
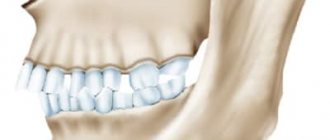
- Micrognathia (also microgenia) is a pathology manifested in the form of defective or delayed development of the entire lower jaw, as well as its individual fragments;
- Prognathia is an intensive growth of the upper part of the jaw apparatus, which results in the visual effect of insufficient development of the lower jaw.
Both pathologies manifest themselves in both infancy and adulthood. Clinical manifestations of the anomaly make it possible to detect the presence of abnormalities at the primary stages of development, which provides the possibility of preventive treatment.
In children
In infancy, improper formation of the lower jaw is caused by various factors, the main one of which is a violation of the uniform process of fetal development in the prenatal period. At this stage, the relationship of jaw proportions is established, which can be influenced by:
- improper maternal diet;
- presence of genetic predisposition;
- consumption of nicotine and alcohol products;
- exposure to serious illnesses with complications.
In the early stages of a child’s life, factors influencing the development of pathology are:
- late formation of bite;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- early loss of baby teeth;
- bad habits (pacifiers, pacifiers);
- improper feeding.
The primary signs of small lower jaw syndrome in children are recession of the chin and lower lip, abnormal tooth growth and impaired sucking function. Timely identification of symptoms allows the anomaly to be stopped without the use of orthodontic treatment methods.
In adults
In older age, factors provoking the formation of pathology are:
- incorrect or incomplete treatment in childhood;
- receiving severe injuries to the jaw apparatus;
- disorders of the body's metabolic processes;
- pathologies formed in bone tissue (rickets, ostiomyelitis);
- abnormal development of the orbicularis oris muscle.
Characteristic manifestations of small lower jaw syndrome in adulthood are distortion of the patient’s facial features, deformation of the dentition, and problems with eating solid foods.
Types of dental malocclusion in children
- Distal bite.
The lower jaw is posterior to the upper jaw
- Mesial bite.
Does the child have an incorrect bite, does the lower jaw protrude forward? This kind of bite is called mesial. In this poetic form, we can give a brief description of another common type of jaw disproportion, when the lower jaw is much more developed than the upper.
- Cross or scissor bite.
A less common, but very unpleasant dental anomaly. With a crossbite in a certain place, the jaws close in the opposite relationship - they close in reverse, which is why the dentition resembles scissors.
- Deep bite.
A very common type of malocclusion in children and adults, when the upper teeth cover the lower teeth by more than half.
- Open bite.
One of the most complex anomalies, causing physical and psychological discomfort to the child. The upper and lower rows of teeth cannot meet completely, causing a noticeable gap to form between them.
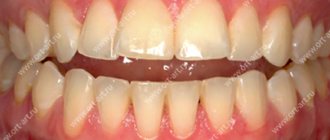
Above we described what a child’s malocclusion looks like in various manifestations, but we should also briefly talk about the correct one, which can be perceived as a kind of guideline. The ideal bite is considered orthognathic. It is distinguished by an absolutely even dentition without gaps, curvature or crowding, when the upper teeth cover the lower ones by one third. There are several types of correct bite, but if your child has dental defects, this almost always indicates problems.
Treatment and prevention
The choice of treatment technique is determined by the clinical picture of the development of the pathology, as well as the age group to which the patient belongs. The main vector of therapy is to stimulate the development and growth of the lower jaw.
In childhood
The period of primary occlusion is one of the most favorable in terms of correction possibilities, since it allows the use of gentle treatment methods. The main methods used at this stage are:
- prosthetics for prematurely fallen milk teeth, ensuring the preservation of the normal shape of the jaw arch;
- sanitation of the oral cavity, accompanied by the restoration of individual damaged teeth and cleaning of defective roots;
- grinding of the areas of jaw closure - fissures - which allows you to eliminate malocclusion in the form of bumps on the chewing surface;
- normalization of breathing and tongue function, including by trimming the lingual frenulum and correcting the nasal septum;
- use of special corrective trays, plates or nipples.
Quite often, in order to stop the primary signs of pathology, it is enough to wean young children from bad habits.
As an adult
The treatment method during the period of permanent or mixed dentition is determined by the specifics of the anomaly.
To treat prognathia at the variable stage, special corrective orthodontic appliances, such as a Frenkel adjuster, a facebow or a Herbst device, can be used. Microdentia is treated with the help of distractors - devices that stretch the bone tissue and then replace it in the jaw with new bone.
At the permanent stage of occlusion, the most effective method is jaw surgery, which involves removing part of the dentition and excision of the alveolar-ridge area. It is also possible to use a radical technique - plastic surgery, in which the lower jaw is broken off from the main bone and moved forward, and in its place new bone material is placed, fixed with special plates.
The easiest way to avoid orthodontic intervention and stimulate the normal development of the lower jaw is in childhood - to do this, it is enough to follow simple preventive measures, prevent the development of bad habits and contact specialists at the first signs of pathology.
How to determine malocclusion in a child?
“How can you tell if a child has a malocclusion?” - This is a question many parents ask. It is important to understand that only an experienced pediatric orthodontist can make an accurate diagnosis here, so we strongly advise you to undergo regular preventive examinations with this specialist from a very early age until the complete replacement of baby teeth with molars. If the baby teeth are located too closely together, this can also become an additional complication when the molars erupt (the latter take up more space because they are larger). In the case of a small child (under 3 years old), it is difficult to be guided by purely visual principles and determine by eye whether the bite is correct or incorrect. Be that as it may, there are a number of signs that directly or indirectly indicate that the child has prerequisites for orthodontic anomalies.
Improper breathing
The child's mouth is constantly in a half-open position, he does not breathe through his nose (of course, if there are no colds).
Snore
If your baby constantly snores in his sleep, this may also be one of the consequences of the development of malocclusion.
Jaw formation
Pay attention to how the child's jaws are formed. Ideally, there should be no noticeable disproportion between the top and bottom. Additionally, if a child continually pushes their lower jaw forward, this is considered a clear sign of pediatric bite problems.
Postural disorders
If your child has postural and spinal problems, this may affect the development of malocclusions.
Trembling of the chin in a newborn is a physiological norm
Tremor caused by immaturity of the nervous system is considered a physiological norm. When a child cries and his chin trembles, it is enough to simply calm the baby. In newborns, such conditions are not treated. 3 months will pass and all phenomena will disappear. Don't worry if you notice your chin shaking while breastfeeding, bathing, or changing clothes. With any load on the nervous system, the baby begins to twitch. Trembling can be caused by:
- Overwork.
- Fright.
- Paradoxical (rapid eye movement) sleep.
- Hunger.
- Painful sensations.
- Uncomfortable air temperature.
- Bright lights and loud sounds.
- Sudden change in body position.
For obvious reasons, when the mother understands what is causing the trembling of the chin, there is no need to worry. If twitching is observed in other situations, occurs for no reason and in complete rest, the child should be examined by a doctor.
Correction of distal occlusion in adults
It is better to treat prognathism in childhood or adolescence, because later, to correct the distal bite, surgical intervention may be necessary - orthognathic surgery, which is also called genioplasty. It consists of correcting the shape of the chin. This is a rather complex operation, and many orthodontists prefer to mask the pathology by correcting the position of the teeth with braces or special mouth guards. In most cases, several teeth have to be removed. As a rule, these are premolars or molars. Thanks to masking treatment, doctors correct the patient's profile. However, in case of severe pathology, it is unlikely that it will be possible to achieve the desired results in this way.
After treatment for prognathia is completed, orthodontists prescribe wearing a retainer, a bite former, and performing myogymnastics. This is done in order to consolidate the result obtained, since at first the teeth will tend to return to their usual abnormal position.
What is overbite
The bite is the relative position of the lower and upper rows of teeth when they are closed. A less common name is occlusion.
If it is correct, the upper teeth slightly cover the lower teeth (less than a third). This allows the chewing load to be distributed evenly and looks aesthetically pleasing.
The bite takes more than one year to form. The process includes 5 time periods:
- 0–6 months (the upper jaw is larger than the lower jaw, which is corrected through the baby’s active efforts during feeding);
- 6 months - 3 years (baby teeth erupt, temporary bite is formed);
- 3 years - 6 years (active jaw growth occurs, the body prepares for the appearance of permanent teeth);
- 6–12 years (jaws continue to grow, permanent teeth erupt);
- 12–16 years (the final bite is formed).
Deviations from the norm at least at one of the stages can lead to anomalies of the dental system.
So, if when talking, eating, or in a free state, closure defects are observed, they speak of a malocclusion.
Signs and diagnostics
The main signs of jaw underdevelopment are visual anomalies that are visible to the naked eye. At a severe stage of microgenia, a person exhibits a “bird profile”. There are some other signs and symptoms that may indicate this pathology. These include:
- malocclusion, which is easily detected during examination by a doctor;
- “recession” of the lower lip and, as a result, a small chin;
- in some cases, a cleft in the palate may form;
- grinding down of the dentition due to constant friction, as well as curvature and uneven growth of teeth;
- difficulties while chewing food and swallowing it;
- difficulty breathing;
- underdevelopment of the tongue, which can cause it to sink when lying on your back;
- abnormal changes in the ENT organs: chronic rhinitis, deviated nasal septum, decreased sense of smell, frequent occurrence of otitis media.
It is necessary to take into account that signs of microgenia can also be observed in the presence of other pathologies. In this regard, it is necessary to conduct a complete diagnosis. The examination is carried out by a qualified dentist.
Braces can correct only mild pathology
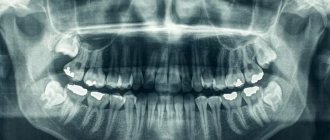
The primary thing is to conduct a visual examination, during which the doctor will identify characteristic external signs. In the future, the patient will be referred for a panoramic image (a type of digital radiography) and tomography.
This will provide complete information about the condition of the chin and help you choose the most appropriate method for eliminating the pathology.
Causes of malocclusion in children
The causes of malocclusion in children can vary, and most of them are difficult to address without orthodontic treatment. Below you can see a list of the key reasons for the occurrence of such anomalies in a child.
Genetics.
If you are wondering why your child has an incorrect bite, look at yourself first. Genetic predisposition is the most obvious and common cause of malocclusion in a child. If one or both parents have pronounced anomalies, then with a very high degree of probability their children will inherit them.
Bad habits.
Children often chew and put into their mouths literally everything they can get their hands on. Often such cravings provoke a violation of the formation and development of teeth. Malocclusion in a child from a pacifier is also quite common.
Breathing problems.
Children with nasal breathing disorders are much more likely to suffer from malocclusion, as experts say.
Problems with the musculoskeletal system.
The spine is the main “bearing structure” of our body, so it is not surprising that the functioning of the musculoskeletal system affects the dental system.
Other diseases.
The risk group (meaning malocclusion) also includes children with diabetes mellitus and central nervous system diseases.
When does tremors become dangerous?
Infant tremor is observed for the first time at 2 months of a child’s life. Sometimes the phenomena disappear at 4 months. In premature babies, chin trembling can be observed up to 1 year. If the symptoms do not go away for up to 6 months, are accompanied by the appearance of perspiration on the skin, increasing intensity and too violent a reaction to external stimuli, this is already a deviation. Spontaneous movements and convulsions can be dangerous.
Parents should be wary if the chin shakes for more than 30 seconds while crying. Simultaneous trembling of the legs, arms and head is also considered abnormal. The manifestation of these symptoms may indicate the presence of a pathology, but there is no need to panic. In infancy, such conditions can be treated easily and without consequences.
A child under 1 year of age needs regular examinations by a neurologist. Don't miss scheduled consultations. They are usually prescribed at the ages of 1 and 3 months, at six months and upon reaching 1 year. During these important periods, specialists evaluate the baby’s motor activity, his emotional state, muscle tone, reflexes, and the functioning of his senses. If deviations are detected, the necessary treatment is prescribed.
Consequences
Any violation of the proportions and symmetry of the face affects the appearance. This leads to the development of complexes. Protruding teeth, underdevelopment of the lower third of the face - all this affects the psychological state of a person. The dental system gradually collapses due to improper load distribution.
There are other problems:
- violation of diction;
- gum inflammation, recession;
- premature wear of enamel;
- the risk of gum and dental diseases increases;
- the appearance of headaches;
- Malocclusion is a contraindication to prosthetics.
It is better to contact an orthodontist immediately at the first signs of occlusion. It is easier to correct deep bites and other dental anomalies at the initial stage. In the future, in addition to dental disorders, diseases of the ENT organs and gastrointestinal tract may occur.