Diseases that provoke painful pulsation in the tooth
Suddenly got a toothache? At the appointment, the dentist usually diagnoses one of the following diseases.
Caries
First, with carious tooth decay, throbbing pain periodically occurs after eating hot/cold food, eating sweets or sour fruits. This means that the pathological process has reached the dentin (the tissue located under the tooth enamel). As the carious cavity deepens, the intensity of the pain increases, but after 10-15 minutes everything goes away without taking painkillers. If you do not consult a dentist in time, the dental crown will be completely destroyed very quickly. However, at this stage it is possible to save not only the tooth, but also avoid removing the nerve.
Important! Sometimes only a small hole is noticeable in the tooth enamel. However, the carious process spreads inside the tooth. A sign of deep caries (in addition to pain) is bad breath.
For caries, it is not recommended to put analgin into the tooth. This drug, although it effectively relieves pain, instantly destroys tooth enamel. It is impossible to save a tooth that is more than 2/3 destroyed.
Pulpitis
Inflammation of the pulp (neurovascular bundle) is a complication of deep caries. During the day, throbbing pain is quite tolerable, it occurs only after eating or inhaling cold air, and is easily relieved with painkillers. By nightfall the tooth begins to twitch.
The worst tactic for pulpitis is to drown out the pain with strong analgesics and again postpone going to the dentist in the morning. It makes no sense to endure pain day after day; in any case, the nerve will have to be removed. However, when the pulp is removed, the tooth stops receiving nutrition, the enamel and dentin become less dense.
Even a filled tooth with the nerve removed is short-lived. Therefore, we recommend that you contact the Matiss Dent dental clinic as soon as painful sensitivity to hot/cold occurs or a small dark spot appears on the enamel.
Periodontitis
If the infection penetrates deeper, a fibrous compaction or granuloma forms at the apex of the root. In this case, the pulsation is usually painless and intensifies when chewing food. The patient feels as if the tooth has lengthened.
With the development of a purulent process, a periapical abscess (cyst) is formed. The throbbing pain in the tooth increases (it jerks more and more), the gums swell, and painkillers only slightly ease the pain. Possible increase in temperature. Sometimes after a few days the abscess forms a white “bump” on the gum.
Important! Under no circumstances should you open a root cyst yourself. Any manipulations at home are fraught with the development of perimandibular abscess and sepsis.
Previously, the cyst was removed along with the tooth. However, modern dentistry makes it possible to preserve the root. The abscess is opened through the root canal (the capsule is scraped out with a curette or dissolved with special substances) or removed surgically in combination with antibiotics. The resulting cavity is filled with a paste that restores bone tissue. The tooth is built up using pins, then a crown is installed. An indicator of successful removal of a periapical abscess is that an x-ray taken 6 months later shows no evidence of new cyst formation.
Periodontitis
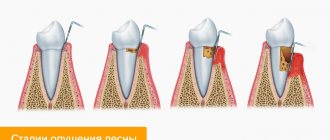
Inflammation of the periodontium (supporting apparatus of the teeth) is the most insidious dental disease. At the initial stage, the pathology is manifested only by increased bleeding of the gums after brushing teeth, eating carrots and other solid foods.
Over time, degenerative changes occur in the gums: the spaces between the crowns increase, the roots of the teeth become exposed, and a metallic taste is constantly felt in the mouth due to increased bleeding. Even brushing your teeth frequently does not eliminate bad breath. Later, the teeth begin to loosen, ache and throb even after eating soft food. The tissues around the tooth become inflamed, and pus and blood are released from the gum pockets. Body temperature often rises and general health worsens.
When bone tissue is involved in the pathological process, the only treatment method is surgery. After professional cleaning and removal of tartar, a flap operation (gum excision and subsequent plastic surgery) is performed. Implantation of bone tissue substitutes (osteoplasty) is often required.
Pericoronitis
Difficult teething provokes swelling and redness of the gums, painful pulsation, and discomfort when swallowing. Most often, a similar picture is observed during the eruption of wisdom teeth. Severe pain does not allow you to open your mouth wide and eat food calmly. Due to the accumulation of food debris under the “hood”, pus forms. You shouldn't endure pain. The dental surgeon will excise the “hood” in 5 minutes, which will ensure painless tooth eruption.
Other treatments
In 2022, there are additional ways for doctors to save people from troubles associated with pulp inflammation:
- laser therapy;
- complex of physiotherapeutic processes.
Both mentioned operations, in principle, can also answer the question of how to cure pulpitis without removing the nerve. True, they can only be used in the early stages, when the pathology has not yet had time to develop and acquire serious symptoms. In addition, to use such funds, a person will need to go to a truly modern and advanced clinic with an experienced medical team. For example, a set of works related to the use of a laser is carried out exclusively in the presence of high-quality, proven equipment. Such installations, of course, are present in dental departments.
Pulsating pain in a tooth can be caused by non-dental problems.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Unbearable, throbbing pain covers the teeth on one side (on the upper and lower jaws on the right or left). At the same time, half of the head hurts, “shoots” in the ear, eye and under the jaw. In severe cases, the tongue becomes temporarily numb, the patient complains of tingling of the face and twitching of facial muscles. The pain usually appears at night. During the day, an attack can be triggered by eating, talking, brushing your teeth, combing your hair, and even yawning. Without treatment, the patient's condition worsens due to the destruction of the protective myelin sheath of the nerve. If you have the slightest suspicion of trigeminal neuralgia, consult a neurologist.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Pulsation of teeth without pain may indicate a dysfunction of the liver, diseases of the stomach and intestines. Characteristic signs of gastrointestinal pathology are a coated tongue, bad breath and an unpleasant taste in the morning, abdominal pain, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea. After successful treatment of the underlying disease, discomfort in the mouth disappears.
Sinusitis
Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is manifested by prolonged nasal congestion, discharge of purulent mucus and headache. The patient breathes through his mouth, his face is puffy. Often, a nagging pain in the area of the maxillary sinuses radiates to the cheekbones and provokes pulsation in the teeth. An ENT doctor treats sinusitis.
Neuralgia and trigeminal neuritis
Neuritis and neuralgia are different diseases, although (as in the case of the trigeminal and facial nerves) some “specialists” combine them or replace one with the other. The main difference lies in the nature of their occurrence. Neuritis is always associated with an inflammatory process, hence its name: the ending -itis - from Lat. -itis always denotes inflammatory diseases. Neuralgia is irritation of the nerve as a result of concomitant diseases or exposure to external factors. Unlike neuritis, neuralgia does not cause changes in the structure of the nerve.
Most doctors consider neuritis to be a much more dangerous disease, since the inflammatory process affects the inner part of the nerve. At an advanced stage, the disease causes nerve damage and spreads to the auditory nerve, and can also lead to ataxia, a motor disorder. In this case, neuritis and neuralgia can occur together and have some similar symptoms. First of all, these are painful sensations, which, however, vary in nature and intensity.
Throbbing after dental procedures
Throbbing pain in a tooth can occur after the installation of a filling, tooth extraction, crown fixation and orthodontic treatment.
Throbbing pain occurred after tooth extraction
Painful sensations after the end of anesthesia and tooth extraction are a normal reaction of the body to a traumatic procedure. To eliminate “twitching”, painkillers are allowed in the first 1-2 days. The intensity of the pain gradually, the discomfort goes away within 3-4 days. After the removal of wisdom teeth and molars (6th, 7th and 8th teeth), the gums hurt and pulsate a little longer.
Increasing pain after removal of a dental unit may indicate the development of alveolitis. Inflammation of the dental socket develops due to the left fragment of granuloma (periodontitis) or root fragment. However, in most cases, alveolitis is caused by premature washing out of the blood clot and infection of the wound.
Important! It is prohibited to actively rinse your mouth after tooth extraction.
Tooth pulsates after filling
The dentist placed a nerve-killing drug into the root canal and installed a temporary filling. Do not panic if you experience throbbing pain from time to time for 3-4 days. However, if discomfort lasts longer, it is necessary to visit your dentist unscheduled. It is possible that the medication under the filling caused irritation to the surrounding soft tissue.
There may be several reasons for tooth pulsation under a permanent filling:
- insufficiently thorough cleaning of the carious cavity,
- poor quality filling installation,
- radiating pain from a neighboring tooth.
To exclude infection of the filled tooth and re-development of caries, it is necessary to take an x-ray.
Tooth pulsates after nerve removal
A filled tooth with a removed nerve should not hurt. The exception is when the dentist cleans out a root cyst and installs a temporary filling. After cementing the cystic cavity and filling the canals, the tooth may pulsate (without pain!) for several days.
If the pulpless tooth still begins to hurt, the dentist probably made a mistake and installed the filling unsealed. A slight painful pulsation will occur after eating. It is possible that the tooth was affected by periodontitis and a fibrous compaction formed on its root. In any case, if discomfort occurs after nerve removal, you should visit a dentist.
Important! To avoid negative consequences, before treating a dental cyst and removing a nerve at the Matiss Dent clinic, the patient is given an X-ray.
The tooth under the crown is pulsating
Painful pulsation after crown installation indicates that a medical error was made during prosthetics:
- tooth root infection occurs,
- the channel is poorly dried,
- the tooth is too ground and the crown does not fit tightly.
The crown will need to be removed, the tooth canal will need to be treated with an antiseptic again and a new prosthesis will be made.
Teeth pulsating under braces
Installation and tightening of braces, especially metal ones, often provokes pulsation in the gums. If the pain does not go away after a few hours, then the arch is too tight. Contact your treating orthodontist. The doctor will adjust the pressure of the braces on the teeth.
Chronic pulpitis
Chronic pulpitis occurs if acute pulpitis is not treated. At some stage, acute pain subsides, but destructive processes in the pulp continue. The infection lies dormant and makes itself felt by periodic “shots” in the presence of hot, cold, sour, and sweet foods. Pain occurs when pressing on a tooth. At any moment, acute inflammation may begin again or the disease may be aggravated by a new complication.
Chronic pulpitis also has several forms:
| Forms of chronic pulpitis | Main characteristics | Nature of pain |
| Fibrous | The pulp bleeds when pressed | Short-term pain, as a reaction to cold and hot. |
| Hypertrophic | Pulp growth, which can extend beyond the open carious cavity, bleeding when eating. | There is no pain, it does not hurt when tapped, there is no reaction to irritants. |
| Gangrenous | Pulp necrosis, tooth darkening, rotten smell. | Short-term pain, as a reaction to hot food. |
Pulpitis of the wisdom tooth
Pulpitis can affect all teeth without exception. But eighth wisdom teeth have an increased risk of pulpitis. They are located far away, it is difficult to clean and treat them, so inflammation of the pulp in third molars occurs more often. Treatment of pulpitis of eights is also complicated by their inconvenient location and numerous roots. The risk of complications during endodontic treatment increases and the long-term prognosis for these teeth worsens. So in the case of acute pulpitis of a wisdom tooth, it makes sense not to treat such a tooth, but to remove it immediately.
How to relieve toothache at home
If toothache is unbearable, medications can help relieve the pain.
- Ibuprofen (Mig-400, Nurofen) - reduces pain after 15 minutes, but does not last long.
- Ketorolac (Ketanov, Ketorol) - a pronounced and long-lasting analgesic effect develops 30-60 minutes after taking the tablet.
- Movalis (Meloxicam) - relieves pain and inflammation, but can cause a burning sensation in the stomach.
- Paracetamol is the safest drug from the NSAID group, approved for children and pregnant women.
- No-spa (Drotaverine) - an antispasmodic enhances the analgesic effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Spasmalgon, Baralgin - analgesics related to Analgin are used as an antispasmodic.
Important! Painkillers are taken strictly according to the instructions, observing the age-specific dosage and frequency of administration. If you do not have the above-mentioned drugs on hand, you can take regular aspirin.
Relief of throbbing pain with medications is supplemented with home remedies:
- cold compress on the cheek
- “mouth baths” (not active rinsing) with sage or chamomile infusions,
- rinsing the mouth with a soda-saline solution (1/3 tsp per glass of lukewarm water),
- apply a cotton wool moistened with eucalyptus oil to the gum,
- chew propolis.
Painkillers will only temporarily relieve pain. Remember that throbbing pain in a tooth is a sign of a disease that necessarily requires treatment. Do not delay your visit to the dentist - the longer the disease develops, the more difficult and expensive the treatment will be.
Sources used in writing the article:
- “Local anesthesia in outpatient dentistry”, Kononenko Yu. G., Rozhko N. M., Ruzin G. P.
- “Modern technologies of local anesthesia in dentistry”, Rabinovich S.A.
- “Emergency conditions in dental practice”, M. Panchishin, I. Got, 3. Masny
Please rate this article
Stanislav Mezheritsky
Chief physician, surgeon, orthopedist
The author of the article is Stanislav Mezheritsky, a practicing dentist with 19 years of experience, chief physician and one of the founders of the Matisse Dent clinic. The main focus is orthopedic and surgical dentistry. Author of numerous publications, regular participant in specialized seminars.
Prevention of pulpitis
The following rules will help to significantly reduce the risk of pulpitis, but they must be followed carefully:
- Treat all oral diseases in a timely manner, especially caries and gum disease.
- Pay close attention to your overall health and treat any infections as soon as they are identified.
- Brush your teeth well every day, and have your teeth professionally scaled by your dentist as needed.
- Attend routine preventive examinations at the dentist every six months. By the way, such examinations once every 6 months are free of charge.
- Treat your teeth in a reliable, trusted place to minimize medical errors and complications after treatment.
Why is pulp needed?
Pulp is a soft connective tissue that fills the internal cavity of the tooth. It ensures the supply of essential nutrients. The pulp contains many nerve endings, as well as blood and lymphatic vessels. This is where the perception of various sensations occurs. And pain too.
The pulp performs a plastic function, participating in the formation of dentin. And also protective, which consists in the disposal of dead cells, the formation of tertiary dentin and the synthesis of immunoglobulins. We are interested in its sensory function, which can be carried out thanks to a fairly large number of nerve fibers.
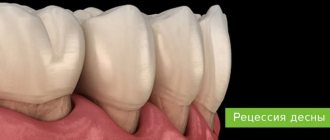
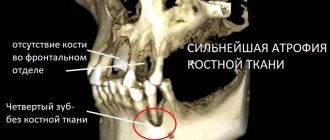
How to Avoid Gum Recession
In order not to expose the neck of the tooth, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, maintain proper nutrition, and carry out prophylaxis with a vitamin and mineral complex (with the doctor’s permission). In addition, regular dental care is recommended. This means not only hygiene, but also timely treatment.
If the neck of the tooth is exposed, you need to contact a qualified specialist at Dr. Sadov’s clinic, who will conduct an examination, prescribe an examination, on the basis of which a treatment plan will be drawn up. Self-medication is strictly prohibited. Use traditional methods only after consulting a doctor. Otherwise, the condition may only get worse.