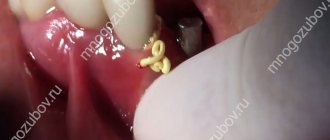
The vitality of the tooth, in particular its sensitivity, is ensured by the neurovascular bundle (pulp). Removal of the pulp (depulpation) is a forced measure, which is resorted to for serious indications (pulpitis, hilar cyst, damage to the pulp chamber due to trauma, etc.). Painful discomfort for several days after depulpation is a normal tissue reaction to the intervention. But if a tooth hurts after removing the nerve and filling the canals after 2-3 weeks
or pain occurs suddenly long after endodontic treatment, this is a good reason to see a dentist.
Even treated teeth should be examined every year to diagnose or rule out complications at an early stage. A pulpless tooth does not hurt, but it is like a time bomb. Poor-quality canal treatment can provoke complications that destroy the jaw bone and cause purulent processes (cysts, abscesses) that are life-threatening. Properly treated canals are the foundation of any restoration. The more modern and high-quality the materials used for their processing, the less likely there are complications.
Indications for nerve removal
- Caries has reached the pulp. Initially, caries appears on the enamel, then moves to dentin, then to the pulp. Inflammation increases: acute pain occurs. To eliminate the pain and save the tooth, you need to remove the nerve.
- Injuries of various types: impact, fracture, chip. With such mechanical impact, traumatic pulpitis develops. The integrity of the tooth is damaged, the infection penetrates into the pulp. Inflammation occurs and pain appears. Treatment involves removing the nerve.
- Retrograde infection. When inflammation occurs at the apex of the tooth root, it then spreads to the nerve.
- Orthopedic treatment. Before placing a crown, in some clinical cases it is necessary to remove the nerves. To avoid complications, a severely damaged tooth is first treated: the nerves are removed.
- Asymptomatic pulpitis (chronic). The patient does not have acute pain, but the nerve is infected. The patient's complaints may include mild pain in the past.
Possible causes of pain
Most often, before installing a crown, the dentist performs depulpation. Pulp is a loose tissue that is located inside the tooth and is penetrated by many blood vessels and nerve endings. Therefore, this procedure is colloquially referred to as nerve removal. It is generally accepted that pulpless teeth do not hurt and do not cause problems. In fact, this is not entirely true, since inflammatory processes often spread to surrounding tissues.
Inflammation is one of the most common causes of pain in a pulpless tooth under the crown. It is important to note that the factors that provoke the development of the inflammatory process are:
- Inadequate tooth preparation. A correctly performed procedure assumes that the pulp will be completely removed, and the canals will be disinfected and sealed to a physiological level. If the canal is not completely sealed, the resulting cavity creates conditions favorable for the development of bacteria. The same thing happens when using low-quality filling materials - over time, they sag and form voids into which infection penetrates, resulting in inflammation.
- Root canal perforation. As a rule, the thickness of the canal walls is small, so in complex anatomical cases they can be damaged. Perforation is the formation of a through hole, which is an “open door” for pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, if this complication occurs, it is necessary to close it carefully.
- Incorrect fit of the prosthesis. If the crown is not installed correctly, a small gap remains between its edge and the gum or the crown and the tooth. Over time, food particles accumulate in it, which causes an increase in the number of bacteria. The result is inflammation and pain under the crown again.
- Failure to follow doctor's recommendations. Poor oral hygiene, excessive consumption of sweets, the habit of opening lids with teeth - all this can also become a factor that provokes pain. In this case, the inflammatory process occurs due to the proliferation of bacteria or traumatic damage to the tissues surrounding the tooth.
- Crack or fracture of a tooth. If a prosthetic design is chosen that is inadequate to the case or the tooth was previously severely weakened, then a root crack may occur, and then a fracture.
What are the methods for removing a nerve?
- Amputation . This method is rarely used: mainly in pediatric dentistry. Its essence lies in the fact that the neurovascular bundle is partially removed. The pulp remains in the roots, and only the coronal part is removed. In adults, it is used in exceptional cases, when the doctor sees that the inflammation has affected only a small part of the nerve.
- Extirpation . The pulp is completely removed from the tooth. After removing the nerve, the canals are cleaned, washed, and filled.
Tooth extraction: features
Tooth extraction is a surgical intervention in the oral cavity with the aim of removing an unhealthy or lifeless unit of dentition from the bone tissue. A simple form of surgery involves loosening the tooth and then pulling it out with forceps, a hook, or other instruments. In case of a complex procedure, preliminary cutting of soft tissues, drilling of the bone, etc. is required.
Obviously, complex removal is much more traumatic, and therefore the pain after it is more pronounced and lasts longer.
Let's note other factors that increase pain:
- concomitant inflammatory process;
- prolonged ignoring of the problem of suppressing symptoms with analgesics;
- alcohol abuse.
Sequence of treatment
- Diagnostics . After the doctor has examined you and collected your medical history, an X-ray is taken. This diagnosis allows you to evaluate the structure of the tooth and plan treatment. To see the full anatomy of the root canals, a computed tomography (CT) scan is performed - a 3D diagnostic that allows you to see all the structures of the tooth.
- Pain relief . Local infiltration or conduction anesthesia is performed. Before the injection, the gums are lubricated with an anesthetic gel so that the injection is not felt.
- Setting up insulation . Root canal work should be done in clean, dry conditions. For this purpose, rubber dam (insulation) is used. It is a latex plate that is placed on the tooth. Advantages of isolation: saliva and plaque do not enter the root canals. Medicines and solutions also do not flow into the patient’s mouth.
- Preparation of hard dental tissues . The doctor uses a drill to remove the destroyed tissue. To prevent overheating of the tooth, water flows from the tip. The doctor creates direct access to the root canals.
- Nerve removal . It is performed with thin sterile instruments similar to long needles. The doctor places an instrument into the root canal and removes the nerve. Machine rotary tools may also be used. This stage is completely painless, since anesthesia was previously performed.
- Mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals . The canals are washed with special antiseptic solutions and passed through with instruments. This allows you to completely remove the diseased nerve and relieve inflammation.
- Temporary filling . Root canal work is complex, so it is not always possible to treat a tooth in one visit. An anti-inflammatory paste is placed into the canals, a temporary filling is placed, and a further stage of treatment is planned.
For permanent restoration of the crown part of the tooth, ]esthetic dentistry[/anchor] will be required.
Contraindications
Doctors at the SDent aesthetic dentistry center collect all data about the patient’s condition before starting treatment. In the health questionnaire, the patient notes the characteristics of his body, and the doctor conducts a survey. Planned nerve removal is not performed if:
- high blood pressure, hypertensive crisis;
- first, third trimester of pregnancy (provided there is no acute pain);
- acute inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes and facial skin;
- acute respiratory and viral diseases, etc.
General recommendations after treatment
- You can eat and drink immediately after treatment;
- Until the anesthesia wears off, you should not eat rough food;
- in the days following treatment on the side of the diseased tooth, do not chew rough, hard food;
- in some cases, anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, and oral baths are prescribed;
- If a temporary filling falls out, consult a doctor immediately;
- If pain occurs after placing a temporary filling, also consult a doctor immediately.
After the anesthesia wears off, the patient may feel discomfort in the area of the treated tooth. If pain, throbbing, or swelling occurs, you should consult a dentist.
Memo to the patient after tooth extraction
- A gauze swab placed on the wound must be spat out 15–20 minutes after removal.
- You should not eat for 2 hours after surgery; then during the day it is recommended to avoid hard and rough foods and chew on the side opposite to the removal.
- On the day of surgery, you should not rinse the wound and you should not spit out any clots that form (otherwise there is a risk of a blood clot formed there falling out of the socket and subsequent bleeding).
- During the day after the operation, you should not drink or eat anything hot, you should not warm the removal area (put your hand to your cheek, sleep on the cheek on the side of the operation, etc.), and you should not use warm compresses. You should also not visit the bathhouse, sauna or take a hot bath on the day of removal.
- You should not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours after tooth extraction. It is advisable to refrain from smoking on the day of surgery.
- It is advisable to avoid physical activity on the day of surgery.
- If bleeding occurs from the hole, you can place a sterile gauze pad on the wound and bite it. To make a tampon, take a piece of sterile bandage or gauze and fold it several times. If bleeding is significant and does not stop within 12 hours after removal, contact the clinic immediately.
- After tooth extraction, swelling of the cheek on the side of the operation may occur. To reduce the risk of swelling, you can apply ice or cold objects to your cheek immediately after surgery and during the first 24 hours. The cold should be kept on the cheek for 15–20 minutes, taking breaks every 3–5 minutes. On the second day, swelling may increase; on the third day, it usually subsides.
- After the anesthesia wears off, aching pain may occur in the area of removal. If necessary, you can take a pain reliever tablet recommended by your doctor. If the pain does not go away or worsens within 2-3 days, you should consult a doctor immediately.
- On the first day after tooth extraction, a slight increase in body temperature is possible.
- It is necessary to brush your teeth even after extraction! During the day after surgery, you are allowed not to brush your teeth only on the extraction side. Next, you need to brush all your teeth, but carefully, trying not to damage the socket.
Long-term consequences after treatment
Patients often experience complications after nerve removal. This is due to many factors: lack of diagnosis, poor quality treatment, incorrect diagnosis, etc. Main consequences:
- poor canal filling. A loose filling leads to the re-emergence of bacteria that extend beyond the tooth root. A cyst forms, due to which the tooth is often removed;
- tool fragments. The complex anatomy of the canals and low-quality instruments can lead to its failure.
- removal of material beyond the root apex. If the filling material is chosen incorrectly or there is too much of it, it extends beyond the root.
- Tooth perforation occurs due to aggressive processing.
To avoid such complications, doctors at the SDent clinic recommend contacting us for medical help, as we have a staff of highly qualified doctors, an equipped X-ray room and advanced equipment!
What causes complications?
After root canal filling, complications sometimes arise such as:
- the canals are sealed loosely, not completely (voids remain): re-treatment of the canals is required;
- broken instrument: during operation, the instrument may break off and remain in the canal (for example, in curved and curved canals);
- root perforation: when the tooth root is injured during work;
- removal of filling material beyond the root;
- repeated inflammation, when not the entire nerve was removed and the infection remained;
- bleeding from root canals.
Our Otradnoe Dental Center provides highly qualified dental care, including nerve removal, which is absolutely painless. Our doctors always conduct a thorough diagnosis and select appropriate treatment. Thanks to the extensive experience of our doctors, advanced equipment, and modern antiseptic solutions, treatment is carried out efficiently and without complications.