Children's baby teeth have weak enamel, so even with good hygiene, they can be affected by caries. It happens that by the age of 4–5 years, most of the child’s teeth rot. This situation cannot be ignored, because the condition and development of baby teeth affects the health of permanent teeth. To prevent a child from having dental problems in the future, rotten teeth must be treated.
How to identify milk caries?
It is quite simple to identify caries in young and older children. White or brown spots appear on the teeth, a painful reaction to hot and cold is observed, and the child may develop bad breath. When these first symptoms of caries appear, it is already worth sounding the alarm, since the carious process is developing very rapidly. It is characterized by almost instantaneous damage to several teeth, and if measures are not taken, the entire dentition may be affected. Of course, it is often difficult for a child to articulate that his baby tooth hurts. He may refuse to eat or chew on only one side. This should also alert parents and encourage them to take their child to pediatric dentistry.
What factors worsen the health of baby teeth?
- Mechanical factors: impacts, bruxism, strong compression. They lead to changes in the tooth and disruption of its integrity.
- Chemical factors: prolonged exposure to sweets on the loose enamel of children's teeth.
- Bacterial factor: the spread of bacteria in the baby’s mouth.
- Sudden temperature changes when eating or drinking.
What are the causes of caries in primary teeth?
There are more reasons for caries of baby teeth in children than meets the eye. This includes improper oral hygiene, sharing cutlery with adults who have caries, and much more. However, the main causes of occurrence are the influence of consumed carbohydrates that destroy the tooth, accidental infection from a carrier of a carious infection, a genetic factor, the immaturity of the children's skeletal system, and improper use of pacifiers and nipples.
- Of course, the main and most common cause of caries in primary teeth in children is poor oral hygiene and the influence of sweets. According to statistics, caries develops in young children in 73% of cases. Sucrose, glucose and fructose are the acids that are formed during the fermentation of carbohydrates and lead to the destruction of enamel. Immediately after ingestion of carbohydrates, the pH of saliva decreases from 6 to 4, and pathogenic bacteria settle in food debris that is not cleaned from the teeth.
- Remember the children's saying “from mouth to mouth you get a germ”? It turns out that she is not so far from the truth. The fact is that caries is an infection, an infection. That is, a loving parent, being a potential carrier of carious microbes, does not even suspect that by kissing his baby or sharing dinner with him, he can personally infect his child!
- Another reason why caries may occur on baby teeth is genetic. Teeth begin to form during the prenatal period, in the first trimester of pregnancy. Therefore, smoking by a negligent parent, her illnesses suffered during this period, or taking medications can lead to disruption of the proper development of the child’s teeth.
- Childhood caries of primary teeth may be associated with the following factor: children’s teeth have a low degree of mineralization and erupt “immature”, and only then “mature” in the oral cavity. Final mineralization lasts for one and a half to two years for baby teeth and about three years for permanent ones. Pediatric dentists call such periods of “maturation” the most susceptible to caries. Therefore, the reasons why caries occurs in primary teeth at an early age may also be chronic diseases, the effects of medications, the composition of saliva and the fluoride content in water and food.
- Another cause of caries of primary teeth in young children is improper use of pacifiers. A baby who falls asleep with a bottle in his mouth runs the risk of getting caries on his front teeth, so-called bottle caries. In this case, prolonged contact of the sweet liquid with the teeth leads to caries of all front teeth. In this case, the disease spreads around the entire visible part of the tooth along the perimeter.
As you can see, there are more than enough reasons for the appearance of childhood caries in baby teeth. But they all boil down, as a rule, to demineralization of teeth and destruction of hard tissues. Characteristic changes occurring in teeth can only be diagnosed by a dentist. Further treatment will depend on how severe the caries has developed. What are the stages of development of caries in primary teeth?
Bad teeth in a child: reasons
A child’s baby teeth rot for various reasons.
Some are impossible to influence, others can be easily eliminated by dentists and caring adults. Most often, destruction of the enamel, and subsequently the coronal part of the primary occlusion units, is facilitated by:
- Disorders of intrauterine development of a child. Developmental pathologies are formed due to maternal toxicosis, non-compliance with nutritional recommendations, and the use of potent medications.
- Early birth of the baby. Prematurity of a baby indicates incomplete formation of internal systems - in particular, weak thin enamel of baby teeth.
- Antibacterial therapy administered to a child in the first year of life.
- Poor hygiene. Lack of systematic cleaning after the first tooth erupts, improper care, and inadequate parental control.
- Unbalanced child nutrition. Predominance of flour and sweets in the menu, lack of fermented milk and dairy products, hard fruits and vegetables.
- Reduced immunity. Congenital or due to a lack of vitamins in the diet.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis.
- Diseases of the endocrine system - diabetes mellitus.
- Previous infections - ARVI, chicken pox, scarlet fever.
- Pathogenic microflora entering the baby’s mouth from the outside. If family members have the habit of licking the baby’s spoon or pacifier, or kissing the baby on the lips.
- Poor ecology is a significant external factor that negatively affects the condition of the child’s teeth and general well-being.
- Heredity - parents or grandparents have bad teeth.
- Mechanical injuries, external damage to tooth enamel - cracks, small chips.
Stages of caries of primary teeth
Dentists distinguish the following stages of caries of primary teeth in children:
- Elementary;
- Surface;
- Average;
- Deep;
Initial caries of primary teeth
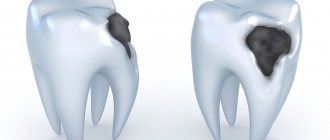
Initial caries of baby teeth can be recognized as follows: white spots of different shapes and sizes appear on the enamel, but there is no pain. In an “advanced” case, the initial caries progresses - the spots darken, becoming brown and then black.
Superficial caries of primary teeth
With superficial caries of primary teeth, the dental tissue defect is located within the enamel, and the carious cavity can be either light or dark. However, in this case, pain occurs when the tooth comes into contact with sweet, sour or salty foods. In this case, treatment of the baby tooth and filling of the cavity is already required.
Average caries of primary teeth
Average caries of primary teeth affects the enamel and internal dental tissue, dentin. In addition to the unpleasant sensations from sweet, sour and salty, pain from hot and cold is added. In this case, just as with superficial caries of primary teeth, filling is necessary.
Deep caries of baby teeth
With deep caries of primary teeth, the enamel and a significant part of the dentin are affected. If treatment is not carried out at this stage, then caries can affect the pulp of the tooth and then reach the root, often causing a cyst in baby teeth. Here you just need to see a doctor before the infection goes further. In this case, severe caries of primary teeth and its treatment will depend on how deep the caries has spread.
What else can be done if a child’s baby teeth are rotting?
There are alternative ways to combat the rapid destruction of children's teeth:
- Silvering
. A solution of silver nitrate strengthens damaged enamel, but this method is only suitable if the damage is not severe. - Remineralization
. It involves applying a special mineral composition to the surface. - Deep fluoridation
. Also indicated for minor lesions.
If you notice signs of tooth decay in your child, don't panic. You need to make an appointment with a pediatric dentist and trust him to draw up a treatment plan. For your part, decide to follow all the specialist’s recommendations, review your son or daughter’s diet, and limit sweets. This approach will help you cope with this acute problem and protect, first of all, your molars.
Is caries treated in baby teeth?
Is it necessary to treat caries on baby teeth? This question still remains open for some parents. Even knowing that the child has caries, they are in no hurry to see a doctor, thinking as follows: “the milk teeth will fall out anyway.” Such judgments are absurd, because infected baby teeth will lead to complications in the growth of permanent teeth or provoke an exacerbation of other diseases in the baby’s body. One way or another, you will have to remove the baby tooth ahead of time. Caries in pediatric dentistry is considered one of the most common diseases, so both parents and specialists should ask the question “why is it necessary to treat caries of primary teeth?” Dentists believe that treatment of caries in a baby tooth will preserve it until the “arrival” of the molars.
Experts' opinion
The complex composition of ASEPTA Baby toothpaste allows you to simultaneously care for your gums and teeth. The product has:
- Certificate of state registration;
- Certificate of conformity No. ROSS RU. AG81.H01070.
The paste does not contain fluoride and does not require consultation with a doctor before use. The product is safe if swallowed, as it does not contain components harmful to the health of the baby.
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
Treatment of caries of primary teeth in children
If the doctor finds that a child has incipient caries, then most likely, treatment of baby teeth will not be required. The specialist will protect the enamel from further destruction using a painless and effective procedure - applying fluoride varnish or a silver fluoride compound. Then, when the baby gets permanent teeth, the dentist can seal the fissures - the depressions between the elevations of the tooth - which will prevent the occurrence of bacterial plaque that destroys the enamel. If caries progresses, you can no longer do without filling. The doctor will quickly and almost painlessly remove the affected tissue and hermetically seal the tooth. Otherwise, caries can develop into pulpitis in a child, and then into periodontitis.
Stages of treatment of caries of primary teeth
- Before administering anesthesia, the doctor must numb the injection site using special gels or spray. Moreover, the content of the anesthetic component should be minimal. Anesthesia is, as a rule, carried out only in cases where pulp removal is required - that is, with medium and deep caries of primary teeth.
- It is advisable to remove affected tissue using hand tools or a drill, taking frequent breaks.
- As fillings, materials that can be applied “one time” should be used in order to reduce the operation time.
- If a child has deep caries of primary teeth and its treatment requires the necessary filling of the roots, then the canals are disinfected without special mechanical treatment and filled with a special paste.
- Treatment of baby teeth in children should take no more than half an hour, otherwise the child will get tired.
- Treatment of severe caries of primary teeth, as a rule, takes place in several stages and requires the use of sedation.
- Dental treatment under general anesthesia in children is carried out strictly according to indications;
You can get rid of carious lesions at the initial stage using modern methods of caries treatment without a drill. Comfortable, painless treatment is suitable for those children who are afraid of manipulation with a dental bur. The cost of treating caries in baby teeth without a drill is slightly higher than the price of traditional dental treatment for children, but it is worth it. If simple caries gives complications, then you will have to resort to classic drilling. The cost of treatment of complicated caries of primary teeth will depend on the degree of neglect of the disease.
How is deep caries treated for young children?
If a one-year-old child is diagnosed with deep caries, it cannot be treated like a superficial one, without drilling. In this case, the teeth are filled with photopolymer composite or glass ionomer cement. To ensure that the baby sits still or as calm as possible during treatment, sedation or general anesthesia is used. Unfortunately, any anesthesia has a number of side effects, so it is better not to start caries and treat it in the early stages, when you can do without preparation and filling.
Prevention of caries in children
Prevention of childhood caries includes several areas, which boil down to proper nutrition, as well as home and professional hygiene.
- Individual oral hygiene. Home hygiene means that as soon as the first tooth hatches, a brush for the baby should appear in a glass next to the parents’ brushes. The same applies to toothpaste. At first, the paste can be applied to gauze or a fingertip to clean your teeth so as not to injure your delicate gums. You need to clean your teeth from all surfaces vertically, then wipe them with a brush soaked in water. Thus, firstly, plaque will be removed, and, secondly, parents will teach the baby to take care of the oral cavity.
- Prevention of caries with the help of a well-chosen diet. As for nutrition, parental duty is to breastfeed the baby from the very beginning. There is no need to talk about the beneficial properties of breast milk, and the sucking process greatly affects the developing jaw system. Then the baby should be accustomed to fermented milk products. By six months, the child should be fed kefir, and later - cottage cheese and cheese. Parents should remember that the main formation and formation of permanent teeth occurs up to 3 years. This means that calcium must always be present in the daily diet.
- Professional oral hygiene. This type of prevention involves periodic visits to the dentist and hygienist. The first visit should occur on your first birthday. The specialist will not only give recommendations for care, but also create a diet regimen and examine the mouth. When the first teeth emerge, you and your child will be shown how to brush their teeth properly at an appointment with a hygienist. If there is a problem such as tartar in children, you cannot do without professional hygienic cleaning. It is important for parents to make it a rule to visit the doctor twice a year. And if there are problems with teeth, then more often - once every three months. This is largely due to the fact that various pathologies develop too quickly in childhood. Meanwhile, early diagnosis will lead to quick, painless and relatively inexpensive treatment of caries.
As you can see, in most cases, when caries can attack children's teeth, parents are able to rebuff it decisively. Of course, there is no escape from genetic predisposition. But it’s not without reason that dental experts say that sweets are the main cause of the development of the disease! So isn’t it better to eliminate the constant source of bacteria and, instead of harmful carbohydrates, offer the child fruits, which are much healthier, after the main meal? Ultimately, your child will thank you in the future for being vigilant and maintaining healthy teeth!
Can teeth turn black not due to caries?
In very rare cases, teenagers may experience darker tooth color if their daily diet includes a lot of soy sauce, coffee, tea, potatoes, or drugs containing fructose. However, such “darkness” is not at all similar to carious lesions and is easy to distinguish.
Do rotten teeth need to be treated?
Undoubtedly. Remember: the opinion that there is no need to treat baby teeth “because they will fall out anyway” is fundamentally wrong and even criminal. Firstly, caries in baby teeth spreads very rapidly: a couple of months ago the child simply had rotten teeth, and today he is already screaming and crying from pulpitis.
Secondly, untreated caries of a baby tooth can cause inflammation of the soft tissues, the appearance of an abscess, as well as such serious consequences as:
- Sepsis;
- Meningitis;
- Damage to large blood vessels in the neck area;
- Otitis;
- Sinusitis;
- Stomach pain, intestinal disorders, stool disorders and other gastrointestinal diseases.
Thirdly, advanced caries and tooth decay can lead to premature loss of a baby tooth, and subsequently to disruption of the even dentition of molars. Don’t forget that a rotten baby tooth can “infect” a molar tooth with caries.
Don’t forget about children’s complexes: rotten teeth look unsightly and cause significant discomfort to the baby.
How to spot rotting at an early stage?
In order not to go through all the horrors of treating rotten teeth with your beloved daughter or son, be able to recognize the first signs of caries in time:
- The characteristic “rotten” odor from a child’s mouth indicates the presence of cavities.
- Small yellowish spots on the teeth are the first stage of caries.
- A child’s complaints about discomfort when drinking cold, hot and sweet drinks and foods indicate thinning of the enamel.
- The characteristic black spots on the teeth are caries that need to be treated.
Do not forget that it is better to treat caries at an early stage, because it will be much more difficult to eliminate the problem of rotten teeth later.
How to cure rotten teeth?
To cure rotten teeth in a child means taking the baby to the dentist. If the baby’s teeth have already turned black, it is useless to treat them with folk remedies. A variety of balms, rinses and masks can only slow down caries.
An experienced dentist treats rotten teeth in children in stages:
- The doctor examines the oral cavity, identifies areas of caries and inflammation of the gums, and, if necessary, sends the child for an x-ray.
- Teeth are cleaned and caries is treated. If lesions have been identified in several teeth, the doctor draws up a treatment regimen. Milk teeth that cannot be cured are removed.
- To disinfect affected gums, the doctor may prescribe special rinses with herbal decoctions; in rare cases, antibiotics are prescribed to destroy the infection.
Parents should not forget that it is not enough to just cure rotten teeth. It is important to eliminate the cause of caries, otherwise in a couple of months the baby will end up in the dentist's chair again. For example, if the doctor said that the cause of caries lies in the gastrointestinal tract, it is important to visit a gastroenterologist with your child. If the teeth begin to rot because the baby is leaning on candy and soda, reconsider the diet.
There are alternative ways to treat teeth that are slightly affected by caries:
- Remineralization. The dentist strengthens the surface of the teeth with a special mineral composition.
- Silvering. If the child does not allow a filling to be placed, and the tooth is not severely affected by caries, the doctor can strengthen the damaged surface with a solution of silver nitrate.
- Laser therapy. In rare cases, shallow caries can be treated with a laser.
- Deep fluoridation is effective for minor enamel damage. After this procedure, the teeth are saturated with useful minerals for a long time.
- Ozonation for mild caries can clean the rotten row from pathogenic microorganisms.
How to prevent the appearance of rotten baby teeth?
To prevent the child’s teeth from rotting and the dental drill from marring the joyful moments of childhood, it is important to carry out proper caries prevention.
1. Be attentive to your baby
Examine your child’s teeth every two to three days and if characteristic carious cavities appear, immediately make an appointment for the baby to see a doctor.
2. Visit your dentist regularly
Even if you have not noticed any changes in your child’s oral cavity, be sure to take him to the doctor on a preventive basis. The pediatric dentist should be visited twice a year. An experienced specialist can even notice the beginning of caries, which appears as a light spot on the tooth. If caries is detected in a timely manner at an early stage, the doctor can slow down or stop its development using an enamel remineralization procedure.
It is recommended to visit the dentist in the morning, when the baby is alert and calm, and most importantly, has not yet had time to “work up” himself with fears.
3. Strengthen your enamel
Of course, the baby does not need to take antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs without a doctor’s prescription. However, you can completely strengthen your child’s enamel with natural ingredients, for example, rinse the mouth with herbal decoctions - oak bark, sage, calendula. These herbs have excellent anti-inflammatory, calming effects.
4. Watch your diet
Believe me, kids in adolescence and young adulthood will have time to eat plenty of chips and drink soda. But in early childhood, you can completely control the diet of your kids. Make sure that your child does not consume a lot of sweets and sours, give the baby more vegetables and fruits - fresh fruits are magic boxes of vitamins and help to naturally cleanse teeth. And, of course, give your child more milk, cottage cheese, kefir and other goodies from cows and goats.
How to properly brush baby teeth?
Teaching a child to take care of his teeth from childhood means ensuring him a happy adolescence and youth without toothache. And caring for your teeth means, first of all, proper brushing. Until the age of 3, it is better to help the child with this procedure, but after three, you can trust the child to brush his teeth on his own.
Remember:
- Teeth need to be brushed from top to bottom - this is the only way to remove the plaque that has formed.
- You need to brush your teeth for at least 2 minutes. Try placing an hourglass in your baby's bathroom, which will teach him to carry out the procedure for a long time. After finishing cleaning, rinse your mouth.
- Children, like adults, should brush their teeth twice a day - morning and evening, before bed. It is important to rinse your mouth after every meal.
To make the process of brushing teeth enjoyable for your baby, it is important to carefully choose toothpaste. For example, ASEPTA BABY gel toothpaste can be used for babies from 0 to 3 years old. The soft gel gently cares for your child's teeth and gums without damaging them. The natural components of the paste provide protection against caries and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity; the bright taste of “tutti-fruiti” makes cleaning a delicious adventure. But the main thing is that “ASEPTA BABY” does not contain abrasives, fluorine, parabens, or sodium lauryl sulfate.
We hope our recommendations for caring for children's teeth and caries treatment will be useful to you. And rotten teeth will never bother either kids or their parents.
Caries on the front milk teeth - what to do?
On the front milk teeth, caries occurs almost as often as on the lateral ones. What should the child’s parents do in such cases? Be sure to take him to the dentist, regardless of the stage of the disease. Even if you notice a white spot on your baby’s front teeth, do not delay visiting the doctor to avoid further development of caries, its complications and other unpleasant consequences that pose a threat to the health of the child’s future permanent teeth.
What to do if children have rotten teeth?
First of all, with such a problem you need to make an appointment with a dentist: traditional methods are useless here and can only aggravate the situation by wasting time. The specialist will examine the cavity, determine inflammation, and, if necessary, take an x-ray. Baby teeth that are subject to treatment will be sanitized. If the problem cannot be solved therapeutically, the tooth will have to be removed.
After the manipulations, which may take more than one day, the dentist will prescribe rinses to disinfect the affected areas. Sometimes antibiotics are necessary to get rid of an infection.
It is important to determine the cause of caries in order to protect the remaining teeth from rotting. If the problem is in the gastrointestinal tract, you need to visit a gastroenterologist. If the problem is an excess of sweets, you should urgently reconsider your diet.
Caries of primary teeth and its ENT complications
Sometimes parents unsuccessfully try to understand why their child often suffers from colds, complains of ear pain, and suffers from a chronic runny nose. And few people realize that the reason for weakened immunity lies in the baby’s untreated teeth. How can this be? It turns out that it’s all about pathogens! Caries develops under the influence of pathogenic bacteria, which can also cause diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system of the child. Therefore, timely treatment of caries is important, including for maintaining the normal functioning of other organs of the baby.
Oral care
Caries in children aged 2-3 years can also develop due to the inattentive attitude of parents. Let's look at the main mistakes that moms and dads make:
- Pacifiers and bottles in a dream.
To teach a child to sleep alone, parents give him a pacifier or even a bottle of milk at night. As a result, the child enjoys the sweet taste of the drink all night, and the teeth are slowly but surely destroyed. Such a habit, of course, will give mom and dad healthy sleep, but in the baby it can lead to bottle caries and malocclusion.
- Sweet life.
Of course, most kids are unfamiliar with the problem of excess weight. Therefore, grandparents strive to treat the child with additional cake or candy. And, as you know, bacteria on enamel love sugar with a tender love, and very soon children under 3 years old develop caries, which requires treatment.
- Insufficient dental care
. Many parents believe that there is no need to care for baby teeth at 2-3 years of age. As a result, plaque accumulates, and carious monsters spread over both grown and still growing teeth.
Symptoms of caries in babies
It can be difficult for parents to notice that their child’s teeth are affected by caries. Dentists distinguish several stages of the development of the disease:
- Initial.
Subtle white spots appear on the baby's teeth. These spots can be large or very small, round or rectangular. The child does not experience any unpleasant sensations at the initial stage. Therefore, parents who do not examine their children's teeth skip this stage, and the enamel continues to deteriorate.
- Superficial
. At this stage of caries, teeth change more noticeably: dark spots appear on the top layer of enamel. Some children complain of pain when eating irritating foods (sour, salty and sweet). The enamel is damaged, the tooth cavity opens to bacteria.
- Average
. Caries bacteria reach the dentin (the tissue located inside the tooth). The baby complains of pain when eating foods that are too cold or too hot.
- Deep.
In children, deep caries is much more difficult than in adults. Most of the internal tissue of the tooth is damaged, and pulpitis develops sharply.
Unfortunately, in children under 3 years of age, unlike adults, caries often affects all teeth at once. Several holes may appear on one crown from different sides at once. Therefore, parents need to be extremely attentive to their children and devote time to oral care even before the first tooth appears.
Do baby teeth hurt due to caries?
Painful sensations when the surface of the teeth comes into contact with sweet, sour or salty food irritants is one of the first signs of incipient caries on baby teeth. Further, the discomfort in the affected teeth will only intensify, and when caries affects the pulp, the teeth begin to hurt like adults. In addition to acute pain, this stage of the disease is characterized by a high risk of premature removal of a baby tooth.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Author of the material: Ekaterina Gasparova
Complications and consequences that will not keep you waiting if your teeth are not treated
A far-fetched fear is extremely harmful: because of it, patients often take the situation to extremes and go to the doctor only when the disease spreads to neighboring teeth and gums, and serious intervention is required.
Deterioration of the general condition of the body
There is a misconception that bad teeth have no effect on the body as a whole. And that “one day the moment will come...” - the teeth will be cured, and there can be no complications. The immune system actually copes with the infection up to a certain point, and the problem is localized in the oral cavity. But one day the strength of the immune system weakens, because... he receives no help from outside. General intoxication of the body develops, which is poorly diagnosed, but manifests itself very clearly.
Intoxication is expressed in constant fatigue, fluctuations in body temperature, etc. The prolonged presence of rotten teeth leads to the following consequences:
- 1. Cardiac dysfunction. Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, which can only be treated surgically;
- 2. Loss of appetite. Impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to the entry of harmful microorganisms into it with saliva. Development of gastritis, food intoxication;
- 3. Frequent headaches due to tooth decay at the base of the root;
- 4. Many doctors are sure that bad teeth can cause problems with bone tissue and harm the musculoskeletal system. Arthrosis and polyarthritis often develop;
- 5. It has been scientifically proven that rotting of large chewing teeth leads to hair loss on the back of the head; destruction of small chewing units leads to baldness of the temporal part;
- 6. Rotting of any bone in the skull leads to brain damage;
- 7. Hearing impairment;
- 8. Poor condition of the skin;
- 9. An advanced putrefactive process spreads to the sinuses and can provoke chronic tonsillitis, hyperplasia of nasopharyngeal tissue, etc.
Pulpitis is a consequence of caries
The most common complication of caries is pulpitis. In fact, it is a natural consequence of caries and does not threaten a healthy tooth. With pulpitis, the dental nerve becomes inflamed; the disease is characterized by particularly severe pain when pressing on a tooth (biting on food).
A person can determine for himself when caries turns into pulpitis. With caries, pain appears only if a certain irritant acts on the diseased tooth. The unpleasant sensations disappear as soon as the irritant is eliminated. With pulpitis, pain can occur on its own. It can only be eliminated by the intervention of a doctor. A pain reliever will also help, but this is a short-term measure that loses effectiveness with frequent use. Taking painkillers is allowed only when it is not possible to visit the dentist. Their effect is only to relieve or weaken the pain syndrome; they do not have a therapeutic effect.
Periodontitis
If for some reason pulpitis has not been cured, the disease develops further. The ligaments that attach the tooth to the bone are affected.
Periodontitis has 2 phases:
- 1. Acute, characterized by severe pain;
- 2. Chronic – this phase may practically not appear.
Negative factors beyond the patient's control
If a person does not smoke, engages in debate, and watches his diet, why do his teeth begin to rot? There may be several reasons for this:
- Bad ecology. Polluted air, poor quality water, an excess of some and a lack of other important components. Fluoride deficiency is often cited as the cause of dental problems.
- Heredity. If the parents had bad teeth or the mother did not visit the dentist during pregnancy, children often experience similar problems.
- Physiological features. Hormonal imbalance in adolescents during the growth period, in pregnant and lactating mothers.
Tooth decay is often a consequence of other diseases. Problems with periodontal tissues - gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease - lead to the development of caries and cause tooth loss. If a purulent cyst forms near the root, the infection quickly spreads to the tooth. Often the deterioration of teeth is caused by diseases of the stomach, intestines, and thyroid gland.
Anesthesia for the treatment of childhood caries
Local anesthesia. Used in the vast majority of cases. There are 2 types: application and injection anesthesia. The first does not involve an injection. The risk here is that the child may swallow saliva containing lidocaine. Injections are safer and more effective.
Anesthesia. Used if the child is restless or simply afraid to have their teeth treated. This method is common in the West. Many parents are afraid of memory impairment due to general anesthesia. However, this happens extremely rarely. In addition, general anesthesia becomes the only option when you need to fill several teeth at once in one trip to the dentist. After all, this can take 2 or more hours. Before general anesthesia is administered, the child must undergo the following tests:
- Blood biochemistry.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Electrocardiography.
- Blood for sugar.
Before the introduction of general anesthesia, you cannot eat for 6 hours, and drink for 4 hours. The child is gently put to sleep using a sedative gas containing sevoflurane. To wake him up, it is enough to increase the oxygen supply. This can be done at any time. After recovery from anesthesia, all reflexes are restored within the first 15 minutes.
What are the dangers of putrefactive processes if they are not treated?
When it comes to treating a small child, it should be understood that destruction very quickly spreads to the internal structures of the tooth. In addition, the processes of decay contribute to the development of inflammatory processes in the surrounding tissues, the appearance of suppuration. If you ignore the problem and miss the precious moment when teeth can still be saved, it is likely that you will have to face very serious complications, including an abscess, severe intoxication of the body and damage to vital organs.
“My daughter has had very bad teeth since birth, just like me. Apparently it was passed on genetically. Almost from the very appearance of the first incisors, we have been constantly struggling with caries. At the same time, I personally make sure that she brushes her teeth twice a day, I don’t give her sweets, but, as they say, you can’t smear genes with your finger. And recently we discovered rot! The doctor immediately took an X-ray - fortunately, they managed to notice it in time, and the destruction did not reach the inner layers. After this, the doctor cleaned us, prescribed special gels and rinses, and put in a temporary filling. A course of antibiotics was prescribed. I’m very worried that there won’t be a relapse.”
Angelina, Saratov, from correspondence on the 24satoma.ru forum
Black teeth look rather unaesthetic and can lead to complexes in a child.
In addition to everything said above, rotten black teeth look extremely unaesthetic, and often become the main reason for the development of serious psychological complexes in a child. The visual picture is unpleasant both for the patient himself and for those around him. In order not to bring the disease to such an advanced stage, when the first suspicious spots appear on the child’s enamel, you should immediately show it to a pediatric dentist.
What to do with a tooth that has rotted to the root?
If the root has rotted and treatment measures do not produce results, the tooth has to be removed. Loss of the upper part leads to the development of pathologies:
- the appearance of a cyst at the root apex;
- fracture or dislocation of the root;
- injury to the gums from a splinter;
- periodontal diseases.
A rotten root becomes a source of infection that spreads to nearby tissues.
In any case, the doctor chooses the treatment. If there is a high probability of negative consequences, removal will be carried out. To avoid this, it is recommended not to skip periodic dental checkups.
When is a person to blame for having bad teeth?
Experts identify a number of causes of tooth decay, for which the patient himself is to blame. Knowing them, you can take timely measures to prevent the development of the disease. These reasons include:
- Smoking. Components released from tobacco disrupt metabolic processes in dental tissues. Due to this, their ability to resist adverse effects is sharply reduced.
- Alcohol, drugs. They negatively affect the functioning of the entire body, impair its protective functions and ability to recover.
- Poor nutrition. Lack of minerals and vitamins in food leads to weakening of the enamel. An excess of sweets, sour fruits, and berries contributes to the destruction of enamel.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. Lack of physical activity, constant presence in dusty rooms, abuse of fatty, fried foods reduces the body's protective functions.
In addition, lack of or improper oral hygiene contributes to the formation of plaque. It becomes a source of food for microorganisms that gradually destroy teeth.