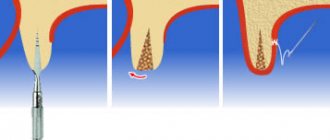
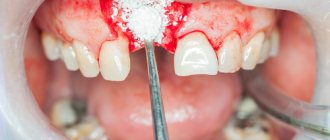
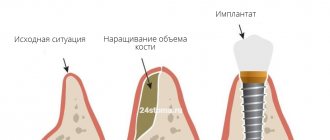
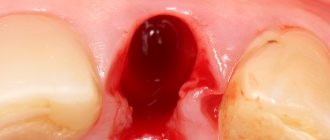
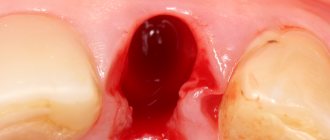
NBR is one of the methods of bone augmentation before implantation. Surgery is used to guarantee the primary stability of the implant and eliminate the risk of rejection of the titanium root and the development of tissue inflammation. The lack of bone is filled with a bone substitute, which is secured with a membrane. They use their own or synthetic materials. The method is safe: surgery is performed under local anesthesia, small tissue incisions are made, bone material is grafted, and the process of graft engraftment is monitored.
What is Guided Bone Regeneration
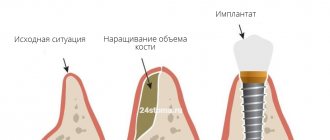
Guided bone regeneration is an operation to compensate for the lack of bone tissue with a substitute, which is secured with a barrier membrane. After the procedure, a framework is formed around the transplant (it is formed by vessels and osteocyte cells that produce new tissue). Natural bone is gradually replacing artificial material.
Extensions using the NDT method are carried out according to classical parameters:
- thickness of the vestibular bone wall (at the cheek) - up to 2-2.5 mm;
- bone thickness between the implant and the root of the adjacent unit - up to 2.5-3 mm;
- The thickness of the bone wall between two titanium roots is up to 3 mm.
Prices
The cost of the operation depends on the chosen technique. The most expensive will be implantation with preliminary osteoplasty: the process is labor-intensive and expensive artificial material is used.
A classic operation and a protocol with an immediate load will cost approximately the same if several elements need to be restored. When a complete or almost entire row of teeth is missing, one-stage implantation is cheaper due to fewer implants and a reduction in the number of operations.
Free online consultation with a dentist
| Service | Price |
| Directed regeneration in the area of 1 tooth (excluding material cost) | from 10,000 rub. |
| Sinus lifting in the area of one tooth (excluding the cost of material) | from 10,000 rub. |
| Installation of a classic implant ROOTT FORM (Switzerland, Trate AG) | from 27,000 rub. from 32,000 rub. promotion |
| Guided bone tissue regeneration (for 1 zone excluding material cost) | from 35,000 rub. |
| Open sinus lift, bone grafting (for 1 zone, excluding material cost) | from 35,000 rub. |
| Osteoplasty with splitting of the alveolar ridge (for 1 zone excluding the cost of material) | from 35,000 rub. |
| Installation of a one-stage implant (Switzerland, Trate AG) with an adaptation crown | from 44,000 rub. |
| Installation of a classic ROOTT implant with an adaptation crown (Switzerland, Trate AG) | from 44,000 rub. |
| Installation of a one-stage multi-unit implant with screw fixation (Switzerland, Trate AG) with an adaptation crown | from 50,000 rub. |
| Installation of a classic Nobel implant (Sweden, Nobel Biocare) | from 60,000 rub. |
| Installation of a classic Nobel implant (Sweden, Nobel Biocare) with an adaptation crown | from 85,000 rub. |
| One-stage complex implantation for completely edentulous one jaw, including an adaptive prosthesis (combination of 6-12 COMPRESSIVE, BASAL implants of the ROOTT system (Switzerland, Trate AG) on a metal frame with cement fixation. | from 265,000 rub. |
| One-stage complex implantation for completely edentulous one jaw, including an adaptive prosthesis (combination of 6-12 COMPRESSIVE, BASAL implants of the ROOTT system (Switzerland, Trate AG) on a titanium frame with cement fixation | from 230,000 rub. from 295,000 rub. promotion |
| One-stage complex implantation for completely edentulous one jaw, including an adaptive prosthesis on a titanium frame supported by 6-12 implants of the ROOTT system (Switzerland, Trate AG) multi-unit with screw fixation | from 295,000 rub. from 325,000 rub. promotion |
| One-stage complex implantation with complete edentia of both jaws, including an adaptive prosthesis (combination of 12-24 COMPRESSIVE, BASAL implants of the ROOTT system (Switzerland, Trate AG) on a metal frame with cement fixation | from 480,000 rub. |
| One-stage complex implantation with complete edentia of both jaws, including an adaptive prosthesis (combination of 12-24 COMPRESSIVE, BASAL implants of the ROOTT system (Switzerland, Trate AG) on a titanium frame with cement fixation | from 495,000 rub. |
| One-stage complex implantation for completely edentulous 1 jaw, including a ceramic-composite prosthesis, put on on days 3-4, a combination of 6-12 screw-fixed implants, ROOTT system (Switzerland, Trate AG). No re-prosthetics required | from 580,000 rub. |
| One-stage complex implantation with complete edentia of both jaws, including an adaptive prosthesis on a titanium frame supported by 12-24 implants of the ROOTT system (Switzerland, Trate AG) multi-unit with screw fixation | from 590,000 rub. |
Consultation and diagnostics are free!
All prices Promotions
Indications
The operation allows you to increase the “necessary” volume for high-quality classical implantation, helps restore the functions of the jaw, and returns the gums to an attractive appearance.
The bone is built up “with reserve”, since after the operation the surface layers will be supplied with a small amount of oxygen due to their lower blood circulation. Therefore, the volume of inevitable tissue resorption is calculated.
In addition to implantation, indications for NRC are:
- rapid restoration of physiological parameters after tooth extraction;
- congenital or acquired defects of the bone around the teeth;
- prevention of tooth displacement, loosening, and loss due to periodontal tissue diseases.
Why does atrophy occur?
Alternative Methods
Removable dentures Recommended if there are absolute contraindications to implantation or if there is a limited budget
ReSmile Modern technology for rapid restoration of teeth with complete edentia with the installation of a permanent prosthesis
Mini-implants Removable prosthetics with mini-implants MDI
Article Expert
Nesterenko Alexey Pavlovich Surgeon-implantologist, doctor of the highest category
Work experience: more than 11 years
What bone materials are used
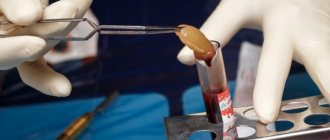
Osteoplasty involves the use of bone replacement materials. Previously, transplants were used that were not widely used due to frequent rejection of foreign material:
- Allografts
are donated bone from other people. The material was obtained from corpses, processed, sterilized, and stored in bone tissue banks. - Xenografts
are animal bones (cattle, pigs). The material was freed from proteins by heating (to eliminate the possibility of an allergic reaction after transplantation).
We do not use outdated techniques. Nowadays, many synthetic components have been developed that promote the growth of our own bone, which we use to build bone tissue.
Synthetic materials have a high degree of affinity and compatibility with natural bone and are its analogues. These are granular formulations based on:
- calcium phosphates;
- chondroitin sulfate;
- bioglass.
The effectiveness and safety of artificial materials has been confirmed by numerous studies. They are easy to use, take root well, promote the regeneration of your own bone, and are hypoallergenic.
With osteoplasty, a combination of an artificial substitute and a person’s own bone in the form of chips (autograft) is possible. The technique helps preserve the volume of built-up bone tissue and speed up the rate of recovery. The same method helps if you have to grow a large amount of tissue.
If there is a slight shortage, you can only get by with synthetic materials.
What does an increase in temperature indicate?
A low-grade or febrile temperature reaction that occurs after surgery is a rather unfavorable sign indicating the occurrence of an inflammatory process. Fever after bone grafting and sinus lifting can be caused by the following factors:
- Infection of a postoperative wound by contact (bacteria from the oral cavity cause inflammation);
- Infection of the maxillary sinus (infection spreads due to perforation of the mucous membrane into the sinus cavity);
- Infection of osteoplastic material (pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate both from the oral cavity and from the maxillary sinus in the presence of chronic sinusitis).
The severity of the febrile syndrome and some other indirect signs make it possible to roughly suspect the origin of the inflammatory process, but in most cases opportunistic and pathogenic strains of staphylococci multiply in the oral cavity.
According to these data, treatment is being developed for complications of surgical intervention, which should not arise at all at the present stage of development of dentistry.
The inflammatory process in the oral cavity leads to an increase in temperature, both systemic and local. The fever in such people, as a rule, does not even reach 38 degrees, but in rare cases exceptions are possible. Contrary to the opinions of uninformed people, such a condition as a decrease in the body’s defenses (especially if we are talking about immunodeficiency) does not lead to a worsening of fever, but on the contrary, it reduces it to a minimum. And this reduced reactivity of the immune system only increases the risk of an unfavorable outcome, since patients do not immediately detect the presence of inflammation.
Types of membranes
The membrane technique used by the surgeon is needed to isolate the space from fibrous tissue - creating conditions for normal tissue regeneration. There are several requirements for membranes:
- biological compatibility;
- strength;
- prevention of migration of epithelial cells;
- corresponding resorption period.
In practice, two types of membranes are used:
- Resorbable.
They dissolve on their own 6-24 weeks after extension. Membranes are used for small defects (when you need to build up no more than 2 mm) - they do not hold their shape as well as the next type. - Non-resorbable.
They do not dissolve - they are eliminated several months after surgery.
To quickly fuse the artificial material with the jaw bone tissue, in some cases membranes from the patient’s blood plasma are used.
How to avoid fever after a sinus lift?
Adverse outcomes after bone grafting and sinus lifting, among other things, arise due to several factors:
- Insufficient examination of the patient at the preparatory stage (the doctor does not identify some contraindications to surgical intervention, for example, oral infections or the presence of immunodeficiency);
- Poor preparation of the patient for surgical procedures (many clinics require professional teeth cleaning before bone grafting);
- Dentist mistakes during the sinus lifting process (perforation of the maxillary sinus or infection with low-quality instruments or consumables);
- Failure to comply with recommendations during the rehabilitation period (refusal to take necessary medications, improper treatment of the oral cavity, and so on).
In the vast majority of cases, the occurrence of fever after sinus lifting and bone grafting is the result of the patient’s carelessness or dishonesty. You can avoid the problem in a simple way: adhere to the necessary rules. These include:
- Completing all prescribed tests to detect health problems (mostly this includes laboratory tests of blood, urine and x-rays of the maxillary sinuses);
- Taking antibacterial drugs for 5-7 days after surgery to prevent infection (as a rule, broad-spectrum drugs are used);
- Treating the oral cavity with an antiseptic solution (rinsing is not allowed, but blotting the wound surface with a moistened cotton wool minimizes the risk of infection);
- Thorough brushing of teeth after each meal (removing food residues will remove an environment suitable for pathogenic microorganisms);
- Control visits to the dentist according to a pre-agreed schedule (the doctor monitors the implantation of the graft, assesses the condition of the postoperative wound and changes recommendations depending on objective data).
By adhering to simple daily rules, the patient can easily prevent the development of an infectious process and, accordingly, an increase in temperature. Bone grafting, like other dental operations, should not result in infectious pathologies, since damage to this area is dangerous due to rapid spread to nearby organs, in particular to the brain. During the rehabilitation period, the human body is in a state of reduced protection, which only aggravates the danger.
NDT stages
The operation is performed under anesthesia. The surgeon acts according to the classical algorithm:
- He cuts the gum along the hole of the lost tooth, makes several cuts on the side - peels off the gum flap.
- Fixes the implant into the exposed bone (if the operation is organized simultaneously with implantation).
- Replaces the missing volume with a graft, covers it with a membrane with a protrusion of 2-3 mm beyond the bone material. If it does not exclude the fact that the membrane is being pressed into the defect, a titanium mesh is placed on top.
- Secures the membrane (with sutures or screws).
- Brings the edges of the wound together and applies stitches.
The operation lasts 1-1.5 hours.
Work examples
All works
Implantation for 2 jaws with artificial gum
Complete restoration of the upper jaw on implants
Complete restoration of the upper jaw using a zygomatic implant
Stage III periodontal disease: complex dental implantation Restoration of both jaws in 4 days
Sinus lifting with simultaneous implantation
Implantation of both jaws with ROOTT implants for stage II periodontal disease
Restoration of two jaws with one-stage implantation using sinus lift
Sinus lift with simultaneous implantation
All works
Sign up for a consultation
three ROOTT specialists + diagnostics as a gift
Can it be done simultaneously with implantation?
Two operations are combined into one if the following conditions are met:
- the shape of the defect allows you to correctly install the artificial root in any of the planes;
- when installed, the implant is located within the bone contour (does not go beyond the tangent drawn to the bone line);
- eliminate a horizontal (not vertical) defect.
The implanted implant can become a barrier to the growth of blood vessels and inhibit the formation of new bone. If the implant protrudes beyond the contour of the bone tissue, the risk of developing fibrous tissue with inclusions of the implanted material cannot be ruled out.