From this article you will learn:
- How much can you not eat after tooth extraction?
- what antibiotics and rinses to use,
- How long after you can smoke after tooth extraction?
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
If you have just had a tooth removed, it is very important to know what to do after tooth extraction. This will prevent complications that often arise as a result of patient behavior errors (inflammation of the socket, development of bleeding or swelling of the soft tissues of the face). And I will try to summarize my experience accumulated over many years of work as a dental surgeon in this article.
The most common mistake is that patients rinse their mouth too much, which leads to the blood clot falling out of the socket. As a result, we will get inflammation of the socket of the extracted tooth - alveolitis of the socket. Either the patient took aspirin before or after tooth extraction (without thinking that aspirin thins the blood) and, accordingly, in this case we will have a high risk of bleeding and hematoma formation.
Tooth extraction: photo
Also at the end of the article you will be able to see what the sockets of extracted teeth should normally look like (at different times after extraction). This will help you decide if you need to re-examine with your dental surgeon.
What to do with a gauze swab -
A tooth was removed today: what to do after removal with a gauze swab on the socket... A swab soaked in blood is an excellent breeding ground for infection. And the longer you keep it in the mouth, the greater the risk of developing inflammation in the socket of the extracted tooth. If you still have a gauze swab on your socket, you need to remove it urgently. It is advisable to do this without jerking and not strictly vertically, but sideways (so as not to pull out the blood clot from the hole along with the tampon).
An exception may be a situation where the hole is still being touched up - in this case, the gauze swab can be held for a little longer. But it’s best to spit out this old gauze swab soaked in saliva and blood, make a new one from a sterile bandage, and place it on top of the hole (biting firmly).
Important: saliva at first may normally turn pink due to the secretion of ichor (this should not be confused with bleeding). At the same time, it is not clear why many patients stop swallowing saliva and accumulate it in the oral cavity. There is absolutely no need to do the latter; saliva can be swallowed as usual.
How soon can you eat after tooth extraction?
Most often, patients are interested in when they can eat after tooth extraction and what food is best to eat. You can safely eat after 2 hours, but on the same side (where the tooth was removed) it is not advisable to chew anything dense or hard in the first days after extraction. This is necessary in order not to injure the fresh blood clot in the socket of the extracted tooth.
You can drink water immediately after tooth extraction. As for food, if you still can’t wait 2 hours, then you can absolutely safely drink a glass of kefir or eat yogurt right away. In general, there is no ban on any specific foods; it is only necessary that the prepared food be soft in the first days (for example, if there is meat, then it must be cured).
What should the patient do after the procedure?
After the procedure has been completed, the specialist must carefully explain to the patient his next steps, as well as the rules for caring for the wound during the healing period.
- The turunda or cotton wool that was left by the surgeon in the hole does not need to be removed by yourself. If the tampon placed by the doctor falls out ahead of schedule, the patient must return to the specialist to install a new turunda. If this is not done, an infection may enter the wound cavity.
You shouldn’t remove turunda with medicine yourself
- If after the procedure the cheek is very swollen, you can apply ice or a cold compress to it. After this procedure, it is forbidden to heat the affected area and apply hot compresses.
- You can eat food after tooth extraction only two hours after the procedure. It is recommended to eat only liquid and light foods that do not contain solid pieces.
- A blood clot forms in the hole where the tooth was pulled out. It is prohibited to remove it or touch it. The first time after the procedure, you must brush your teeth with caution and do not use any rinses.
- For 7 days after tooth extraction, it is prohibited to carry out other interventions in the oral cavity.
- During the healing period, it is not recommended to overheat, for example, take a steam bath, and also exercise with caution. It is also strongly recommended to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking cigarettes for two days after the procedure.
- After tooth extraction, pain often occurs at the extraction site. In this case, quite often not only the hole, but the whole head as a whole can hurt. Also, the patient may experience pain while eating, regardless of which side of the teeth he chews on. Experts recommend coping with these problems with the help of painkillers, such as Pentalgin or Tempalgin. In this case, it is advisable to take the drug in combination with Suprastin.
To relieve pain, you can take painkillers
Despite the fact that there is medicine in the hole, a person may still feel pain and some burning. Such unpleasant sensations will have to be ignored.
Important ! If the sensations intensify, it is recommended to consult a doctor again so that he can examine the wound and, if necessary, take action.
Video - Briefly about iodoform turundas
Apply cold to prevent swelling -
What to do after tooth extraction to prevent the development of swelling... As soon as you come home, your first actions are to take ice or a piece of frozen meat from the freezer, wrap it in a towel and apply it to your cheek in the projection of the extracted tooth (24stoma.ru). This is necessary to avoid or reduce possible swelling of the soft tissues of the face that may develop (especially if the removal was difficult).
It is necessary to hold the ice 3-4 times for 5 minutes, with an interval of 5-10 minutes between each approach. It makes sense to keep ice only in the first hours after removal, then it is useless. But heating and applying heat is strictly forbidden, because... In this case, suppuration is guaranteed.
Important: if you want to avoid the development of swelling of the soft tissues of the face as much as possible, then in addition to using cold, be sure to take antihistamines (anti-allergic) medications in the first 2-3 days after removal. This group of drugs also has a good anti-edematous effect. Suprastin is especially suitable: 1 tablet per day before bed (for 2-3 days).
Manufacturing
To make a turunda, sterile gauze wipes, screws, and cotton wool are used. It is important to observe the proportions of dilution of the impregnation product and the choice of composition. For preparation, medicinal ether is used in the proportion of ten parts of ether to one part of iodoform.
The finished solution is not stored; it quickly loses its properties. therefore, the doctor makes the amount that will be sufficient for use during one appointment.
To make turunda, a piece of gauze is cut into thin ribbons. The length of each depends on the characteristics of the hole; impregnation is carried out before use. Additional medications are used if an anti-inflammatory, therapeutic effect is required.
Is it possible to drink alcohol after tooth extraction?
Due to the stress they have experienced, many patients separately ask whether it is possible to drink alcohol after tooth extraction. In general, drinking alcohol is contraindicated during the first 24 hours after removal, but if the doctor has prescribed antibiotics, then alcohol should not be taken during the entire course of antibiotic therapy (i.e. 5-7 days).
If antibiotics were not prescribed, then, of course, a small amount of weak alcohol is unlikely to cause any consequences. But large doses can lead to the fact that the hole may begin to bleed again, or a hematoma may appear.
How long does it take for a hole to heal?
The wound left after tooth extraction has a certain healing pattern.
- After the tooth extraction procedure is completed, the circular ligament located around the crown of the extracted tooth begins to contract.
- A short amount of time after the procedure, you may notice an accumulation of blood in the hole. The resulting clot helps protect the wound from infection or small food particles. Over time, the hole begins to become overgrown with fibrous tissue.
- After a certain amount of time, which depends on the characteristics of the human body, as well as on the correct care of the hole after the procedure, the surface of the wound heals and the affected area of the gum is restored.
- After this, over time, new epithelium grows on the surface of the gum, as well as the development of bone tissue at the site of tooth extraction.
The hole will heal after two to three weeks
Important ! The normal healing of the hole is facilitated by the medicine that is placed in the hole. Without it, the wound will not heal.
Many patients worry about the healing of the wound that remains after tooth extraction. The doctor must explain to the patient that the wound can heal completely only after two or three weeks, provided that all care rules are followed. If they were nevertheless broken or an infection was still able to penetrate the wound, then with repeated disinfection, complete restoration of the affected area will occur in five months.
What is allowed during the healing period?
- Non-solid semi-liquid food.
- Gentle oral hygiene.
What is prohibited during the healing period?
- Drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes.
- Drinking liquids with a plastic straw.
- Harsh brushing of teeth in general and especially in the healing area.
- Eating dry and solid food.
- Sudden movements of the cheekbones for one week after the procedure.
During the healing period of the hole, you should not eat solid food.
What not to do after tooth extraction -
What absolutely cannot be done after tooth extraction...
- for the first 1-2 days, you should not take a hot bath (a warm shower is fine), or sleep lying on the side of the extracted tooth - all this will contribute to the appearance of swelling,
- visit the pool or sauna during the week,
- engage in heavy labor (to avoid bleeding),
- picking at the wound with foreign objects, tongue,
- open your mouth wide and make active facial movements, because if stitches were placed, they may come apart,
- do not take aspirin as a pain reliever (it thins the blood and thereby promotes bleeding and bruising),
- You should not rinse your mouth intensively in the first 2-3 days, because intensive rinsing can lead to a blood clot falling out of the socket (this will certainly lead to its inflammation).
About the medicine
The medicine that is placed in the hole can be applied to a piece of gauze, which is subsequently inserted into the hole. In this case, after a certain amount of time indicated by the doctor, it needs to be taken out. This can be done either independently or during your next visit to the dentist. If this is not done in time, the process of putrefaction may begin, which will greatly complicate the situation. It is also not recommended to take out the gauze ahead of time, since food particles can get into the hole and the tongue can touch it, which will interrupt the healing process and also cause complications.
There is another way to install the medicine - in a hemostatic sponge. It already contains a medicine that helps disinfect the socket cavity and helps stop bleeding. You cannot take this sponge out - it will dissolve on its own. Most often this happens within 1-2 days, but in some cases the sponge may remain in the hole for 5-6 days. There is no need to be afraid of this. As a last resort, you can consult a doctor who will examine the wound and determine whether healing is proceeding normally.
Often the medicine in the sponge is very bitter, and this causes severe discomfort to the person. Unfortunately, nothing can be done about this, since getting rid of the sponge ahead of time is strictly contraindicated. To eliminate bitterness, you can drink sweet tea or juice.
Remember ! No circumstances can influence the ability to remove the medicine from the hole ahead of time. After 3-4 days, the surface of the hole will heal, and you will no longer have to experience discomfort.
People often wonder what kind of medicine is used for these purposes. Sometimes the gauze that is placed in the hole is treated with iodine - this will both disinfect the wound and prevent bleeding. The hemostatic sponge is already treated with a special substance consisting of boric acid, collagen and nitrofural, which helps stop the bleeding and protect the hole from various influences. But most often dentists use Alvozhil.
No other means are used for inserting into the hole.
Painkillers –
If the extraction was simple, you may not need pain relief after tooth extraction. But if you want to completely prevent the appearance of pain, then it is better to take a strong tablet analgesic even before the anesthesia wears off (which one is better to choose - see the link, but remember that after removal you cannot take aspirin).
Sometimes the pain is very severe. As a rule, this happens if the removal was performed by a doctor in a very traumatic way or if inactive bone fragments were left behind. The pain is most severe when the doctor used a drill to drill out the bone, and water cooling was not used (this leads to necrosis of bone tissue as a result of overheating).
Important: numerous studies show that the severity of pain after tooth extraction is reduced by an average of 30-50% if the doctor places sutures on the socket of the extracted tooth. In addition, bringing the edges of the mucous membrane together by applying sutures helps protect the blood clot from loss and injury, sharply reduces the risk of developing inflammation of the socket, and almost completely eliminates the occurrence of bleeding.
After a simple simple extraction, most dental surgeons very rarely use sutures. I can recommend for the future - always before removal, ask your surgeon to put 1-2 stitches on you, even if the removal is simple, and even if you have to pay an extra 300-400 rubles for it. As a rule, sutures do not have to be removed (they dissolve on their own), but they will reduce pain and reduce the risk of complications.
Local complications arising after tooth extraction surgery.
Bleeding
Tooth extraction, like any other operation, may be accompanied by bleeding. After a few minutes, the blood in the hole coagulates and the bleeding stops. However, in some cases it does not stop on its own and continues for a long time (primary bleeding). Sometimes the bleeding stops within the usual time frame, but after some time it appears again (secondary bleeding). Prolonged bleeding is most often caused by local causes, less often by general ones.
Local reasons.
Bleeding can occur after tooth extraction when an acute inflammatory process has developed in the surrounding tissues, since the vessels in them are dilated and do not collapse. Late secondary bleeding from the socket occurs a few days after tooth extraction. It is caused by the development of the inflammatory process in the wound and purulent melting of the organizing blood clots in the vessels damaged during surgery.
Common reasons
. Prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction occurs in diseases characterized by impaired blood clotting or damage to the vascular system. These include hemorrhagic diathesis: hemophilia, thrombocytopenic purpura (Werlhof's disease), hemorrhagic vasculitis, hemorrhagic angiomatosis (Ren-du-Osler's disease), angiohemophilia (Von Willebrand's disease), C-vitaminosis; diseases accompanied by hemorrhagic symptoms (acute leukemia, infectious hepatitis, septic endocarditis, typhus and typhoid fever, scarlet fever, etc.).
The blood clotting process is disrupted in patients receiving indirect anticoagulants that suppress the function of prothrombin formation by the liver (neodicoumarin, phenylin, syncumar), as well as in case of an overdose of the direct anticoagulant - heparin. A tendency to bleeding is observed in patients suffering from hypertension.
Local methods to stop bleeding.
The blood clot is removed with tweezers and a surgical spoon, and the socket and surrounding areas of the alveolar process are dried with gauze swabs. After examining the wound, determine the cause of bleeding, its nature and location.
To stop bleeding from the hole, tamponade is performed using various means. The simplest and most accessible method is tight tamponade with iodoform turunda. After removing the blood clot, the hole is irrigated with a solution of hydrogen peroxide and dried with gauze swabs. Then they take an iodoform turunda 0.5-0.75 cm wide and begin to tamponate the hole from its bottom. Pressing and folding the turunda tightly, gradually fill the hole to the brim (Fig. 6.24). If bleeding occurs after the removal of a multi-rooted tooth, the hole of each root is tamponed separately.
To bring the edges of the wound closer together and hold the turunda in the hole, sutures are placed on top of it, retreating from the edge of the gum by 0.5-0.75 cm. Removing the gurunda prematurely may lead to re-bleeding.
In addition to iodoform turunda, the hole can be tamponed with absorbable biological hemostatic drugs (hemostatic sponge, fibrin film, hemostatic collagen sponge, gelatin sponge “Krovostan”, antiseptic sponge with gentamicin or kanamycin, hemostatic sponge with Ambien). In case of late secondary bleeding, the disintegrated blood clot is removed from the socket, irrigated with an antiseptic solution, dried and filled with some hemostatic drug. In these cases, it is preferable to use an antiseptic sponge with kanamycin or gentamicin, which has hemostatic and antimicrobial properties.
General methods to stop bleeding.
At the same time as stopping bleeding, agents that increase blood clotting are used using local methods. They are prescribed after determining the state of the coagulation and anti-coagulation systems of the blood (detailed coagulogram). In emergency cases, before obtaining a coagulogram, 10 ml of a 10% calcium chloride solution or 10 ml of a 10% calcium gluconag solution, or 10 ml of a 1% Ambien solution are administered intravenously. Simultaneously with these drugs, 2-4 ml of a 5% solution of ascorbic acid is administered intravenously.
Prevention of bleeding.
Before tooth extraction, it is necessary to find out whether the patient has had prolonged bleeding after accidental tissue damage and previous operations. If there is a tendency to bleeding, before surgery, a general blood test is performed, the number of platelets, blood clotting time and duration of bleeding are determined, and a detailed coagulogram is drawn up. If hemostasis parameters deviate from the physiological norm, measures are taken to increase the functional activity of the blood coagulation system, and the patient is consulted by a hematologist or therapist. For patients with blood disease, teeth are removed in a hospital setting. They are prepared for surgery together with a hematologist.
Socket postoperative pain
After tooth extraction and the cessation of the anesthetic, slight pain occurs in the wound, the severity of which depends on the nature of the injury. Painful sensations most often pass quickly. However, sometimes 1-3 days after the operation a sharp pain appears in the area of the socket of the extracted tooth. Patients do not sleep at night, take analgesics, but the pain does not stop. Such acute pain is most often a consequence of disruption of the normal healing process of the tooth socket and the development of inflammation in it - alveolitis.
Alveolitis
- inflammation of the walls of the socket - often develops after a traumatic operation that reduces the protective properties of tissues. The cause of alveolitis can be an infection in the socket when a tooth is removed due to acute and aggravated chronic periodontitis or complicated periodontitis. A predisposing factor is a decrease in the general immunological reactivity of the patient’s body in old age and under the influence of previous common diseases. Clinical picture. In the initial stage of alveolitis, an intermittent aching pain appears in the socket, which intensifies while eating. The general condition of the patient is not disturbed, body temperature is normal. The tooth socket is only partially filled with a loose, disintegrating blood clot. In some cases, there is no clot in it at all. The hole contains food debris, saliva, and its walls are exposed. The mucous membrane of the gum edge is red, touching it in this place is painful. With further development of the inflammatory process, the pain intensifies, becomes constant, and radiates to the ear, temple, and the corresponding half of the head. The patient's general condition worsens, malaise and low-grade body temperature appear. Eating is difficult due to pain. The tooth socket contains the remains of a disintegrated blood clot, its walls are covered with a gray coating with an unpleasant putrefactive odor. The mucous membrane around the hole is hyperemic, swollen, and painful on palpation. The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and painful. Sometimes there is slight swelling of the soft tissues of the face. In turn, alveolitis can cause a number of complications: periostitis and osteomyelitis of the jaw, abscess, phlegmon, lymphadenitis.
Treatment.
After local anesthesia or anesthetic blockade with lincomycin has been performed, the wound is treated. Using a syringe with a blunt needle, a stream of warm antiseptic solution (hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin, chlorhexidine, ethacridine lactate, potassium permanganate) is used to wash out particles of a disintegrated blood clot, food, and saliva from the tooth socket. Then, using a sharp surgical spoon, carefully (so as not to injure the walls of the socket and cause bleeding) the remains of the decomposed blood clot, granulation tissue, bone fragments, and teeth are removed from it. After this, the hole is again treated with an antiseptic solution, dried with a gauze swab, powdered with anesthetic powder and covered with a bandage. The bandage protects the socket from mechanical, chemical and biological irritants.
In the initial stage of alveolitis, after such treatment, pain in the socket does not recur. The inflammatory process stops after 2-3 days.
Sharp edges of the alveoli.
Socket pain can be caused by protruding sharp edges of the socket, which injure the mucous membrane located above them. Sharp edges of the alveoli most often form after the removal of several adjacent teeth or a single tooth (due to bone atrophy in adjacent areas). Pain appears 1-2 days after tooth extraction, when the edges of the gums above the socket begin to approach each other. Bone protrusions injure the gum mucosa located above them, irritating the nerve endings located in it. The pain intensifies during chewing and when touching the gums. This pain can be distinguished from the pain of alveolitis by the absence of inflammation in the socket area and the presence of an organizing blood clot in it. When you feel the hole with your finger, a protruding sharp edge of the bone is detected, and a sharp pain occurs.
To eliminate pain, an alveolectomy is performed, during which the sharp edges of the socket are removed (Fig. 6.25).
Antiseptic rinses/baths –
Remember that you should not rinse your mouth vigorously during the first few days after removal, because... you can easily rinse the blood clot out of the socket. Food will constantly accumulate in a hole without a clot and rot there, causing inflammation and pain. It is better to replace rinses with baths (pour an antiseptic solution into your mouth, hold it and spit it out, or lightly “squelch” it).
When are antiseptic baths necessary?
- if the tooth was removed due to inflammation,
- an incision was made on the gum to expose the gumboil,
- if you have teeth with untreated caries or dental plaque, infection in which can lead to suppuration of a blood clot.
Antiseptic baths are best done with an aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine 0.05-0.12%. This drug has a pronounced antiseptic effect and is slightly bitter in taste. Baths should be done 3 times a day (keep the solution in your mouth for about 1 minute each time).
What painkillers can be taken in the postoperative period?
Most often, when local anesthesia wears off after a tooth extraction procedure, the patient feels pain in the area of intervention. The best way to eliminate pain is to take NSAIDs. This group of drugs is the most effective in eliminating toothache.
- The drugs "Nurofen" or "Ibuprofen" cope well with pain after surgery. It is necessary to take the drug 500-800 mg three to four times a day, depending on the intensity of the pain.
- "Ketorol" is one of the most effective and powerful drugs from the NSAID group, which can eliminate pain after the procedure in a fairly short time. It is also used two tablets three to four times throughout the day.
Antibiotics after tooth extraction –
Antibiotics after tooth extraction should be prescribed by a dental surgeon and not taken independently. An antibiotic for tooth extraction is always prescribed in situations where -
- the tooth was removed due to inflammation,
- it was difficult to remove
- there is a risk of complications.
Amoxiclav after tooth extraction is one of the most effective and popular drugs among dental surgeons, because it has affinity for bone tissue. Adults need Amoxiclav 625 mg (each tablet contains amoxicillin 500 mg and clavulanic acid 125 mg). The drug is taken 2 times a day for 5 to 7 days. But we DO NOT RECOMMEND taking this drug, because... immediately in 10-25% of patients - it causes antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Follow the link above to read a review article on the use of antibiotics in dentistry.
Reduce the risk of developing diarrhea when taking Amoxiclav or Augmentin - if you combine it with taking Metronidazole (Trichopol). This combination is not only safer in terms of diarrhea, but also significantly enhances the antibacterial effect. The antibiotic Metronidazole is especially effective against anaerobic bacteria and protozoa, which are especially numerous in chronic purulent inflammation (for example, in the area of the roots of teeth), while Amoxiclav and Augmentin do not have a clinically significant effect on protozoa.
But the risk of diarrhea will be lowest when using fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Among the antibiotics of this group, we especially highlight the combination drugs “Tsiprolet-A” or “Tsifran-ST”, which in addition to 500 mg of ciprofloxacin also contain 600 mg of tinidazole. Fluoroquinolones themselves cause diarrhea in only 1-2% of cases, but the above drugs also contain tinidazole (an analogue of metronidazole). Tinidazole also has antiprotozoal activity, i.e. it will be effective against anaerobic microorganisms, including Clostridium difficile and Clostridium perfringens, which are responsible for the development of diarrhea while taking antibiotics,
Important: because These antibiotics are not cheap - as an alternative, we will also indicate such a drug as the usual “Tsiprolet”, which contains only ciprofloxacin (without tinidazole). This antibiotic costs only 90 rubles per pack, but it is slightly less effective for purulent inflammation than the antibiotics Tsiprolet-A or Tsifran-ST.
Another antibiotic that everyone knows about is Lincomycin 0.25 (taken 2 capsules 3 times a day, usually 5 days). This is an inexpensive, moderately effective drug, but it kills all life in the intestines due to poor bioavailability (only 30% of the drug is absorbed from the intestines if taken on an empty stomach, and only 6% when taken with food). Therefore, it may turn out that, having bought a cheap antibiotic, you will then have to “expensively” restore the intestinal microflora.
How to reduce the risk of diarrhea after taking antibiotics -
Of course, parallel intake of probiotics (i.e., drugs that contain bacteria beneficial to our intestines) can help you with this. There are a large number of probiotics, but the best of them are Linex and Bifiform. Keep in mind that it is better to choose multicomponent preparations that contain several types of beneficial bacteria. Probiotics may contain lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, enterococci, and their combinations.
Probiotic Bifiform (30 capsules) –
Auxiliary medications for tooth extraction
If, after the tooth is removed, any complications begin at the intervention site, then modern pharmaceuticals can cope with them. With the help of various medications, the patient can not only eliminate the resulting secondary complications, but also strengthen his immunity as a whole. Quite often, specialists, to ensure against possible complications, in particular, various inflammations and suppurations, prescribe antibacterial drugs in the postoperative period. At the same time, the patient also needs to strengthen the immune system, which will help the wound heal faster. To do this, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes to the patient. Thus, in addition to the medicine placed in the hole and affecting its healing, the patient is recommended to take other drugs to speed up the process.
If during the procedure the patient was identified with any peculiarities or complications and tooth extraction was not without additional trauma, then a number of medications are prescribed in the postoperative period, since in this case there are additional risks of complications. The main thing is that the patient treats the postoperative period responsibly and does not neglect the doctor’s advice and the medications prescribed to him.
Important ! According to statistics, every third patient who has had a tooth removed needs to take antibiotics.
If there is blood coming from the hole -
There are several effective methods to stop bleeding.
Most often, the wound bleeds in people who have high blood pressure (hypertension). However, a rise in blood pressure can be triggered in completely healthy people due to psychological stress. The first thing to do is to apply a tightly twisted swab of sterile bandage to the wound, and then immediately measure the pressure. And if it is elevated, take the appropriate drug. For more information on how to stop bleeding, read the article: → “How to stop bleeding from a tooth socket at home”
If you have high blood pressure -
If you regularly measure your blood pressure, if it is higher than normal, take the appropriate medication. Otherwise, there is a very high risk of bleeding or hematoma formation. The first can lead to weakness and dizziness, and the formation of a hematoma is fraught with its suppuration and the need to open it.
If you have diabetes -
If you have a device for determining blood sugar, it is advisable to immediately measure your sugar. The stress of removal contributes to the release of adrenaline, the concentration of which largely determines blood sugar levels. This will help you prevent feeling unwell.
Removing sutures after removal –
After tooth extraction, the sutures are usually removed no later than 7-8 days. However, removal of sutures may not be necessary if, for example, catgut is used as a suture material. This material dissolves on its own within 10 days. When you see that the seams are very loose, you can simply remove them with clean fingers.
Treatment of teeth after extraction –
It is advisable to continue treatment after tooth extraction no earlier than 7 days later. If the removal was difficult, then sometimes it may take up to 14 days. This is due to the fact that carious teeth contain a lot of pathogenic infection, which, when drilling a tooth, can easily get into a blood clot and lead to suppuration.
Prevention
There are a number of actions that the patient must take immediately after this procedure and which will allow him to prevent possible complications.
- After the extraction, the patient needs to tightly compress the dentition. This is necessary in order to press firmly on the tampon placed in the wound.
- The medicine should not be removed by yourself.
- The hole should not be touched with your tongue or fingers. This is necessary so as not to accidentally damage the blood clot that has formed in the wound.
- If the patient experiences unbearable pain, it can be relieved with the help of analgesics that were recommended by a specialist. The dosage should also be prescribed by the doctor, since each patient reacts individually to the tooth extraction procedure.
- During the period until the wound is completely healed, the patient should stop smoking. This process greatly interferes with the normal healing of the hole.
- If the patient detects symptoms of complications, then, without delay, he should consult a dentist.
The patient needs to be aware of symptoms that may indicate the occurrence of suppuration or any other complications. Having noticed any of the signs, the patient should immediately contact a specialist for advice and subsequent treatment. We must not forget that only proper maintenance of oral hygiene and compliance with all the necessary rules will help the wound heal much faster. You will find out the proportions of soda solution for rinsing teeth in the article.
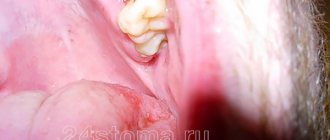
What should a socket of an extracted tooth normally look like?
As you will see below, the blood clot after tooth extraction first has an intense burgundy color. Gradually, the surface of the clot becomes whitish/yellowish (this is normal, because fibrin effusion occurs). Normally, the blood clot should be dense the next day. If the clot becomes loose, this means it has disintegrated, and you should familiarize yourself with the symptoms of inflammation of the socket in order to consult a doctor in time.
What does the gum look like after tooth extraction (normal) –
Oral care after tooth extraction –
The oral cavity requires careful care after tooth extraction. Teeth should be brushed as usual, including the group of teeth in the area of the extracted tooth. The latter are simply cleaned more carefully so as not to injure the blood clot. You also need to carefully rinse your mouth from foam so as not to rinse the clot out of the hole.
You also need to care for your gums after tooth extraction (antiseptic baths, which we described above, are sufficient for this). But the lack of proper hygiene will cause the accumulation of soft microbial plaque, which is fraught with suppuration of the hole and the development of alveolitis. We hope that the article on the topic: Tooth pulled out, what to do - was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.), 5. “Propaedeutics of surgical dentistry” (Soloviev M.).
How is the affected tooth removed?
The procedure itself should only be performed by an experienced surgeon and only when other treatment methods can no longer help. There are a number of reasons that can trigger the removal of an affected tooth:
- if the crown of the tooth is completely destroyed;
- when the patient is indicated for prosthetics;
- if complications arise during the eruption of a wisdom tooth;
- if filling requires perforation of the root canal.
Important ! There are cases when there is every reason to remove a tooth, but the patient has contraindications to this. In such cases, most often the intervention is carried out within the walls of a hospital with subsequent monitoring of the patient’s condition.
There are a number of main contraindications to surgical tooth extraction. These include:
- previous heart attacks;
- high blood pressure;
- arrhythmia;
- blood diseases;
- mental problems or neurological diseases.
If no contraindications have been identified in a patient who needs surgical removal of the affected tooth, then he is referred to the procedure itself, which should be carried out according to the following scheme.
| Stage | Description |
| Visit doctor | Before performing the procedure, the doctor must find out whether the patient has allergic reactions to any anesthetics, cardiovascular pathologies, or whether the patient suffers from hypertension. |
| Anesthesia | After all the necessary information has been obtained, the patient is sent for anesthesia. A fairly large number of different means are currently used to remove teeth. Their duration of action is from forty minutes to three hours. |
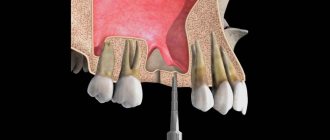
| Preparation | Next comes preparation for the intervention itself: in order not to injure the gum during manipulation, it first peels off from the tooth bone by at least five millimeters. This procedure is carried out using a special tool. The surgeon places special forceps on the tooth, and then begins to swing the tooth itself with them in order to destroy the ligaments attached to the jaw bone. |
| Removal | The affected tooth itself is pulled out, that is, extraction. After the affected tooth has been removed, the resulting hole must be thoroughly examined. This is necessary so as not to leave tooth fragments or a cyst in the wound cavity. If the extraction of the affected tooth took place in the presence of flux, then after its removal the gums are cut in the right place and the pus is released. After this manipulation, a drainage is inserted into the wound cavity. |
| Treatment | After the procedure is completed, you need to treat the wound itself. If pus is found at the site of the lesion, then in this case the hole must be washed with an antiseptic solution, and then an anti-inflammatory agent should be placed in the wound. If the hole itself is too large after extracting the tooth, then a suture is necessary. |
| Consultation | After the procedure has been completely completed, before discharge, the doctor must instruct the patient in detail on how to care for the hole during the healing period, and also prescribe any medications if necessary. |
After the tooth is removed and before the patient goes home, the doctor inserts a special medicine into the tooth socket. It is necessary to protect the wound from various influences, as well as for faster and more proper healing. Some patients complain that the turunda with the medicine interferes greatly, but this will have to be endured.
Important ! If you remove the turunda ahead of time, serious complications may develop, which will have to be dealt with not only by the dentist, but also by other doctors.
The doctor prescribes exactly the medicine that is safe for every person. True, it does not have the most pleasant taste, but a person will have to ignore this factor if he wants the wound to heal as quickly as possible.
There are exceptional cases when it is simply impossible to remove the affected tooth according to the scheme above. The reason for this may be the following factors:
- if the tooth root is crooked;
- if the bone tissue of the tooth is too fragile;
- if the crown of the affected tooth is already completely destroyed;
- if the figure eight is in a position of incomplete eruption or in a horizontal position.
If a patient who needs tooth extraction has any of these characteristics, then the intervention is performed in a different way. First, the gum is cut and peeled away from the bone. After this, the specialist drills out the desired area using a drill, which creates access to the root of the required tooth.
Important ! In some cases, the partitions between the roots of the tooth are sawed, after which each root is removed one by one.
After such procedures, healing is more difficult and longer. Such an intervention may cause the patient to develop stomatitis. In many cases of such intervention, a secondary infection is attached to the affected area.
However, no matter which tooth is removed, medicine must be placed in the hole. This procedure is required.