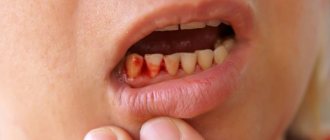
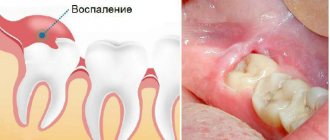
Bleeding gums in children and adults is a fairly common phenomenon. Someone will say that this is a small thing - bleeding from the gums. But this is not true; bleeding may be a sign of a serious oral disease or infectious pathology. If this is not the first time you have seen blood when brushing your or your child’s teeth, you should contact your dentist.
By the way, many girls and women’s gums begin to bleed during pregnancy. The main reason, as a rule, is hormonal changes in the body. 2-3 months after giving birth, the situation will change for the better, you will no longer feel the unpleasant taste of blood in your mouth.
Self-help: ways to stop bleeding
When blood bleeds for a long time after the removal of a wisdom tooth, it brings discomfort on a physical and emotional level. If you can't get to the dentist, use gauze swabs. Fold a small piece of bandage into several layers, apply it to the hole and bite firmly. Keep for 20 minutes. To disinfect, you can soak a swab in hydrogen peroxide. Bleeding after wisdom tooth removal can be stopped by this method both day and night. Another option is to use ice. Apply to your cheek and apply for 5 minutes with short pauses. If the patient has a history of hypertension, a high blood pressure pill should be taken.
Causes
The most common factors that lead to bleeding gums are:
- Improper oral hygiene:
using a brush with hard bristles, strong pressure when brushing, inaccurate use of dental floss, picking with toothpicks and other objects, improper installation of dentures. Due to frequent trauma, gum pockets form, which provoke inflammation.
- Tartar.
With irregular and improper brushing of teeth, plaque forms, which gradually hardens. The stone moves the gum away from the tooth, the tissue becomes inflamed and begins to bleed.
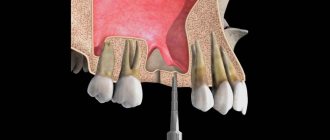
- Dental procedures.
Bleeding may occur after professional cleaning, tooth extraction, or the installation of a filling or implant. A poorly manufactured or fitted structure constantly injures the edge of the gum. In addition, filling material and dentures can cause an allergic reaction.
- Diseases of gums and teeth:
gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease. Inflammatory processes are accompanied by swelling, swelling, exposure of the neck, abrasion and loosening of teeth.
- Infections and viruses.
Herpes, fungus, tonsillitis, influenza, ARVI, tuberculosis, HIV lead to the destruction of the periodontal structure and provoke inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
- Hypovitaminosis.
Bleeding from the gums occurs when there is a deficiency of vitamins B, K, C, E. A monotonous and unbalanced diet, frequent diets, and inducing vomiting lead to pathology. With a lack of vitamin C, scurvy can develop. During the disease, teeth become loose and begin to fall out.
- Hormonal disbalance.
The problem is observed during pregnancy and puberty, with diabetes. Due to an imbalance of biologically active substances, tissues swell and become looser. In this case, bleeding from the gums occurs not only when brushing teeth and eating solid food, but also from the slightest touch.
- Taking a number of medications.
Blood thinners, including Aspirin, Heparin, and Warfarin, can lead to the problem. Some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have similar side effects.
- Blood diseases.
Bleeding disorders often lead to gum pathology: hemophilia, thrombocytopenia. The condition of the mucous membranes also worsens with tumor processes - leukemia and leukemia.
First aid for venous bleeding
Blood clots that are bleeding from a vein should not be removed, as this may cause even greater blood loss. As first aid, apply a pressure aseptic bandage made of a strong bandage or fabric. If this method is ineffective, it is recommended to use a tourniquet. Under it, in order to avoid unwanted injury to the skin, there should be cotton wool or other soft material and a note with the time of application. The maximum duration of stay of the tourniquet on the victim’s body is 1 hour in the cold season (winter, autumn) and 2 hours in the warm season. If this time frame is exceeded, there is a risk of tissue anesthesia. Instead of a tourniquet, you can use various available materials - tight belts, ties, short sticks with fabric, twisted towels, etc.
[td]
Attention! Vaccination against COVID-19 is underway
PATIENT REMINDER about vaccination against COVID-19
- About the hospital Information about JSCB
- Information about separate structures. subsection BTsRP
- Sergeevskaya medical outpatient clinic
- Volkovskaya medical outpatient clinic
- Novopetrovsk medical outpatient clinic
- Therapy departments Admission department
- Ophthalmology department
- Department of Ultrasound Diagnostics
- Centers
Center for Family Health and Reproduction - Perinatal center
- Regional Vascular Center
- Territorial Center for Disaster Medicine
- Occupational Pathology Center
- Anti-rabies assistance center
- Medical center rehabilitation
- Adult clinic
- Blagoveshchensk Central District Clinic
- Schedule of reception of citizens by the administration
- Regulatory framework
- Organizations that control activities
- Price lists
- Paid or free?
- Territorial state program guarantees
- for the 2nd half of 2016
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases How to suspect a heart attack?
- How to prevent a stroke?
- How to protect yourself from infection?
- Encephalitis and prevention measures
- 10 reasons to quit smoking
- World Blood Donor Day
- How to protect a child from burns?
- Can a computer cause allergies?
- Preventing diabetes
- Tuberculosis
- Leave feedback
- Procedures for providing medical services. help
- No. 45-Yubileiny
- JSCB documents
- Controlling organizations
- JSCB
Symptoms accompanying gum disease
Pathologies that cause blood from the mouth may be accompanied by a number of other unpleasant symptoms:
- swelling of the gums;
- pain when pressing or eating solid foods (sometimes the pain is quite severe);
- itching and discomfort in the gum tissue;
- bad breath;
- tooth mobility (with advanced dental diseases).
Even if nothing bothers you throughout the day, and blood appears only when brushing your teeth, this may indicate a problem.
Preventive measures
To avoid gum problems, you must follow a number of simple rules:
- Perform high-quality and correct hygiene procedures aimed at oral health. It is necessary to select care products that will not injure the mucous membrane. You should brush your teeth morning and evening. Use dental floss with caution. Instead, you can use an irrigator, which will help effectively remove food debris. Your toothbrush should be changed every three months.
- Balance your diet. The body must receive all the necessary vitamins and minerals. To strengthen teeth and gums, it is important to eat solid plant foods, such as apples and carrots.
- Give up bad habits, in particular smoking. Toothpicks should be used with caution.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations at the dentist - at least twice a year. This will allow timely detection of oral diseases.
Paying close attention to your oral health will help you maintain a beautiful and healthy smile for many years.
Types and signs of external bleeding
Methods to stop bleeding largely depend on their location. Each type has its own external manifestations, to which you need to react in time:
- capillary bleeding - occurs due to damage to small vessels as a result of injury or illness. It manifests itself first in the form of blood dew, and then as a slow flow of blood beyond the skin. This condition can be especially dangerous for people with bleeding disorders;
- internal (parenchymal) bleeding is a rather dangerous condition observed as a result of damage to internal organs that have a large blood supply network (spleen, liver, kidneys);
- arterial bleeding is the result of damage to the aorta, femoral and other arteries and manifests itself in the form of a stream of bright scarlet color with pulsation. The danger of such blood loss is its rapid nature, and therefore the timeliness of assistance in fractions of a second plays a vital role in avoiding death caused by damage to the main artery;
- venous bleeding is the slowest. The blood flows out thick, dark burgundy in color, and clots may form. Bleeding from a damaged vein is dangerous due to the detachment of a blood clot, significant loss of blood, or the entry of air bubbles into a pulmonary vessel.