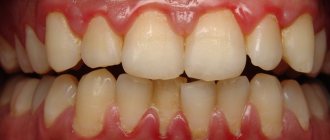
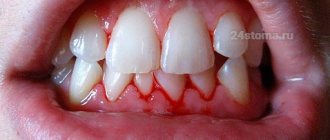
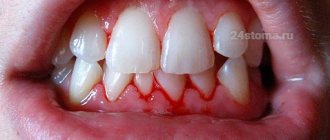
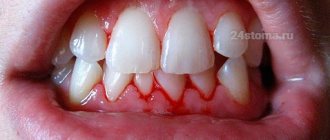
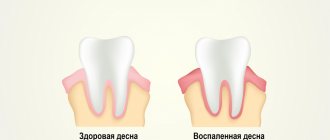
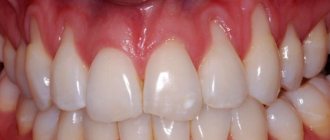
Why do my gums bleed?
Often the gums begin to bleed due to diseases of the oral cavity:
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gum tissue, due to which they cease to perform their protective functions. Due to tartar and plaque, bacteria begin to multiply, which become the cause of the inflammatory process.
- Periodontitis is inflammation of the internal periodontal tissues. If the disease is not treated, the inflammation will become chronic and can cause tooth loss.
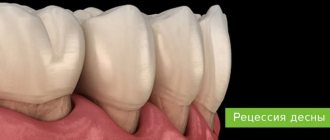
- The third cause of bleeding gums is periodontal disease. Because of it, the structure of tissues and blood flow change, and teeth can become mobile. Bacteria first infect the oral cavity and then end up in the gum pockets. After this, the gums swell and begin to bleed, especially when brushing your teeth.
- Bleeding can be caused by the formation of tartar in the gum area. It occurs due to improper oral care. Dentists advise cleaning off plaque at least once a day.
- Bleeding from the gums can begin during pregnancy, as a woman's hormonal levels in the body change.
- Another reason is a too hard toothbrush. To avoid damaging delicate tissues, preference should be given to soft or medium-hard bristles.
- Sometimes gums swell and bleed due to a lack of certain vitamins or minerals in the body.
- Bleeding gums can cause a worsening throat condition.
Medicines
Among the medications that are traditionally used for bleeding gums, we can name Cholisal, Metrogyl Denta, Kamistad, Asepta. All these gels have both an analgesic, antiseptic and wound-healing effect. If a child has problems with gums, then such gels will be the best first aid medicine.
Among the herbal remedies, we found the liquid rinse preparation Stomatofit. It is made on the basis of extracts of medicinal herbs that heal gums. It has no side effects, but is not recommended for people allergic to chamomile and arnica.
How to treat bleeding gums?
If your gums bleed frequently, you should consult a dentist. Treatment of this pathology consists of several stages.
First, professional oral hygiene is performed. It is in dental plaque that ideal conditions are formed for the proliferation of harmful bacteria, which threaten not only the condition of the gums, but also the condition of the teeth. Plaque formation under the gums is especially dangerous. To get rid of it, dentists prescribe sandblasting or ultrasonic cleaning procedures.
After this, the doctor checks the condition of the fillings and dentures. If there are poorly treated teeth or crowns, pathogenic bacteria can develop there. To stop the inflammation, they may have to be replaced.
Your doctor will give you recommendations on how to properly brush your teeth. In some cases, a specialist may recommend special oral care products. The doctor will help you choose a brush and toothpaste that is suitable for a particular patient. If you brush your teeth incorrectly, inflammation can become chronic.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe certain medications:
- antiseptic solutions for rinsing the mouth;
- special gels or ointments that eliminate inflammation or have an antiseptic effect;
- antibiotics and drugs that relieve inflammation.
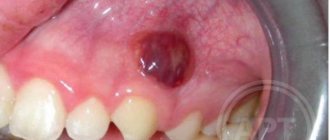
In difficult cases, the doctor may suggest surgical treatment.
Rinse
By rinsing, we remove food debris, pathogenic bacteria, and treat gums locally. You can rinse your mouth with a solution of soda, decoctions and diluted herbal tinctures (chamomile, St. John's wort, nettle, sage, oak bark) or special dental rinses. Read the instructions for use carefully! In folk medicine, hydrogen peroxide, carrot juice, and sauerkraut are used (it must be chewed periodically). Please note that rinsing for many diseases is only an additional, concomitant method of treatment.
Treating bleeding gums at home
In addition to pharmaceutical gels and rinses, folk remedies can also be used to treat gums. Herbal infusions are best suited for this:
- a spoonful of sage flowers in a glass of boiling water;
- a teaspoon of calendula flowers per 200 ml of water (leave for half an hour);
- boil two tablespoons of oak bark in 500 ml of water and let stand for 10 minutes;
- boil a decoction of 2 tablespoons of yarrow and 0.5 liters of water for 15 minutes;
- Infuse 200 ml of boiling water with 1 tablespoon of chamomile flowers.
It is recommended to rinse your mouth 3 to 6 times a day after meals.
Dental care
Try to take care of your dental health regularly. Be sure to remove plaque, as it is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. Plaque and tartar can also be removed in the dentist’s office using professional teeth cleaning and the AirFlow method. This significantly improves the health of the oral cavity, restores the natural balance of bacteria, cleans hard-to-reach places, and restores the natural whiteness of teeth. Moreover, such care is absolutely painless for the patient! It is recommended to have professional teeth cleaning once a year.
Stages of treatment
Treatment for bleeding gums is usually carried out in several stages.
- First of all, the dentist must find out the cause and make the correct diagnosis.
- Next, the doctor will prescribe special treatment, which usually consists of taking antibiotics, using local anti-inflammatory drugs, and rinsing the mouth with special solutions. It is also possible to supplement treatment with folk remedies.
- At the final stage of treatment, the patient must see a doctor to monitor the condition several weeks after the start of treatment.
Typically, treatment for inflammation and bleeding gums lasts several weeks; after this period, the doctor must examine the patient’s oral cavity and decide whether to complete or continue treatment until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear.
Toothpastes
Oral hygiene plays an important role in the treatment of dental diseases. Toothpaste against bleeding gums helps reduce pain, swelling, hyperemia, prevents heavy bleeding, and stops the spread of the inflammatory process.
You should not use medicinal pastes for too long, replacing them with full-fledged treatment, since they do not cure the disease, but only reduce the intensity of its symptoms.
Lakalut Active
The most effective of all medicated toothpastes. It contains chlorhexidine, fluorides, aluminum lactate, allantoin and other active substances. Significantly reduces bleeding and reduces tooth sensitivity. You should not use it constantly; it is better to switch to regular preventive toothpaste after the symptoms disappear.
Lakalut Phytoformula
Intended for long-term use due to the lack of antiseptics. Contains additional anti-inflammatory plant components, sodium fluoride. Strengthens tooth enamel and prevents caries.
Parodontax and Parodontax F
It consists of zinc citrate, mineral salts, extracts of medicinal plants, and is available with and without fluoride. Does not contain chemical antiseptics or antibiotics.
Read more about toothpastes in the article: Toothpastes for gums
How to stop bleeding
Of course, it is best to prevent bleeding, that is, not to subject the gums to mechanical damage, not to provoke the development of inflammatory diseases, and to systematically brush your teeth. But if the problem has already arisen, the following methods will help stop it:
- attach a tea bag;
- apply a cotton swab soaked in hydrogen peroxide;
- anoint the gums with a special gel.
If the bleeding is not severe, you can use a tea bag. A wet tea bag (green tea is best) should be applied to the damaged and bleeding gum. Tea leaves contain tannic acid, which promotes blood clotting. If you hold the tea bag for 5-10 minutes, the blood will stop flowing, and the wound will quickly heal and heal.
An ordinary pharmacy 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide will also help stop the bleeding. Apply a cotton swab soaked in hydrogen peroxide to the bleeding wound on the gum and hold there for several minutes. Hydrogen peroxide will quickly stop bleeding, and will also serve as an excellent cleanser and disinfectant that will prevent the wound from becoming infected and causing inflammation.
Medicines in the form of a gel will also help to cope with bleeding - for example, Dental, Solcoseryl, Metrogyl Denta and others. The gel-like form allows the drug to envelop the gums with a protective film, which not only quickly stops bleeding, but also has anti-inflammatory and antibactericidal properties.
Foods necessary for healthy gums and teeth
In addition to vitamin-mineral complexes for teeth and gums, you should eat foods such as:
- hard vegetables and fruits: cucumbers, apples, beets, pears and carrots;
- citrus fruits: especially grapefruit and orange, which reduce bleeding gums;
- berries: cloudberries, lingonberries, cranberries and other forest products are especially useful for tooth enamel;
- dairy products: fresh cottage cheese and cheese can replenish calcium reserves in the body;
- nuts, in particular cashews and almonds;
- honey;
- seafood;
- eggs.
Experts' opinion
Clinical studies of Asepta products conducted at the Ryazan State Medical University of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia allowed the following conclusions to be drawn:
- All patients, after using Asepta line products, noted a decrease in complaints of discomfort in the oral cavity 1-2 days after use.
- On the 7th day, when examining patients, a decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums is noted, but bleeding persists upon probing.
- On the 14th day of using the products, upon examination, a significant decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was recorded.
Improved dynamics of indicators allows us to recommend the Asepta line of products for the local treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
Sources:
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of the use of therapeutic and prophylactic agents of the ASEPTA series in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases in children and adolescents (I.V. Klimova) Irina Vladimirovna Klimova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Novosibirsk State Medical University. Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Novosibirsk State Medical University.
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
Other useful techniques
You can treat bleeding gums yourself with some other simple and affordable means. For example, black radish juice, which cleans dental surfaces of plaque. To obtain juice, the vegetable is grated on a fine grater, and then squeezed out with sterile gauze. It is best to apply the liquid to the gums not with your fingers, but with a cotton swab.
It will be useful to carry out a therapeutic massage of the gums from time to time, for which a regular toothbrush and sea salt are used. When doing a massage, be careful with your movements: too much pressure on the brush can cause injury to the sensitive mucous membranes.
To prevent plaque buildup that causes bleeding gums, after eating, either brush your teeth or use sugar-free chewing gum.
Signs of bleeding gums
The symptom of bleeding is a pathological condition that indicates damage to the epithelial cover as a result of injury or inflammation, and is one of the signs of a wound (gaping, pain, bleeding)
“Therapeutic Dentistry,” ed. G. M. Barera.
There are simple markers that help detect the problem of bleeding gums:
- a metallic taste in the mouth, usually worse after brushing teeth or eating;
- pink toothpaste foam when spitting;
- burning sensation in the gum area when drinking sour, salty drinks or food;
- traces of blood on solid food when biting into it [1,2].
The degree of damage to soft tissues due to bleeding can only be detected by a doctor with special vertical and horizontal probing