Dental implantation, despite the presence of incomprehensible and sometimes frightening terms that only prosthetists or dentists can decipher, is considered an absolutely safe procedure. It is possible to restore the dentition using several technologies, but each of them is performed according to a single algorithm. First of all, an examination and consultation with a doctor, after which the implant is inserted, and only at the final stage prosthetics occurs.
Abutments for implants
A crown or prosthesis is installed on a dental implant, but there is another element that is attached between them - this is an abutment. The role of the abutment is simple: it is the connecting link in this design, and besides, there are other definitions for it, such as part of the implant, the basis for the prosthesis, and so on. More details about abutments for implants will be discussed in this article.
Implant abutment: what is it, the functional purpose of the element
Dental implants are a special type of structure that is used in dentistry to restore lost teeth. The design consists not only of the implant itself - a titanium rod implanted into the bone tissue of the jaw; it includes several elements at once, including an abutment, which can be called an adapter between the implant and the crown.
In the article we will talk in detail about what an abutment is, what functional tasks this element of the implantation system solves, and what types of abutments exist.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
How is it different from standard
An individual abutment, unlike a regular one, is not a round stump, but a full-fledged tooth stump, similar to a natural crown sharpened for a prosthesis. Due to the fact that the standard adapter is much narrower, during fixation, excess cement flows into the space between the implant and the gum. An error can provoke tissue inflammation and rejection of the titanium root in the early or medium term. Such consequences can be easily prevented by installing an individual design.
«
What is a dental implant abutment?
Dental implantation is a progressive technology for restoring lost teeth, but ordinary people have too superficial an understanding of how the operation of implantation is carried out and, even more so, of the structural design of dental implants. The abutment is one of the main parts of the implant system and its purpose is to connect the implanted titanium rod to the dental crown.
It is impossible to install a crown on an implant without an abutment; in addition, the service life of the prosthesis, its functionality, and aesthetic appearance depend on this element. Just a few years ago, manufacturers of implantation systems offered only one option for abutments - a standard design. These days, dental brands produce entire lines of abutments, which may differ from each other in appearance, shape, and production material.
We will talk in detail about the types of abutments in the next section of the article.
Types of implant-abutment connection
Companies producing implant products are constantly looking for new solutions so that their dental systems stand out from competitors, are liked by patients and dentists, and have an eternal service life.
It has long been proven that the connection plays an important role and affects the service life of the entire system. Therefore, manufacturers are trying to improve the types of connections or acquire the rights to successful solutions from premium segment implantology companies. Let's take a closer look at the most common types of connections.
Internal hexagon
The most commonly used type of connection in implantology today is an internal hexagon. It is worth noting that there can be more or fewer faces - 3, 4 or even 8 (it all depends on the manufacturer). How does an internal hex connection work? Imagine that the lower part of the superstructure is made in the form of a kind of “nut” with 6 edges, and inside the implant there is a special groove that has exactly the same outline. The two elements are connected to each other in one of six positions - as required by the treatment conditions.
This type of connection is quite easy to work with, because... it simplifies fitting and installation and allows the use of individual superstructures. The presence of an internal hexagon allows you to achieve high strength indicators for the entire system and evenly distribute the load. The disadvantage is the presence of a technological gap between the components, which makes the connection leaky.
External hexagon
Here everything is exactly the opposite. The entrance hole of the implant from above is made in the form of an external hexagon; it is placed inside the superstructure, which is why the connecting part itself is on top of the artificial root. At the moment, the system is recognized as less reliable, which is why it is used less and less.
Conical and hexagonal connection system
The superstructure has a conical shape, tapering downwards, and at the very end is made in the form of a hexagon. And on the implant (or inside it) there is a special hexagonal hole where the superstructure is placed. A system of a combination of a cone and a hexagon can be with or without an anti-rotation effect (i.e., eliminates rotation), and is also divided into 2 types based on the location of fixation:
- external: a more problematic option, because there is a risk of parts moving,
- internal: the lower part of the superstructure is installed inside the implant, which ensures the reliability and tightness of their connection to each other. Here, the risk of system elements unwinding during operation is practically eliminated.
Straight conical or cylindrical connection
There is no fastening in the form of connecting screws and contact edges (both external and internal), and fixation occurs only due to the tight fit of the surfaces to each other. The lower part of the superstructure is made in the form of an inverted cone (like Astra Tech) or a cylinder (like Bicon).
The positive side of this type of fixation is the freedom of positioning on the implant. The disadvantages include the complexity of manufacturing - so that after installation there are no gaps between the connection elements.
Interesting fact! Nobel Biocare has an option that comes in the form of an internal three-channel connection. The original model is called Replace Platform Shift and is used in complex and aesthetically significant areas.
Monolithic system
When considering cast models, it was already noted that this type of implantation product is created in one piece even during the production process. Those. the implant is firmly welded to the abutment, and they cannot be separated. The key advantage of one-piece products is the absence of any gaps, which prevents the penetration of infection or physiological fluids into the implant. However, the negative side of limiting the use of monolithic models is that they are not suitable for every patient based on clinical characteristics.
Classification of abutments into types, overview of the characteristics of different types of structures
Abutments are classified according to a set of performance characteristics, as well as by area of application. Let's look at the most popular types of abutments in modern dental implantation.
Standard abutments
They are universal designs, manufactured according to templates.
Standard abutments are produced in different sizes, diameters, and various shapes. Suitable for use in a wide variety of clinical situations. The price of standard abutments is quite reasonable; if necessary, it is easy to remove and replace the structure with a new one. With all the advantages, standard design abutments also have a number of disadvantages:
They do not provide the opportunity to obtain ideal aesthetics in the gum area;
May not be suitable for a patient with anomalies in the structure of the dental system;
When choosing a standard abutment, an additional and thorough quality check is definitely recommended.
Custom abutments
This type of construction is so called because the abutment is made individually for each patient.
To produce an individual abutment, a virtual model of the jaw in 3D format is used, and therefore the finished abutment will take into account all the anatomical features of the patient’s dental system. Pure titanium is most often used for the manufacture of structures; they can also be made from zirconium dioxide. The advantages of individual abutments include the following characteristics:
High quality, strict compliance with the characteristics of the anatomical structure of the jaw;
Improved aesthetics and functionality;
A tighter and better fit to the gum line, which eliminates the need for additional manipulations with sensitive tissues of the oral cavity;
There is only one drawback of individual abutments - high cost, but it is fully compensated by the benefits that the patient can receive by choosing abutments made personally for him.
Angled abutments
Used for installation on implants implanted at a non-standard angle. Angled abutments are in demand when performing implantation in patients with a non-standard structure of the dental system. Thanks to the unique type of design, which provides for a certain angle of inclination, it is possible to achieve the most durable connection between the implant and the crown.
Ball abutments
Abutments of this type are spherical in shape and are used during mini-implantation operations.
A conditionally removable denture is usually fixed on spherical abutments. Separate types of products are temporary and solid abutments. The first type of abutment is a plug that is placed on the implanted implant and contributes to the process of forming an aesthetic relief of the gums at the site of the operation. After the titanium rod has healed, the temporary abutment is removed.
In one-stage implantation, systems can be used in which the implant and abutment act as a single whole. After implantation of such an implant, a temporary crown is immediately placed on it.
What to consider when choosing
Thanks to this variety, the patient can choose absolutely any type of abutment, but the most effective is considered to be a one-piece design, which involves the production of a dental implant with an already built-in abutment. This choice eliminates the need to screw in and seat the abutment on cement, since the product is fused at the factory. The shape of the patient's teeth can be achieved by slightly filing the product.
On a note! The main advantage of this type is that the structure is installed immediately (crown, abutment, and dental implant). It can also withstand high loads.
How to choose an abutment
During the installation process, the soft tissue is not injured, so whenever possible it is advisable to choose a one-piece design. Of course, it costs an order of magnitude more than other types of abutments, but the installation procedure will be faster and easier. If this is not possible, then you can install the abutment separately - this is also very effective.
Key points to consider when choosing:
- cost of the product;
- abutment fixation method;
- aesthetic features. If you are going to install dentures on your front teeth, you should avoid using metal abutments (they are translucent);
- individual characteristics of the patient. Here, the distance of the implant from the tooth, the height of the patient’s mucosa and the depth of the implant must be taken into account.
Aba
When choosing, try not to focus on the price category of the product, since the aesthetics, durability and strength of the abutment should remain the main priority.
Video - Abutment
Abutment materials
The material used to produce abutments is important because it affects both the functionality of the prosthesis installed on the implant and the aesthetics of the implantation result. According to the material of manufacture, abutments are:
Titanium abutments
Titanium abutments are in greatest demand on the market due to the optimal combination of price and quality. They have excellent strength and reliability, but do not always provide the desired aesthetics, since titanium can noticeably show through the crown.
Zirconium abutments
They are the most expensive type of product, especially if you plan to use an individual zirconium abutment in the operation. Abutments made of zirconium dioxide provide impeccable aesthetics of restorations and have no analogues in terms of strength and durability.
Combined abutments
Manufactured from a titanium-zirconium alloy, they allow you to obtain the optimal combination of functionality and aesthetics, but the price of the products will be quite high, and in addition, combined abutments are presented in the lines of a small number of manufacturers of implantation systems.
Ceramic abutments
An ideal solution for patients with allergic reactions to metals and their alloys.
Ceramic abutments can be successfully used for implantation and restoration of teeth included in the smile zone. A separate type of product is plastic abutments - they are used exclusively for temporary restorations and are subsequently replaced by structures made of more durable and reliable materials.
Classification of models - advantages and disadvantages of each type
In modern dentistry, high-quality solutions are created thanks to innovative technologies. Each implant manufacturer has product lines that include not only implants, but also superstructures, instruments, and biomaterials. Support elements can differ in size (diameter, length and height), angle of inclination, type of platform (narrow, standard and wide), shape, material and even installation method. Below we will consider in detail the different types of abutments.
Very often, doctors offer to install an abutment, which is produced by another company (for example, Korean), and is conditionally suitable for all implants. This option should be abandoned. The implant and superstructure that are installed on the patient must be original and come from the same manufacturer. Otherwise, they may not have perfect contact with each other - the gaps may be microscopic and completely invisible to the naked eye. But even this will be enough for the development of complications, up to complete rejection of the implants due to overload from the abutment and prosthesis.
Classic or stamped models
This is the most common option; in another way, such products are also called stamped, because. they are manufactured at all implant manufacturing plants exclusively for their own products. The models are universal, have a standard shape, and are created mainly from titanium, less often from alloys of other metals or zirconium dioxide. They differ in height, diameter, and tilt options relative to the root (20º–45º). Suitable for a large number of patients, have an affordable price, because... The production of such abutments is maximally optimized, thought out, load-tested and automated.
In general, it is standard products that are the most popular and optimal in all respects. They, of course, have their drawbacks, but, in fact, there are still no alternatives - individual systems are not at all aimed at long-term functioning (we will explain why below).
Disadvantages of traditional superstructures:
- Sometimes there are problems with aesthetics: such products are most often created from metal, which has a gray tint. Therefore, in the frontal area, the support can be seen through the thin veneering material of the crowns. In addition, over time, the gums will definitely sag, so the structure may become noticeable, or it will be visible through the gums (at the point of contact with the gum crown it will “darken”). However, this is an inevitable fact and the most important thing is to monitor hygiene and regularly visit a doctor to correct this situation,
- sometimes the standard model cannot be applied in complex situations: here you really have to develop an individual system. But this may only be relevant when restoring the front teeth and is not acceptable for the side teeth, which bear an increased chewing load.
- Sometimes problems may arise when fixing the prosthesis with cement: some models do not have a ledge at the base, so if the crown is attached with cement, the liquid material can simply “fill” the space around the installed implant. Especially if the doctor did not select the concentration or amount of the product correctly. If there is a ledge, then the cement remains exclusively above it (i.e., within the coronal part) and does not fall under the mucosa. In addition, screw-retained models are increasingly being used today as a more effective alternative (read more about this type below).
The success of using any elements of the system largely depends on the professionalism of the doctor. So, a specialist needs to correctly select the correct angle of inclination and size from all the options for standard “connectors”, because An adapter that is too large or, on the contrary, small, simply will not allow you to achieve high-quality prosthetics. It is also possible to overload the root, which can lead to failure of the entire system.
Models created individually for each patient
Such a detail is already created exclusively for the bite characteristics of a particular patient. To make it, after implantation of the implant, the doctor takes impressions, then a prototype of the future model is created, the information is scanned and, using 3D technologies and CAD/CAM equipment, the dental technician develops an individual support for the crown. Everything takes no more than one week, and the end result is a product that allows you to achieve fairly high aesthetic standards. Also, individual models have a small ledge, which prevents cement from getting under the gum when installing them.
Materials for creating individual superstructures:
- Zirconium dioxide: used even more often than titanium. When individualizing treatment, the emphasis is most often on aesthetics, and zirconium dioxide (like ceramics) is white. This means that the product will not show through the crown, will not cause the gums to turn blue at the point of contact with the mucous membrane, but at the same time will be characterized by increased strength and hypoallergenicity,
- titanium or its alloy with aluminum and vanadium: such a product can be partially lined with ceramics to improve aesthetics,
- ceramics: which can be given any shade,
- gold plating.
There is such a thing as a “zirconium abutment”. But here it is important to understand the differences between the two materials: zirconium is a metal, but zirconium dioxide is no longer. It is white in color and bioinert - it does not cause allergic reactions, is extremely durable and is even comparable in hardness to many metals.
At first glance, it may seem that individual superstructures are better than template ones. But that's not true. Custom ones are created in a regular dental laboratory rather than in a manufacturing plant. And the dental technician physically does not have the opportunity to conduct multiple tests for functional load, which means it is completely unclear what pressure the superstructures will ultimately be able to withstand. That is why this option is not suitable for the lateral teeth with which we chew.
Read on the topic: everything about individual abutments in one article - manufacturing features, advantages and disadvantages.
There is a similar question regarding implants - will such supports really correctly distribute pressure on the intraosseous part of the system? It is important to understand that at the factory all elements of the system undergo a huge number of tests. And if the question is only about aesthetics, then today almost all manufacturers produce supporting superstructures created from snow-white zirconium dioxide - these are not individual, but standard, i.e. template models.
Temporary structure
The temporary abutment is made of plastic, less often of titanium (cheap MIS[1] implants and premium Nobel models have these). It serves as a temporary adapter between the implant and the adaptation prosthesis, which is installed immediately after implantation of artificial roots. For wearing a crown or simply taking impressions. They can also be used for the period of fitting and correction of permanent prosthetic products. These models are lightweight, aesthetic, but at the same time quite durable and inexpensive.
Ball-shaped systems
At the top they have the shape of a sphere, for which special recesses are created in the inner part of the prosthesis. Suitable for installing conditionally removable and removable dentures. This form of fastening helps patients not to think about dentures falling out of their mouth at the most inopportune moment. But it is very short-lived and can quickly fail, since it is not designed for strong mechanical loads. After a few years, such supports are subject to natural wear and need to be replaced. Moreover, sometimes it is necessary to change not only the superstructure, but also the implant.
For conditionally removable prosthetics, some manufacturing companies supply superstructures that work using the Locator system. These are unique solutions that, compared to spherical systems, have a flat base and provide the patient with easy, reliable fixation and removal of dentures. Essentially they work like buttons. They are more wear-resistant and last several times longer than spherical ones.
Also, some manufacturers supply products of the OT Equator type for removable prosthetics on implants, which are miniature in size and coated with titanium nitride, which increases wear resistance.
Direct superstructures
Most of the models currently in use have exactly this structure. Straight products are made both with and without a shoulder; they can have different neck heights for connection to the implant - 1, 2, 3, 4 millimeters. Designed primarily for the restoration of anterior teeth located in the smile zone, where implants are inserted strictly vertically.
Corner models
They have a certain axis tilt (usually 17° or 30°), which allows the dental crown to be placed directly on the implant if it is installed at an angle. Most often, such abutments are used for complex dental implantation. As a rule, we are talking about lateral areas, in which, due to the anatomy and unevenness of bone tissue atrophy, it is necessary to find the optimal solution for implantation. Installation of implants into the bone at an angle is necessary in the following situations:
- to bypass the sinuses and nerves,
- to use the most dense and sterile tissues: for better fixation of implants, installation is carried out in the buttresses of the skull - thickenings or force lines of the maxillary and zygomatic bones.
Thus, with the help of angular support components, the doctor is able to align the position of the crown or prosthetic device itself - so that they look as beautiful as possible and are comfortable to use.
Dental implantation using the Osstem system = 20,000 rubles. until March 31, 2022!
All inclusive, treatment guaranteed!
Premium implants at an affordable price. Free consultation with an implantologist +7 (495) 215-52-31 or write to us
Multiunit-abas are designed for reliable fixation of crowns or any other prostheses using a screw fastening system. They are multi-component structures, and due to the presence of a screw, they allow you to secure a crown or prosthesis so that, if necessary, it can be easily removed without sawing the entire system. Such abutments can be either straight or angular - a specific model is used depending on the situation.
Cast system integral with the implant
Monolithic models, where the abutment is connected to the dental implant at the production stage, are called one-piece. Essentially, it is just a one-piece implant that has no boundaries between the abutment and the intraosseous part. This allows dental implantation to be performed in just one visit to the doctor, which significantly reduces treatment time and also minimizes tissue trauma. A single-component type of implant is used mainly for one-stage implantation protocols, which involve immediate loading with the prosthesis.
The International Implant Foundation, based on numerous studies, has concluded that one-piece implants significantly reduce the likelihood of developing peri-implantitis and inflammation of the soft tissue around them. Thanks to the tightness, there is no risk of gaps and crevices forming between the components, into which pathogenic bacteria and plaque can enter. The connecting thread of such implants does not weaken during operation.
In order to prevent peri-implantitis, experienced doctors advise choosing either one-piece implant models (important in complex clinical cases with generalized periodontitis or periodontal disease) or two-piece types of implants with a polished neck-apex. Also suitable are models that have a smooth antibacterial coating on which plaque will not accumulate.
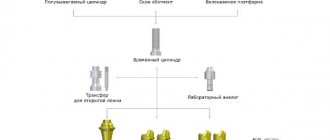
Installation and fixation of the abutment on the implant
If a one-stage implantation is carried out, then the implant and abutment are installed simultaneously and usually one-piece structures are used in this type of operation. After implantation of a titanium rod with an abutment, the implant is immediately loaded with a temporary crown. When carrying out implantation according to the classical protocol, the installation of all elements of the implantation system is divided into several successive stages:
1. General preparation for surgery (consultation, diagnosis, panoramic image, preliminary treatment, sanitation of the oral cavity);
2. Installation of an implant into the jaw bone. A gum former is placed on the implant - a temporary plug that allows you to achieve an attractive gum relief in the implantation area.
3. Installation of the abutment (performed after complete osseointegration of the implant);
4. Installation of the crown.
Fixation of the abutment to the implant can be done in two ways:
Using cement. The technique is simple and reliable, but requires care when removing excess cement mortar. There shouldn't be any left! In addition, if it is necessary to remove the crown, certain difficulties may arise;
Using screw type fasteners. A hole is made in the crown and the abutment screw is inserted through it. After installing the abutment and crown on it, the hole is masked with material and polished.
The screw fixation technology will help you easily remove the crown and abutment if necessary, but at the same time, the screw fastening of the abutment is inferior in reliability to traditional cement fastening, as it increases the risk of structure breakage.
How to care for abutments
Since the adapters are hidden under the crowns, there is no need to directly care for them. But hygienic procedures require both crowns and all the tissues that surround them. You can clean the denture with a soft brush 3–4 days after fixation. In the very first days, in order to avoid injury to the mucous membranes, careful baths of antibacterial solutions are recommended (it is important not to rinse so that the stitches do not come apart, but simply keep the product in your mouth). Additional antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agents can also be used as prescribed by a doctor. Oral hygiene must be carried out in full accordance with the dentist’s recommendations to avoid gum inflammation or peri-implantitis.
Is it possible to replace an abutment that has become unusable?
Under certain circumstances, any element of the implantation system may become unusable. The titanium rod itself rarely needs to be replaced, since most manufacturers provide a lifetime guarantee for implants, and the material they produce is highly durable. But the abutment or crown may well fail and then it will be necessary to urgently replace it.
To quickly replace a broken abutment with a new design, it is recommended that you initially select an implantation system from a trusted manufacturer. It doesn’t have to be a premium brand - you can choose a system from a manufacturer that produces more budget-friendly, but still high-quality products. All recommendations on choosing the optimal implantation system can be given to you by the doctors of our clinic in Moscow - Vanstom. Our clinic is located in the center of Moscow, a 5-minute walk from the Baumanskaya metro station.
To make an appointment with a clinic specialist, dial our contact phone number or leave a request for a call back in the interactive form on the site. Vanstom dentistry in Moscow means modern technologies and high professionalism of doctors for the health of your teeth and the natural beauty of your smile!
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Manufacturing (modeling) technique in the laboratory
- After the artificial root has healed and the gingival contour has been formed, an impression coping is screwed onto the implant to take an impression .
- The impressions are sent to a dental laboratory to make plaster models .
- The finished model is scanned and transferred to a computer program for modeling.
- An abutment is cut out of a solid block blank using a computerized machine using CAD/CAM technology .
»
Cost of abutments for dental implants
The price of an abutment depends on its type and material of manufacture. A standard titanium abutment will cost from 2,000 rubles, a titanium product made from an individual impression will cost more - from 6,000 rubles.
Zirconium individual abutments have the highest price - their cost can reach up to 30,000 rubles.
Usually, the patient is not told the price of the abutment separately, but the cost of implantation - that is, the operation of implanting a titanium rod with the installation of a gum former (if necessary) and then the abutment. Do you want to know the exact cost of implantation? Come to Vanstom, we are located at: Moscow, Baumanskaya metro station, st. Bakuninskaya, 17/28.
Types of abutments used for dental implantation
Depending on the manufacturing method:
- Standard - produced on the basis of a universal template. There are several options for length, diameter, and angle of inclination. During production, the personal parameters of the fabrics are not taken into account, so the aesthetics of the restoration is not at a high level. Standard suprastructures are divided into: gingival former, angular, straight, spherical.
- Individual - modeled based on the patient’s impressions in the CAD/CAM program and made by a dental technician on a milling machine in a single copy. Such adapters well support the contour of soft tissues and prevent cement from leaking under the gum.
Disadvantages of custom abutments
The only disadvantage of an individual abutment is its price. Due to the complex and relatively lengthy manufacturing process, a custom abutment is significantly more expensive than a standard one.
If it is important for you to save money, then with uncomplicated prosthetics and the correct jaw structure, you can get by with standard designs. But in case of problems with bite, peculiarities of the shape of the dentition and other non-standard situations, you cannot do without an individual abutment. Ultimately, this issue is resolved together with a doctor, who will analyze the situation and offer the best options for you.
“Weak points” of standard abutments
- Factory abutments do not support the gum, which affects aesthetics. After implantation, correction of the gingival margin through plastic surgery may be required.
- Abutments have a standard shape, so they do not follow the shape of the tooth. Their diameter is much smaller than a crown, which also increases the risk of poor installation.
- When fixing a crown, there is a high risk of the cement with which it is attached to flow under the gum. The crown is pressed into the gum to mask the metal of the abutment, which can allow cement to penetrate inside. Over time, this leads to serious complications, including peri-implantitis and implant rejection.
- Poor quality joining of the abutment can subsequently lead to the formation of gaps between the root rod and the crown. This is fraught with inflammation and the ingress of food debris.
- Factory products are made from titanium, and when the gums recede or recede, a dark stripe sometimes becomes noticeable. In addition, the metal can shine through in the light.