The essence of bone grafting Condition after surgery Duration of recovery Accelerated rehabilitation Medicines Oral care General recommendations Possible complications Preventive measures
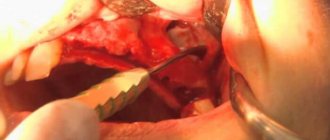
Bone grafting is a surgical operation during which the surgeon “completes” the volume of tissue required for implantation using osteomaterials. In our Center, it is performed according to low-traumatic modern protocols by experienced maxillofacial surgeons. The duration of the rehabilitation period is determined by the amount of postoperative consequences, which depend on the scale of the operation and the individual reaction of the body.
Introduction to bone grafting surgery
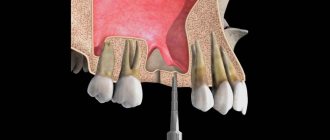
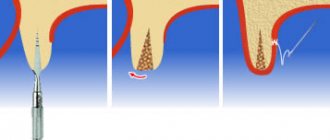
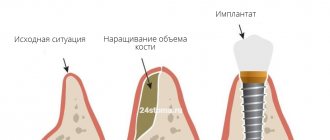
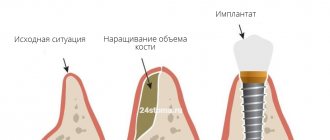
Bone grafting is an operation to correct bone deficiency in the area of the jaw required for implantation. There are 4 main methods:
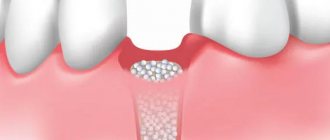
- GBR or directed bone regeneration involves the use of bone replacement materials and growth stimulants that accelerate the regeneration of one’s own bone cells. The top is covered with barrier membranes to prevent displacement.
- Splitting of the alveolar process Installation of the graft inside the bone, where there are the most favorable conditions for engraftment. Rarely used, suitable only for patients with dense jaw walls.
- Bone block grafting Fixation of a graft from the patient's own bone taken from another area of the jaw. A traumatic method, practically not used. Suitable for patients if the body does not accept any other material other than its own.
- Sinus lifting is performed on the upper jaw under the bottom of the maxillary sinus. The sinus lining is lifted and filled with osteomaterial to create the necessary volume of bone to support the implant.
Surgical interventions differ in technology and degree of tissue trauma. Our Center uses gentle protocols without a hammer, saw or chisel. NSK VarioSurg ultrasound technology allows minimal trauma to bone tissue during surgery, eliminating damage to blood vessels, nerves, and the lining of the maxillary sinus. Unpleasant consequences after surgery appear to a minor extent.
The operations are performed under sedation - in a state of controlled drug sleep without the pain of unpleasant memories. The drugs do not have a negative effect on the body; this is not general anesthesia with a difficult recovery.
The duration of the procedure is from 30 minutes (for bone restoration in the area of 1-2 teeth) to 3 hours (for large-scale interventions).
hospitalization required after surgery
After waking up, you can go home 30-40 minutes later. For patients with cardiac problems, our Center provides a day hospital, where you can lie down under the supervision of an anesthesiologist.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Founder and Chief Doctor of the Center
Content:
- What is bone tissue?
- Why does atrophy occur?
- What does it lead to?
- How to recover
- How to avoid atrophy
Bone atrophy after tooth extraction is a very common problem.
If you do not resort to implantation in time, the gums will gradually begin to sag. Subsequently, when a decision is made about implantation, it may turn out that there is simply nowhere to place the implant. To exclude atrophy, it is important not to postpone dental treatment until later. In the near future, after tearing out the unit, you should discuss the possibility of prosthetics with your dentist.
Condition after bone grafting - normal and complications
Within 10 days, unpleasant conditions are possible that accompany any surgical operation and are considered a physiological norm. The intensity of the manifestations depends on the experience of the surgeon, the technologies used, the type of bone grafting, the scope of the operation and the individual characteristics of the body.
Pain
You will not feel pain immediately after the operation; our anesthesiologist will administer an anesthetic along with sedatives. Anxiety may appear towards the end of the day or the next day. The initial intensity of sensations can be completely different, depending on the person’s pain threshold.
To relieve pain, take the medications from the kit you received at the reception. The sensations should completely go away within the first week after surgery.
Bleeding
Bloody discharge may occur during the first 2-3 days. Normally, they should be quite scanty, just tint the saliva a little. The appearance of blood clots or severe bleeding is a reason to immediately visit a doctor.
You can stop the bleeding yourself by pressing the wound surface with a sterile bandage. Avoiding severe bleeding will help avoid taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, in particular acetylsalicylic acid. Some patients, according to indications, are forced to take antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants; it is worth warning the surgeon about this at the stage of preparation for surgery; a corrective plan may be needed.
Edema
Tissue damage and the introduction of osteoplastic material always lead to the development of swelling. It is most pronounced 2-3 days after surgery, then quickly subsides. Swelling can be managed by applying ice compresses. You need to sleep on a large pillow so that your head is elevated.
The swelling goes away by the end of the first week after surgery. Otherwise, there is suspicion of a pathological process of inflammation of the wound surface or deep-lying structures.
Please be extremely attentive to your own condition. For any questionable symptoms, if there is a worsening of discomfort or lack of positive dynamics, consult a doctor. The 24-hour helpline number is located on the post-op advice card .
At what stages of implantation is bone tissue augmentation performed?
Jawbone atrophy occurs with varying intensity and is classified into 3 stages, according to which our implantologists decide on the need for bone grafting, the methods and order of its implementation:
- Initial Accompanied by slight bone resorption, which does not affect the blood supply and severity of the alveolar process. At this stage, a basic extension along the neck of the implant with a growth stimulator is sufficient. In this way, natural regeneration processes are activated, which contributes to the independent restoration of bone tissue.
- Moderate Characterized by increased atrophic process of bone tissue, slight smoothing of the alveolar ridge, and gum recession. It is no longer possible to do without bone grafting. However, it can still be carried out simultaneously with the installation of implants .
- Critical There is pronounced atrophy, smoothing of the contours of the jaw bone from the inside and outside. The bite is disrupted, the teeth adjacent to the defect move in the direction of the missing ones, and the proportions of the face change. Before implantation, a separate stage is used to build up the missing bone volume.
Accelerated rehabilitation
For patients who want to quickly overcome the period of operational inconvenience, our Center provides an accelerated rehabilitation complex.
- Injections of lymphatic drainage drugs The composition of the drugs includes biostimulants, peptides, a complex of microelements and vitamins. They improve blood and lymph circulation and have anti-inflammatory properties. Minimize swelling and hematomas, accelerate wound healing.
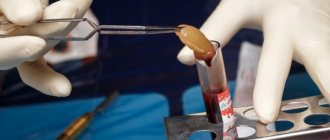
- PRP plasma therapy Blood plasma is rich in platelets, which use the body's reserve forces. The work of the immune system is enhanced, regeneration processes proceed faster. Swelling and bruising disappear, soft tissues heal faster.
- Microcurrent therapy Exposure of facial skin to weak currents activates cell function. Recovery processes are accelerated, blood circulation improves. Swelling and pain go away, spasms of the muscles of the face and neck decrease.
Minimizing swelling and bruising, reducing muscle tension is possible on the day of your visit
After restorative procedures, the condition improves instantly. You can lead your usual lifestyle - walking, going to work and visiting. But do not forget to follow postoperative recommendations to avoid complications!
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Founder and Chief Doctor of the Center
Medicines during the rehabilitation period
After the operation, you will receive a set of medications to take home and instructions for their use. Taking medications can reduce the risk of infection and relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Patients are prescribed:
- Antibacterial agents Most often, combination drugs are used that cope well with infections of the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract. A standard seven-day course is prescribed, which minimizes the risk of an inflammatory process. During this period, you should not drink alcoholic beverages or take medications that suppress the immune system, such as hormonal drugs (prednisolone).
- Antihistamines Help relieve swelling, which is pronounced in the first days after bone grafting and can cause serious inconvenience to the patient. As a rule, tablet forms of the drug are used.
- Antiseptic solution In most cases, Chlorhexidine is used. It is used to treat the oral cavity, but not to rinse. Helps fight pathogenic microorganisms in the wound surface area.
- Analgesics Painkillers that help eliminate severe pain during the first days after bone grafting. The drugs should be taken as prescribed by a doctor, most often one tablet with a break between doses of at least 4 hours.
- Healing ointment Topical application accelerates tissue regeneration. Used for rapid healing of the wound area.
An individual set is compiled for each patient , depending on the type and volume of the operation. Self-administration of medications is strictly prohibited; it can significantly increase the risk of complications or harm the body as a whole.
Read more here - Medications after surgery
Why does atrophy occur?
Removal of dental bone tissue is not carried out on purpose. Atrophy is almost always the result of a long “downtime” of a certain area of the dentition. Among the factors contributing to the problem:
- advanced inflammatory gum diseases;
- periodontal damage;
- purulent inflammation of the maxillary sinuses;
- acute/chronic pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- long-term use of glucocorticosteroids and some other medications;
- congenital anomalies of the upper or lower jaw;
- hereditary tendency to the disorder.
But most often, bone tissue subsides after tooth extraction. This is the main cause of the disease. While chewing food, the blood supply to the bone increases. It is due to this that its original volume is preserved. After tearing out the unit, the empty area is no longer subject to the necessary chewing load. Local blood supply deteriorates. Then the bone decreases. In one year, its volume decreases by approximately 25%.
Oral care after bone grafting
Proper oral hygiene is important to prevent complications. Caring for your teeth and the operated area should be thorough and gentle.
- Brushing your teeth is recommended after every meal for several days after surgery.
- Use only a soft toothbrush
- During cleansing, do not touch the operated area.
- Active rinsing of the mouth with antiseptics is prohibited; oral baths are allowed
- Treatment of operated areas is carried out with moistened cotton swabs
- The wound surface and sutures should be treated extremely carefully to avoid mechanical damage.
Cleaning the mouth after eating should be thorough but gentle. In the first days after surgery, it is quite easy to cause bleeding or suture dehiscence.
Read more about the rules of care - Oral care
How to avoid atrophy
It is much easier to avoid a problem than to look for ways to solve it later. The only way to prevent jaw atrophy is timely implantation. Under no circumstances should you walk around with an unsightly toothless smile for a long time.
If the bone begins to decrease due to periodontitis, severe thyroid disease, or hormonal imbalance, you should undergo proper treatment. At the same time, the patient needs to carefully monitor the health of his teeth and gums and unquestioningly follow all medical prescriptions.
A healthy and balanced diet is crucial in the prevention of atrophy. All people should eat fresh vegetables and fruits every day. While chewing them, the necessary load is created on the jaws, and the blood supply to the tooth roots increases.
General recommendations after bone grafting
Following your doctor's recommendations during the rehabilitation period will prevent possible complications. The list is in the medicine package.
General recommendations after bone grafting:
- At first, it is better to refrain from chewing on the operated side.
- For the first 2-3 days it is recommended to eat only crushed food at room temperature
- You should not smoke or drink alcohol for 2 weeks after surgery.
- Do not drink through a straw
- It is recommended to cough gently and with your mouth open so as not to increase the pressure in the mouth.
- Sleep better with the head of the bed raised
- Serious physical activity and diving for several weeks are prohibited
- Prolonged exposure to the sun is not recommended; you should avoid visiting solariums.
- It is prohibited to visit the sauna or bathhouse
- You should avoid flying in the first few weeks after bone grafting.
The patient must maintain physical and emotional rest. The doctor will monitor your condition and monitor you during scheduled visits.
When should you see a doctor outside of your plan?
Postoperative symptoms are most often an explainable physiological reaction. However, under certain circumstances they can turn into signs of dangerous complications. The patient must be able to distinguish pathology from normality.
Among the complications that arise during the rehabilitation period, the first place always remains infection of the wound site and internal structures, for example, the maxillary sinus after sinus lifting. In this situation, the patient notes:
- severe pain;
- worsening swelling;
- redness of the gums;
- the appearance of purulent discharge;
- temperature increase.
Contact a doctor should be immediate . The surgeon treats the oral cavity, sometimes it is necessary to remove sutures and clean the area with bone material. A course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs will be prescribed.
There is another unpleasant complication - suture dehiscence. In such a situation, you should immediately go to the clinic, where the dentist will apply new surgical sutures. As a rule, no additional action is required, but in rare cases the graft may become dislodged, which requires almost a second surgical intervention.
Complications associated with rejection of the osteoplastic material or poor fixation of the implants require another bone grafting. Such adverse outcomes may be associated with improper implementation of the dentist's recommendations, so it is important to strictly follow them.
Read more here - Complications after sinus lift and bone grafting